The world of electric vehicles (EVs) is rapidly evolving, and with it, the incentives and financial support for EV adoption. One crucial aspect of this support is the availability of tax credits for electric vehicle purchases. However, there's a catch: these credits are often subject to certain limitations, including a cap on the amount of Advanced Electric Vehicle (AEV) credits that can be claimed. This raises an important question: Is there a limit to the AEV credit that EV buyers can receive? Understanding this limit is essential for EV enthusiasts and policymakers alike, as it can significantly impact the financial feasibility of EV ownership and the overall success of government-led initiatives to promote sustainable transportation.
What You'll Learn
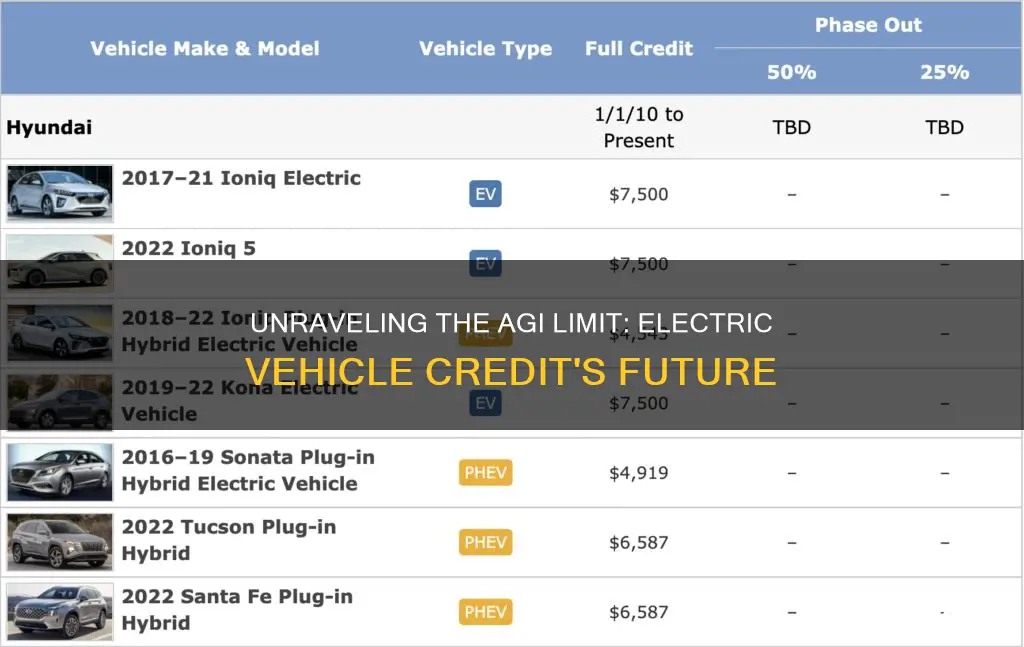
- Tax Credit Cap: Maximum tax credit for electric vehicles is $7,500
- Income Thresholds: Income limits may affect eligibility for EV tax credits
- Manufacturing Requirements: EVs must be manufactured in North America to qualify
- Credit Phasing Out: Tax credit decreases over time for certain vehicle types
- Used EV Credits: Some states offer credits for purchasing used electric vehicles

Tax Credit Cap: Maximum tax credit for electric vehicles is $7,500
The concept of a tax credit cap for electric vehicles is an important aspect of the broader discussion on incentivizing the adoption of eco-friendly transportation. This cap, set at $7,500, serves as a critical threshold that determines the maximum financial benefit an individual can receive when purchasing an electric vehicle (EV). Understanding this cap is crucial for both consumers and policymakers, as it directly impacts the accessibility and affordability of EVs.
For consumers, the $7,500 cap means that the tax credit for electric vehicles is not unlimited. This limit ensures that the financial incentive remains substantial but also manageable, preventing an excessive burden on the public finances. It encourages a balanced approach, where the government provides significant support while also ensuring the sustainability of the program. This cap is particularly relevant for high-end electric vehicles, which often carry premium prices, as it sets a clear maximum benefit for buyers.
Policymakers should consider the implications of this cap on the EV market. It can influence consumer behavior, potentially steering buyers towards more affordable EV models that fall below the cap. This shift could have a positive impact on the overall market, making electric vehicles more accessible to a broader range of consumers. Additionally, the cap might encourage manufacturers to focus on producing a wider variety of EV models, catering to different price points and consumer preferences.
Furthermore, the $7,500 cap can be a strategic tool for policymakers to monitor and adjust the effectiveness of the tax credit program. By setting this limit, they can assess the impact on the market and make informed decisions about future adjustments. This could include extending the credit period, increasing the cap, or introducing additional incentives to further boost EV sales and promote environmental sustainability.
In summary, the tax credit cap of $7,500 for electric vehicles is a critical component of the strategy to encourage EV adoption. It provides a financial incentive while maintaining fiscal responsibility. This cap has the potential to shape consumer choices, influence market dynamics, and guide policymakers in their efforts to support the transition to sustainable transportation. Understanding and effectively utilizing this cap can contribute to a successful and well-managed EV tax credit program.
Sustainable Solutions: Navigating EV Battery Disposal and Recycling
You may want to see also

