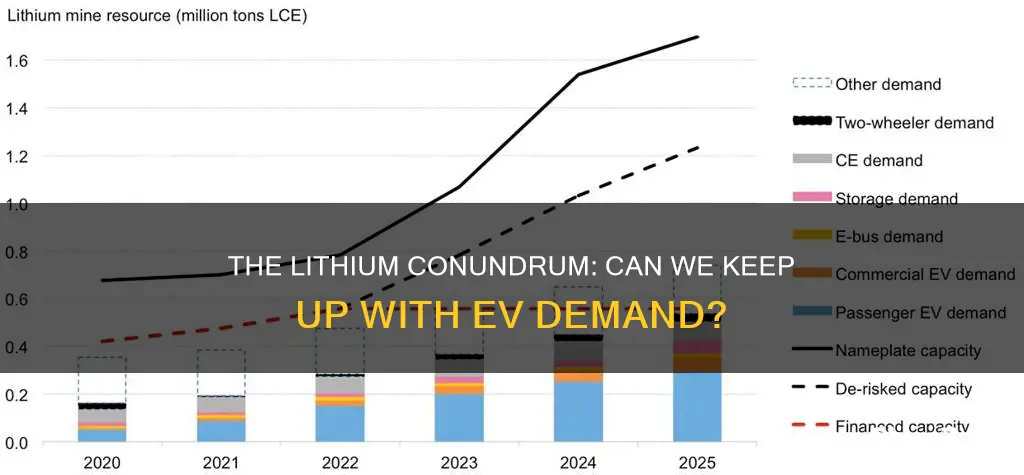
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) has sparked a growing demand for lithium, a critical component in their batteries. As the world transitions towards more sustainable transportation, the question of whether there is sufficient lithium supply to meet the increasing demand for EVs has become a pressing concern. This paragraph aims to explore the current state of lithium resources and the potential challenges and opportunities in ensuring a sustainable supply for the EV industry.
What You'll Learn
- Global Lithium Reserves: Exploring the current and future availability of lithium resources worldwide
- Mining and Extraction: Techniques and challenges in extracting lithium from various geological sources
- Recycling and Reuse: Potential for recycling lithium from batteries and the environmental impact
- Geopolitics of Lithium: The political and economic implications of lithium supply and demand
- Innovation in Battery Tech: Advances in battery technology to improve lithium efficiency and sustainability

Global Lithium Reserves: Exploring the current and future availability of lithium resources worldwide
The global demand for lithium is rapidly increasing due to its crucial role in the production of electric vehicles (EVs). As the world transitions towards a more sustainable future, the focus on lithium resources becomes even more critical. This is because lithium is a key component in the batteries that power EVs, and its availability directly impacts the scalability and sustainability of the EV industry.
Exploring the current and future availability of lithium resources worldwide is essential to understanding the potential challenges and opportunities in the EV market. The primary sources of lithium include hard-rock mining, brines (saline solutions), and clay deposits. Each method has its own advantages and limitations, and the choice of extraction method often depends on the specific geological characteristics of a region.
Hard-rock mining, for instance, is a traditional method that has been used for decades and is prevalent in countries like Australia and Chile. This method involves extracting lithium from mineral-rich rocks, which can be processed to produce lithium carbonate or lithium hydroxide. While hard-rock mining has been successful, it often requires significant energy and water resources, and the environmental impact can be substantial.
Brine deposits, on the other hand, are found in underground saline formations and are a significant source of lithium in countries like the United States and Argentina. This method involves extracting lithium through a process of evaporation, which is more energy-efficient compared to hard-rock mining. However, brine extraction can be challenging due to the need for specialized equipment and the potential for water contamination if not managed properly.
Clay deposits, another potential source of lithium, are found in various regions worldwide, including China and Germany. Clay-based lithium extraction is an emerging technology that involves processing clay minerals to extract lithium. This method is considered more environmentally friendly and has the potential to provide a significant amount of lithium. However, the process is still in the development stage and requires further research and optimization.
