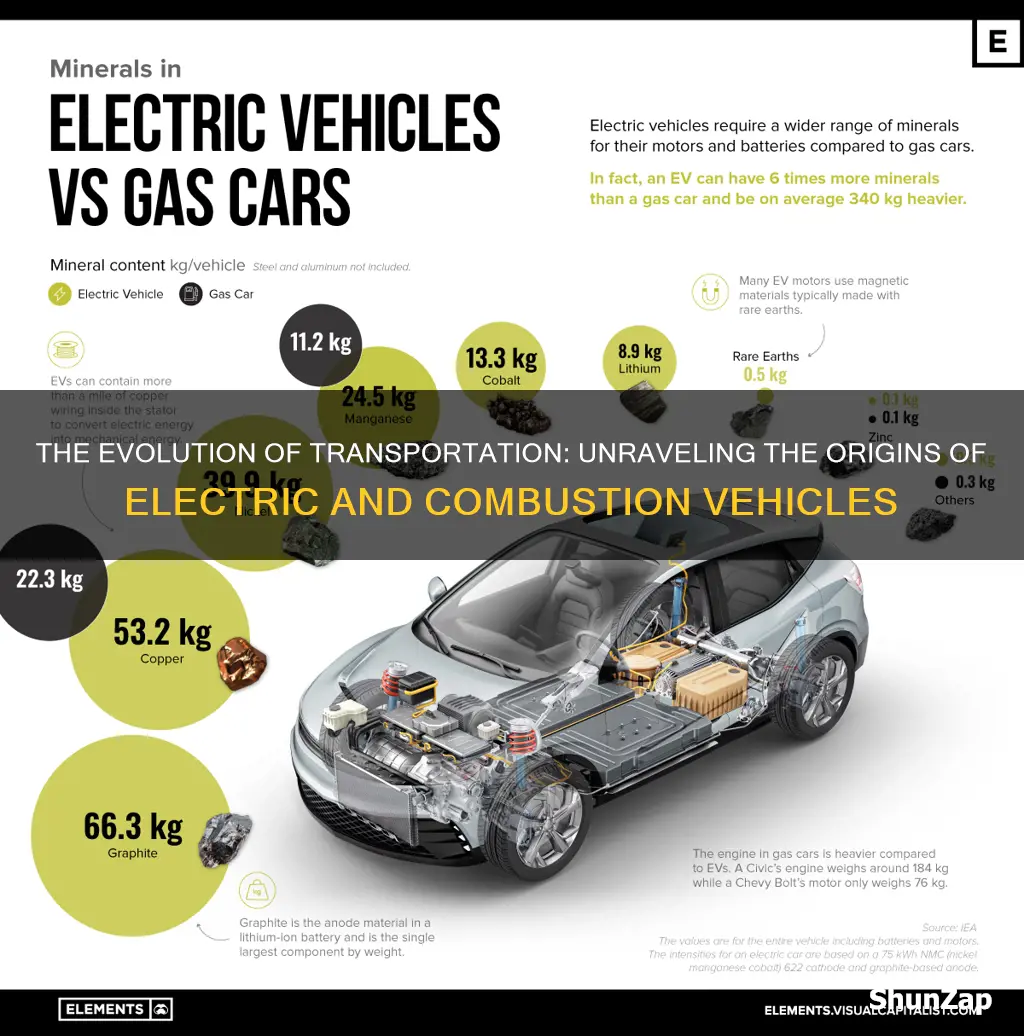
The evolution of the automobile industry has been a fascinating journey, and one of the most intriguing questions in this context is: What came first, electric or combustion vehicles? The answer to this question delves into the history of transportation and highlights the pioneering efforts of inventors and engineers. Early experiments with electric-powered vehicles date back to the 19th century, with pioneers like Robert Anderson and Thomas Davenport creating crude electric carriages. However, it was the internal combustion engine that gained prominence, thanks to the groundbreaking work of Nikolaus Otto and others, leading to the dominance of gasoline-powered cars in the early 20th century. Despite the success of combustion engines, the idea of electric vehicles persisted, and the 21st century has seen a resurgence in interest, driven by environmental concerns and technological advancements, challenging the long-held notion of what came first in the world of automobiles.