Income Thresholds: Income limits may affect eligibility for EV tax credits
Income thresholds and limits are crucial factors when it comes to determining eligibility for electric vehicle (EV) tax credits. These financial incentives are designed to encourage the adoption of environmentally friendly transportation, but they often come with specific income-based criteria. Understanding these income limits is essential for individuals and families to take advantage of the benefits and make informed decisions about purchasing an EV.
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in the United States has set guidelines for EV tax credits, including income thresholds that vary depending on the vehicle's price and the taxpayer's adjusted gross income (AGI). AGI is a measure of a person's income after certain deductions are considered. For the 2023 tax year, the IRS introduced a phase-out rule for the EV tax credit, which means that the credit amount gradually decreases as the taxpayer's AGI exceeds certain limits. These limits are set at $150,000 for single filers and $300,000 for joint filers. When the AGI surpasses these thresholds, the credit starts to phase out, and at a certain point, it becomes completely unavailable.
For instance, if a single filer has an AGI of $140,000, they may be eligible for a partial EV tax credit, but as their income increases, the credit amount will decrease until it reaches zero at an AGI of $150,000. Similarly, joint filers with an AGI of $290,000 or higher will also face a phase-out of the credit. These income limits ensure that the tax credits are targeted towards lower- to middle-income earners, promoting a more equitable distribution of the benefits.
It is important to note that these income thresholds are subject to change and may vary across different regions and countries. Some governments offer similar incentives but with distinct eligibility criteria. Therefore, individuals should research and consult official sources to understand the specific income limits applicable to their jurisdiction.
In summary, income thresholds play a significant role in determining eligibility for EV tax credits. Taxpayers need to be aware of their AGI and how it compares to the set limits to ensure they can maximize the benefits of purchasing an electric vehicle. Staying informed about these financial guidelines is crucial for making sustainable transportation choices.
Electric Vehicle Resale Value: Strategies for Accurate Forecasting
You may want to see also

Manufacturing Requirements: EVs must be manufactured in North America to qualify
The manufacturing requirements for electric vehicles (EVs) to qualify for certain incentives and credits are stringent, and one of the key criteria is the place of production. EVs must be manufactured in North America to meet the eligibility criteria for various financial benefits. This requirement is in place to encourage and support the domestic production of electric vehicles, fostering the growth of the North American automotive industry and reducing reliance on imports.
The North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and its successor, the United States-Mexico-Canada Agreement (USMCA), have played a significant role in shaping these manufacturing requirements. The USMCA, in particular, includes provisions that mandate a certain percentage of a vehicle's components to be sourced from North American countries. This percentage is often referred to as the 'regional value content' (RVC) or 'regional production standard'. For EVs to qualify for the federal tax credit in the United States, they must meet a specific RVC threshold, which is typically around 75%. This means that a substantial portion of the vehicle's production, including its battery components, must originate from North America.
Manufacturers aiming to produce EVs for the North American market need to carefully plan their supply chain and production processes. This includes identifying and securing suppliers for critical components, such as batteries, motors, and electronics, that meet the regional sourcing requirements. Additionally, the manufacturing facilities themselves should be located in North America to ensure compliance with the eligibility criteria. This may involve establishing new production lines or modifying existing ones to meet the specific standards and regulations.
It is essential for EV manufacturers to stay informed about the evolving manufacturing requirements and regulations. These rules can change over time, and staying up-to-date is crucial to ensure that their vehicles remain eligible for the desired incentives. Manufacturers should also be aware of the specific guidelines set by different governments and agencies, as these may vary across regions.
In summary, the manufacturing requirements for EVs to qualify for credits and incentives are stringent, with a strong emphasis on North American production. Meeting these criteria is essential for manufacturers to take advantage of the financial benefits and support the growth of the domestic EV industry. Staying informed about the latest regulations and planning the supply chain accordingly are key steps for successful EV production in North America.
Diagnosing Electrical Shorts: A Guide for Vehicle Owners
You may want to see also

