Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained significant popularity due to their environmental benefits and technological advancements. One of the most critical aspects that influence the adoption of EVs is their battery range, which determines how far a vehicle can travel on a single charge. This article aims to explore the various factors that contribute to the battery range of electric vehicles and how these factors impact their overall performance and usability. By understanding the nuances of battery range, consumers can make informed decisions when choosing an EV that aligns with their specific needs and preferences.
What You'll Learn
- Battery Capacity: Compare EV range based on battery size and energy density
- Efficiency: Analyze how energy is used and lost in different EVs
- Climate Impact: Explore the environmental benefits of electric vehicles over their lifetime
- Charging Infrastructure: Discuss the availability and speed of charging stations
- Consumer Behavior: Examine how range affects EV adoption and usage patterns

Battery Capacity: Compare EV range based on battery size and energy density
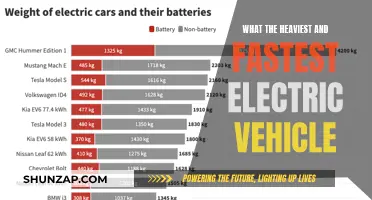
The battery capacity of an electric vehicle (EV) is a critical factor in determining its range, which is the distance it can travel on a single charge. The range of an EV is influenced by several factors, but the size and energy density of the battery pack are the most significant.
Battery size is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), which represents the total energy stored in the battery. A larger battery pack will generally provide a longer range, as it can store more energy. For example, a 100 kWh battery pack will offer a much greater range than a 50 kWh pack, assuming all other factors are equal. However, it's important to note that increasing battery size also increases the weight and cost of the vehicle, which can impact its overall performance and efficiency.
Energy density, on the other hand, refers to the amount of energy that can be stored in a given volume or weight of the battery. Higher energy density means more energy can be packed into a smaller space, allowing for a more compact and lightweight battery design. This is crucial for EVs, as it directly affects their overall efficiency and driving range. For instance, lithium-ion batteries, commonly used in EVs, have an energy density of around 250-350 Wh/kg, which is relatively high compared to other battery technologies.
The relationship between battery size, energy density, and EV range is complex. While a larger battery pack can provide more range, the energy density of the battery also plays a vital role. A battery with high energy density can store more energy in a smaller, lighter package, allowing for a more efficient use of space and weight. This is particularly important for EVs, as it enables designers to create vehicles with better performance, faster acceleration, and improved handling while still maintaining a competitive range.
In summary, when comparing EV range, it is essential to consider both battery size and energy density. A larger battery pack will generally offer more range, but a battery with high energy density can provide a more efficient and compact solution. The ideal EV battery should strike a balance between these factors to ensure optimal performance, range, and efficiency. As battery technology continues to advance, we can expect to see even more impressive range capabilities in electric vehicles, making them a more viable and attractive alternative to traditional internal combustion engine cars.
Electric Vehicles: Safer or Riskier on the Roads?
You may want to see also

Efficiency: Analyze how energy is used and lost in different EVs
The efficiency of electric vehicles (EVs) is a critical aspect when considering their overall performance and sustainability. When analyzing energy usage and losses, several factors come into play, offering insights into how different EVs rate in terms of battery range and efficiency. One key area of focus is the energy consumption during various driving conditions and modes.
In urban environments, where frequent stop-and-go traffic and frequent acceleration and deceleration are common, EVs can experience higher energy losses. This is primarily due to the increased electrical resistance and inefficiencies in the motor and drivetrain during rapid changes in speed. Modern EVs often employ regenerative braking systems, which help recover some of the lost energy by converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy, thus improving overall efficiency. However, the effectiveness of regenerative braking can vary depending on the vehicle's design and the driver's input.
Another factor influencing efficiency is the thermal management of the battery pack. As EVs operate, the batteries generate heat, and managing this heat is essential to maintain optimal performance and longevity. Inefficient thermal management can lead to increased energy losses, as the system may require additional energy to cool the batteries, especially during high-demand driving conditions. Advanced cooling systems and materials are being developed to minimize these losses and ensure efficient energy utilization.
The efficiency of EVs also depends on the driving habits and preferences of the operator. Aggressive driving, frequent high-speed travel, and rapid acceleration all contribute to higher energy consumption. On the other hand, adopting a more conservative driving style, utilizing cruise control, and maintaining a steady speed can significantly improve efficiency. Additionally, factors like tire pressure, aerodynamic design, and vehicle weight play a role in energy efficiency, as they directly impact the power required to move the vehicle.
To further enhance efficiency, EV manufacturers are continually innovating. This includes optimizing motor designs, improving power electronics, and developing more efficient battery chemistries. Some EVs also offer various driving modes that adjust the vehicle's performance and efficiency based on the driver's selection. These modes can optimize energy usage for specific driving conditions, such as eco-mode for improved range or sport mode for enhanced performance while still maintaining efficiency.
Unlocking California's Tesla Tax Credit: A Green Car Incentive Guide
You may want to see also