What You'll Learn
- Historical Context: The invention of the electric vehicle predates the combustion engine, dating back to the 19th century
- Technological Advancements: Electric vehicles gained popularity due to advancements in battery technology, offering a cleaner alternative to combustion engines
- Environmental Impact: Combustion vehicles have a higher environmental impact due to emissions, prompting the development of electric alternatives
- Government Incentives: Governments have incentivized electric vehicle adoption through subsidies and regulations, accelerating their market penetration
- Consumer Preferences: Consumer demand for sustainable transportation has driven the growth of the electric vehicle market

Historical Context: The invention of the electric vehicle predates the combustion engine, dating back to the 19th century
The concept of electric vehicles (EVs) has a rich history that predates the widespread adoption of combustion engines. In the 19th century, a time of rapid technological advancement, inventors and engineers began experimenting with electric propulsion as an alternative to traditional internal combustion. This era marked the beginning of a journey that would eventually lead to the modern electric car industry.
One of the earliest known electric vehicles was created by Robert Anderson, a British inventor, in the 1830s. Anderson's design was a crude prototype, consisting of a crude electric motor powered by non-rechargeable batteries. Despite its limitations, Anderson's invention laid the foundation for future developments. Around the same time, Hungarian scientist Ányos Jedlik and Dutch professor Sibrandus Stratingh also independently invented crude electric carriages, further highlighting the early interest in electric mobility.
The 1870s and 1880s witnessed significant advancements in battery technology, which played a crucial role in the evolution of electric vehicles. In 1859, French physicist Gaston Planté invented the first rechargeable battery, known as the lead-acid battery. This breakthrough enabled the development of more practical and efficient electric cars. During this period, inventors like Thomas Davenport and William Morrison in the United States, and Robert Anderson in the UK, began creating more sophisticated electric carriages. Davenport's invention, in particular, is often credited as one of the first practical electric vehicles, as it was used for commercial purposes, such as carrying passengers in a park.
The late 19th century saw the rise of electric vehicles as a viable transportation option. In 1890, Thomas Parker, a British inventor, is credited with creating the first practical production electric car. Parker's vehicle was a significant improvement over earlier prototypes, featuring a more efficient motor and a practical design. This period also saw the introduction of electric taxis in London, further solidifying the potential of electric mobility. The success of these early electric vehicles sparked interest and investment in the technology, leading to further innovations and the eventual decline of electric cars in favor of their combustion engine counterparts.
The historical context of electric vehicles is often overlooked in favor of the more prominent story of the combustion engine. However, the 19th-century advancements in electric propulsion technology laid the groundwork for the modern EV revolution. This early experimentation and innovation set the stage for the resurgence of electric vehicles in the 21st century, offering a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to traditional internal combustion engines.
Powering Up: Understanding the Safety of Plugging In Your EV
You may want to see also

Technological Advancements: Electric vehicles gained popularity due to advancements in battery technology, offering a cleaner alternative to combustion engines
The evolution of electric vehicles (EVs) and their rise in popularity is closely intertwined with significant technological advancements, particularly in battery technology. The development of efficient and powerful batteries has been a pivotal factor in the growing acceptance and adoption of electric cars.
Battery technology has seen remarkable progress over the years, addressing the primary concern of range anxiety associated with early electric vehicles. The initial electric cars, introduced in the late 19th century, struggled with limited battery capacity and short driving ranges. This led to a decline in their popularity as consumers sought more practical transportation options. However, advancements in lithium-ion battery technology have revolutionized the EV market. Lithium-ion batteries offer higher energy density, allowing for increased driving ranges and reduced charging times. Modern electric vehicles can now travel over 300 miles on a single charge, making them a viable and attractive alternative to traditional combustion engine cars.
The improved battery technology has not only enhanced the performance of electric vehicles but has also contributed to their environmental benefits. Electric motors are inherently more efficient than internal combustion engines, and when coupled with advanced batteries, they produce zero tailpipe emissions. This has led to a significant reduction in air pollution and a smaller carbon footprint compared to conventional vehicles. As a result, governments and environmental organizations worldwide have encouraged the adoption of electric cars through incentives and regulations, further driving the demand for these technologically advanced vehicles.
Additionally, the development of fast-charging infrastructure has played a crucial role in the popularity of electric vehicles. Rapid charging stations enable drivers to recharge their batteries quickly, addressing the convenience factor often associated with longer refueling times of combustion engine vehicles. This technological advancement has made electric vehicles more practical for daily use, especially for long-distance travel.
In summary, the widespread acceptance of electric vehicles can be attributed to the remarkable progress in battery technology. The advancements have resulted in longer driving ranges, reduced charging times, and zero-emission performance, making electric cars a cleaner and more sustainable transportation option. As technology continues to evolve, we can expect further improvements, potentially leading to even more widespread adoption of electric vehicles in the future.
