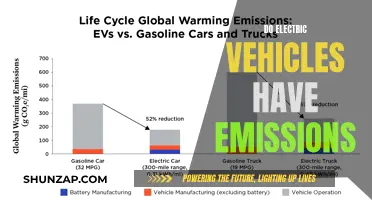
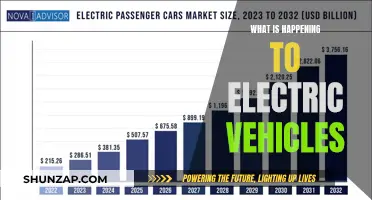
Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming increasingly popular, and with their rise comes the need for effective regulation. The regulation of EVs involves a complex interplay of various stakeholders, including government agencies, industry bodies, and environmental organizations. These entities work together to ensure that EVs meet safety, environmental, and performance standards. Regulatory bodies oversee the production, sale, and use of EVs, setting guidelines for emissions, charging infrastructure, and consumer protection. This collaborative effort aims to accelerate the transition to sustainable transportation, promote innovation, and address the challenges associated with the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
What You'll Learn
- Government Agencies: Regulatory bodies oversee EV standards and safety
- Industry Standards: Manufacturers adhere to guidelines set by industry associations
- Environmental Impact: Agencies monitor emissions and sustainability of electric vehicles
- Consumer Protection: Legal frameworks protect buyers from fraudulent EV sales
- Infrastructure Development: Regulators manage the expansion of charging station networks

Government Agencies: Regulatory bodies oversee EV standards and safety
Government agencies and regulatory bodies play a crucial role in the development and implementation of electric vehicle (EV) standards and safety measures. These organizations are responsible for ensuring that EVs meet specific criteria to protect consumers, the environment, and public health. Here's an overview of their involvement:
In many countries, government agencies are tasked with establishing and enforcing regulations for electric vehicles. These agencies set the standards for vehicle performance, emissions, and safety. For instance, the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) in the United States is a key player in regulating EV safety. They define the requirements for crash testing, vehicle structure, and other safety-related aspects to ensure EVs are as safe as, or safer than, conventional vehicles. Similarly, the European Union's European Commission has been actively involved in setting EV standards, including those related to range, charging infrastructure, and vehicle-to-grid communication.
Regulatory bodies often collaborate with industry experts, researchers, and manufacturers to develop comprehensive guidelines. These guidelines cover various aspects, such as battery safety, charging protocols, and vehicle design. For example, the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) has developed numerous standards related to EVs, including ISO 16750 for vehicle-to-vehicle communication and ISO 18143 for charging systems. By setting these standards, regulatory bodies ensure that EVs are designed and manufactured with consistent and safe practices worldwide.
Government agencies also monitor and inspect EV manufacturers to ensure compliance with these standards. They conduct regular audits, issue recalls if necessary, and provide guidelines for manufacturers to improve their products. This oversight is essential to maintain the integrity of the EV market and protect consumers from potential hazards. Moreover, these agencies often collaborate with environmental protection agencies to address the ecological impact of EVs, such as the sourcing and disposal of batteries.
In summary, government agencies and regulatory bodies are vital in establishing and maintaining the safety and performance standards for electric vehicles. Their work ensures that EVs are reliable, environmentally friendly, and compliant with legal requirements. Through their efforts, these organizations contribute to the widespread adoption of electric vehicles while minimizing risks to consumers and the environment.
Uncover the Hidden EV Tax Credits: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Industry Standards: Manufacturers adhere to guidelines set by industry associations
The regulation of electric vehicles (EVs) is a multifaceted process that involves various stakeholders, including government bodies, industry associations, and manufacturers. While governments play a crucial role in setting policies and standards, industry associations are instrumental in establishing guidelines and best practices that manufacturers must adhere to. These industry standards are essential to ensure the safety, reliability, and performance of electric vehicles, fostering a competitive and sustainable market.
Industry associations, such as the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE) and the International Organization for Standardization (ISO), have developed comprehensive sets of guidelines and specifications for electric vehicles. These standards cover a wide range of aspects, including vehicle design, performance, safety, and environmental impact. For instance, the SAE has established a series of J2847 standards that define the communication protocols between EVs and their charging infrastructure, ensuring seamless and efficient charging processes. Similarly, the ISO has introduced various standards like ISO 16750-2 and ISO 16750-3, which focus on the electrical and electronic systems of vehicles, including those in electric powertrains.
