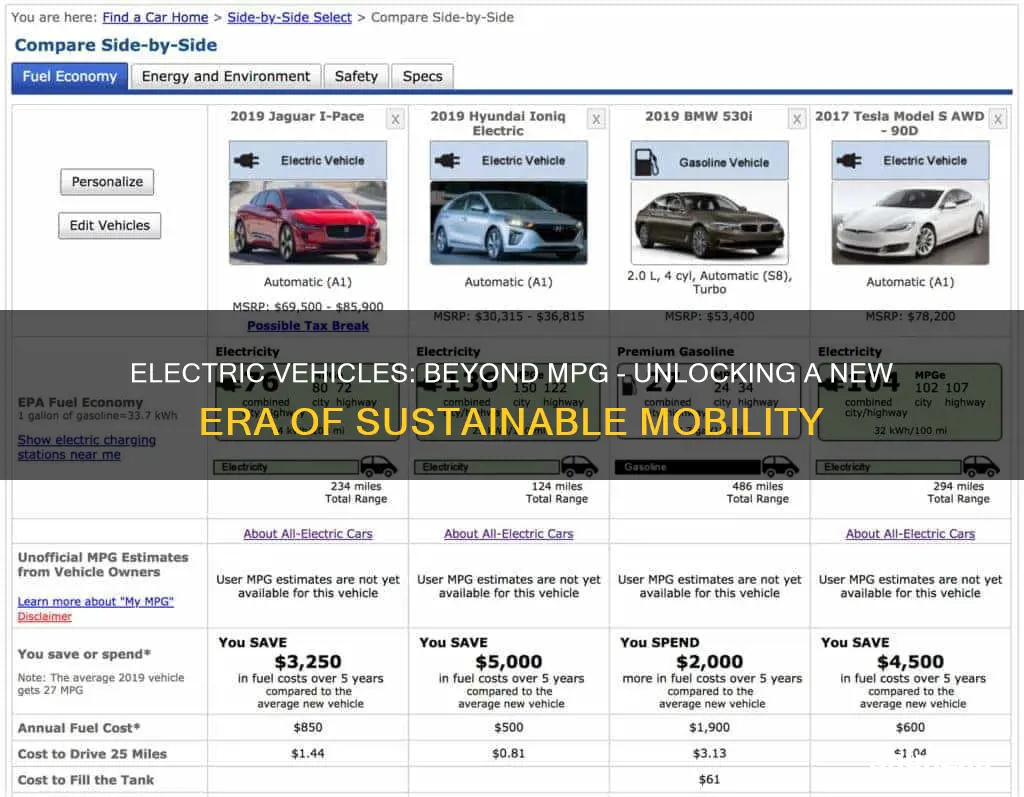
Electric vehicles (EVs) are often compared to traditional gasoline-powered cars using miles per gallon (MPG) as a metric to assess their efficiency. This comparison is important because it allows consumers to understand the energy efficiency of EVs in a familiar context. While EVs don't burn gasoline, they do consume energy, and understanding their energy consumption in terms of MPG helps drivers gauge the cost-effectiveness and environmental impact of their vehicle choices. This comparison is particularly relevant as the automotive industry transitions towards more sustainable transportation options, and it highlights the need for standardized metrics to evaluate and communicate the performance of electric vehicles.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency | Electric vehicles (EVs) are compared to MPG (miles per gallon) to provide a standardized way to understand their energy efficiency. MPG is a common metric for internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, and EVs are often compared to this standard to help consumers make informed choices. |
| Performance | EVs offer instant torque, resulting in quick acceleration, which is often compared to the performance of high-MPG ICE vehicles. |
| Environmental Impact | EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, reducing air pollution and carbon footprint. MPG ratings are used to highlight the environmental benefits of EVs compared to less efficient ICE vehicles. |
| Driving Range | The range of an EV is a critical factor, and MPG-like comparisons help consumers understand how far they can travel on a single charge. |
| Cost of Ownership | EVs often have lower running costs due to reduced maintenance and fuel expenses. MPG ratings can be used to estimate the cost savings over time. |
| Technology Advancement | The comparison to MPG ratings showcases the technological advancements in EVs, including improved battery technology and efficient power trains. |
| Consumer Behavior | MPG-like comparisons help consumers understand the practicality and convenience of EVs, especially for long-distance travel. |
| Government Incentives | Many governments offer incentives for EV adoption, and MPG-based comparisons can highlight these benefits. |
| Market Trends | The EV market is growing, and MPG-like ratings provide a reference point for consumers to understand the market's progress and trends. |
| Future Outlook | As the world moves towards sustainable transportation, the comparison to MPG ratings will likely become even more relevant and important. |
What You'll Learn
- Performance: EVs offer instant torque, delivering rapid acceleration and a thrilling driving experience
- Environmental Impact: MPG ratings obscure EVs' zero-emission nature, highlighting their role in reducing air pollution
- Energy Efficiency: EVs convert more energy into power, surpassing traditional cars in overall efficiency
- Charging Infrastructure: The focus on MPG overlooks the growing network of charging stations, enabling convenient EV ownership
- Cost Savings: EVs' lower fuel and maintenance costs make them economically advantageous over time

Performance: EVs offer instant torque, delivering rapid acceleration and a thrilling driving experience
Electric vehicles (EVs) have revolutionized the automotive industry, offering a unique driving experience that sets them apart from traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars. One of the most remarkable aspects of EVs is their performance, particularly in terms of acceleration and torque. When you step into an EV, you'll quickly notice the instant response and power it delivers, which is a stark contrast to the gradual build-up of power in conventional vehicles.
