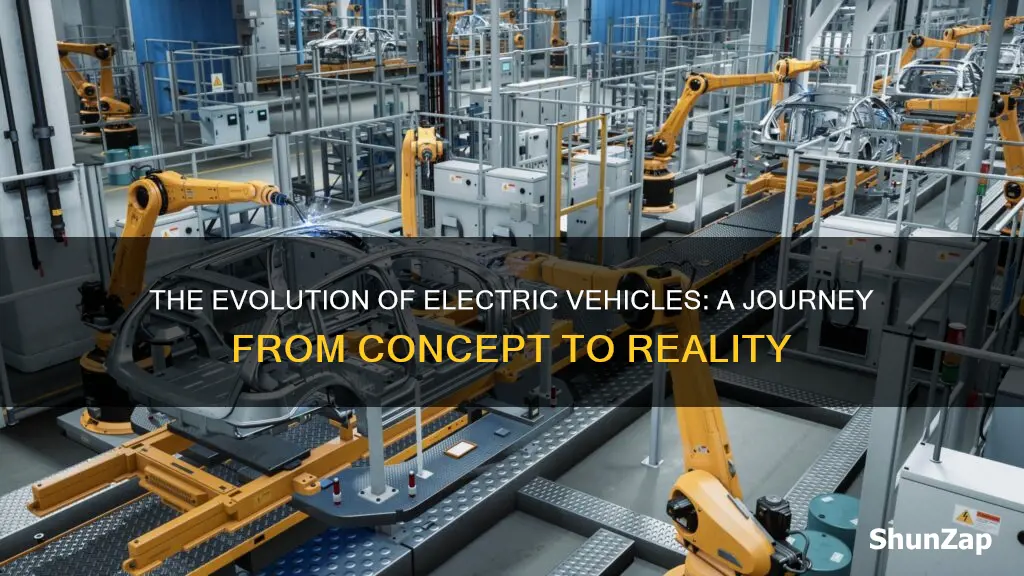
Electric vehicles (EVs) are revolutionizing the automotive industry, offering a sustainable and eco-friendly alternative to traditional gasoline-powered cars. The manufacturing process of EVs involves several key steps. Firstly, the production of electric powertrains, which include electric motors, batteries, and power electronics, is a complex and crucial aspect. These components are designed and assembled with precision to ensure optimal performance and efficiency. Secondly, the body and chassis of EVs are crafted using lightweight materials like aluminum and carbon fiber to enhance energy efficiency and reduce weight. The manufacturing process also involves advanced techniques such as 3D printing and automated assembly lines to streamline production. Lastly, the integration of smart technologies and connectivity features, such as advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) and over-the-air updates, sets EVs apart, providing a seamless and innovative driving experience.
What You'll Learn
- Battery Technology: Advancements in lithium-ion batteries enable longer ranges and faster charging for EVs
- Motor Design: Electric motors have evolved to be more efficient and powerful, powering various vehicle types
- Charging Infrastructure: The development of fast-charging stations and home charging solutions has improved EV convenience
- Materials Science: New materials reduce weight and increase performance, contributing to EV efficiency
- Software Integration: Advanced software enables smart driving, autonomous features, and seamless connectivity in electric vehicles

Battery Technology: Advancements in lithium-ion batteries enable longer ranges and faster charging for EVs
The evolution of electric vehicles (EVs) has been significantly driven by advancements in battery technology, particularly in lithium-ion batteries. These innovations have played a pivotal role in addressing some of the most pressing challenges associated with EVs, such as range anxiety and slow charging times.
Lithium-ion batteries have become the cornerstone of EV technology due to their high energy density, lightweight nature, and relatively low cost. The key to extending the range of EVs lies in improving the energy storage capacity of these batteries. Researchers and engineers have been working tirelessly to enhance the energy density of lithium-ion cells, allowing EVs to travel longer distances on a single charge. This has been achieved through various means, including the development of new electrode materials, such as lithium nickel manganese cobalt (NMC) oxides, which offer improved performance and stability. For instance, NMC 811, a variant of the NMC family, has gained prominence for its exceptional energy density, making it a preferred choice for next-generation EVs.
Another critical aspect of battery technology advancements is the development of faster charging solutions. Traditional lithium-ion batteries often require hours to fully charge, which can be a significant drawback for EV owners. To address this, scientists have been exploring ways to accelerate the charging process without compromising battery health. One approach is the use of advanced charging algorithms that optimize the charging rate based on the battery's state of charge and temperature. Additionally, the development of high-power charging stations, which can deliver a substantial amount of power to the battery in a short time, is gaining momentum. These stations utilize specialized equipment and infrastructure to enable rapid charging, reducing the time required to recharge an EV's battery.
Furthermore, the integration of solid-state batteries is a promising development in the field. Solid-state batteries replace the liquid electrolyte with a solid conductive material, offering several advantages. These include higher energy density, faster charging capabilities, and improved safety due to the reduced risk of thermal runaway. Companies are investing in this technology, aiming to bring solid-state batteries to the market, which could revolutionize the EV industry by providing even longer ranges and quicker charging times.
In summary, advancements in lithium-ion battery technology have been instrumental in transforming the EV industry. These innovations have led to increased energy density, enabling EVs to travel longer distances, and have also facilitated the development of faster charging solutions, addressing the issue of long charging times. As research and development in this field continue, we can expect further breakthroughs, making electric vehicles more practical and appealing to a broader audience.
EV Credit: Navigating the Right Form for Your Electric Vehicle Purchase
You may want to see also

