Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained significant attention as a potential solution to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change. However, the question of whether EVs truly contribute to a lower carbon footprint is complex and multifaceted. While EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, the environmental benefits depend on various factors, including the source of electricity generation, the manufacturing process of the vehicle, and the overall lifecycle analysis. This paragraph will explore the various aspects of this debate, examining the advantages and challenges of EVs in reducing carbon emissions and providing a comprehensive understanding of their environmental impact.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Environmental Impact | Electric vehicles (EVs) have a lower environmental impact compared to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. They produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions, primarily due to the use of electric motors powered by renewable energy sources. |
| Tailpipe Emissions | EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, which means they do not release pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), or carbon monoxide (CO) during driving. |
| Well-to-Wheel Emissions | When considering the entire lifecycle, including production, electricity generation, and battery manufacturing, EVs still have a lower carbon footprint compared to ICE vehicles. The 'well-to-wheel' emissions of EVs are significantly lower, especially when charged with electricity from renewable sources. |
| Renewable Energy Integration | The reduction in carbon footprint is more pronounced when EVs are charged using electricity generated from renewable sources such as solar, wind, or hydropower. This further decreases the environmental impact. |
| Battery Production and Recycling | The production and disposal of EV batteries can have environmental consequences. However, ongoing research and development focus on improving battery recycling technologies, which can mitigate these issues over time. |
| Energy Efficiency | EVs are generally more energy-efficient than ICE vehicles, converting a higher percentage of energy into vehicle movement, resulting in lower overall energy consumption. |
| Grid Impact | The widespread adoption of EVs can impact the electricity grid. However, smart grid technologies and vehicle-to-grid (V2G) systems can help manage this, allowing EVs to charge during periods of low demand and feed excess energy back to the grid. |
| Carbon Intensity of Electricity | The carbon footprint of EVs depends on the carbon intensity of the electricity grid in the region where they are charged. In regions with high renewable energy sources, the carbon footprint is significantly reduced. |
| Long-Term Benefits | Over their lifetime, EVs can contribute to a substantial reduction in carbon emissions, especially when replacing high-emission vehicles. This long-term benefit is a key advantage of EV adoption. |
| Policy and Infrastructure Support | Government policies and investments in charging infrastructure play a crucial role in promoting EV adoption and further reducing their carbon footprint. |
What You'll Learn
- Energy Efficiency: EVs use less energy per mile than gasoline cars, reducing overall emissions
- Renewable Energy Sources: Charging EVs with renewable energy significantly lowers carbon emissions
- Battery Production: Manufacturing EV batteries can be energy-intensive, but lifecycle analysis shows net benefits
- Infrastructure Impact: Electric grids must adapt to handle increased demand, but this can be managed sustainably
- Use Patterns: Driving habits and vehicle usage affect emissions, emphasizing the need for responsible EV ownership

Energy Efficiency: EVs use less energy per mile than gasoline cars, reducing overall emissions
Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained significant attention as a potential solution to reduce carbon emissions and improve energy efficiency in the transportation sector. One of the key advantages of EVs is their ability to use less energy per mile compared to traditional gasoline-powered cars, leading to a substantial reduction in overall emissions. This energy efficiency is a critical factor in the debate about the environmental benefits of electric vehicles.
The energy efficiency of EVs is primarily attributed to their electric motors, which are highly efficient at converting electrical energy into mechanical power. Unlike internal combustion engines, which waste a significant amount of energy as heat, electric motors can achieve higher efficiency, especially at lower speeds and during city driving. This is because electric motors can provide torque at zero RPM, allowing for smooth acceleration and improved performance in stop-and-go traffic, which is common in urban areas.
When comparing energy consumption, EVs excel in reducing energy usage per mile. Gasoline cars typically have an energy efficiency of around 20-30 miles per gallon (mpg) in real-world driving conditions. In contrast, EVs can achieve energy efficiencies of 50-70 miles per kilowatt-hour (kWh) or more. This means that for every kWh of electricity used, an EV can travel a much greater distance compared to a gasoline car. As a result, EVs consume less energy overall, even when considering the energy required to generate electricity from various sources.
The reduced energy consumption of EVs has a direct impact on lowering carbon emissions. The carbon footprint of a vehicle is largely determined by the amount of fuel it burns and the associated emissions. Since EVs use less energy per mile, they produce fewer greenhouse gas emissions, including carbon dioxide (CO2), during their lifetime. This is especially true when the electricity used to charge EVs is generated from renewable sources, such as solar or wind power, which have a much lower carbon footprint compared to fossil fuel-based power plants.