The current global lithium reserves are estimated to be sufficient to meet the demand for the next few decades, according to industry reports. However, the distribution of these reserves is uneven, with a few countries holding a significant portion of the world's lithium resources. This concentration of resources can lead to geopolitical tensions and supply chain vulnerabilities.
To ensure a sustainable future for the EV industry, it is crucial to explore and develop new lithium extraction methods, improve recycling processes, and promote the use of alternative battery technologies. Additionally, investing in research and development to enhance the efficiency and environmental sustainability of lithium mining and processing will be essential.
In conclusion, the availability of lithium resources is a critical aspect of the EV industry's growth and sustainability. While current reserves appear sufficient, the uneven distribution and the need for efficient extraction methods highlight the importance of continued exploration and innovation. By addressing these challenges, the world can ensure a reliable supply of lithium to support the widespread adoption of electric vehicles and contribute to a greener future.
Firefighting Tips: Battling Electric Vehicle Blazes
You may want to see also

Mining and Extraction: Techniques and challenges in extracting lithium from various geological sources
The extraction of lithium, a critical element for electric vehicles (EVs), is a complex process that varies depending on the geological source. This mineral is primarily found in two main forms: hard-rock lithium deposits and brines, which are naturally occurring saltwater solutions. Each method presents unique challenges and techniques, and understanding these is essential to ensuring a sustainable supply for the growing EV market.
Hard-Rock Mining: This technique is used for lithium deposits found in igneous and metamorphic rocks. The process involves extensive drilling to identify and map out the lithium-rich zones. Once the target areas are identified, blasting and crushing techniques are employed to extract the lithium-bearing minerals. The crushed material is then processed through various methods, such as froth flotation, to separate the lithium minerals from the waste rock. This method is energy-intensive and can have significant environmental impacts, including soil erosion and water pollution, if not managed properly.
Brine Extraction: Brine deposits are often found in arid regions and are a significant source of lithium. This method involves drilling deep wells into the ground to access the lithium-rich saltwater. The brine is then pumped to the surface, where it is treated to extract the lithium. This process is more environmentally friendly compared to hard-rock mining, as it minimizes soil disturbance and has a smaller carbon footprint. However, it requires precise control of the extraction and treatment processes to ensure the removal of impurities and the efficient recovery of lithium.
One of the primary challenges in lithium extraction is the varying concentrations of the mineral in different geological sources. Hard-rock deposits often contain lower grades of lithium, requiring extensive processing to achieve economically viable concentrations. In contrast, brines can have higher lithium content, but the extraction process must be carefully managed to prevent the loss of other valuable minerals and to maintain water quality.
Another critical aspect is the energy requirements for these extraction processes. Both hard-rock and brine mining need substantial energy inputs, which can be a concern in regions with limited access to renewable energy sources. This issue highlights the need for continuous innovation in energy-efficient extraction techniques and the development of more sustainable practices in the industry.
In conclusion, the extraction of lithium for electric vehicles is a multifaceted process, requiring careful consideration of the geological source and the implementation of appropriate techniques. Addressing the challenges of varying mineral concentrations and energy requirements is crucial to ensuring a stable supply of lithium for the EV market while minimizing environmental impacts. As the demand for EVs continues to rise, the development of more efficient and sustainable extraction methods will be essential to meet the growing need for this critical resource.
Powering Up: A Beginner's Guide to Home EV Charging
You may want to see also

Recycling and Reuse: Potential for recycling lithium from batteries and the environmental impact
The growing demand for electric vehicles (EVs) has sparked a crucial question: Is there enough lithium to meet the increasing need for this essential battery component? While the answer is complex, one potential solution lies in the realm of recycling and reuse. Recycling lithium from batteries not only helps to ensure a more sustainable supply but also offers significant environmental benefits.
