Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained significant attention as a sustainable transportation alternative, but their efficiency is a topic of ongoing debate. While EVs offer numerous environmental benefits, such as reduced carbon emissions, their overall efficiency can vary depending on various factors. This paragraph will explore the efficiency of electric vehicles, considering aspects like energy consumption, charging infrastructure, and the environmental impact of battery production. By examining these elements, we can gain a comprehensive understanding of whether electric vehicles are indeed efficient and how they contribute to a greener future.
What You'll Learn
- Energy Consumption: Compare EV efficiency to traditional vehicles over various driving conditions
- Battery Technology: Explore advancements in battery tech and their impact on efficiency
- Range Anxiety: Discuss strategies to mitigate range concerns in electric vehicles
- Charging Infrastructure: Analyze the role of charging stations in EV efficiency and adoption
- Environmental Impact: Evaluate the overall environmental benefits of electric vehicles

Energy Consumption: Compare EV efficiency to traditional vehicles over various driving conditions
The efficiency of electric vehicles (EVs) compared to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles is a topic of great interest, especially when considering the various driving conditions that vehicles encounter. EVs have gained popularity due to their potential to reduce environmental impact and offer a more efficient driving experience. Let's delve into the energy consumption aspect and compare the efficiency of EVs and traditional vehicles under different scenarios.
City Driving: In urban areas, where frequent stops and starts are common, EVs excel in efficiency. Electric motors provide instant torque, allowing EVs to accelerate quickly and efficiently. During city driving, EVs often achieve higher energy efficiency due to their ability to maintain a steady speed without the need for frequent gear changes. Additionally, regenerative braking in EVs helps capture and store energy that would otherwise be lost as heat during braking, further improving overall efficiency.
Highway Driving: When it comes to highway driving, the efficiency comparison becomes more nuanced. EVs generally maintain a consistent power output, which can be advantageous on highways where steady speeds are prevalent. However, the efficiency of EVs on highways can be influenced by factors such as wind resistance and the weight of the vehicle. Traditional ICE vehicles, on the other hand, may offer slightly better efficiency on highways due to their ability to optimize engine performance at higher speeds.
Long-Distance Travel: For long-distance travel, the efficiency of EVs can be a concern. EVs typically have a lower energy density than gasoline or diesel fuel, which means they may require more frequent charging during extended trips. This can impact the overall efficiency, especially when considering the time and energy spent on charging stops. However, advancements in battery technology and the development of extensive charging infrastructure are addressing these challenges, making EVs more viable for long-haul travel.
Cold Weather and Efficiency: Operating in cold weather can affect the efficiency of both EVs and traditional vehicles. In cold climates, EVs might experience a temporary decrease in range due to the increased energy required to heat the cabin and maintain battery temperature. ICE vehicles may also face efficiency losses in cold weather, but the impact on EVs can be more pronounced due to the additional energy demands of heating systems.
In summary, the efficiency of EVs compared to traditional vehicles varies depending on the driving conditions. EVs demonstrate superior efficiency in city driving due to their instant torque and regenerative braking. Highway driving may offer similar efficiency for EVs, but long-distance travel and cold weather can present challenges. As technology advances, addressing these specific conditions will further enhance the overall efficiency and practicality of electric vehicles.
The Electric Vehicle Leader: Unveiling the Top State's EV Revolution
You may want to see also

Battery Technology: Explore advancements in battery tech and their impact on efficiency
The evolution of battery technology is a pivotal factor in the efficiency of electric vehicles (EVs). Over the years, advancements in battery technology have played a crucial role in improving the overall efficiency and performance of EVs. One of the key areas of focus has been the development of more energy-dense batteries, which can store more energy in a smaller volume. This is achieved through the use of advanced materials and innovative cell designs. For instance, lithium-ion batteries, the most common type used in EVs, have seen significant improvements in their energy density, allowing for longer driving ranges.
A major breakthrough in battery technology is the introduction of solid-state batteries. These batteries replace the liquid or gel electrolyte with a solid conductive material, offering several advantages. Solid-state batteries can potentially provide higher energy density, faster charging, and improved safety compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. The solid-state approach also reduces the risk of thermal runaway, a critical safety concern in lithium-ion batteries. As a result, solid-state batteries are expected to revolutionize the EV market by offering even greater efficiency and performance.
