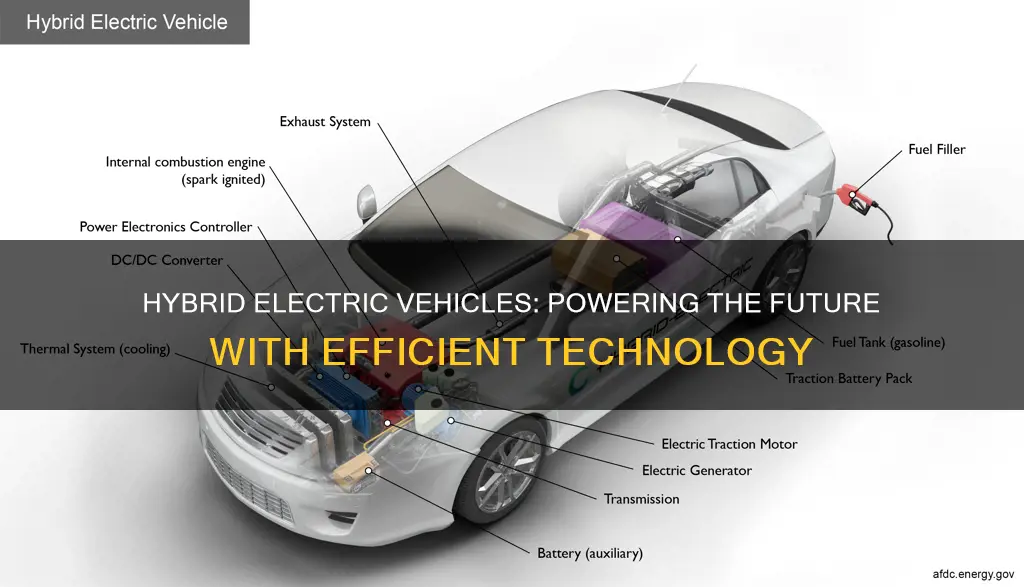
A hybrid electric vehicle (HEV) is a type of vehicle that combines a traditional internal combustion engine with an electric motor and a battery pack. This innovative design allows the vehicle to switch between the two power sources, providing both efficiency and performance. The electric motor powers the vehicle at low speeds or during acceleration, while the internal combustion engine takes over at higher speeds or when more power is needed. HEVs are designed to reduce fuel consumption and emissions, making them an environmentally friendly choice for drivers. With their ability to seamlessly switch between power sources, hybrid electric vehicles offer a unique driving experience that balances power, efficiency, and sustainability.
What You'll Learn
- Power Sources: Hybrid EVs combine an internal combustion engine with an electric motor and battery pack
- Energy Efficiency: These vehicles optimize energy use, reducing fuel consumption and emissions
- Performance: Hybrid EVs offer improved acceleration and handling compared to traditional gasoline-powered cars
- Environmental Impact: Lower carbon footprint due to reduced reliance on fossil fuels
- Cost Benefits: Hybrid EVs can save money on fuel and maintenance over time

Power Sources: Hybrid EVs combine an internal combustion engine with an electric motor and battery pack
Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) are a fascinating innovation in the automotive industry, offering a unique blend of traditional combustion engines and electric power. At the heart of these vehicles' design is a clever combination of power sources, which provides an efficient and environmentally friendly driving experience.
The power sources in a hybrid EV consist of two main components: an internal combustion engine and an electric motor, both of which work in tandem with a high-capacity battery pack. The internal combustion engine, typically a gasoline or diesel engine, provides the primary source of power, especially during higher-speed driving or when more power is required. This engine is designed to be more fuel-efficient than traditional engines, reducing fuel consumption and emissions. When the vehicle is in motion, the engine operates, generating power to drive the wheels and charge the battery pack.
The electric motor, on the other hand, provides an additional power source and is a key feature of hybrid vehicles. It assists the internal combustion engine, especially during acceleration and when extra torque is needed. Electric motors are highly efficient and can provide instant torque, resulting in smooth and responsive acceleration. When the driver demands more power, the electric motor kicks in, delivering a burst of energy to the wheels, ensuring a seamless driving experience.
The battery pack is a critical component, storing electrical energy to power the electric motor and various accessories. These batteries are designed to be lightweight and compact, allowing for efficient energy storage. During regenerative braking, the electric motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery. This process helps to recharge the battery and improve overall efficiency.
In a hybrid EV, the power sources work in harmony. The internal combustion engine and electric motor can operate independently or simultaneously, depending on the driving conditions and the driver's needs. For example, when cruising at a steady speed, the engine may shut off temporarily, and the electric motor and battery power the vehicle, reducing fuel consumption and emissions. This technology showcases a sophisticated approach to power management, ensuring that hybrid vehicles offer a balance of performance, efficiency, and environmental sustainability.