Climate Impact: Explore the environmental benefits of electric vehicles over their lifetime
The environmental advantages of electric vehicles (EVs) are significant and far-reaching, particularly when considering their entire lifecycle, from production to disposal. One of the most notable benefits is the reduction in greenhouse gas emissions. EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, which means they don't release harmful pollutants like carbon dioxide (CO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx) during operation. This is a stark contrast to conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, which are a major contributor to air pollution and climate change. The burning of fossil fuels in ICEs is a primary source of CO2 emissions, a potent greenhouse gas that traps heat in the Earth's atmosphere, leading to global warming.
Over their lifetime, EVs offer a substantial reduction in carbon footprint compared to their ICE counterparts. The production of an EV, including the manufacturing of the battery and other components, typically has a higher initial carbon emission compared to the production of an ICE vehicle. However, as EVs are driven, the carbon savings become evident. The electricity used to power EVs can be generated from renewable sources like solar and wind, which have much lower carbon footprints than fossil fuels. As the global energy mix shifts towards more sustainable sources, the environmental benefits of EVs become even more pronounced.
The environmental impact of EVs extends beyond their operational phase. The batteries used in EVs, particularly lithium-ion batteries, have a significant environmental impact during manufacturing and end-of-life disposal. However, research and development in this field are leading to more sustainable battery technologies. For instance, advancements in recycling processes for lithium-ion batteries can reduce the environmental impact of EV batteries. Additionally, the development of more efficient and sustainable battery chemistries can further minimize the ecological footprint of EVs.
In the long term, the widespread adoption of EVs can contribute to a substantial decrease in air pollution, especially in urban areas. This is because EVs, when charged with clean energy, produce no harmful emissions during use, improving air quality and public health. Moreover, the shift towards EVs can help in reducing the dependence on finite fossil fuel resources, which are major contributors to climate change and environmental degradation. This transition can also stimulate the development of a more sustainable and circular economy, where resources are used efficiently and waste is minimized.
In summary, electric vehicles offer a compelling solution to mitigate climate change and environmental degradation. While there are initial challenges and considerations regarding their production and disposal, the long-term benefits are substantial. EVs provide a cleaner, more sustainable mode of transportation, contributing to reduced air pollution, lower carbon emissions, and a more resilient energy system. As technology advances and infrastructure improves, the environmental impact of EVs will continue to be a powerful argument for their adoption, paving the way for a greener and more sustainable future.
Debunking the Myth: Do Electric Vehicles Still Emit Greenhouse Gases?
You may want to see also

Charging Infrastructure: Discuss the availability and speed of charging stations
The charging infrastructure for electric vehicles (EVs) is a critical aspect of their widespread adoption and integration into our transportation systems. The availability and speed of charging stations play a pivotal role in addressing range anxiety, a common concern among potential EV buyers. Range anxiety refers to the fear of running out of battery power before reaching a charging station, which can significantly hinder the adoption of electric vehicles.
The current charging infrastructure landscape varies across regions and countries. In many developed nations, the availability of charging stations is improving, with a growing network of public and private charging points. These stations are often strategically located along highways, in urban areas, and in residential complexes, ensuring convenience for EV owners. For instance, in the United States, the federal government, along with private companies, has been investing in the development of a comprehensive charging network, including fast-charging stations along major highways. Similarly, in Europe, countries like Norway and the Netherlands have implemented extensive charging networks, making EV ownership more appealing.
The speed of charging stations is another crucial factor. Fast-charging technology has significantly improved the efficiency of EV charging. These stations can replenish a substantial portion of an EV's battery in a relatively short time, often within 20-30 minutes for a 200-mile range. The development of fast-charging stations has addressed the issue of long charging times, which was a significant deterrent for potential EV buyers. Companies like Tesla have pioneered fast-charging technology, with their Supercharger network, allowing drivers to travel long distances without a lengthy stop for charging.
However, the charging infrastructure still faces challenges. In rural areas and less developed regions, the availability of charging stations is limited, and the network is not as extensive as in urban centers. This lack of infrastructure can deter potential EV buyers in these areas. Additionally, the speed of charging can vary depending on the type of charger and the EV model. While fast-charging stations are becoming more common, standard charging points, which are slower, are still prevalent, and their widespread availability is essential to cater to different charging needs.
To address these challenges, governments and private entities are collaborating to expand and improve charging infrastructure. This includes the installation of more fast-charging stations, the development of smart charging networks that optimize energy usage, and the integration of renewable energy sources to power these stations. As the demand for EVs grows, the focus on enhancing charging infrastructure will be crucial in ensuring a seamless and convenient experience for EV owners, ultimately contributing to the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
The Green Revolution: Should You Go Electric?
You may want to see also