The secret behind this thrilling performance lies in the electric motor's ability to provide instant torque. Unlike ICE cars, where the engine needs to reach a certain speed or RPM (revolutions per minute) to deliver full power, electric motors can generate maximum torque from a standstill. This means that when you press the accelerator pedal in an EV, you experience a surge of power that propels the vehicle forward with incredible rapidity. The result is a breathtaking acceleration that can leave you with a smile on your face, especially when overtaking or merging onto highways.
This instant torque characteristic of EVs is a game-changer for drivers who crave a dynamic and responsive driving experience. It provides a sense of immediacy and control, making every journey an adventure. For instance, when driving an EV on a winding road, the quick acceleration allows for precise and confident maneuvers, ensuring you stay in control even in challenging driving conditions. The absence of a traditional gear shift also contributes to this seamless power delivery, as EVs often use single-speed transmissions or direct-drive systems, further enhancing the overall driving feel.
Furthermore, the performance of EVs is not just about the thrill of acceleration; it also contributes to a more efficient and environmentally friendly driving experience. The instant torque delivery means that EVs can accelerate smoothly and quickly, reducing the need for frequent gear changes and the associated fuel consumption. This efficiency in power delivery also translates to better energy management, as EVs can optimize their battery usage, ensuring a longer range and reduced charging requirements.
In summary, the performance of electric vehicles, particularly their ability to offer instant torque, is a significant factor in their growing popularity. The rapid acceleration and thrilling driving experience they provide are a far cry from the traditional ICE vehicles, making EVs a top choice for those seeking a more engaging and environmentally conscious driving adventure. This unique performance characteristic is a testament to the innovation and advancement in automotive technology, pushing the boundaries of what was once thought possible in the world of automobiles.
Troubleshooting: Removing a Stuck Electrical Plug from Your Vehicle
You may want to see also

Environmental Impact: MPG ratings obscure EVs' zero-emission nature, highlighting their role in reducing air pollution
The comparison of electric vehicles (EVs) to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars using miles per gallon (MPG) ratings can be misleading, especially when it comes to understanding their environmental impact. MPG ratings, while useful for assessing the efficiency of ICE vehicles, do not accurately represent the zero-emission nature of EVs. This is a critical distinction, as it highlights the significant role EVs play in reducing air pollution and improving overall environmental sustainability.
MPG ratings provide a measure of how far a vehicle can travel on a gallon of fuel, which is a standard metric for ICE cars. However, this metric fails to account for the environmental cost of the fuel itself. When an ICE vehicle burns gasoline, it emits pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and particulate matter, all of which contribute to air pollution and have detrimental effects on human health and the environment. In contrast, EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, meaning they do not release these harmful pollutants during operation.
The environmental impact of EVs is particularly evident when considering the entire lifecycle of the vehicle, from production to disposal. While the manufacturing process of EVs may have a higher environmental footprint due to the extraction of raw materials and energy-intensive production, the cumulative effect of their operation is vastly different. EVs powered by renewable energy sources, such as solar or wind, can achieve a net-zero carbon footprint, as the electricity used to charge them is generated without direct emissions. This is a stark contrast to ICE vehicles, which continuously emit pollutants throughout their operational life.
By comparing EVs to ICE cars using MPG ratings, we risk downplaying the true environmental benefits of electric mobility. Instead, we should emphasize the zero-emission nature of EVs and their potential to significantly reduce air pollution. This shift in perspective is crucial for policymakers, consumers, and the automotive industry to fully recognize the advantages of EVs and accelerate the transition to a more sustainable transportation system.