The Electric Revolution: Ford's Model T Redefined the Automotive World
You may want to see also

Energy Efficiency: These vehicles optimize energy use, reducing fuel consumption and emissions
Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) are designed with a primary focus on energy efficiency, aiming to optimize energy use and significantly reduce fuel consumption and emissions. This is achieved through a combination of advanced technologies and innovative engineering. At the heart of an HEV is a parallel hybrid system, which typically consists of a conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) and an electric motor. The ICE provides the primary power source, while the electric motor assists, especially during acceleration and when extra power is needed. This dual-power system allows for a more efficient use of energy, as the electric motor can take over when the ICE is not operating at its most efficient point, such as during low-speed driving or when idling.
One of the key advantages of HEVs is their ability to switch seamlessly between the ICE and the electric motor, or even shut down the ICE entirely under certain conditions. This is made possible by sophisticated control systems that manage the energy flow between the battery, the ICE, and the electric motor. When the vehicle is stationary or moving at low speeds, the ICE can be turned off, and the vehicle will run solely on the electric motor, eliminating fuel consumption and reducing emissions to zero. This feature, known as "electric-only" or "stop-start" operation, is a significant contributor to the overall energy efficiency of HEVs.
Regenerative braking is another critical aspect of energy efficiency in HEVs. Unlike conventional vehicles, HEVs employ regenerative braking systems that capture and store the kinetic energy that would otherwise be lost as heat during braking. This energy is then reused to recharge the vehicle's battery, extending the range that can be achieved on electric power alone. As a result, HEVs can maintain higher efficiency levels, especially in city driving conditions where frequent stopping and starting are common.
The design and materials used in HEVs also play a vital role in energy efficiency. Lightweight materials, such as aluminum and high-strength steel, are often employed to reduce the overall weight of the vehicle, which in turn improves fuel efficiency. Additionally, the packaging of components, such as the battery and electric motor, is optimized to minimize energy losses and maximize the use of space, ensuring that every aspect of the vehicle contributes to its energy-efficient performance.
In summary, hybrid electric vehicles are engineered to optimize energy use, leading to reduced fuel consumption and lower emissions. Through the use of parallel hybrid systems, seamless power transitions, regenerative braking, and thoughtful design choices, HEVs achieve a level of energy efficiency that is significantly higher than that of conventional vehicles. This not only benefits the environment by reducing the carbon footprint of transportation but also contributes to cost savings for vehicle owners due to lower fuel and maintenance expenses.
A Green Revolution: The Electric Vehicle Takeover
You may want to see also

Performance: Hybrid EVs offer improved acceleration and handling compared to traditional gasoline-powered cars
Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) have revolutionized the automotive industry by combining the benefits of electric power and traditional internal combustion engines, resulting in significant performance enhancements. One of the most notable advantages of HEVs is their improved acceleration, which sets them apart from conventional gasoline-powered vehicles.
The power delivery in hybrid cars is designed to be smooth and responsive. When you press the accelerator pedal, the electric motor instantly provides a burst of torque, allowing the vehicle to accelerate quickly and efficiently. This electric-assist feature ensures that HEVs can accelerate faster from a standstill compared to their gasoline counterparts. For instance, a well-known hybrid sedan can accelerate from 0 to 60 mph in just 7.5 seconds, outperforming many traditional mid-size sedans. This rapid acceleration is particularly noticeable when overtaking or merging onto highways, providing a more confident and dynamic driving experience.
The handling characteristics of hybrid vehicles also contribute to their overall performance. The electric motor's ability to provide instant torque helps improve traction and stability, especially during cornering. Hybrid EVs often feature advanced suspension systems and precise steering, further enhancing their handling capabilities. As a result, drivers can experience better control and responsiveness, making the vehicle more predictable and easier to maneuver, even in challenging driving conditions.
Furthermore, the regenerative braking system in HEVs plays a crucial role in optimizing performance. When the driver applies the brakes, the electric motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery. This process not only improves energy efficiency but also provides additional power during acceleration, further enhancing the vehicle's performance. The regenerative braking system also contributes to a more comfortable and controlled driving experience, especially in city driving conditions where frequent stopping and starting are common.
In summary, hybrid electric vehicles offer a unique blend of performance benefits. With their electric-assist technology, HEVs provide superior acceleration, ensuring a more responsive and engaging driving experience. The improved handling and regenerative braking systems further contribute to the overall driving dynamics, making hybrid EVs a compelling choice for those seeking both performance and efficiency in their vehicles. This combination of electric and traditional power sources has paved the way for a new era of automotive performance, challenging the conventional norms of gasoline-powered cars.
Unveiling Tesla's Electric Vehicle: A Patent Mystery
You may want to see also

Environmental Impact: Lower carbon footprint due to reduced reliance on fossil fuels
Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) are a significant step towards a more sustainable transportation future, offering a unique approach to reducing environmental impact. These vehicles combine a traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) with an electric motor and a battery pack, allowing for a more efficient and environmentally friendly driving experience. The primary environmental benefit lies in the reduced reliance on fossil fuels, which are the primary source of greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution.
