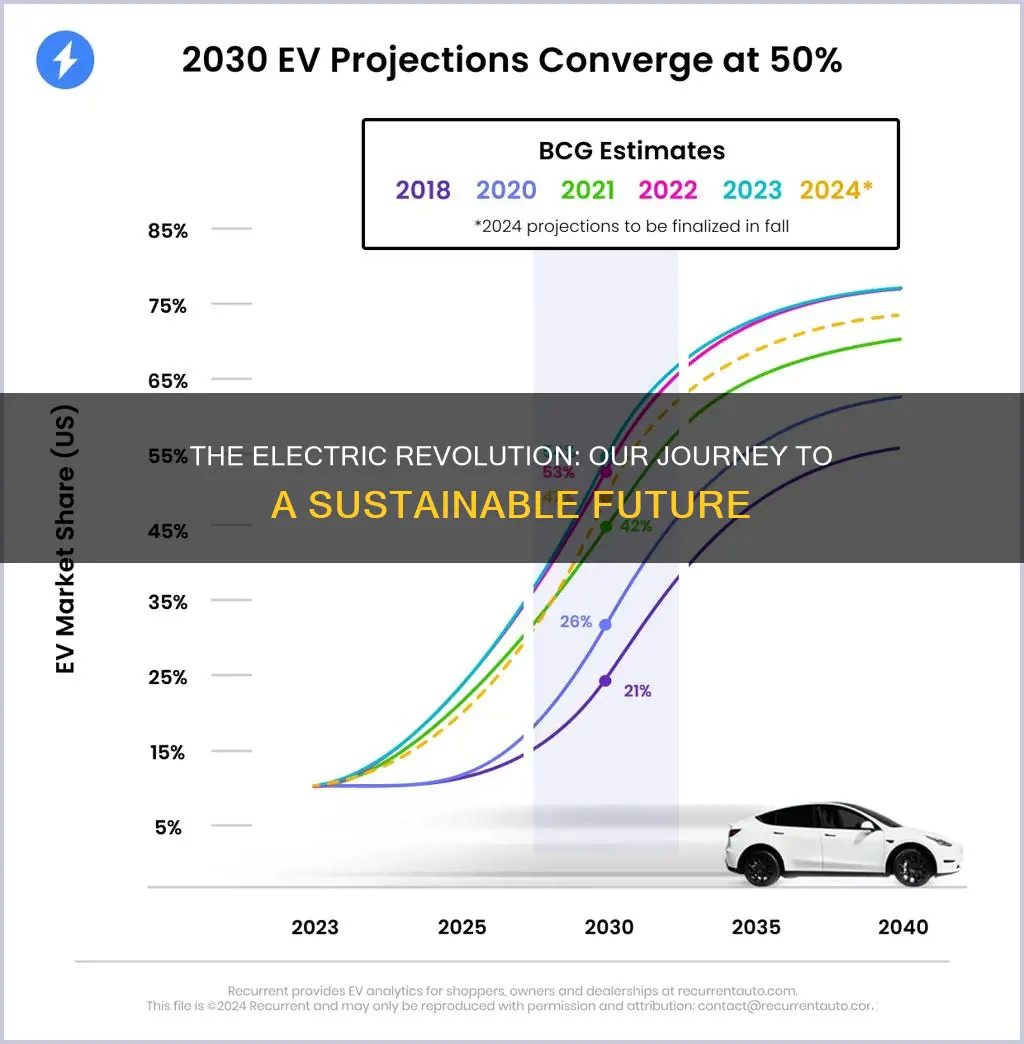
The world is witnessing a transformative shift towards electric vehicles (EVs), marking a pivotal moment in the automotive industry's history. This transition is not just a trend but a necessary evolution driven by environmental concerns and technological advancements. As we stand at the crossroads of this revolution, it's essential to understand the current landscape and the path ahead. The adoption of electric vehicles has been rapid, with governments and consumers alike embracing the benefits of reduced emissions and improved efficiency. This paragraph will explore the progress made, the challenges faced, and the future prospects of the electric vehicle market, highlighting the key milestones and innovations that have shaped this exciting journey.