Credit Phasing Out: Tax credit decreases over time for certain vehicle types
The tax credit for electric vehicles (EVs) is a significant incentive for consumers to make the switch to cleaner transportation. However, it's important to understand that this credit is not permanent and is subject to a phase-out period. This means that the amount of tax credit available will decrease over time for certain vehicle types, and it's crucial for potential EV buyers to be aware of these changes to plan their purchases accordingly.
For electric vehicles, the tax credit is typically available for a specific period, and the amount decreases as the vehicle's price increases. This is designed to encourage the purchase of more affordable EVs and promote a faster transition to electric mobility. The credit amount is generally higher for lower-priced vehicles, ensuring that a wider range of consumers can benefit from this incentive. As the vehicle's price rises, the credit amount gradually decreases, eventually reaching a point where it may no longer be available.
The phase-out period for the tax credit varies depending on the vehicle's price and the year of manufacture. For instance, in the United States, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) has set guidelines for the credit phase-out. The credit starts to decrease for vehicles with a manufacturer's suggested retail price (MSRP) above $80,000 for individuals and $100,000 for married couples filing jointly. For plug-in hybrid vehicles, the threshold is lower, starting the phase-out at $50,000 for individuals and $70,000 for joint filers. These limits are adjusted annually, ensuring that the credit remains relevant and effective.
It's essential for EV buyers to stay informed about these changes to make well-informed decisions. When considering an EV purchase, potential buyers should research the current tax credit amount and the vehicle's price to determine if the credit is still available. Additionally, keeping an eye on the vehicle's price history can help buyers understand if the credit will be phased out in the future. This information is crucial, especially for high-end EV models, as it can significantly impact the overall cost of ownership.
In summary, the tax credit for electric vehicles is a valuable incentive, but it's a temporary measure with a phase-out period. Understanding the credit's limitations and how it decreases over time is essential for consumers to make the right choices. By staying informed, buyers can ensure they take advantage of the credit while it's available and plan their EV purchases accordingly. This knowledge is particularly important for those considering more expensive EVs, as it can influence their decision-making process.
Ford's Future: Electric Vehicles in Transition
You may want to see also

Used EV Credits: Some states offer credits for purchasing used electric vehicles
In an effort to promote the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and reduce greenhouse gas emissions, several states in the United States have implemented programs that offer financial incentives for purchasing EVs. While many of these programs focus on new vehicle purchases, some states have also recognized the environmental benefits of used EVs and have introduced specific credits for buying pre-owned electric cars. This initiative is particularly important as it encourages the circular economy, extends the lifespan of vehicles, and provides an affordable entry point for consumers who might not otherwise be able to afford a new EV.
For instance, California, a state renowned for its aggressive environmental policies, offers the Clean Vehicle Rebate Project (CVRP). This program provides rebates to residents who purchase or lease new or used electric cars, plug-in hybrids, or fuel cell vehicles. The amount of the rebate depends on the vehicle's model year, battery capacity, and the state's current funding levels. Interestingly, the CVRP includes a provision for used EVs, ensuring that older electric cars are not overlooked in the push towards a cleaner transportation sector.
Similarly, New York State's EV and Hybrid Vehicle Rebate Program offers incentives for the purchase of new and used electric vehicles. The program provides rebates of up to $2,000 for used EVs, with the amount based on the vehicle's battery capacity and the model year. This initiative not only supports the environment but also stimulates the local economy by creating jobs in the automotive sector.
These state-level programs are designed to complement federal incentives, such as the federal tax credit for electric vehicles, which can further reduce the cost of purchasing an EV. By offering additional credits for used EVs, these state programs aim to make electric cars more accessible to a broader range of consumers, including those on a tighter budget. This approach also helps to close the gap between the cost of new and used EVs, making the transition to electric mobility more feasible for many families and individuals.
It is worth noting that the availability and specifics of these used EV credits can vary significantly from one state to another. Therefore, prospective buyers should research their state's specific policies and requirements to understand the full extent of the financial incentives available. This research will ensure that individuals can make informed decisions about their vehicle purchases and take full advantage of the financial benefits offered by their state.
Rivian's Electric Revolution: Unlocking the Future of Sustainable Driving
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The EV tax credit is a federal incentive to promote the adoption of electric vehicles. The AGI limit for this credit is not a strict cap, but rather a phase-out rule. For the 2023 tax year, the credit starts to phase out for individuals with an AGI of $150,000 or more ($75,000 for married filing separately). The credit is completely phased out for AGI above $200,000 ($100,000 for married filing separately).
The credit amount is not directly tied to your AGI, but rather the vehicle's price and your eligibility. However, the phase-out rule mentioned above will reduce the credit amount as your income increases. For example, if your AGI is $150,000, you might receive a partial credit, and if it exceeds $200,000, you won't be eligible for the credit at all.
No, if your AGI exceeds the phase-out threshold, you won't be eligible for the EV tax credit. The credit is designed to support lower- to middle-income households in purchasing electric vehicles. Higher-income earners may still benefit from other incentives or tax benefits related to EVs.
Yes, there are a few additional considerations. The credit is generally limited to the purchase of new electric vehicles, not used cars. Additionally, the credit is capped at $7,500 per vehicle for most models. Some luxury vehicles may have different credit limits or requirements. It's important to review the IRS guidelines and consult a tax professional for personalized advice based on your specific financial situation.







