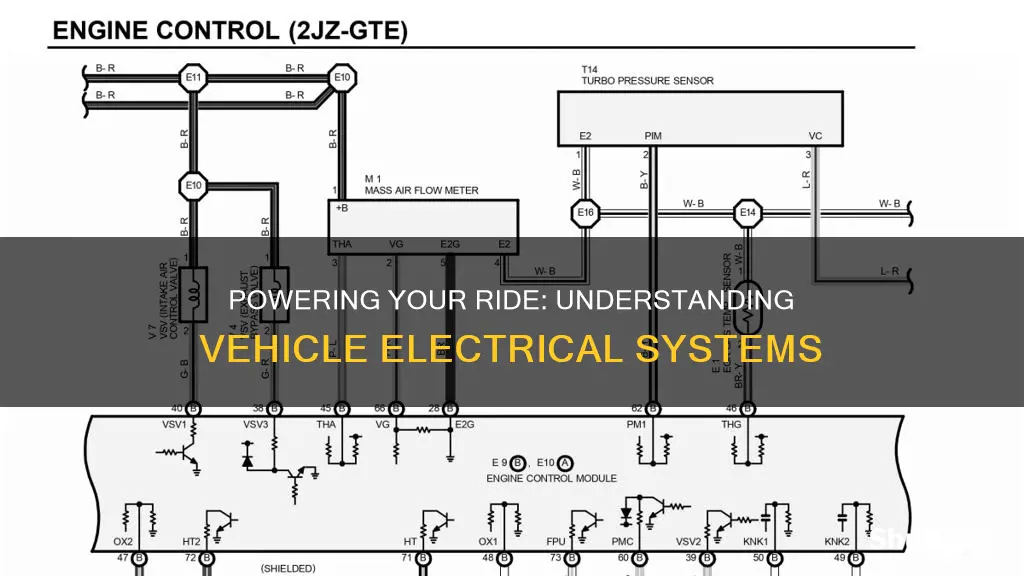
The vehicle electrical system is a complex network of components that powers and controls various functions in a car, from the ignition to the lights and everything in between. It relies on a combination of batteries, alternators, and fuses to deliver the necessary power and ensure the smooth operation of the vehicle. This system is the backbone of modern automobiles, enabling the use of advanced features and technologies that enhance safety, comfort, and performance. Understanding the intricacies of this system is crucial for vehicle owners and mechanics alike, as it plays a vital role in keeping the car running efficiently and safely.
What You'll Learn
- Vehicle Electrical System Basics: Power source, wiring, and components
- Sensors and Actuators: Devices that monitor and control vehicle operations
- Engine Control Unit (ECU): Central processor for engine management
- Lighting and Signaling: Functions of headlights, taillights, and turn signals
- Safety Systems: Airbags, seatbelts, and crash sensors

Vehicle Electrical System Basics: Power source, wiring, and components
The vehicle electrical system is a complex network that powers and controls various components in a car, ensuring its safe and efficient operation. This system is the backbone of modern automobiles, enabling features like engine control, lighting, entertainment, and safety mechanisms. Understanding its fundamentals is crucial for any vehicle owner or enthusiast.
Power Source:
The primary power source in a vehicle is the battery, typically a lead-acid or lithium-ion battery. These batteries store electrical energy and provide the initial power required to start the engine. When the engine is running, it generates electricity through the alternator, which charges the battery and powers the electrical system. The battery's voltage is usually around 12 volts, and it is designed to provide a consistent power supply. In some vehicles, auxiliary batteries are used to power specific systems, such as the radio or air conditioning, when the main battery is depleted.
Wiring and Connections:
Wiring harnesses are an essential part of the vehicle electrical system, connecting various components to the power source. These harnesses consist of multiple wires, each carrying a specific function, such as power, ground, or data signals. The wiring is carefully routed throughout the vehicle to ensure proper connections and minimize interference. All connections must be secure and free from corrosion to maintain a reliable power supply. Fuses and circuit breakers are also integral, protecting the wiring and components from excessive current, thus preventing potential damage or hazards.
Key Electrical Components:
- Engine Control Unit (ECU): The ECU is the brain of the vehicle's electrical system, managing engine performance and diagnostics. It receives input from various sensors and controls fuel injection, ignition timing, and other critical functions.
- Sensors and Actuators: Sensors monitor engine conditions, such as temperature, pressure, and oxygen levels. Actuators, like fuel injectors and solenoids, respond to the ECU's commands, adjusting engine parameters.
- Lighting and Signaling: Headlights, taillights, turn signals, and hazard lights are powered by the electrical system. These components ensure visibility and communication with other drivers.
- Entertainment and Comfort: Modern vehicles offer a range of entertainment and comfort features, including audio systems, navigation, climate control, and power windows, all dependent on the electrical network.
- Safety Systems: Airbag sensors, anti-lock braking systems (ABS), and traction control units rely on the electrical system for their operation, ensuring driver and passenger safety.
In summary, the vehicle electrical system is a sophisticated network that powers and controls various car functions. Understanding its power source, wiring, and components is essential for vehicle maintenance, troubleshooting, and ensuring optimal performance.
Electric Vehicles: The Indian Advantage? Exploring the Benefits
You may want to see also