What You'll Learn
- Market Growth: Rising sales and adoption rates of electric vehicles (EVs) globally
- Infrastructure Development: Expansion of charging networks and battery swapping stations
- Battery Technology: Advances in battery chemistry and energy density for longer ranges
- Government Policies: Incentives and regulations driving EV adoption and industry growth
- Environmental Impact: Reduced carbon emissions and environmental benefits of widespread EV use

Market Growth: Rising sales and adoption rates of electric vehicles (EVs) globally
The global market for electric vehicles (EVs) is experiencing a remarkable surge, driven by a combination of technological advancements, environmental concerns, and supportive government policies. This growth is evident in the rising sales figures and increasing adoption rates worldwide, indicating a significant shift towards sustainable transportation.
In recent years, the sales of EVs have seen a consistent upward trend, with major automotive manufacturers investing heavily in electric powertrains. The global EV market reached a milestone in 2021, with over 6 million units sold, a 100% increase from the previous year. This surge in sales can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, the improving performance and range of electric vehicles have addressed long-standing consumer concerns. Modern EVs offer impressive driving ranges, often exceeding 300 miles on a single charge, making them a viable alternative to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. Secondly, the declining costs of battery technology have made EVs more affordable for a broader consumer base. As battery production scales up, economies of scale reduce the overall price, making electric cars more accessible to the average buyer.
Government incentives and subsidies play a crucial role in this market growth. Many countries have implemented policies to encourage EV adoption, such as tax credits, rebates, and reduced registration fees. For instance, the United States' Inflation Reduction Act provides substantial incentives for EV purchases, making them more attractive to consumers. Similarly, European nations have introduced strict emissions regulations, pushing automakers to accelerate their EV development and sales. These policies not only stimulate market demand but also contribute to a more sustainable future by reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
The rise in EV sales has led to a positive feedback loop, further accelerating adoption. As more people purchase EVs, the demand for charging infrastructure increases, prompting governments and private entities to invest in charging networks. This infrastructure development, in turn, alleviates range anxiety, a common concern among potential EV buyers, and encourages further adoption. Additionally, the second-hand market for EVs is gaining traction, as used electric cars become more available and affordable, providing an entry point for those who were previously hesitant to make the switch.
The global adoption of EVs is also influenced by the increasing awareness of environmental issues and the need to reduce carbon footprints. Consumers are becoming more environmentally conscious, and the shift towards sustainable transportation is a significant driver of EV demand. As a result, the market is witnessing a diverse range of EV models, from compact city cars to luxury SUVs, catering to various consumer preferences and needs. This market growth is a testament to the successful transition towards a more sustainable and eco-friendly transportation ecosystem.
Gartner's Hype Cycle: Navigating the EV Revolution's Peaks and Troughs
You may want to see also

Infrastructure Development: Expansion of charging networks and battery swapping stations
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is an ongoing journey, and a critical aspect of this journey is the development of supporting infrastructure. One of the key areas of focus is the expansion of charging networks and the establishment of battery swapping stations, which are essential for addressing range anxiety and ensuring a seamless driving experience for EV owners.
Charging Networks:
The growth of charging networks is vital to support the increasing number of EVs on the road. These networks consist of various charging stations strategically placed along highways, in urban areas, and at residential locations. The goal is to provide EV owners with convenient access to charging points, ensuring they can travel long distances without worrying about running out of battery. Fast-charging stations, which can rapidly replenish a significant portion of the battery in a short time, are particularly important for long-distance travel. These stations are often located along major routes, allowing drivers to quickly recharge and continue their journey. Additionally, the integration of smart charging technologies is revolutionizing the charging infrastructure. These technologies enable dynamic pricing, load balancing, and the ability to manage charging sessions remotely, optimizing the use of available electricity and reducing strain on the power grid.
Battery Swapping Stations:
Battery swapping stations offer a unique solution to the time-consuming nature of traditional charging. These stations allow drivers to exchange their depleted batteries for fully charged ones in a matter of minutes. This concept is particularly appealing for commercial fleets and ride-sharing services, where vehicles need to be back on the road quickly. By implementing battery-swapping infrastructure, the time spent waiting for a battery to charge can be significantly reduced, improving overall efficiency. Battery swapping stations also contribute to a more sustainable model, as they can help optimize battery usage and reduce the need for extensive charging infrastructure. This approach is especially relevant in regions with limited access to charging facilities, providing a viable alternative for EV owners.