In summary, the energy efficiency of electric vehicles is a significant contributor to their ability to reduce carbon emissions. EVs' superior energy usage per mile, coupled with their potential for using renewable energy sources, makes them a more environmentally friendly transportation option. As the world seeks to transition towards cleaner energy, the widespread adoption of EVs can play a crucial role in mitigating the environmental impact of the transportation sector.
The Mystery of LCO Batteries in EVs: Unlocking the Secret
You may want to see also

Renewable Energy Sources: Charging EVs with renewable energy significantly lowers carbon emissions
The environmental benefits of electric vehicles (EVs) are often a topic of discussion, and one of the key advantages is their potential to reduce carbon emissions. When it comes to charging EVs with renewable energy sources, the positive impact on the environment becomes even more pronounced. Here's an exploration of this concept:
Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal power, offer a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to traditional fossil fuels. By utilizing these renewable sources to charge EVs, we can significantly lower the carbon footprint associated with transportation. For instance, when solar panels generate electricity to power an EV, the process emits far fewer greenhouse gases compared to burning gasoline or diesel. This is because renewable energy production typically involves little to no direct carbon emissions during the generation process.
The integration of renewable energy with EV charging infrastructure is a crucial step towards a greener future. As more renewable energy projects come online, the electricity grid becomes cleaner, and the carbon intensity of EV charging decreases. This is particularly important in regions where the electricity mix is heavily reliant on renewable sources, making the overall environmental benefit even more substantial.
Furthermore, the use of renewable energy for EV charging can contribute to energy independence and security. By diversifying the energy sources and reducing reliance on finite fossil fuel reserves, countries can ensure a more stable and sustainable energy supply. This shift can also stimulate economic growth, as the development and maintenance of renewable energy infrastructure create jobs and foster innovation.
In summary, charging electric vehicles with renewable energy is a powerful strategy to combat climate change and reduce carbon emissions. It not only benefits the environment by lowering the carbon footprint of transportation but also promotes a more sustainable and resilient energy system. As the world embraces the transition to cleaner energy, the role of renewable sources in powering EVs will become increasingly vital.
Electric Vehicle Options: Georgia's Top Dealers and Showrooms
You may want to see also

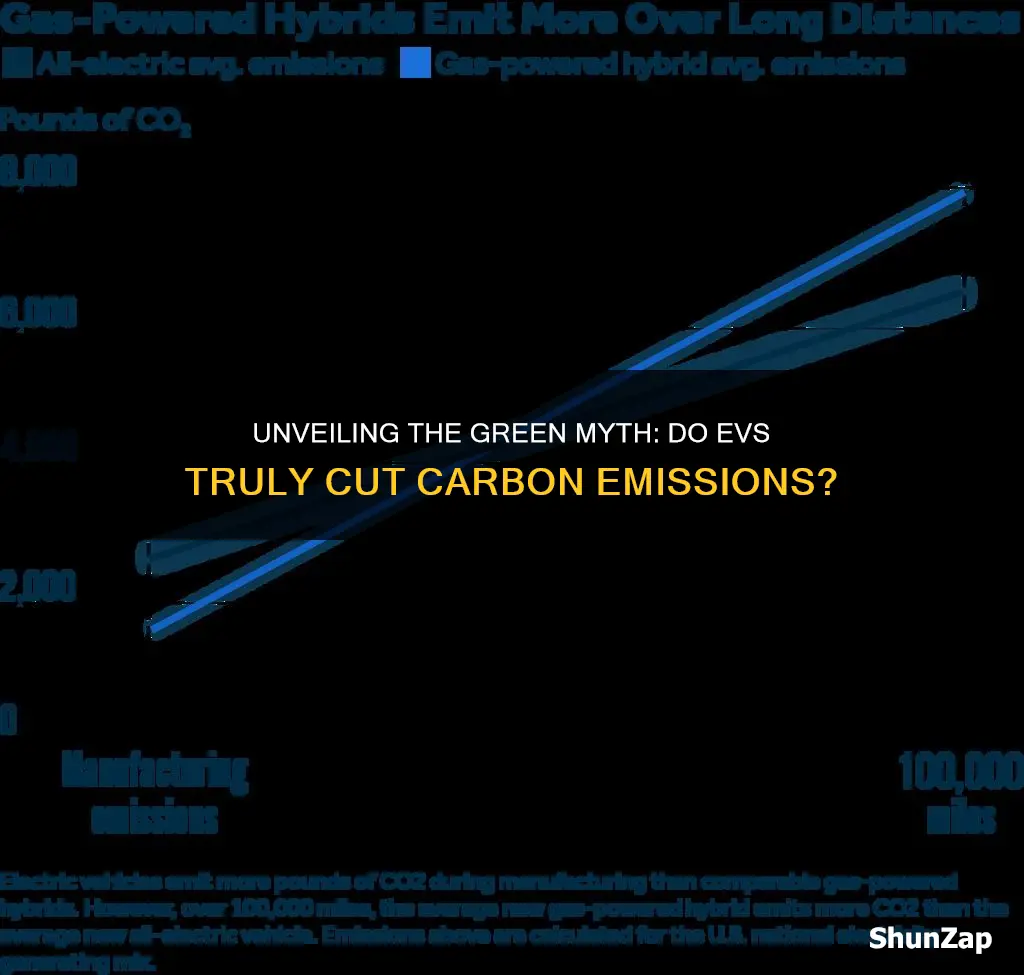
Battery Production: Manufacturing EV batteries can be energy-intensive, but lifecycle analysis shows net benefits
The manufacturing of electric vehicle (EV) batteries is a complex process that has raised concerns about its environmental impact, particularly in terms of energy consumption and carbon emissions. However, a comprehensive lifecycle analysis reveals that despite the initial energy-intensive phase, EV batteries ultimately contribute to a significant reduction in the carbon footprint over their entire lifecycle.