Consumer Behavior: Examine how range affects EV adoption and usage patterns
The range of an electric vehicle (EV) is a critical factor that significantly influences consumer behavior and adoption rates. When considering the purchase of an EV, consumers often prioritize range as a key specification, as it directly impacts their daily driving needs and overall satisfaction with the vehicle. Research shows that battery range is a top concern for potential EV buyers, with many individuals seeking vehicles that can cover longer distances without the need for frequent charging. This preference for extended range is particularly evident among those who frequently embark on long-distance journeys or have limited access to charging infrastructure.
Consumer surveys and market analysis reveal that a higher battery range often correlates with increased consumer confidence in EV ownership. For instance, vehicles with a range of 300 miles or more are considered more appealing, as they alleviate range anxiety, a common concern among early EV adopters. Range anxiety refers to the fear of running out of battery power during a journey, which can significantly impact the overall driving experience and consumer satisfaction. By offering vehicles with longer ranges, manufacturers can address this anxiety and encourage more people to make the switch from traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles to EVs.
The impact of range on consumer behavior extends beyond initial adoption. As EV owners gain experience with their vehicles, they may develop specific usage patterns and habits related to range management. Some consumers might adopt a more conservative driving style, optimizing their speed and acceleration to maximize energy efficiency and extend the range. Others may plan their trips more meticulously, taking into account charging station locations and the vehicle's range to ensure they can reach their destinations without running out of power. This shift in behavior highlights the importance of range awareness and its influence on how EV owners utilize their vehicles in real-world scenarios.
Moreover, the range of an EV can also influence the overall ownership experience and long-term satisfaction. Consumers who find their vehicle's range adequate or exceeding their expectations are more likely to recommend it to others and develop a positive perception of the EV market. Positive word-of-mouth and personal experiences can significantly impact the adoption of EVs, especially among those who were initially hesitant due to range-related concerns. As a result, manufacturers that offer a wide range of EV models with varying battery capacities can cater to diverse consumer needs and preferences, fostering a more inclusive and sustainable transportation ecosystem.
In summary, the range of an electric vehicle plays a pivotal role in shaping consumer behavior and the overall EV market. Consumers are increasingly seeking vehicles with longer ranges to address range anxiety and meet their daily driving requirements. This trend has led to a more informed and confident approach to EV adoption, with manufacturers responding by offering a diverse range of models to cater to varying consumer needs. Understanding the relationship between range and consumer behavior is essential for both manufacturers and policymakers to encourage a smoother transition to electric mobility and ensure a positive user experience.
Electric Vehicle Fire Risks: Understanding the Rare but Serious Issue
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Battery range is a critical factor in determining the practicality and appeal of an EV. It refers to the distance an electric car can travel on a single charge. Modern EVs offer a wide range of battery capacities, typically measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). A higher kWh rating generally means a longer range. For example, a 60 kWh battery might provide a range of around 300-350 miles, while a 100 kWh battery could offer over 400 miles on a full charge. This range varies depending on driving conditions, vehicle efficiency, and factors like climate control use.
Longer-range EVs provide several benefits. Firstly, they offer more flexibility and peace of mind for daily commutes and longer trips, reducing the anxiety associated with running out of power. These vehicles are ideal for those who frequently travel long distances or live in areas with limited charging infrastructure. Additionally, longer-range EVs often have faster charging capabilities, allowing for quicker top-ups during longer journeys. This makes them more convenient for road trips and reduces the time spent waiting for a charge.
While longer-range EVs are advantageous, they often come with a higher price tag due to the advanced battery technology and larger battery pack. This can make the initial purchase costlier. Additionally, the weight of a large battery can impact the vehicle's performance, affecting acceleration and handling. Some drivers might also prefer the convenience of shorter charging times, which can be achieved with smaller battery capacities. Therefore, the choice between range and other factors like performance, charging speed, and cost should be carefully considered based on individual preferences and needs.