The expansion of these infrastructure elements is crucial for the successful transition to a fully electric transportation system. It encourages the adoption of EVs by addressing range-related concerns and providing a convenient and efficient charging/swapping experience. As the industry continues to evolve, the development of smart and interconnected charging networks, along with the strategic placement of battery swapping stations, will play a pivotal role in shaping the future of electric mobility. This infrastructure development is a key enabler, ensuring that the road to electric vehicles is not only sustainable but also practical and accessible to a wide range of users.
The Electric Revolution: Is the EV Market Booming?
You may want to see also

Battery Technology: Advances in battery chemistry and energy density for longer ranges
The evolution of battery technology is a pivotal aspect of the electric vehicle (EV) revolution, driving advancements in energy density and chemistry to extend the range of these vehicles. One of the key challenges in the early days of EVs was the limited range due to the constraints of battery technology. However, significant progress has been made in recent years, with a focus on improving battery chemistry and energy storage capabilities.
A major breakthrough in battery chemistry has been the development of lithium-ion batteries, which have become the standard for EVs. These batteries offer a higher energy density compared to their predecessors, allowing for more efficient energy storage. The use of lithium, a lightweight and highly reactive metal, has enabled the creation of compact and lightweight batteries that can power vehicles for longer distances. Researchers have been working on enhancing the performance of lithium-ion batteries by modifying the cathode and anode materials. For instance, the introduction of nickel-rich cathodes has increased energy density, while silicon-based anodes show promise in storing more energy.
Energy density, a critical factor in EV range, has seen remarkable improvements. Modern EVs can now travel over 300 miles on a single charge, a significant leap from the early models that struggled to cover even 100 miles. This increase in range is attributed to the development of advanced battery packs that utilize multiple cells in series and parallel configurations. By stacking these cells, manufacturers can achieve higher voltage and current ratings, resulting in improved energy output and, consequently, extended driving ranges.
Another area of focus is the development of solid-state batteries, which replace the liquid electrolyte with a solid conductive material. This innovation has the potential to revolutionize EV battery technology by offering higher energy density, faster charging, and improved safety. Solid-state batteries can store more energy in a smaller volume, leading to even longer ranges for electric vehicles. Additionally, the use of solid electrolytes reduces the risk of thermal runaway, a critical safety concern in lithium-ion batteries.
In summary, the advancements in battery chemistry and energy density have been instrumental in the rapid progress of electric vehicles. The continuous research and development in this field aim to further enhance battery performance, making EVs more practical and appealing to a wider audience. As battery technology continues to evolve, we can expect even more significant improvements in the range and efficiency of electric vehicles, bringing us closer to a future where long-distance travel in EVs is commonplace.
Hybrid Vehicles: Are They Electric? Unraveling the Power of Hybrid Technology
You may want to see also

Government Policies: Incentives and regulations driving EV adoption and industry growth
Government policies play a pivotal role in accelerating the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and fostering the growth of the EV industry. These policies often take the form of incentives and regulations, which collectively aim to address the challenges associated with the transition from traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles to electric powertrains.
Incentives:
- Tax Credits and Rebates: Many governments offer financial incentives to consumers purchasing EVs. These incentives can take the form of tax credits, which directly reduce the purchase price of EVs, making them more affordable. For instance, the United States' Inflation Reduction Act provides a substantial tax credit for EV buyers, encouraging the market's growth.
- Grant Programs: Governments may also provide grants to individuals or businesses to facilitate EV purchases. These grants can be particularly beneficial for low-income households or small businesses, ensuring a broader range of consumers can access EVs.
- Tax Breaks for EV Chargers: Incentives can also extend to the infrastructure side, with tax breaks or subsidies for the installation of EV charging stations. This encourages the development of a robust charging network, addressing range anxiety and making EVs more convenient for potential buyers.
Regulations:
- Emission Standards: One of the most significant regulatory measures is setting stringent emission standards for vehicles. Governments worldwide are implementing stricter regulations to reduce greenhouse gas emissions, which often results in a faster shift towards EVs. For example, the European Union's CO2 standards mandate that car manufacturers achieve specific emission targets, pushing the industry to invest in electric powertrains.
