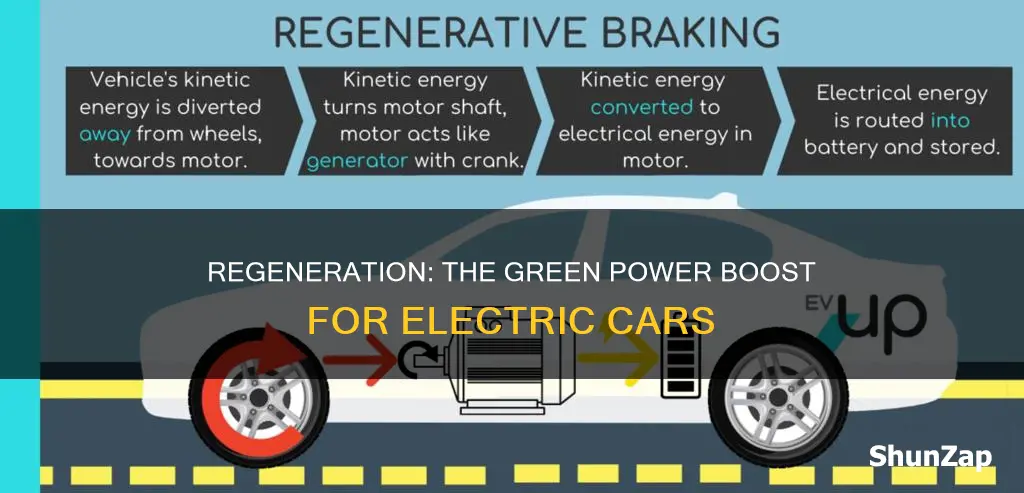
Regeneration in electric vehicles refers to the process of converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy, which is then stored in the vehicle's battery. This technology, often called regenerative braking, is a key feature of electric cars and plays a crucial role in improving their efficiency and range. When the driver applies the brakes, the electric motor switches to generator mode, capturing the energy that would otherwise be lost as heat during conventional braking. This innovative system not only helps extend the vehicle's range but also reduces wear and tear on traditional braking components, contributing to a more sustainable and cost-effective driving experience.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | Regenerative braking is a process in electric vehicles (EVs) that converts the kinetic energy of the moving vehicle into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery pack. |
| Energy Recovery | It recovers and stores energy that would otherwise be lost as heat during braking. |
| Efficiency | Can improve overall efficiency by up to 10-15% compared to conventional braking systems. |
| Types | There are two main types: kinetic energy recovery system (KERS) and regenerative braking. KERS is used in racing and high-performance EVs, while regenerative braking is more common in everyday EVs. |
| Components | In regenerative braking, the electric motor acts as a generator, converting the vehicle's forward motion into electrical energy. The energy is then directed back to the battery. |
| Benefits | Reduces wear and tear on brake pads and rotors, improves range, and provides a more responsive driving experience. |
| Range Extension | By capturing and reusing energy, it can extend the driving range of an EV, especially during frequent stop-and-go driving. |
| Environmental Impact | Regenerative braking contributes to reducing the environmental footprint of EVs by minimizing energy waste. |
| Implementation | It is available in various levels, from mild to strong, depending on the vehicle's design and intended use. |
| Driver Experience | Provides a smoother and quieter driving experience, as it reduces the need for frequent manual braking. |
| Research and Development | Ongoing research focuses on improving efficiency, response time, and implementing more advanced energy recovery systems. |
What You'll Learn
- Regeneration Basics: The process of converting kinetic energy back into stored energy
- Regenerative Braking: Using brakes to slow down and generate electricity
- Energy Recovery: Capturing and storing energy from braking and driving
- Efficiency Boost: Regeneration improves overall efficiency and reduces fuel consumption
- Environmental Impact: Regeneration reduces emissions and promotes sustainable energy use

Regeneration Basics: The process of converting kinetic energy back into stored energy
Regeneration in electric vehicles is a fascinating process that plays a crucial role in optimizing their performance and efficiency. It is a technology that harnesses the power of kinetic energy, which is often wasted during the braking process, and converts it back into stored energy, typically in the form of electrical energy. This innovative feature is a key differentiator between electric vehicles (EVs) and traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles.