Chrysler's Electric Evolution: A New Era of Sustainable Mobility
You may want to see also

Environmental Impact: Combustion vehicles have a higher environmental impact due to emissions, prompting the development of electric alternatives
The environmental implications of combustion vehicles have long been a subject of concern, primarily due to their significant emissions. These vehicles, which rely on internal combustion engines, release a multitude of pollutants into the atmosphere, including carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter. The burning of fossil fuels in these engines is a major contributor to air pollution and climate change. Over the years, the detrimental effects of combustion vehicles have become increasingly evident, prompting a shift towards more sustainable transportation options.
One of the key environmental impacts is the release of greenhouse gases, particularly CO2, which is a primary driver of global warming. The transportation sector, including road vehicles, is a significant contributor to CO2 emissions. Combustion engines burn gasoline or diesel, a process that results in the release of large amounts of CO2, a potent greenhouse gas. This has led to a growing awareness of the need for cleaner and more sustainable transportation methods.
In addition to CO2, combustion vehicles emit various other pollutants. Nitrogen oxides, for instance, are released during the combustion process and contribute to the formation of smog and acid rain. Particulate matter, which consists of tiny particles and liquid droplets, can be inhaled and cause respiratory issues. These emissions not only affect air quality but also have adverse effects on human health and the environment.
The realization of these environmental challenges has spurred the development and adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). EVs are designed to run on electric motors powered by rechargeable batteries, eliminating the need for traditional combustion engines. By doing so, they significantly reduce the emission of harmful pollutants and greenhouse gases. Electric vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, meaning they do not release pollutants directly into the air, making them a cleaner and more environmentally friendly option.
The transition from combustion to electric vehicles is a crucial step towards mitigating the environmental impact of the transportation sector. As technology advances, the performance and range of electric vehicles continue to improve, making them more viable and attractive to consumers. This shift not only benefits the environment but also contributes to a more sustainable and resilient future for the automotive industry. The development of electric alternatives is a direct response to the need for reducing emissions and combating the adverse effects of combustion vehicles on our planet.
Unlocking EV Tax Credits: A Guide to Maximizing Your Federal Benefits
You may want to see also

Government Incentives: Governments have incentivized electric vehicle adoption through subsidies and regulations, accelerating their market penetration
The development of electric vehicles (EVs) and internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles has been a long and evolving process, with both technologies having their own unique histories and milestones. While it is often debated which came first, the answer lies in understanding the historical context and the factors that drove the development of these two transportation methods.
The concept of electric vehicles can be traced back to the 19th century, with early experiments and prototypes. In 1832, Robert Anderson, a British inventor, created one of the first crude electric carriages. This early vehicle used a non-rechargeable battery and was a significant step towards electric mobility. However, it was not until the late 19th and early 20th centuries that electric vehicles gained more traction. In 1899, Thomas Parker, a British inventor, introduced the first practical production electric car, which was a significant milestone. These early electric vehicles were popular for their quiet operation and ease of use, especially in urban areas.
On the other hand, internal combustion engine vehicles have a longer history, with their origins dating back to the late 18th century. In 1794, François Isaac de Rivaz, a Swiss inventor, designed an internal combustion engine that ran on a mixture of hydrogen and oxygen. This early engine laid the foundation for the development of gasoline and diesel engines. The first practical automobile powered by an internal combustion engine was built by Karl Benz in 1885, marking a significant milestone in the history of automobiles. Benz's invention revolutionized transportation and led to the widespread adoption of ICE vehicles.
The early 20th century saw a rapid evolution of both electric and combustion vehicles. Electric cars gained popularity due to their convenience and environmental benefits, especially in the early 1900s. However, the rise of affordable gasoline vehicles and the discovery of vast oil reserves led to a shift in focus towards ICE vehicles. By the mid-20th century, electric vehicles had largely been overshadowed by the dominance of gasoline-powered cars.
In recent decades, there has been a renewed interest in electric vehicles due to environmental concerns and technological advancements. Governments around the world have played a crucial role in incentivizing the adoption of EVs through various means. One of the primary methods is through subsidies and financial incentives. Many governments offer tax credits, rebates, and grants to individuals and businesses purchasing electric vehicles. These incentives reduce the upfront cost of EVs, making them more affordable and attractive to consumers. For example, the United States has provided significant tax credits for EV purchases, encouraging many Americans to make the switch.
Additionally, governments have implemented regulations and standards to accelerate the market penetration of electric vehicles. These regulations often include mandates for vehicle manufacturers to meet certain EV sales targets or achieve specific emissions standards. By setting these targets, governments create a demand for electric vehicles and encourage the development of the necessary infrastructure, such as charging stations. For instance, the European Union's CO2 emissions standards have pushed car manufacturers to invest in electric powertrains, resulting in a faster transition to a more sustainable transportation sector.