Manufacturers of electric vehicles are expected to adhere to these industry standards as a prerequisite for market entry. Compliance with these guidelines ensures that their products meet the required performance, safety, and environmental standards. For example, manufacturers must ensure that their EVs have efficient energy management systems, meet specific range requirements, and adhere to safety regulations, such as those related to battery management and thermal control. By following these industry-wide standards, manufacturers can ensure that their electric vehicles are reliable, safe, and environmentally friendly.
Industry associations also provide a platform for manufacturers to collaborate and share knowledge. Through these networks, companies can exchange information on emerging technologies, best practices, and potential challenges. This collaboration is vital for driving innovation and ensuring that industry standards remain relevant and adaptable to the rapidly evolving EV market. Additionally, industry associations often offer certification programs that manufacturers can use to demonstrate their compliance with specific standards, providing consumers with a clear indication of the vehicle's quality and reliability.
In summary, industry standards play a pivotal role in the regulation of electric vehicles by providing manufacturers with a set of guidelines to follow. These standards, developed by reputable industry associations, ensure that EVs meet essential performance, safety, and environmental criteria. Adherence to these standards not only promotes consumer confidence but also encourages innovation and competition within the industry. As the market for electric vehicles continues to grow, the collaboration between industry associations and manufacturers will be crucial in shaping a sustainable and robust EV ecosystem.
Honda's Electric Revolution: Unveiling the Quiet Power
You may want to see also

Environmental Impact: Agencies monitor emissions and sustainability of electric vehicles
The regulation of electric vehicles (EVs) is a multifaceted process, with various agencies and organizations playing crucial roles in ensuring their environmental impact is minimized and their sustainability is maximized. One of the primary focuses of these regulatory bodies is on emissions, which are a significant concern in the automotive industry.
Environmental agencies and government bodies are tasked with monitoring and regulating the emissions of EVs to ensure they meet specific standards. These standards are designed to limit the release of harmful pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter, which can have detrimental effects on air quality and human health. By setting and enforcing these emission limits, regulators aim to encourage the development and adoption of cleaner technologies in the EV sector.
The process of monitoring emissions involves rigorous testing and inspection of EVs. This includes on-road and laboratory testing to measure real-world performance and ensure compliance with emission regulations. Agencies often use specialized equipment to analyze exhaust gases and other emissions, providing detailed data on the vehicle's environmental impact. This data is then used to assess the overall sustainability of different EV models.
Sustainability is another critical aspect of EV regulation. Agencies are responsible for evaluating the entire lifecycle of an EV, from production to end-of-life disposal. This comprehensive approach ensures that the environmental benefits of EVs extend beyond their use phase. For instance, regulators might assess the sustainability of EV batteries, considering their production, recycling, and potential environmental impact during disposal. This holistic view helps identify areas where improvements can be made to enhance the overall sustainability of the EV industry.
In addition to emissions and sustainability, these regulatory bodies also focus on other environmental factors. This includes the impact of EV manufacturing processes, the sourcing of raw materials, and the potential for renewable energy integration in the EV ecosystem. By addressing these aspects, agencies contribute to a more comprehensive understanding of the environmental implications of electric vehicles, allowing for informed decision-making and policy development.
The Ultimate Guide to Electric Scooter Shopping
You may want to see also

Consumer Protection: Legal frameworks protect buyers from fraudulent EV sales
Consumer protection is a critical aspect of the electric vehicle (EV) market, as it ensures that buyers are not taken advantage of by fraudulent practices. Legal frameworks play a vital role in safeguarding consumers' rights and providing a safety net in case of unfair or deceptive sales practices. Here's an overview of how these legal systems protect EV buyers:
In many countries, consumer protection laws are designed to prevent and address fraudulent activities in the automotive industry, including the rapidly growing EV sector. These laws often require dealerships and sellers to adhere to strict guidelines, ensuring transparency and fairness. For instance, regulations might mandate that sellers provide detailed information about the vehicle's history, including its previous ownership, maintenance records, and any accidents or repairs. This transparency empowers buyers to make informed decisions and reduces the risk of purchasing a vehicle with hidden issues.
Legal frameworks often include provisions that outline the rights of consumers in case of a fraudulent sale. If a buyer discovers that the EV they purchased has been misrepresented or is not as advertised, they can seek legal recourse. This may involve filing a complaint with the relevant consumer protection agency or taking legal action against the seller. In some jurisdictions, buyers may be entitled to a refund, a replacement vehicle, or compensation for any financial losses incurred due to the fraud.