The concept of regeneration is based on the principle of energy conservation, where energy is not destroyed but transformed from one form to another. In the context of EVs, when the driver applies the brakes, the electric motor, which is also the generator, switches into a regenerative mode. This mode allows the motor to act as a generator, converting the vehicle's kinetic energy into electrical energy. The process is similar to what happens when you pedal a bicycle and the chain turns the gears, generating resistance and slowing you down.
During regeneration, the kinetic energy of the moving vehicle is captured and stored in the battery pack. This stored energy can then be used to power the vehicle when needed, reducing the reliance on the internal combustion engine or the charging station. The efficiency of this process is remarkable, as it can recover a significant portion of the energy that would otherwise be lost as heat during conventional braking systems.
The technology behind regeneration is relatively simple yet highly effective. When the driver initiates the braking action, the electric motor's rotation is reversed, causing it to act as a generator. This generates an electric current that flows back into the battery, recharging it. The amount of energy that can be recovered depends on various factors, including the vehicle's speed, the weight, and the efficiency of the motor and battery system. Modern EVs are designed to optimize this process, ensuring that the kinetic energy is efficiently converted and stored.
Regeneration offers several advantages. Firstly, it improves the overall efficiency of the vehicle, reducing energy waste. Secondly, it extends the range of electric vehicles, as the recovered energy can be utilized during the journey. This feature is particularly beneficial for long-distance travel, where efficient energy management is crucial. Additionally, regeneration contributes to a smoother and more responsive driving experience, as the electric motor provides instant torque, enhancing acceleration and overall performance.
Electric Ride Safety: Age-Appropriate Choices for Kids
You may want to see also

Regenerative Braking: Using brakes to slow down and generate electricity
Regenerative braking is a revolutionary feature in electric vehicles (EVs) that harnesses the power of braking to enhance efficiency and performance. When applied, this technology converts the kinetic energy of the vehicle into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery pack. This process is a significant departure from traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, where braking primarily serves to dissipate energy as heat.
The mechanism of regenerative braking is straightforward yet innovative. When the driver applies the brakes, the electric motor switches from driving the wheels to acting as a generator. This transformation occurs seamlessly, allowing the vehicle to slow down while simultaneously recharging the battery. The amount of energy generated depends on the speed of the vehicle and the force applied to the brakes. During this process, the kinetic energy that would otherwise be lost as heat is captured and transformed into a valuable resource—electricity.
This technology offers several advantages. Firstly, it increases the overall range of the EV by optimizing energy usage. By capturing and reusing energy that would otherwise be wasted, regenerative braking reduces the strain on the battery, allowing for longer journeys on a single charge. Secondly, it provides a more responsive and controlled driving experience. The instant generation of electricity during braking gives drivers a sense of immediacy and precision, making the vehicle more agile and easier to handle.
The implementation of regenerative braking varies across different EV models. Some systems are designed to be highly responsive, providing strong regenerative forces even at low speeds. This ensures that energy is captured efficiently during everyday driving, including frequent stops and starts. Other vehicles might offer a more gradual regeneration process, providing a balance between energy conservation and maintaining a comfortable driving feel.
In summary, regenerative braking is a game-changer in the world of electric vehicles, offering a sustainable and efficient approach to braking. By converting kinetic energy into electrical power, this technology not only extends the range of EVs but also contributes to a more environmentally friendly and responsive driving experience. As EV technology continues to evolve, regenerative braking is set to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of sustainable transportation.