In summary, MPG ratings, while relevant for ICE vehicles, do not adequately represent the environmental superiority of EVs. The zero-emission capability of EVs is a powerful argument for their adoption, as it directly contributes to improving air quality and mitigating the environmental impact of transportation. This understanding is essential in promoting the widespread use of electric vehicles and fostering a cleaner, greener future.
Electric Vehicles: Educating Pedestrians on Proximity Awareness
You may want to see also

Energy Efficiency: EVs convert more energy into power, surpassing traditional cars in overall efficiency
Electric vehicles (EVs) have revolutionized the automotive industry by offering a more sustainable and efficient alternative to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars. One of the key advantages of EVs is their superior energy efficiency, which sets them apart from conventional vehicles. When comparing the energy efficiency of EVs to that of traditional cars, it becomes evident that EVs offer a more comprehensive and environmentally friendly solution.
The concept of energy efficiency in vehicles is often measured using a metric called miles per gallon (MPG). However, when it comes to EVs, the comparison is made using a different metric, such as kilowatt-hours (kWh) per 100 kilometers. This shift in measurement highlights the unique nature of electric powertrains. EVs convert a higher percentage of the energy they consume into useful power compared to traditional cars. While ICE vehicles waste a significant amount of energy as heat, EVs utilize advanced electric motors and power electronics to minimize energy loss. This results in a more efficient power generation and transmission process.
The efficiency of EVs is primarily attributed to their electric powertrains, which consist of electric motors, batteries, and power electronics. These components work in harmony to deliver power to the wheels with minimal energy wastage. Electric motors are inherently more efficient than internal combustion engines, especially at varying speeds and loads. They provide instant torque, ensuring smooth acceleration and efficient power delivery. Additionally, the use of regenerative braking in EVs allows for the recovery of kinetic energy, further enhancing overall efficiency.
In contrast, traditional cars with ICEs face several inefficiencies. The combustion process in ICEs is inherently less efficient, especially when compared to the direct conversion of electrical energy in EVs. ICEs lose a substantial amount of energy as heat, which is dissipated into the environment. This heat loss is a significant contributor to the overall inefficiency of traditional vehicles. Moreover, the complex mechanical systems in ICE cars, such as transmissions and various lubricated moving parts, introduce additional friction and energy losses.
The overall efficiency of EVs surpasses that of traditional cars, leading to several advantages. Firstly, EVs have higher energy density, allowing them to store more energy in a smaller volume. This enables EVs to travel longer distances on a single charge, addressing range anxiety concerns. Secondly, the efficient power conversion in EVs results in reduced energy consumption, leading to lower operating costs for vehicle owners. Lastly, the environmental benefits are substantial, as EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, contributing to improved air quality and reduced carbon footprints.
Unraveling the Rules: Electric Vehicle Support Regulations Explained
You may want to see also

Charging Infrastructure: The focus on MPG overlooks the growing network of charging stations, enabling convenient EV ownership
The comparison of electric vehicles (EVs) to traditional gasoline cars in terms of miles per gallon (MPG) is a common practice, but it often overshadows the critical aspect of charging infrastructure. As the popularity of EVs rises, so does the need for a robust and accessible charging network. This network is the backbone that supports the widespread adoption of electric mobility, ensuring that EV owners can conveniently charge their vehicles whenever and wherever needed.
The focus on MPG ratings might lead some to believe that EVs are less practical due to their perceived higher costs and longer refueling times. However, the reality is quite different. The development of charging infrastructure has been rapid and extensive, addressing the range anxiety often associated with early EVs. Today, a comprehensive network of charging stations is being established, offering fast and efficient charging options. These stations are strategically located along highways, in urban areas, and even at residential complexes, ensuring that EV owners have multiple convenient charging choices.
Charging infrastructure has evolved to include various types of charging stations, catering to different needs. Rapid chargers, for instance, can provide a significant charge in a short time, ideal for long-distance travel. These stations are typically found along major routes, allowing EV owners to quickly top up their batteries during journeys. Additionally, slower, more accessible charging points are available in residential areas, workplaces, and public spaces, providing a convenient way to charge overnight or during extended periods of parking.