- Mandates and Quotas: Some countries have taken a more direct approach by introducing mandates or quotas for EV sales. These policies ensure a certain percentage of EV sales in the overall market, providing a clear direction for the industry. Norway, for instance, has been highly successful in its EV adoption due to a combination of incentives and strict regulations, including a zero-emission quota for public procurement.
- Infrastructure Development: Governments are also investing in regulations to support the necessary infrastructure for EV adoption. This includes the development of charging networks, smart grid integration, and the establishment of EV-friendly policies for parking and road usage.
The combination of incentives and regulations is proving to be a powerful catalyst for EV adoption. Incentives make EVs more attractive and affordable, while regulations ensure a structured and sustainable market. As governments continue to refine these policies, the EV industry is expected to grow exponentially, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable transportation ecosystem. This approach is crucial in the global effort to combat climate change and reduce the environmental impact of the transportation sector.
Kia K4: Electric or Not? Unveiling the Truth
You may want to see also

Environmental Impact: Reduced carbon emissions and environmental benefits of widespread EV use
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is a pivotal step towards mitigating the environmental crisis we face. One of the most significant advantages of EVs is their potential to drastically reduce carbon emissions. Traditional internal combustion engine vehicles are major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions, primarily carbon dioxide (CO2), which is a leading driver of climate change. In contrast, EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, meaning they do not release any harmful pollutants or greenhouse gases during operation. This shift from fossil fuel-based transportation to electric power is a crucial strategy to combat climate change and improve air quality.
The environmental benefits of widespread EV use extend beyond the elimination of direct emissions. Firstly, the process of manufacturing EVs is generally less energy-intensive and less polluting compared to the production of conventional vehicles. This is because electric powertrains have fewer moving parts, reducing the need for extensive assembly processes and minimizing the use of raw materials. Secondly, the electricity used to charge EVs can often be sourced from renewable energy, further lowering the carbon footprint of the entire transportation system. Many countries and regions are investing in renewable energy infrastructure, making it increasingly feasible to power EVs with clean energy.
As the demand for EVs rises, the overall environmental impact of the transportation sector can be significantly reduced. This is particularly evident in urban areas, where traffic congestion and air pollution are major concerns. Widespread EV adoption can lead to improved air quality, benefiting public health and reducing the burden on healthcare systems. Moreover, the shift to EVs can contribute to a more sustainable and resilient energy system. With the integration of smart grids and energy storage solutions, the charging of EVs can be optimized, ensuring a stable and efficient energy distribution network.
The environmental advantages of EVs also have a positive impact on ecosystems and biodiversity. By reducing the reliance on fossil fuels, we can minimize the extraction and transportation of these finite resources, which often involve destructive practices that harm natural habitats. Additionally, the reduced noise pollution from EVs can have a positive effect on wildlife, as many animals are sensitive to noise and can be disturbed by the constant rumble of conventional vehicles.
In summary, the widespread use of electric vehicles offers a promising pathway to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future. The reduction of carbon emissions, improved manufacturing processes, and the potential for renewable energy integration all contribute to a cleaner and healthier planet. As technology advances and infrastructure supports the EV market, the environmental benefits will continue to accrue, making the transition to electric mobility an essential step in addressing global environmental challenges.
The Electric Revolution: Key Players in the EV Industry
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The EV market has seen significant growth and interest in recent years, with a wide range of models available from various manufacturers. Many countries and regions are witnessing a rapid shift towards electric mobility, with government incentives and a growing consumer demand for sustainable transportation. The market is becoming increasingly competitive, with traditional automakers investing heavily in EV technology and startups introducing innovative designs.
Adoption rates of electric vehicles have been steadily increasing, with a focus on reducing carbon footprints and promoting environmental sustainability. Many early adopters and environmentally conscious consumers have embraced EVs, leading to a positive feedback loop. The availability of charging infrastructure is improving, and the range anxiety associated with early EVs is being addressed by newer models offering longer driving ranges.
Despite the progress, there are still challenges to overcome for the widespread adoption of EVs. These include the initial higher cost of purchase compared to traditional vehicles, the availability of charging stations, and the time required for charging. Range limitations, especially in colder climates, and the need for more efficient battery technology are also areas of focus. Additionally, the transition to a fully electric transportation system requires significant changes in energy infrastructure and grid management.