Motor Design: Electric motors have evolved to be more efficient and powerful, powering various vehicle types
The evolution of electric motors has been a pivotal factor in the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), enabling them to become a viable and increasingly popular alternative to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars. This transformation is primarily driven by advancements in motor design, which have focused on enhancing efficiency and power output.
One key aspect of motor design is the development of more compact and lightweight electric motors. By reducing the physical size and weight of these motors, engineers have made it possible to integrate them into a wider range of vehicle platforms. This is particularly important for EVs, as it allows for better overall vehicle design and performance. For instance, the use of lightweight motors in electric cars and motorcycles has contributed to improved handling and acceleration, making these vehicles more responsive and enjoyable to drive.
The efficiency of electric motors has also seen significant improvements. Modern electric motors are designed to convert a higher percentage of electrical energy into mechanical power, resulting in reduced energy consumption. This is achieved through the use of advanced materials, such as rare-earth magnets and silicon steel laminations, which enhance the motor's magnetic fields and reduce energy losses. As a result, electric vehicles can travel longer distances on a single charge, addressing a critical concern for potential EV buyers.
Power output is another critical area of motor design. Electric motors have evolved to deliver higher torque and power, making them capable of accelerating vehicles more quickly and efficiently. This is particularly evident in high-performance electric cars, which can rival or even surpass their ICE counterparts in terms of acceleration. The design of these motors often involves sophisticated cooling systems to manage the increased heat generated during high-power operations, ensuring optimal performance and longevity.
Furthermore, the versatility of electric motors has allowed for their application in various vehicle types. From electric buses and trucks to motorcycles and scooters, the adaptable nature of electric motors means they can be tailored to meet the specific requirements of different vehicles. This adaptability, combined with their efficiency and power, has contributed to the widespread adoption of electric vehicles across various industries.
Electric Vehicles: The Cost-Saving Truth Revealed
You may want to see also

Charging Infrastructure: The development of fast-charging stations and home charging solutions has improved EV convenience
The evolution of electric vehicles (EVs) has been significantly influenced by advancements in charging infrastructure, particularly the development of fast-charging stations and home charging solutions. These innovations have played a pivotal role in enhancing the convenience and practicality of owning an electric car, addressing a major concern among potential buyers—range anxiety.
Fast-charging stations are designed to replenish an EV's battery quickly, significantly reducing the time required for a full charge. These stations utilize advanced technologies, such as direct current (DC) fast charging, which can add up to 100 miles of range to an EV in just 20-30 minutes. The widespread deployment of these stations along major highways and in urban areas has transformed long-distance travel, making it more feasible and less stressful for EV owners. For instance, networks of fast-charging stations are now common along popular routes, allowing drivers to quickly top up their batteries during extended journeys.
Home charging solutions have also played a crucial role in improving EV convenience. Many EV owners now have the option to install charging points in their garages or driveways, providing a convenient and cost-effective way to keep their vehicles charged overnight or during extended periods of inactivity. These home charging systems can be connected to standard power outlets or, for faster charging, to a dedicated circuit, ensuring that EVs are always ready for the next day's use. Additionally, smart charging technologies enable owners to schedule charging during off-peak hours, taking advantage of lower electricity rates and further reducing operational costs.
The combination of fast-charging stations and home charging solutions has not only addressed the issue of range but has also contributed to the overall sustainability and efficiency of the EV ecosystem. By providing rapid and convenient charging options, these technologies encourage the widespread adoption of electric vehicles, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and contributing to a cleaner, more sustainable future. As the infrastructure continues to expand, the convenience of owning an EV is set to increase, making it an increasingly attractive option for environmentally conscious consumers.
Electric Vehicles: A Beauty Conundrum
You may want to see also