The impact of these government incentives cannot be overstated. They have played a pivotal role in reducing the cost of electric vehicles, improving their performance, and addressing range anxiety among consumers. As a result, the market for electric vehicles has grown exponentially, with many major car manufacturers now offering a range of EV models. This shift towards electrification has not only benefited the environment by reducing greenhouse gas emissions but has also created new job opportunities and stimulated economic growth in the green technology sector.
In summary, while the debate over which came first, electric or combustion vehicles, may continue, the historical context and government incentives have been instrumental in shaping the automotive industry. Governments' role in incentivizing electric vehicle adoption through subsidies and regulations has accelerated the market's growth, leading to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation future. This transformation is a testament to the power of policy and innovation in driving technological advancements.
Honda's Electric Vehicle Lineup: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Consumer Preferences: Consumer demand for sustainable transportation has driven the growth of the electric vehicle market
The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) can be attributed, in large part, to the growing consumer preference for sustainable transportation options. In recent years, there has been a significant shift in consumer behavior, with an increasing number of individuals prioritizing environmental consciousness and sustainability in their vehicle choices. This change in consumer demand has played a pivotal role in the rapid expansion of the electric vehicle market.
Environmental concerns and the desire to reduce carbon footprints have been key catalysts for this transformation. Many consumers are now actively seeking alternatives to traditional combustion engine vehicles, which are known to contribute significantly to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. Electric cars, with their zero-emission technology, offer a cleaner and greener solution, appealing to those who want to minimize their environmental impact. As a result, the market has responded by introducing a wide range of electric vehicle models, catering to diverse consumer preferences and needs.
Consumer awareness and education have also played a crucial role in this shift. With the increasing availability of information, people are becoming more informed about the benefits of electric vehicles. They understand that EVs not only reduce environmental harm but also provide a cost-effective and efficient driving experience. The perception of electric cars as a viable and desirable alternative to traditional vehicles has grown, especially among younger generations who are more environmentally conscious.
Additionally, government incentives and policies have further encouraged the adoption of electric vehicles. Many countries and regions have implemented subsidies, tax benefits, and other incentives to promote the purchase and use of EVs. These measures have made electric cars more affordable and attractive to consumers, especially those who were initially hesitant due to higher upfront costs. As a result, the market has witnessed a surge in electric vehicle sales, with manufacturers investing heavily in EV technology and infrastructure.
The growth of the electric vehicle market is a testament to the power of consumer preferences and their ability to shape the automotive industry. As consumer demand for sustainable transportation continues to rise, we can expect further innovation and diversification in the EV sector. This trend not only benefits the environment but also drives economic growth, creating opportunities for new technologies and business models in the sustainable transportation space.
Ford's Electric Future: Shifting Focus or Staying Committed?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The concept of electric vehicles (EVs) has a longer history than combustion engine vehicles. The first practical electric car was invented in the 19th century, with Robert Anderson creating a crude electric carriage in 1832. However, it was in the late 19th and early 20th centuries that electric vehicles gained popularity, especially for urban transportation. During this period, many cities had electric taxis and delivery vehicles. In contrast, the internal combustion engine, which powers traditional gasoline or diesel cars, was invented by Nicolaus Otto in 1876, and it took several decades for these vehicles to become widely adopted.
The decline of electric vehicles in the early 20th century can be attributed to several factors. One significant reason was the improvement and affordability of the internal combustion engine. Gasoline engines became more efficient and cost-effective, making them a more attractive option for consumers. Additionally, the development of the assembly line by Henry Ford revolutionized car manufacturing, making gasoline-powered cars more accessible to the general public. The limited range and slower charging times of early electric vehicles also made them less practical for long-distance travel compared to the faster and more convenient combustion engines.
The late 20th and early 21st centuries witnessed a resurgence in interest in electric vehicles. This revival was primarily driven by environmental concerns and the need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The development of more efficient batteries and the recognition of the environmental benefits of EVs played a crucial role in this resurgence. Many automotive manufacturers started investing in electric powertrains, leading to the launch of several successful electric car models. Governments also played a part by offering incentives and subsidies to promote the adoption of electric vehicles.
Yes, electric vehicles offer several advantages over their combustion engine counterparts. Firstly, EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, reducing air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. This makes them more environmentally friendly. Secondly, electric motors are generally more efficient, converting a higher percentage of energy into power compared to internal combustion engines. This results in lower energy consumption and reduced running costs. Additionally, electric vehicles often provide a smoother and quieter driving experience due to the instant torque delivery of electric motors.