Sensors and Actuators: Devices that monitor and control vehicle operations
The vehicle electrical system is a complex network of components that work together to ensure the safe and efficient operation of a vehicle. Among these components, sensors and actuators play a crucial role in monitoring and controlling various vehicle operations. These devices are the eyes and ears of the electrical system, providing vital information and executing commands to keep the vehicle running smoothly.
Sensors are electronic devices designed to detect and measure specific parameters within the vehicle. They are strategically placed throughout the vehicle to monitor critical aspects such as temperature, pressure, speed, and position. For instance, a temperature sensor can detect the engine's temperature, ensuring it doesn't overheat, while a speed sensor provides real-time data on the vehicle's velocity. These sensors convert physical quantities into electrical signals, which can then be processed by the vehicle's control unit.
Actuators, on the other hand, are devices that receive signals from the vehicle's control unit and perform specific actions. They are responsible for executing commands, often in response to sensor data. For example, an actuator might adjust the throttle position based on the engine's load, or it could control the braking system to ensure optimal stopping power. Actuators can be mechanical, such as solenoids or electric motors, or they can be electronic, like the components in a fuel injection system.
The integration of sensors and actuators allows for precise control and monitoring of various vehicle functions. For instance, in a modern anti-lock braking system (ABS), sensors monitor wheel speed and slip, while actuators modulate brake pressure to prevent wheel lockup during braking. This real-time feedback loop ensures that the vehicle maintains control and stability, even in emergency situations.
Furthermore, these devices contribute to improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. By optimizing engine performance, controlling air-fuel mixture, and managing vehicle dynamics, sensors and actuators play a vital role in meeting environmental regulations. Modern vehicles often utilize advanced sensor arrays and sophisticated control algorithms to achieve this balance between performance and environmental responsibility.
Electric Vehicles: Educating Pedestrians on Proximity Awareness
You may want to see also

Engine Control Unit (ECU): Central processor for engine management
The Engine Control Unit (ECU) is a critical component of a vehicle's electrical system, often referred to as the 'brain' of the engine. It is a sophisticated electronic control unit that manages and controls various aspects of the engine's operation, ensuring optimal performance, fuel efficiency, and emissions control. This small yet powerful device is at the heart of modern vehicle technology, making it an essential part of any vehicle's overall functionality.
In simple terms, the ECU is a central processor that receives input from various sensors and actuators within the engine and then processes this information to make precise decisions. These decisions are then translated into actions that control the engine's performance. For instance, it can adjust the fuel injection, timing, and idle speed to optimize power output and fuel consumption. The ECU's primary role is to ensure that the engine operates efficiently and within safe parameters, adapting to various driving conditions and loads.
This unit is designed to monitor and control multiple parameters simultaneously, such as engine speed, load, temperature, and exhaust gas composition. It uses this data to make real-time adjustments to the engine's operation. For example, during acceleration, the ECU increases the fuel flow to the engine, ensuring a quick response while maintaining optimal combustion. Conversely, during deceleration, it may reduce fuel supply to save fuel and reduce emissions. The ECU's ability to make these quick and precise decisions is what makes modern vehicles more responsive and efficient.
One of the key advantages of the ECU is its ability to learn and adapt. Through a process called 'learning', the ECU can adjust its settings based on the vehicle's usage and driving patterns. This learning capability allows the engine to perform better over time, as it becomes more attuned to the specific conditions and requirements of the vehicle. Additionally, the ECU can store diagnostic trouble codes, which help mechanics identify and troubleshoot issues, ensuring the vehicle remains reliable and safe.
In summary, the Engine Control Unit is a complex and vital component of a vehicle's electrical system. It acts as the central processor, managing and optimizing engine performance by making real-time decisions based on sensor input. Its ability to learn and adapt ensures that the engine operates efficiently and effectively, contributing to the overall reliability and performance of modern vehicles. Understanding the ECU's role is essential for anyone looking to maintain or enhance their vehicle's electrical system.
The Future of Driving: Understanding the EV Mandate
You may want to see also