Another significant advancement is the development of lithium-sulfur (Li-S) batteries. Li-S batteries have a theoretical energy density that is several times higher than that of lithium-ion batteries, making them an attractive option for increasing EV efficiency. However, challenges such as the short cycle life and poor rate capability of Li-S batteries have hindered their widespread adoption. Researchers are working on addressing these issues through the use of advanced sulfur-based materials and innovative cell architectures, aiming to make Li-S batteries a viable alternative for high-efficiency EVs.
Furthermore, the integration of smart battery management systems (BMS) has been instrumental in optimizing battery performance and efficiency. These systems monitor and control various aspects of the battery, including temperature, state of charge, and current flow. By optimizing the charging and discharging processes, BMS can extend battery life, improve efficiency, and ensure safe operation. Advanced BMS algorithms can also predict battery health and performance, enabling better decision-making for EV owners regarding maintenance and usage.
In summary, advancements in battery technology have been instrumental in enhancing the efficiency of electric vehicles. From increased energy density in lithium-ion batteries to the promising potential of solid-state and lithium-sulfur batteries, these innovations are driving the EV market forward. Additionally, smart battery management systems are playing a crucial role in maximizing the efficiency and longevity of EV batteries. As battery technology continues to evolve, we can expect further improvements in the overall efficiency and sustainability of electric vehicles.
Electric Vehicle Fires: Unraveling the Mystery Behind the Blazes
You may want to see also

Range Anxiety: Discuss strategies to mitigate range concerns in electric vehicles
Range anxiety is a common concern for potential electric vehicle (EV) buyers, referring to the fear of running out of battery power during a journey. This anxiety can be a significant barrier to the widespread adoption of EVs, as it may prevent people from considering them for long-distance travel or daily commutes. However, several strategies can help mitigate range concerns and make electric vehicles a more appealing and practical choice for a broader audience.
One effective approach to addressing range anxiety is to improve battery technology. Modern EVs are equipped with advanced lithium-ion batteries that have higher energy densities and faster charging capabilities compared to earlier models. Manufacturers are continually researching and developing more efficient battery chemistries, aiming to increase the range of electric cars. For instance, solid-state batteries promise higher energy density and faster charging, potentially doubling the range of EVs. Additionally, battery warming systems can optimize performance in cold climates, ensuring that the range remains consistent regardless of external temperatures.
Another strategy is to encourage the development of an extensive charging infrastructure. Governments and private companies are investing in the creation of fast-charging stations along highways and in urban areas. These stations can provide a significant charge in a short time, allowing drivers to cover long distances without extensive stops. The availability of multiple charging options, including home charging, public charging stations, and fast-charging networks, can alleviate range anxiety by providing convenient and efficient charging solutions.
Route planning and optimization can also play a crucial role in managing range anxiety. EV owners can utilize dedicated apps or in-car navigation systems to plan their journeys, taking into account charging station locations and battery efficiency. These tools can suggest optimal routes, estimate travel times, and provide real-time charging station availability, ensuring that drivers can make informed decisions and avoid unexpected range limitations. Furthermore, over-the-air software updates can enhance the efficiency of EV systems, improving performance and range over time.
Lastly, car manufacturers are offering various solutions to ease range concerns. Some vehicles are equipped with regenerative braking systems that capture and store energy during deceleration, extending the range. Others feature dual-motor systems, allowing for improved efficiency and performance. Additionally, the development of hydrogen fuel cell technology offers an alternative to battery-powered EVs, providing longer ranges and faster refueling times. These innovations contribute to a more diverse and efficient EV market, catering to different consumer needs and preferences.
Unveiling Electro-Hydraulic Power: The Heart of Modern Vehicle Systems
You may want to see also

Charging Infrastructure: Analyze the role of charging stations in EV efficiency and adoption
The development of charging infrastructure is a critical aspect of the widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and plays a significant role in their efficiency and overall environmental impact. Efficient charging stations are essential to ensure that EVs can be charged quickly and conveniently, reducing the time and effort required for charging, which in turn encourages more people to make the switch from traditional internal combustion engine vehicles.