The expansion of this charging network has been a collaborative effort between governments, energy companies, and private entities. Incentives and subsidies have been introduced to encourage the installation of charging stations, making them more accessible and affordable. As a result, the charging infrastructure is becoming increasingly widespread, mirroring the convenience of traditional fuel stations. This development is crucial in fostering public confidence in EV ownership, as it addresses the practical concerns related to range and charging convenience.
In summary, while MPG ratings provide a useful comparison, they should not overshadow the significant advancements in charging infrastructure. The growing network of charging stations is a testament to the commitment to making electric vehicles a practical and convenient choice for the masses. With continued investment and development, the charging infrastructure will further enhance the appeal of EVs, ensuring a smooth transition to a more sustainable transportation future.
The Legal Status of Electric Wheelchairs: A Vehicle or Not?
You may want to see also

Cost Savings: EVs' lower fuel and maintenance costs make them economically advantageous over time
Electric vehicles (EVs) offer a compelling economic advantage over traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars, primarily due to their lower operational costs. One of the most significant cost-saving benefits of EVs is the elimination of fuel expenses. Unlike gasoline or diesel vehicles, EVs run on electricity, which is generally much cheaper per mile. The cost of electricity to power an EV is significantly lower than the cost of gasoline or diesel, and this difference can add up over time. For instance, the average cost of electricity in the United States is around 12 cents per kilowatt-hour (kWh), while the cost of gasoline is approximately 20 cents per mile. This means that for every mile driven, an EV costs about half as much to operate as a conventional car. Over the lifetime of a vehicle, these savings can be substantial, especially for those who drive long distances or frequently.
In addition to the savings on fuel, EVs also offer reduced maintenance costs. Traditional cars require regular maintenance, including oil changes, fluid replacements, and engine repairs, which can be expensive. EVs, on the other hand, have fewer moving parts, which means they require less frequent servicing. Electric motors, for example, do not need oil changes or have the same wear and tear issues as gasoline engines. This simplicity in design translates to lower maintenance costs for EV owners. While some components, like the battery, may require replacement over time, the overall maintenance expense is generally lower compared to ICE vehicles. This is further supported by the fact that EVs have fewer service intervals, and when they do require maintenance, it often involves simpler and less costly procedures.
The economic advantage of EVs is also evident in the long-term savings they offer. While the initial purchase price of an EV might be higher than that of a comparable ICE vehicle, the total cost of ownership over the vehicle's lifetime is often lower. This is because EVs have fewer moving parts, which means they are less likely to break down or require major repairs. Additionally, the cost of electricity is generally more stable and predictable than the cost of gasoline or diesel, providing a level of financial security for EV owners. Over time, the savings on fuel and maintenance can offset the higher upfront cost, making EVs an economically sound choice for many consumers.
Furthermore, the environmental benefits of EVs contribute to their overall cost-effectiveness. By reducing reliance on fossil fuels, EVs help lower carbon emissions and improve air quality. Many governments and utilities offer incentives and subsidies to encourage the adoption of EVs, which can further enhance their economic appeal. These incentives often include tax credits, rebates, and reduced registration fees, making EVs even more affordable and attractive to consumers. In summary, the combination of lower fuel costs, reduced maintenance expenses, and long-term savings makes EVs a financially viable and sustainable transportation option. As technology advances and infrastructure improves, the economic benefits of EVs are likely to become even more pronounced, solidifying their position as a cost-effective and environmentally friendly choice for drivers.
Unlocking California's Tesla Tax Credit: A Green Car Incentive Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
MPGe is a standardized measure used to compare the energy efficiency of EVs to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. It provides a common metric to help consumers understand and compare the fuel economy of different electric cars, making it easier to choose the right vehicle for their needs.
MPGe is calculated by converting the vehicle's energy consumption in kilowatt-hours (kWh) per 100 miles into a gallon-equivalent. This is done by multiplying the kWh consumption by 3.755 (a conversion factor), and then dividing by the number of miles traveled. The result is expressed as MPGe, allowing for a direct comparison with traditional fuel efficiency ratings.
A higher MPGe rating indicates that an electric vehicle is more energy-efficient. It means the car can travel more miles using a given amount of electricity, which often translates to lower operating costs and reduced environmental impact compared to conventional vehicles. Higher MPGe ratings are desirable as they demonstrate the vehicle's efficiency in converting energy into miles.
No, MPGe is just one aspect of evaluating an electric vehicle's performance. While it provides valuable information about energy efficiency, other factors like range, charging time, battery capacity, and performance metrics should also be considered. MPGe is particularly useful for understanding the cost-effectiveness of an EV, especially when comparing different models and their respective energy consumption.