Unlocking EV Tax Savings: A Guide to Maximizing Your Credit
You may want to see also

Energy Recovery: Capturing and storing energy from braking and driving
Energy recovery systems in electric vehicles (EVs) are designed to capture and reuse the kinetic energy that would otherwise be lost during braking and driving. This process, known as energy regeneration or regenerative braking, is a key feature that sets EVs apart from traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. By converting kinetic energy back into usable electrical energy, these systems improve overall efficiency and extend the range of electric vehicles.
The primary method of energy recovery is through regenerative braking, which utilizes an electric motor as a generator during deceleration. When the driver applies the brakes, the motor switches to generator mode, converting the vehicle's kinetic energy into electrical energy. This energy is then fed back into the battery pack, recharging it and reducing the need for external power sources. The system is particularly effective in urban driving conditions where frequent stops and starts are common, as it can capture and store energy that would otherwise be wasted.
In addition to regenerative braking, some electric vehicles employ other energy recovery techniques. One such method is dynamic energy recovery, which involves capturing energy from the vehicle's suspension system. As the vehicle moves, the suspension compresses and extends, creating a repetitive energy exchange. This energy can be captured and stored using specialized devices, such as hydraulic or electromagnetic systems, which convert the kinetic energy into electrical power. This approach is particularly useful in high-performance EVs, where the suspension system can contribute significantly to overall energy efficiency.
Another innovative energy recovery method is the use of waste heat recovery systems. These systems capture and convert the waste heat generated during the combustion of fuel or the operation of the electric motor into usable electrical energy. Waste heat is a byproduct of various vehicle operations, and by utilizing it, these systems can further enhance the efficiency of the vehicle. This technology is often combined with other energy recovery methods to maximize the overall energy efficiency of the vehicle.
The captured and stored energy from these recovery systems contributes to the overall efficiency and sustainability of electric vehicles. By reducing the reliance on the internal combustion engine for power generation and recharging the battery, energy recovery systems extend the vehicle's range and decrease the environmental impact. This technology is a crucial aspect of EV design, ensuring that electric vehicles can compete with traditional cars in terms of performance and efficiency while also contributing to a more sustainable transportation future.
Powering Up: A Beginner's Guide to Electric Vehicle Ownership
You may want to see also

Efficiency Boost: Regeneration improves overall efficiency and reduces fuel consumption
Regeneration in electric vehicles is a process that significantly enhances efficiency and reduces fuel consumption, making it a crucial aspect of modern automotive technology. This innovative feature harnesses the kinetic energy that would otherwise be wasted during braking and converts it into electrical energy, which is then stored in the vehicle's battery. By doing so, regeneration effectively extends the range of electric vehicles and reduces the reliance on external power sources, making it an essential component for sustainable transportation.
The efficiency boost provided by regeneration is particularly notable in electric cars, which often have smaller and lighter batteries compared to their internal combustion engine counterparts. In traditional vehicles, braking systems primarily serve to dissipate energy as heat, leading to significant energy loss. However, with regeneration, this wasted energy is captured and reused, resulting in a substantial improvement in overall efficiency. This technology is especially beneficial in urban driving conditions, where frequent stops and starts are common, as it helps to optimize energy usage and reduce the strain on the battery during these short-distance journeys.
The mechanism of regeneration is relatively simple yet highly effective. When the driver applies the brakes, the electric motor reverses its direction, acting as a generator. This process slows down the vehicle while simultaneously charging the battery. The amount of energy recovered depends on various factors, including the vehicle's speed, the braking force, and the efficiency of the motor and inverter systems. Modern electric vehicles are equipped with sophisticated control systems that optimize regeneration, ensuring that the process is seamless and responsive to the driver's inputs.
Regeneration also contributes to a more responsive and smooth driving experience. Unlike traditional braking systems, which rely solely on friction, regeneration provides a more progressive and controlled deceleration. This is particularly advantageous in downhill driving or when maintaining a steady speed, as it reduces the need for excessive braking input, thereby improving driver comfort and control. Additionally, the regenerative braking system can be customized to suit different driving preferences, allowing for a more personalized driving experience.