Charging stations are the backbone of the EV ecosystem, providing the necessary power to replenish batteries. The efficiency of these stations is not just about the speed of charging but also about the overall user experience and the impact on the grid. Rapid charging stations, for instance, can significantly reduce charging times, which is crucial for long-distance travel and reducing range anxiety among potential EV buyers. These stations often use direct current (DC) to rapidly charge the vehicle's battery, making them faster than standard alternating current (AC) chargers. However, rapid charging requires more sophisticated infrastructure and can put additional strain on the power grid, requiring careful management to ensure stability.
The availability and accessibility of charging stations are key factors in EV adoption. A well-distributed network of charging stations can encourage potential buyers to make the purchase, knowing they have convenient access to charging facilities. This is especially important in urban areas where parking spaces are limited, and charging stations can be integrated into existing parking structures. Public charging stations, often found in shopping malls, parking lots, and rest stops, provide an essential service to EV owners, allowing them to charge their vehicles while on the move or during extended periods away from home.
Furthermore, the efficiency of charging stations is closely tied to the integration of smart grid technologies. Smart charging systems can optimize the charging process by adjusting the power draw based on grid demand and supply. This not only reduces the strain on the power grid but also allows for more efficient use of renewable energy sources, which are often intermittent. By implementing smart charging, utilities can manage peak loads, ensuring a stable and reliable power supply for both EVs and other grid customers.
In summary, charging infrastructure is a vital component in the efficiency and adoption of electric vehicles. Efficient and accessible charging stations, combined with smart grid technologies, can significantly reduce charging times, improve user experience, and encourage the transition to electric mobility. As the EV market continues to grow, investing in robust and intelligent charging infrastructure will be essential to support the increasing demand and ensure a sustainable future for transportation.
The Electric Revolution: Are All Vehicles Going Green?
You may want to see also

Environmental Impact: Evaluate the overall environmental benefits of electric vehicles
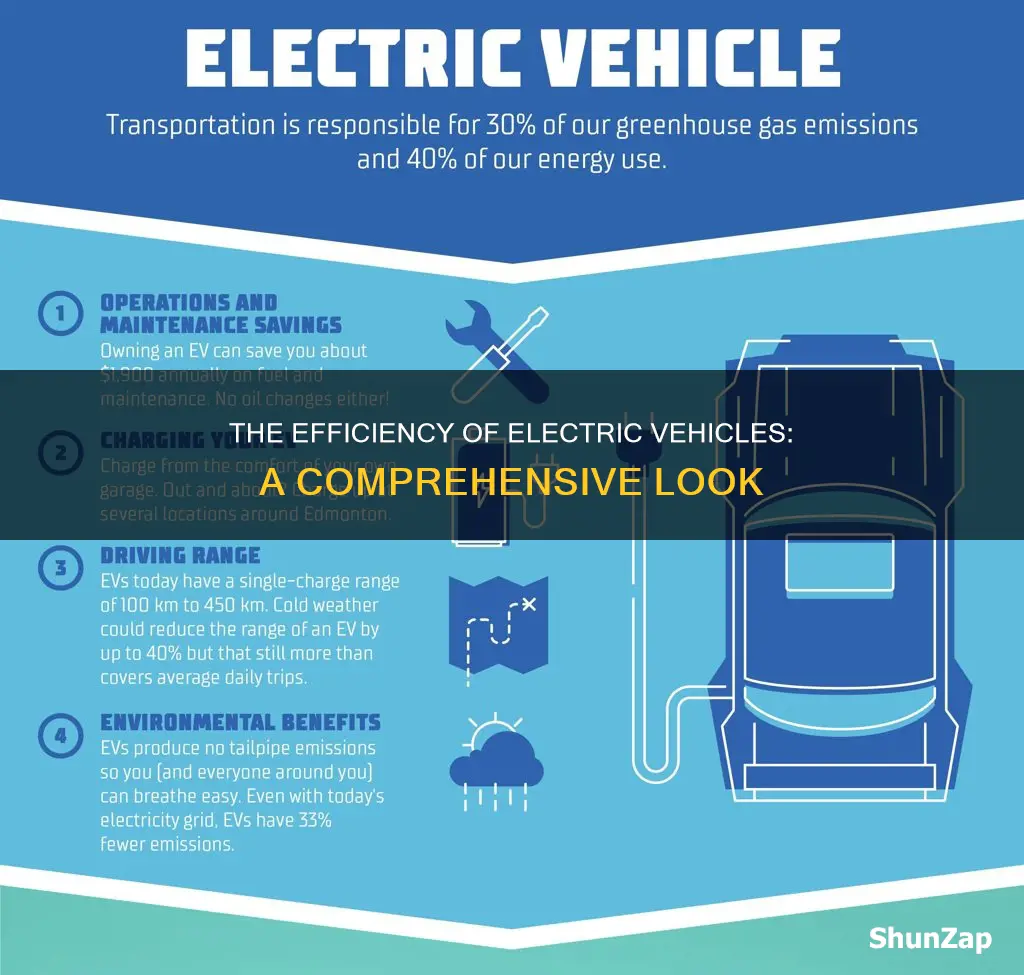
The environmental benefits of electric vehicles (EVs) are significant and multifaceted, offering a more sustainable alternative to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. One of the primary advantages is the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions. EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, meaning they do not release harmful pollutants such as carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter during operation. This is a crucial factor in combating climate change, as the transportation sector is a major contributor to global CO2 emissions. By transitioning to EVs, we can significantly lower the carbon footprint of the automotive industry and improve air quality, especially in densely populated urban areas.