Materials Science: New materials reduce weight and increase performance, contributing to EV efficiency
The development of electric vehicles (EVs) has been significantly influenced by advancements in materials science, which have played a pivotal role in enhancing their performance, efficiency, and overall appeal. One of the most notable contributions of materials science to EVs is the creation of lightweight, high-strength materials that reduce the overall weight of the vehicle while maintaining structural integrity. This is a critical aspect of EV design as it directly impacts performance and efficiency.
Lighter materials, such as advanced composites and alloys, are now being utilized in various components of EVs, including the body, chassis, and battery enclosures. These materials offer a superior strength-to-weight ratio, allowing engineers to design vehicles that are both robust and lightweight. For instance, carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (CFRPs) have gained popularity in high-performance EVs due to their exceptional strength and stiffness, enabling the creation of stiff yet lightweight structures. This not only improves the vehicle's handling and acceleration but also contributes to a more efficient energy usage, as less power is required to accelerate the lighter vehicle.
In the realm of battery technology, materials science has been instrumental in developing advanced materials that can store more energy while being lighter and safer. Lithium-ion batteries, the standard for EVs, have seen significant improvements in their energy density and cycle life. Researchers and engineers are now exploring solid-state batteries, which promise higher energy density and improved safety compared to liquid electrolytes. These advancements in battery materials are crucial for extending the range of EVs and reducing charging times, addressing some of the primary concerns of potential EV buyers.
Additionally, the use of advanced materials in EV motors and power electronics has led to more efficient and powerful systems. High-temperature superconductors and advanced semiconductors are being employed to create more compact and efficient power electronics, which are essential for managing the high-voltage power in EVs. These materials enable the development of smaller, lighter, and more efficient electric motors, further contributing to the overall performance and range of electric vehicles.
The impact of materials science on EVs extends beyond the vehicle's physical attributes. It also influences the environmental sustainability of these vehicles. By reducing the weight of EVs, materials science contributes to lower energy consumption during manufacturing and operation. Lighter materials also mean less raw material usage, reducing the environmental impact of production. Furthermore, the development of recyclable and biodegradable materials in EV components can significantly enhance the sustainability of the entire lifecycle of these vehicles.
Electric Vehicles: Powering Without Alternators
You may want to see also

Software Integration: Advanced software enables smart driving, autonomous features, and seamless connectivity in electric vehicles
The integration of advanced software is a pivotal aspect of modern electric vehicle (EV) development, revolutionizing the driving experience and enhancing safety. This software integration enables a range of smart driving capabilities and autonomous features that were once unimaginable in conventional vehicles. At the heart of this transformation is the sophisticated software that powers the EV's brain, allowing it to perceive its surroundings, make decisions, and execute actions accordingly.
One of the key software components is the Vehicle Control Unit (VCU), which acts as the central processor, managing various vehicle functions. The VCU is responsible for interpreting sensor data, such as lidar, radar, and camera inputs, to create a comprehensive understanding of the vehicle's environment. This data processing enables the vehicle to detect obstacles, read traffic signs, and predict potential hazards, all of which are crucial for autonomous driving. Advanced algorithms and machine learning techniques are employed to continuously improve the vehicle's decision-making abilities, ensuring safer and more efficient navigation.
Software integration also facilitates smart driving features like adaptive cruise control, lane-keeping assist, and automatic parking. These features utilize software algorithms to monitor the vehicle's speed, maintain its position within the lane, and park the car automatically, all while ensuring the safety of the vehicle and its occupants. The software can adjust the vehicle's speed and braking in response to surrounding traffic, providing a more comfortable and safer driving experience.
Furthermore, seamless connectivity is made possible through software integration, allowing EVs to communicate with each other and with external infrastructure. This connectivity enables features like vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication, where vehicles can share information about their speed, direction, and potential hazards, enhancing overall road safety. Additionally, EVs can connect to smart grids, allowing for efficient energy management and charging optimization. Software-enabled connectivity also opens doors for over-the-air updates, ensuring that the vehicle's software remains up-to-date with the latest improvements and security patches.
In summary, software integration is a critical element in the evolution of electric vehicles, enabling smart driving, autonomous capabilities, and seamless connectivity. This technology empowers EVs to make informed decisions, adapt to various driving conditions, and provide a more efficient and safer transportation experience. As software continues to advance, we can expect even more innovative features and improved performance in the future of electric mobility.
America's Electric Vehicle Revolution: Top Models and Trends
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Electric vehicles (EVs) are typically constructed using a combination of lightweight and durable materials. The most common materials include steel, aluminum, and carbon fiber composites. These materials are chosen for their strength, corrosion resistance, and ability to reduce vehicle weight, which is crucial for improving efficiency and performance.
Battery packs are a critical component of EVs, and their assembly involves several steps. The process starts with the selection and testing of individual battery cells, which are then arranged in modules. These modules are further stacked to form the battery pack, often with cooling systems and protective enclosures. Quality control is essential to ensure the safety and reliability of the battery system.
While there are some similarities, electric vehicles have unique manufacturing processes. EVs often have simpler engine compartments due to the absence of complex ICEs. The focus is on the battery pack, electric motor, and associated electronics. Manufacturing may also involve specialized equipment for handling high-voltage components and ensuring proper insulation.
Automation is integral to the manufacturing of electric vehicles to ensure precision and efficiency. Robotic arms are used for welding, assembly, and painting. Automated systems handle the placement of components, reducing human error. Advanced robotics also enables the rapid assembly of complex systems like the drivetrain and electronics, contributing to faster production times.
Environmental considerations are essential in EV manufacturing. Manufacturers aim to minimize the carbon footprint by using renewable energy sources for powering factories. Recycling and reusing materials is also a priority. Additionally, the production of electric vehicles generally results in lower emissions over their lifetime compared to traditional cars, contributing to a more sustainable transportation ecosystem.