Battery production requires substantial energy input, primarily from electricity generation, which can vary in its environmental impact depending on the source. For instance, batteries produced in regions with a high reliance on renewable energy sources may have a lower carbon footprint compared to those manufactured in areas dominated by fossil fuel-based power plants. Despite this initial energy demand, the lifecycle analysis demonstrates that the overall environmental benefits of EV batteries far outweigh the production costs.
The lifecycle assessment takes into account various stages, including raw material extraction, manufacturing, transportation, and end-of-life recycling or disposal. Over the vehicle's lifetime, the energy saved from reduced greenhouse gas emissions during operation significantly offsets the energy used in production. This is because electric vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, leading to substantial reductions in air pollution and carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions compared to conventional internal combustion engine vehicles.
Furthermore, the recycling and reuse of materials in EV batteries play a crucial role in minimizing environmental impact. As technology advances, recycling processes become more efficient, allowing for the recovery of valuable metals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel. This recycling aspect further reduces the need for energy-intensive mining and processing of raw materials, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly battery production process.
In summary, while the manufacturing of EV batteries does require significant energy, lifecycle analysis confirms that the net benefits are substantial. The reduction in greenhouse gas emissions and air pollutants from widespread EV adoption far surpass the initial energy costs, making electric vehicles a powerful tool in the fight against climate change and a key component in the transition to a more sustainable transportation system.
India's Electric Vehicle Revolution: Top Manufacturers Unveiled
You may want to see also

Infrastructure Impact: Electric grids must adapt to handle increased demand, but this can be managed sustainably
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) presents a significant opportunity to reduce carbon emissions, but it also poses challenges for existing power infrastructure. As more EVs hit the roads, the demand for electricity will surge, particularly during peak hours. This sudden increase in load can strain the capacity of electric grids, which were designed for a different era of energy consumption. The potential impact on infrastructure is a critical consideration in the transition to a more sustainable transportation system.
Electric grids, while efficient, may not be equipped to handle the rapid growth in EV charging. The current infrastructure often relies on centralized power generation and transmission, which might struggle to meet the decentralized and intermittent nature of EV charging demands. During peak times, when multiple EVs are charging simultaneously, the grid's stability and reliability could be at risk. This is especially true in regions where the grid is already under stress due to aging infrastructure or limited capacity.
To address this challenge, a comprehensive approach to grid management and development is necessary. One strategy is to invest in smart grid technologies that can monitor and control electricity flow in real-time. These systems can optimize energy distribution, allowing for more efficient use of existing infrastructure. For instance, smart meters can provide detailed usage data, enabling utility companies to identify and manage peak demand periods. By implementing such technologies, the grid can adapt to the changing dynamics of EV charging without compromising stability.