Recycling lithium-ion batteries, which are commonly used in EVs, is a challenging but necessary process. The batteries contain valuable materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which can be recovered and reused. The recycling process typically involves several steps: collection, disassembly, separation of components, and then processing to extract the desired materials. Specialized facilities and technologies are required to handle the recycling process safely and efficiently.
One of the key advantages of recycling is the potential to reduce the environmental impact of lithium mining. Mining lithium from natural sources can have detrimental effects on ecosystems and local communities. It often involves extensive water usage and can lead to soil and water contamination. By recycling lithium, we can minimize the need for new mining operations, thereby reducing the potential harm to the environment and preserving natural habitats.
Furthermore, recycling lithium batteries can help to conserve natural resources. Lithium is a finite resource, and its extraction can be energy-intensive. By reusing the lithium from recycled batteries, we can extend the lifespan of this resource and reduce the pressure to source new lithium through mining. This approach contributes to a more circular economy, where materials are continually recycled and reused, minimizing waste and the need for excessive resource extraction.
The environmental impact of lithium recycling extends beyond resource conservation. Proper recycling methods can also prevent the release of hazardous substances into the environment. When batteries are not recycled, they may end up in landfills, leading to potential soil and water pollution. Recycling facilities employ controlled processes to ensure that toxic materials are safely contained and treated, minimizing the risk of environmental contamination. This aspect is crucial in maintaining ecological balance and protecting ecosystems from the potential hazards associated with battery disposal.
The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Best EV: A Comprehensive Comparison
You may want to see also

Geopolitics of Lithium: The political and economic implications of lithium supply and demand
The global transition to electric vehicles (EVs) has sparked a new era of competition and cooperation in the realm of geopolitics, with lithium at the heart of this revolution. As the demand for lithium soars to meet the growing number of EVs on the road, the political and economic landscape is undergoing a profound transformation. This shift is not just about the availability of a raw material but also about the strategic importance of lithium-rich regions and the potential for both collaboration and conflict.
The geopolitical implications of lithium supply are significant. Countries with abundant lithium reserves are now in a position of power, as they can dictate the terms of trade and potentially influence global EV markets. For instance, South America, particularly Chile, Argentina, and Bolivia, holds a substantial share of the world's lithium resources. These countries are strategically positioning themselves as key players in the EV industry, recognizing the economic opportunities that come with being a primary supplier. The political dynamics in these regions are shifting as governments and private companies vie for control over lithium mining projects, often leading to complex negotiations and, in some cases, international disputes.
The demand for lithium is expected to increase exponentially as the EV market expands. This surge in demand has already led to a race for secure supply chains, with countries and corporations investing heavily in lithium mining and processing capabilities. The economic implications are far-reaching, as the lithium industry becomes a significant driver of growth and development in lithium-rich regions. However, this rapid industrialization also raises concerns about environmental degradation and social impacts, particularly in areas where mining activities are concentrated. Balancing economic growth with environmental sustainability and social equity is a critical challenge for policymakers in these regions.
The political and economic implications of lithium supply and demand have far-reaching effects on international relations. As the competition for lithium intensifies, diplomatic efforts are being made to establish fair and transparent trade agreements. Countries are forming alliances to secure their access to lithium, often through international partnerships and investment agreements. These alliances can shape global trade networks and influence the distribution of economic benefits from the EV industry. Moreover, the geopolitical dynamics around lithium can impact global security, as the control of strategic resources can be a factor in international tensions and conflicts.
In conclusion, the geopolitics of lithium is a complex and rapidly evolving field. The race to secure lithium supplies for the EV market has significant political and economic consequences. As the world navigates this new era, finding a balance between meeting the demand for lithium, ensuring environmental sustainability, and fostering international cooperation will be crucial. The future of the EV industry and the global energy transition may depend on how effectively nations manage the geopolitical challenges and opportunities presented by the increasing demand for lithium.