Lighting and Signaling: Functions of headlights, taillights, and turn signals
The vehicle's electrical system plays a crucial role in ensuring safe and efficient driving, and one of its most essential functions is lighting and signaling. Headlights, taillights, and turn signals are integral components that enhance visibility, communicate the vehicle's presence and intentions, and improve overall road safety.
Headlights are perhaps the most fundamental part of a vehicle's lighting system. They provide illumination to the road ahead, allowing drivers to navigate through various lighting conditions, including darkness, fog, or low-visibility weather. Modern headlights often feature advanced technologies like LED or xenon lighting, which offer brighter and more energy-efficient illumination compared to traditional halogen bulbs. These headlights can be adjusted to direct light downward, improving visibility on the road and reducing glare for oncoming traffic.
In addition to headlights, taillights are equally vital for road safety. These lights are positioned at the rear of the vehicle and serve multiple purposes. Firstly, they provide a visible rearward illumination, making the car more noticeable to other drivers, especially during night drives or in low-light conditions. Secondly, taillights often incorporate brake lights, which illuminate when the vehicle's brakes are applied, signaling to following drivers that the car is slowing down or stopping. This function is crucial for preventing rear-end collisions and ensuring that other drivers are aware of the vehicle's intentions.
Turn signals are another critical component of the vehicle's electrical system for lighting and signaling. These indicators are located on the front and rear of the vehicle and are used to communicate the driver's intention to turn or change lanes. When activated, the turn signals flash, providing a clear visual cue to other road users, including pedestrians and nearby vehicles. This simple yet effective signaling mechanism helps prevent accidents by clearly indicating the vehicle's movement, allowing other drivers to react accordingly and maintain safe distances.
Furthermore, the integration of these lighting systems with the vehicle's electrical architecture is essential. Modern vehicles utilize sophisticated control units and sensors to manage the operation of headlights, taillights, and turn signals. These systems ensure that the lights are activated at the appropriate times, providing optimal visibility and signaling without causing confusion or distraction for other road users.
In summary, the lighting and signaling functions of headlights, taillights, and turn signals are fundamental to a vehicle's electrical system, contributing to safer driving conditions and effective communication between vehicles on the road. These components work in harmony to provide visibility, warn other drivers, and ensure that vehicles can navigate the roads with confidence and security.
Unleash the Power: Is an Electric Vehicle Your Next Ride?
You may want to see also

Safety Systems: Airbags, seatbelts, and crash sensors
The vehicle electrical system is a complex network of components that work together to ensure the safe operation of a car. One of the most critical aspects of this system is the safety mechanisms designed to protect occupants in the event of an accident. These safety systems include airbags, seatbelts, and crash sensors, which are all integral parts of modern vehicle design.
Airbags are a crucial safety feature, providing a cushioning effect to reduce the impact of a collision on the driver and passengers. They are designed to deploy rapidly when a crash is detected, inflating to fill the space between the occupant and the steering wheel or dashboard. Modern vehicles often have multiple airbags, including front, side, and curtain airbags, which offer comprehensive protection. The deployment of airbags is controlled by sensors that detect the severity and type of impact, ensuring that the airbags deploy only when necessary.
Seatbelts, also known as safety belts, are another fundamental safety system. They are designed to restrain occupants in their seats during a collision, preventing them from being thrown from the vehicle or hitting hard surfaces inside the car. Modern seatbelts are often equipped with pretensioners, which tighten the belt rapidly upon impact detection, and load limiters to reduce the force exerted on the occupant's body. The use of seatbelts significantly reduces the risk of serious injury or death in accidents.
Crash sensors, also referred to as collision avoidance or impact detection systems, are sophisticated electronic devices. They monitor various parameters such as speed, acceleration, and deceleration to detect an impending collision. When a crash is imminent, these sensors trigger the deployment of airbags and, in some cases, activate other safety features like automatic braking. Crash sensors can also provide valuable data to the vehicle's computer systems, allowing for improved handling and stability during critical situations.
The integration of these safety systems into the vehicle electrical network is essential for their effective operation. Sensors and actuators are connected to the vehicle's central computer, which processes data and sends commands to deploy airbags, tighten seatbelts, and activate crash-avoidance measures. This interconnectedness ensures that all safety systems work in harmony, maximizing the chances of a safe outcome in various accident scenarios.
Ford's Future: Electric Vehicle Cuts and the Industry's Shift
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The vehicle electrical system is an intricate network of components and wiring that powers and controls various functions in a car, truck, or any other motor vehicle. It is responsible for delivering the necessary electricity to start the engine, operate lights, power accessories, and control essential functions, ensuring the vehicle runs smoothly and safely.
The electrical system in a vehicle operates by converting the mechanical energy of the engine into electrical energy through the alternator. This electrical energy is then distributed to different parts of the car via the wiring harness, which includes fuses, relays, and switches. Each component has a specific role, such as controlling the ignition system, powering the headlights, or managing the engine's performance.
The vehicle electrical system comprises several key components, including the battery, alternator, starter motor, wiring harness, fuses, relays, sensors, and actuators. The battery stores electrical energy, the alternator recharges it, the starter motor cranks the engine, and the wiring harness connects all these components. Sensors provide critical data to the engine control unit, while actuators control various functions like the fuel pump, power windows, and windshield wipers.