Additionally, the integration of renewable energy sources into the grid can significantly reduce the environmental impact of increased EV demand. Solar and wind power, for example, offer clean and sustainable alternatives to traditional fossil fuel-based generation. By diversifying the energy mix and encouraging the use of renewable sources, the grid can become more resilient and environmentally friendly. This approach not only supports the EV transition but also contributes to a broader goal of decarbonizing the energy sector.
Managing the infrastructure impact of EV adoption requires a multi-faceted strategy. It involves not only technological advancements but also policy interventions and consumer behavior changes. Governments and utility companies can play a crucial role by incentivizing the development of smart grids and renewable energy infrastructure. Encouraging off-peak charging, implementing dynamic pricing, and promoting energy storage solutions can all help in smoothing out the demand curve and reducing strain on the grid. With careful planning and sustainable practices, the electric grid can adapt to the growing demand from EVs, ensuring a cleaner and more efficient transportation future.
Electric Vehicle Home Installers: Who's Leading the Charge?
You may want to see also

Use Patterns: Driving habits and vehicle usage affect emissions, emphasizing the need for responsible EV ownership
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) has been hailed as a significant step towards reducing carbon emissions and combating climate change. However, the environmental benefits of EVs are not solely dependent on their zero-emission nature; they are also heavily influenced by how they are used. Driving habits and vehicle usage patterns play a crucial role in determining the overall impact of EVs on the environment.
One of the key factors affecting emissions is the frequency and duration of EV usage. Unlike traditional gasoline or diesel vehicles, EVs are designed to be used regularly and for extended periods. Frequent short-distance travel in EVs can lead to increased energy consumption and, consequently, higher emissions. For instance, driving an EV for daily commutes within a limited range can result in frequent charging, which, if not managed efficiently, may contribute to a larger carbon footprint. Therefore, responsible EV ownership involves understanding and optimizing usage patterns to minimize such emissions.
Driving habits also contribute significantly to the environmental impact of EVs. Aggressive driving, rapid acceleration, and frequent braking can lead to increased energy consumption, negating the potential benefits of electric powertrains. Additionally, maintaining a steady speed and adopting a smooth driving style can help optimize energy efficiency. By adopting eco-friendly driving habits, EV owners can significantly reduce their vehicle's energy consumption and, in turn, lower their carbon emissions.
Furthermore, the need for responsible EV ownership extends beyond individual driving habits. It also involves understanding the broader context of vehicle usage. For example, the charging infrastructure and the source of electricity used to power EVs are essential considerations. If the electricity grid relies heavily on fossil fuels, the environmental benefits of EVs may be diminished. Therefore, EV owners should be aware of the local energy mix and consider charging their vehicles during periods of higher renewable energy generation to maximize the positive impact on the environment.
In summary, while electric vehicles offer a promising solution to reduce carbon emissions, their effectiveness is closely tied to responsible ownership and usage patterns. By adopting efficient driving habits, optimizing vehicle usage, and considering the broader energy context, EV owners can ensure that their vehicles contribute to a cleaner and more sustainable future. It is through these responsible practices that the true potential of EVs to reduce the carbon footprint can be fully realized.
Unveiling NASA's Electric Revolution: Powering Space Exploration
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Yes, electric vehicles have the potential to greatly reduce carbon footprints. EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, meaning they don't release greenhouse gases like carbon dioxide (CO2) during driving. This is a significant advantage over conventional vehicles, which are major contributors to air pollution and climate change.
The environmental benefits of EVs come from their power source. Most EVs are charged using electricity generated from renewable sources like solar, wind, or hydropower, which have much lower carbon emissions compared to burning fossil fuels. Even when charged from the grid, which may still rely on some fossil fuels, EVs generally emit fewer pollutants over their lifetime.
While the manufacturing process of EVs can have some environmental impact, it is generally considered a temporary cost. The production of batteries and other components may release greenhouse gases, but the overall carbon savings from reduced fuel consumption and lower emissions during operation typically outweigh these initial emissions. Over the vehicle's lifetime, EVs can save significantly more carbon than their conventional counterparts.
The carbon intensity of the electricity grid varies by region and country. In areas with a high proportion of renewable energy, the carbon footprint of charging EVs is relatively low. As the global energy mix shifts towards more sustainable sources, the environmental benefits of EVs will continue to improve. Additionally, many governments and utilities offer incentives for EV owners to charge during off-peak hours, further reducing the carbon impact of charging.