In summary, regeneration in electric vehicles is a game-changer for efficiency and fuel economy. By capturing and reusing kinetic energy, it significantly reduces the energy wasted during braking, resulting in improved overall efficiency. This technology not only extends the range of electric vehicles but also contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly mode of transportation. With its ability to optimize energy usage and provide a responsive driving experience, regeneration is a key factor in the widespread adoption of electric vehicles, making them a more attractive and practical choice for drivers seeking efficient and eco-conscious transportation solutions.
The Green Revolution: Unlocking the True Value of Electric Cars
You may want to see also

Environmental Impact: Regeneration reduces emissions and promotes sustainable energy use
Regeneration in electric vehicles (EVs) is a crucial technology that significantly contributes to reducing environmental impact and promoting sustainable energy use. When an EV is in motion, it typically generates electricity through the rotation of its wheels, which is a result of the vehicle's kinetic energy. This kinetic energy can be harnessed and converted back into electrical energy through a process called regenerative braking.
During regenerative braking, when the driver applies the brakes, the electric motor switches to generator mode, converting the vehicle's kinetic energy into electrical energy. This energy is then stored in the battery pack, which can be used to power the vehicle when needed. The beauty of this system lies in its ability to capture and reuse energy that would otherwise be lost as heat during traditional braking methods. By doing so, regeneration not only improves the overall efficiency of the vehicle but also reduces the amount of energy required to operate it.
The environmental benefits of regeneration are substantial. Firstly, it directly reduces emissions. Since the vehicle's kinetic energy is being reused instead of wasted, the need for frequent stops and starts, which often require the internal combustion engine to idle, is minimized. This results in lower fuel consumption and reduced emissions of harmful pollutants, such as carbon dioxide (CO2) and nitrogen oxides (NOx). Lower emissions contribute to improved air quality, especially in urban areas where EVs are commonly used.
Moreover, regeneration promotes sustainable energy use. The captured electrical energy is stored in the battery, which can be utilized during the vehicle's next drive cycle. This stored energy can power the EV, reducing the reliance on external power sources, such as those generated by burning fossil fuels. By extending the range of EVs and reducing the frequency of charging, regeneration encourages the widespread adoption of electric vehicles, which is essential for a more sustainable transportation system.
In summary, regeneration in electric vehicles is an innovative technology that has a profound environmental impact. It reduces emissions by capturing and reusing kinetic energy, leading to improved air quality. Additionally, it promotes sustainable energy use by extending the vehicle's range and reducing the need for frequent charging, thus contributing to a greener and more efficient transportation network. As the world moves towards a more sustainable future, the role of regeneration in EVs becomes increasingly vital.
Unveiling the Power of Pev Electric Vehicles: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Vehicle regeneration, often referred to as regenerative braking, is a process in electric vehicles (EVs) that converts the kinetic energy of the moving car into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery. This technology allows EVs to recover some of the energy that would otherwise be lost as heat during braking, improving overall efficiency and range.
When the driver applies the brakes in an electric vehicle, the electric motor switches to generator mode. The motor's rotation is slowed down, and this action generates electricity. This electricity is then directed back to the battery, recharging it and extending the vehicle's range. The system is designed to mimic the feel of a traditional car's brakes while providing the added benefit of energy recovery.
AA: Regenerative braking offers several advantages. Firstly, it increases the efficiency of the EV by reducing energy waste. This results in a longer driving range for the same amount of energy used. Secondly, it provides a more responsive and smooth driving experience, as the braking feel is adjustable and can be tailored to the driver's preference. Additionally, the recovered energy can significantly reduce the wear and tear on traditional braking systems, leading to lower maintenance costs.
Regeneration is a feature primarily associated with electric and hybrid vehicles due to their use of electric motors and batteries. However, similar concepts are used in other vehicle types, such as regenerative suspension systems in some racing cars. These systems capture and store energy from the vehicle's movement, which can be used to power auxiliary systems or enhance overall performance.