The environmental impact extends beyond the vehicle's operation. The manufacturing process of EVs has also become more sustainable over time. Modern EV production focuses on using recycled materials, reducing the need for virgin resources, and minimizing waste. Many EV manufacturers are adopting circular economy principles, aiming to create a closed-loop system for materials, which can significantly reduce the environmental impact of production. Additionally, the shift towards EVs can lead to a decrease in the demand for fossil fuels, which are often extracted through environmentally destructive processes.
Another aspect to consider is the energy source used to power EVs. As the world moves towards a more sustainable energy mix, the environmental benefits of EVs become even more pronounced. When charged using renewable energy sources like solar or wind power, EVs can be virtually emission-free, even during their entire lifecycle. This is a powerful advantage, especially in regions where renewable energy adoption is increasing. Governments and energy providers are investing in large-scale renewable projects, making it more feasible for EVs to be powered by clean energy, further reducing their environmental impact.
Furthermore, the widespread adoption of EVs can contribute to a more efficient and resilient energy grid. As more vehicles are integrated into the grid, they can act as mobile energy storage devices, helping to balance supply and demand. This concept, known as vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology, allows EVs to feed electricity back into the grid during peak hours, reducing the strain on the power infrastructure. V2G technology also enables the potential for smart charging, where EVs can be charged during off-peak hours when energy is cheaper and more abundant, further optimizing energy usage.
In summary, electric vehicles offer a compelling solution to reduce the environmental impact of transportation. Their zero-emission nature, coupled with the potential for renewable energy integration and efficient energy management, makes them a key player in the transition to a more sustainable future. As technology advances and infrastructure improves, the overall environmental benefits of EVs will continue to grow, making them an increasingly attractive choice for environmentally conscious consumers and policymakers alike.
Chevy Spark: Electric Vehicle or Gas-Powered Mystery?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Electric vehicles (EVs) are generally considered more efficient than conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars. EVs convert a higher percentage of the energy stored in their batteries into actual vehicle movement, often achieving higher miles per gallon equivalent (MPGe). For example, a fully electric car with a range of 300 miles might have an efficiency of around 100 MPGe, while a similar gasoline car might get 30-40 miles per gallon.
Yes, electric cars are known for their energy-saving capabilities. EVs have fewer moving parts compared to ICE vehicles, resulting in less energy loss during operation. Additionally, regenerative braking systems in EVs capture and store energy that would otherwise be lost as heat during braking, further improving overall efficiency. Over the lifetime of an EV, the savings can be significant, especially with the increasing cost of gasoline.
Several factors can impact the efficiency of electric cars. These include the vehicle's design, aerodynamics, weight, battery capacity, driving habits, and weather conditions. For instance, a well-designed, lightweight EV with a large battery pack and efficient aerodynamics will generally be more efficient. Driving habits also play a crucial role; aggressive acceleration and frequent high-speed driving can reduce efficiency.
Charging electric vehicles can be efficient, especially when using fast-charging stations or home charging setups. Modern charging infrastructure is designed to minimize energy loss during the charging process. Level 3 (DC fast charging) can provide a significant charge in a short time, making it efficient for long-distance travel. However, it's important to note that the efficiency of charging also depends on the type of charger, the vehicle's charging port, and the charging station's power source.