Electric Vehicle Decision: Factors to Consider for Your Next Car
You may want to see also

Innovation in Battery Tech: Advances in battery technology to improve lithium efficiency and sustainability
The quest for sustainable and efficient energy storage solutions has driven significant advancements in battery technology, particularly in the context of lithium-ion batteries used for electric vehicles (EVs). As the demand for EVs continues to rise, addressing the limitations of lithium resources becomes crucial for the long-term viability of the industry. Researchers and engineers are actively exploring innovative approaches to enhance lithium efficiency and sustainability in battery technology.
One key area of innovation is the development of novel cathode materials. Traditional lithium-ion batteries often use cobalt-based cathodes, which are expensive and environmentally challenging to source. Scientists are now turning to alternative materials such as nickel-manganese-cobalt (NMC) and lithium-rich layered oxides. These new cathodes offer improved energy density and reduced reliance on scarce resources like cobalt. For instance, NMC cathodes provide a higher voltage and better thermal stability, making them attractive for next-generation EV batteries.
Another strategy to enhance lithium efficiency is through the optimization of battery design and architecture. Researchers are exploring solid-state batteries, which replace the liquid electrolyte with a solid conductive material. This innovation has the potential to increase energy density, reduce weight, and improve safety compared to conventional lithium-ion batteries. Solid-state batteries can also operate at higher temperatures, further extending their performance and longevity. Additionally, advancements in battery management systems are crucial. These systems monitor and control various parameters, such as temperature, state of charge, and current, to optimize battery performance and longevity while minimizing lithium degradation.
Furthermore, recycling and reusing lithium-ion batteries is an essential aspect of sustainability. Innovative recycling processes aim to recover valuable materials, including lithium, from end-of-life batteries. By implementing efficient recycling methods, the industry can reduce its reliance on virgin resources and minimize environmental impact. This includes developing advanced separation techniques to extract lithium salts from spent batteries and finding new applications for recycled materials in battery manufacturing.
In summary, the push for more sustainable and efficient energy storage solutions has spurred significant progress in battery technology. Innovations in cathode materials, battery design, and recycling processes are collectively working towards improving lithium efficiency and sustainability. These advancements are vital to ensuring the widespread adoption of electric vehicles while addressing the challenges posed by limited lithium resources. As research continues, the goal is to create high-performance batteries that are environmentally friendly, cost-effective, and capable of powering the next generation of EVs.
The Ultimate Guide to Owning a Plug-In EV in Your Apartment
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
While lithium is abundant in the Earth's crust, the supply chain for lithium mining and processing is complex. The current demand for lithium is increasing rapidly due to the EV market's growth, and some regions are more resource-rich than others. However, with proper management and investment in sustainable mining practices, it is possible to meet the demand, especially with the development of recycling technologies to recover lithium from used batteries.
There is a growing concern about the sustainability of lithium mining, especially in regions where lithium is extracted through environmentally damaging methods. The extraction process can have ecological impacts, and some countries are implementing regulations to ensure responsible mining practices. Additionally, the development of alternative battery technologies and recycling processes can help reduce the strain on lithium resources.
The distribution of lithium resources is not uniform globally. Countries like Chile, Australia, and the United States have significant lithium reserves. For example, Chile is a major player in lithium production, while Australia has vast lithium deposits. The proximity of these regions to major EV markets can influence the availability and cost of lithium for EV manufacturers.
Recycling is indeed a crucial aspect of ensuring a sustainable supply of lithium. Recycling technologies are being developed to recover lithium, cobalt, and other materials from end-of-life batteries. This process can significantly reduce the need for primary lithium mining. Many companies are investing in recycling infrastructure, and as the EV market expands, recycling will play a vital role in meeting the demand for lithium while promoting a circular economy.
Several strategies can contribute to a stable lithium supply. These include diversifying mining locations to reduce reliance on a single region, implementing efficient mining and processing techniques, and encouraging the use of second-life batteries (used batteries with reduced performance, but still usable) for energy storage applications. Additionally, research and development in battery technology can lead to more efficient and sustainable lithium-ion batteries, reducing the overall demand for raw materials.