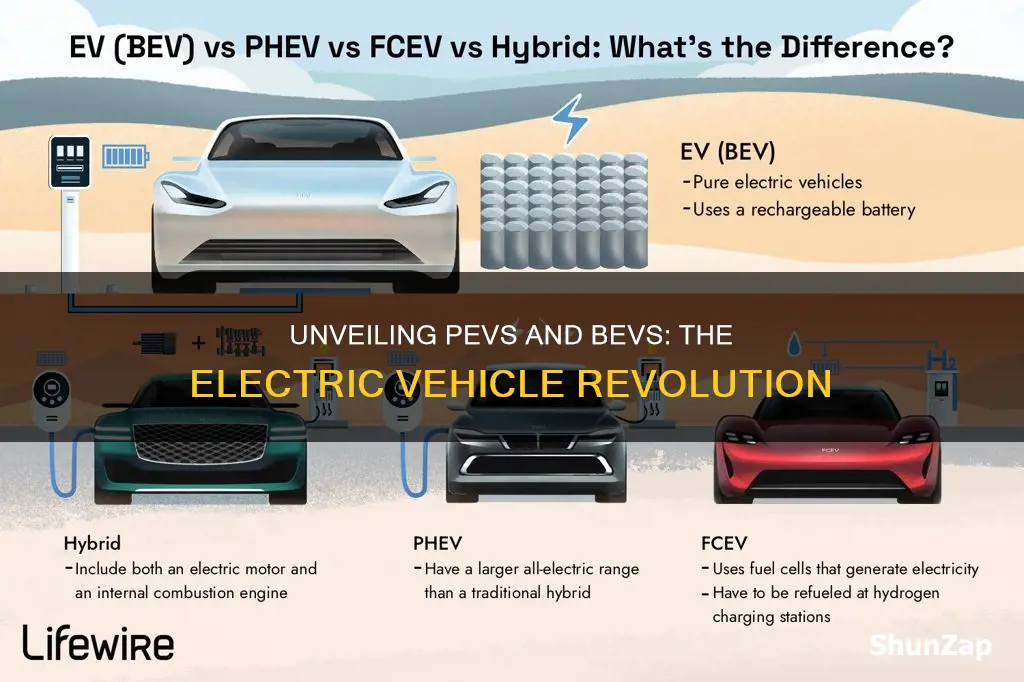
PEVs and BEVs are types of electric vehicles that are revolutionizing the automotive industry. PEVs, or Plug-in Electric Vehicles, are a broad category that includes both Battery Electric Vehicles (BEVs) and Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs). BEVs, as the name suggests, are fully electric vehicles that run exclusively on electricity stored in batteries, offering zero-emission transportation. On the other hand, PHEVs combine an electric motor with a conventional internal combustion engine, allowing for both electric-only and hybrid operation. Both PEVs and BEVs are key components of the global shift towards sustainable transportation, aiming to reduce carbon footprints and promote cleaner, more efficient driving experiences.
What You'll Learn
- Battery Types: Lithium-ion, nickel-metal hydride, and solid-state batteries power EVs
- Charging Infrastructure: EVSE (Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment) and charging stations are essential
- Range Anxiety: Addressing range limitations and consumer concerns
- Performance: EVs offer instant torque, smooth acceleration, and high top speeds
- Environmental Impact: Reduced emissions and a greener transportation alternative