In traditional vehicles, the ICE is the sole power source, burning gasoline or diesel to propel the car. This process releases a substantial amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other harmful pollutants into the atmosphere. HEVs, however, utilize both the ICE and the electric motor, which runs on electricity stored in the battery. When the vehicle is driven at lower speeds or during stop-and-go traffic, the electric motor takes over, eliminating the need for the ICE to run continuously. This results in a significant reduction in fuel consumption and, consequently, lower CO2 emissions.
The electric motor provides an efficient and clean alternative, especially during urban driving conditions. It offers instant torque, delivering smooth acceleration and reducing the need for frequent gear changes. This feature not only enhances the driving experience but also contributes to lower fuel consumption and reduced emissions. By utilizing the electric motor for short-distance travel, HEVs can minimize the time the ICE operates, thereby decreasing the overall carbon footprint.
Furthermore, the regenerative braking system in HEVs plays a crucial role in reducing environmental impact. When the driver applies the brakes, the electric motor acts as a generator, converting the kinetic energy of the moving vehicle back into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery. This process, known as regenerative braking, helps to recharge the battery and further reduces the need for the ICE to provide power, thus lowering fuel consumption and emissions.
In summary, hybrid electric vehicles offer a compelling solution to environmental concerns related to transportation. By combining the benefits of both electric and traditional power sources, HEVs significantly reduce the reliance on fossil fuels, leading to a lower carbon footprint and improved air quality. This technology showcases a practical approach to sustainable mobility, encouraging a shift towards cleaner and more efficient transportation options.
Green Revolution: Unlocking the Power of Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Cost Benefits: Hybrid EVs can save money on fuel and maintenance over time
Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) offer a compelling solution for those seeking an eco-friendly and cost-effective mode of transportation. One of the most significant advantages of HEVs is their ability to save money on fuel and maintenance, making them an attractive option for environmentally conscious consumers.
In terms of fuel efficiency, HEVs are designed to optimize energy usage. They combine a traditional internal combustion engine with an electric motor, allowing for a seamless transition between the two power sources. During city driving, where frequent stops and starts are common, the electric motor takes the lead, providing smooth acceleration and reducing fuel consumption. This is particularly beneficial in congested urban areas, where HEVs can offer significant fuel savings compared to conventional vehicles. The electric motor's ability to regenerate energy during braking further enhances efficiency, converting kinetic energy back into usable power.
Over time, these fuel savings can add up to substantial financial benefits. HEVs are known to achieve higher miles per gallon (mpg) than their gasoline counterparts, often exceeding 40 mpg in city driving conditions. This increased efficiency translates to reduced fuel costs, especially for those who frequently commute in urban environments. For example, a driver traveling 15,000 miles annually in a city with an average fuel price of $3.00 per gallon could save hundreds of dollars per year with an HEV, depending on its specific fuel economy.
Maintenance costs are another area where HEVs excel. The simpler power train of an HEV, with fewer moving parts, often results in lower maintenance requirements. The electric motor, for instance, has no transmission or complex gear systems, reducing the need for frequent servicing. Additionally, HEVs typically feature regenerative braking systems that minimize wear on traditional brake pads, further lowering maintenance expenses. While the initial purchase price of an HEV may be higher than that of a conventional vehicle, the long-term savings on fuel and maintenance can offset this difference, providing a more economical choice for vehicle owners.
Furthermore, the environmental benefits of HEVs contribute to their overall cost-effectiveness. By reducing fuel consumption and emissions, HEVs help drivers comply with environmental regulations and contribute to a greener future. Many governments and cities offer incentives and tax benefits for HEV owners, further enhancing the financial appeal of these vehicles. In summary, the combination of improved fuel efficiency, reduced maintenance needs, and potential environmental incentives makes HEVs a financially wise choice, offering long-term savings and a reduced environmental footprint.
Green Revolution: A Guide to Fleet Conversion to Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A hybrid electric vehicle is a type of automobile that combines a traditional internal combustion engine with an electric motor and a battery pack. It is designed to improve fuel efficiency and reduce emissions by utilizing both electric power and gasoline.
HEVs operate by switching between the electric motor and the internal combustion engine. During low-speed driving or when the battery is charged, the vehicle runs on electric power, providing a smooth and quiet ride. When more power is needed or during regenerative braking, the engine kicks in to assist. The system optimizes energy use, allowing the vehicle to run more efficiently.
Hybrid electric vehicles offer several advantages. They provide improved fuel economy, reducing the cost of ownership over time. The electric motor also results in lower emissions, contributing to a cleaner environment. Additionally, HEVs often have a longer range compared to all-electric vehicles, making them suitable for various driving conditions.
Yes, hybrid electric vehicles typically have a charging port, usually located on the front or side of the car. You can plug it into a standard electrical outlet or a dedicated charging station to recharge the battery. However, it's important to note that the charging process for HEVs is different from that of all-electric vehicles, and the battery is usually charged during regenerative braking and by the internal combustion engine.
The battery in a hybrid electric vehicle is a high-capacity rechargeable battery pack. It stores electrical energy and powers the electric motor. During regenerative braking, the motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy to recharge the battery. The battery also receives power from the internal combustion engine when needed, ensuring a continuous supply of energy for the vehicle's operation.