To further protect consumers, regulatory bodies often maintain a database or registry of reputable EV sellers and dealerships. This helps buyers verify the credibility of the seller and reduces the chances of falling victim to fraudulent schemes. Additionally, these regulatory bodies may offer guidance and resources to consumers, educating them about their rights and providing tips on how to avoid scams.
Consumer protection laws also encourage the development of industry standards and certifications. These standards ensure that EVs meet certain quality and safety criteria, and they can be a useful tool for buyers to identify reliable vehicles. By promoting transparency and accountability, these legal frameworks create a more trustworthy environment for EV purchases.
In summary, legal frameworks are essential in protecting consumers from fraudulent EV sales. Through strict regulations, consumer rights enforcement, and industry standards, these laws ensure that buyers can make informed choices and seek redress when necessary. As the EV market continues to grow, robust consumer protection measures will be crucial in maintaining trust and fostering a healthy automotive industry.
Can Australia Lead the EV Revolution? Exploring Local Manufacturing Potential
You may want to see also

Infrastructure Development: Regulators manage the expansion of charging station networks
The development of electric vehicle (EV) infrastructure, particularly charging station networks, is a critical aspect of the transition to a sustainable transportation system. Regulators play a pivotal role in managing this expansion to ensure a seamless and efficient charging experience for EV owners. Here's an overview of their involvement:
Regulators, such as government agencies and transportation departments, are responsible for creating and implementing policies that govern the establishment and operation of charging stations. These policies aim to address various challenges, including the lack of standardized charging protocols, inconsistent power supply, and the need for widespread accessibility. By setting clear guidelines, regulators ensure that charging stations are built to meet specific standards, making them compatible with different EV models and ensuring a consistent user experience. This standardization is crucial for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
One of the key tasks for regulators is to identify and allocate suitable locations for charging stations. This involves mapping out areas with high EV ownership rates, busy transportation corridors, and locations that cater to various demographics. By strategically placing charging stations, regulators aim to reduce range anxiety among EV drivers and encourage the purchase of electric vehicles. For instance, they might prioritize locations near highways, shopping centers, and residential areas to provide convenient charging options for different user groups.
To facilitate the expansion of charging infrastructure, regulators often offer incentives and grants to businesses and organizations willing to invest in EV charging stations. These financial incentives can significantly reduce the initial costs associated with building and maintaining charging networks. Additionally, regulators may provide tax benefits or subsidies to encourage private sector participation, ensuring a diverse and widespread charging station network. Such initiatives are essential to accelerate the growth of EV infrastructure and support the growing demand for electric vehicles.
Furthermore, regulators establish rules and regulations to ensure fair competition and prevent monopolies in the charging station market. This includes setting pricing guidelines, preventing exclusive agreements that could limit consumer choice, and promoting open access to charging facilities. By fostering a competitive environment, regulators encourage innovation and ensure that EV owners have access to a variety of charging options, promoting a healthy and sustainable market.
In summary, regulators are instrumental in shaping the development of charging station networks, which is vital for the success of electric vehicle adoption. Through policy-making, strategic planning, and financial incentives, they guide the expansion of charging infrastructure, ensuring accessibility, compatibility, and a competitive market. Effective regulation will ultimately contribute to a more sustainable and efficient transportation ecosystem.
Unraveling the Mystery: Common Causes of Electric Fires in Vehicles
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The regulation of electric vehicles (EVs) in the US is a shared responsibility between various federal and state agencies. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) are key players in setting safety and emissions standards for EVs. NHTSA oversees vehicle safety, including the design and construction of EVs, while the EPA focuses on their environmental impact, particularly in terms of zero-emission vehicle (ZEV) requirements.
Yes, several federal laws and acts have been instrumental in shaping the EV market. The Energy Policy Act of 2005 introduced tax credits for EV purchases, encouraging consumers to adopt electric vehicles. The Energy Independence and Security Act of 2007 further expanded these incentives and set corporate average fuel economy (CAFE) standards, which indirectly influenced the development and production of EVs. Additionally, the Infrastructure Investment and Jobs Act of 2021 allocated significant funding for EV charging infrastructure, aiming to support the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
State governments have the authority to implement their own regulations and policies related to EVs, often building upon federal guidelines. Some states have enacted their own zero-emission vehicle (ZEV) programs, mandating a certain percentage of EVs in the state's vehicle sales. These programs vary in their requirements and timelines. For instance, California's ZEV program is particularly stringent, setting ambitious targets for EV sales and influencing other states to follow suit. State-level regulations also include incentives, subsidies, and licensing processes for EV manufacturers and dealers.