Battery Types: Lithium-ion, nickel-metal hydride, and solid-state batteries power EVs
The world of electric vehicles (EVs) is rapidly evolving, and at the heart of this revolution are the batteries that power these cars. Three primary battery types dominate the EV market: lithium-ion, nickel-metal hydride (NiMH), and solid-state. Each has its own advantages and disadvantages, influencing the performance, range, and overall experience of electric vehicles.
Lithium-ion batteries are the most common and widely recognized technology in EVs. They offer high energy density, allowing for longer driving ranges. These batteries are lightweight, compact, and have a low self-discharge rate, making them ideal for electric cars. Lithium-ion batteries have been the go-to choice for many EV manufacturers due to their ability to provide high power output and relatively long cycle life. However, they are susceptible to thermal runaway, a dangerous situation where the battery overheats and can catch fire. Despite this, lithium-ion technology continues to advance, with ongoing research focusing on improving safety and extending the battery's lifespan.
Nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) batteries were one of the earliest types used in EVs and are still found in some older models. NiMH batteries offer a higher energy density than lead-acid batteries but are less powerful than lithium-ion. They are known for their excellent low-temperature performance, making them suitable for colder climates. Additionally, NiMH batteries have a longer cycle life and are more resistant to degradation over time. However, they are heavier and larger than lithium-ion batteries, which can impact the overall efficiency and range of the vehicle.
Solid-state batteries are a relatively new technology that promises to revolutionize the EV industry. These batteries replace the liquid or gel electrolyte in traditional lithium-ion cells with a solid conductive material, typically a ceramic or polymer. Solid-state batteries offer several advantages, including higher energy density, faster charging, and improved safety. They can store more energy in a smaller space, potentially doubling the range of electric vehicles. Furthermore, solid-state batteries are less prone to thermal issues and can operate at a wider temperature range. However, manufacturing these batteries is more complex and expensive, which has limited their widespread adoption.
The choice of battery type significantly impacts the performance and characteristics of electric vehicles. Lithium-ion batteries provide a balance of power and range, making them a popular choice for most EV manufacturers. NiMH batteries offer reliability and low-temperature performance, while solid-state batteries represent the future with their potential for higher energy density and improved safety. As technology advances, we can expect to see a wider variety of battery options, allowing EV manufacturers to cater to specific consumer needs and preferences.
Deadhead Miles: The Hidden Cost of Electric Vehicle Ownership
You may want to see also

Charging Infrastructure: EVSE (Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment) and charging stations are essential
The development of electric vehicles (EVs) has been a significant shift in the automotive industry, offering an eco-friendly and sustainable alternative to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars. As the popularity of EVs rises, so does the need for robust and efficient charging infrastructure to support their widespread adoption. This is where Electric Vehicle Supply Equipment (EVSE) and charging stations play a crucial role.
EVSE refers to the equipment and systems used to supply electricity to electric vehicles for charging purposes. It includes various components such as charging connectors, cables, and communication interfaces. The primary function of EVSE is to provide a safe and efficient power supply to EVs, ensuring that the charging process is reliable and compatible with different vehicle models. These systems are designed to handle various charging modes, from slow to rapid charging, catering to the diverse needs of EV owners.
Charging stations, also known as EV charging points, are physical locations where EVSE is installed to facilitate the charging of electric vehicles. These stations can be found in various settings, including public areas, residential complexes, workplaces, and along highways. Public charging stations are particularly important for long-distance travel, providing EV owners with the convenience of charging their vehicles during journeys. They often offer different charging speeds and payment options, allowing users to choose the most suitable charging solution for their needs.
The importance of charging infrastructure cannot be overstated. It is a critical enabler for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. Without a comprehensive network of charging stations, the range anxiety associated with EVs might hinder their acceptance. A well-distributed charging infrastructure network ensures that EV owners have convenient access to charging points, encouraging more people to make the switch from traditional fuel-based vehicles. This, in turn, contributes to reducing carbon emissions and promoting a more sustainable transportation ecosystem.
In summary, EVSE and charging stations are vital components of the electric vehicle ecosystem. They provide the necessary infrastructure to support the charging of EVs, ensuring convenience, safety, and efficiency. As the demand for electric mobility grows, investing in and expanding charging infrastructure will be key to accommodating the increasing number of electric vehicles on the road. This will also drive innovation in charging technologies, making the charging process faster, more accessible, and potentially more cost-effective for EV owners.
Electric Convenience: Your Guide to Flying with Style
You may want to see also

Range Anxiety: Addressing range limitations and consumer concerns
The concept of 'range anxiety' has been a significant barrier to the widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), particularly among potential buyers who are concerned about the limited driving range of these vehicles compared to traditional gasoline cars. This anxiety is deeply rooted in the fear of running out of power while on the road, especially during long journeys or in areas with fewer charging infrastructure options. However, the automotive industry has been actively working to address this issue through various innovations and improvements in EV technology.
One of the primary strategies to combat range anxiety is the development of more advanced battery technologies. Modern EVs are equipped with high-capacity lithium-ion batteries that offer significantly improved energy density and longer lifespans. These advancements have led to substantial increases in the driving range of electric cars, with some models now capable of traveling over 300 miles on a single charge. For instance, the latest generation of the Tesla Model 3 boasts an EPA-estimated range of 363 miles, addressing the concerns of many potential buyers.
Another approach to mitigating range anxiety is the expansion of charging infrastructure. Governments, businesses, and individuals are investing in the creation of extensive charging networks, making it more convenient for EV owners to recharge their vehicles. Fast-charging stations, which can replenish a substantial portion of a battery's charge in just minutes, are becoming increasingly common along highways and in urban areas. This development significantly reduces the time required for long-distance travel, alleviating the fear of running out of power.
Additionally, many EV manufacturers are incorporating advanced driver assistance systems and navigation tools to help alleviate range anxiety. These systems provide real-time driving range estimates, suggesting optimal routes and charging station locations based on the vehicle's battery status. Some cars even offer predictive analytics, forecasting remaining range based on driving patterns and external factors like weather conditions. By empowering drivers with accurate and timely information, these technologies contribute to a more confident and stress-free driving experience.
Furthermore, the rise of plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) and extended-range electric vehicles (EREVs) has provided consumers with more flexibility. These vehicles combine an electric motor with a conventional engine, allowing for extended driving range and the ability to switch to gasoline power when necessary. PHEVs and EREVs offer the best of both worlds, providing the environmental benefits of electric driving while addressing range limitations. As a result, they have gained popularity among those who frequently embark on long journeys or require added reassurance regarding driving range.
In conclusion, the automotive industry's efforts to tackle range anxiety have been multifaceted, focusing on battery technology advancements, charging infrastructure development, and innovative vehicle designs. These collective actions have significantly improved the practicality and appeal of electric vehicles, making them a more viable and attractive option for consumers. As the market continues to evolve, it is expected that range anxiety will become an increasingly rare concern, paving the way for a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation future.
Ford's Electric Future: Rumors of a Shift Unveiled
You may want to see also

Performance: EVs offer instant torque, smooth acceleration, and high top speeds
Electric vehicles (EVs) have revolutionized the automotive industry with their exceptional performance capabilities, offering a unique driving experience that sets them apart from traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. One of the most remarkable aspects of EVs is their ability to deliver instant torque, which is a game-changer in terms of performance.
When an EV is started, the electric motor provides a rapid surge of torque, resulting in an immediate and powerful response. This instant torque delivery is a significant advantage over ICE vehicles, which typically require a few seconds to build up power. With EVs, the driver experiences a thrilling acceleration from a standstill, making everyday driving more engaging and responsive. This characteristic is particularly beneficial in city driving, where quick starts and stops are common, and it enhances the overall driving experience, making EVs feel more dynamic and agile.
The smooth acceleration of EVs is another performance highlight. As the driver presses the accelerator, the electric motor seamlessly delivers power to the wheels, providing a fluid and continuous acceleration without the typical lag associated with ICE vehicles. This smooth power delivery contributes to a comfortable and refined driving experience, making EVs feel more like a luxury sedan than a typical car. The absence of the traditional gear shift and the direct connection between the accelerator and the wheels create a seamless and almost silent driving sensation.
Furthermore, EVs are known for their high top speeds, which challenge the perception that electric cars are underpowered. Modern EVs can reach impressive velocities, often surpassing 200 km/h, and some even exceed 300 km/h. This top-end performance is made possible by the instant power delivery and the high-torque output of electric motors. The powerful acceleration and high top speeds of EVs not only make them exciting to drive but also provide a sense of confidence and control, especially on highways and during long-distance travel.
In summary, the performance characteristics of EVs, including instant torque, smooth acceleration, and high top speeds, have transformed the driving experience. These features offer a unique and exhilarating drive, making EVs a compelling choice for those seeking a more dynamic and responsive vehicle. The technology behind EVs continues to advance, ensuring that the performance gap between electric and traditional vehicles widens, providing drivers with an ever-improving and more enjoyable driving experience.
Debunking Myths: Are Electric Vehicles' Range Claims Reliable?
You may want to see also

Environmental Impact: Reduced emissions and a greener transportation alternative
The environmental benefits of electric vehicles (EVs) are significant, particularly when compared to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. This is where the concepts of PEVs (Plug-in Electric Vehicles) and BEVs (Battery Electric Vehicles) come into play, offering a cleaner and more sustainable approach to transportation.
One of the most notable advantages of EVs is their ability to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. PEVs and BEVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, meaning they do not release harmful pollutants such as carbon dioxide (CO2), nitrogen oxides (NOx), and particulate matter during operation. This is a crucial factor in combating climate change and improving air quality, especially in urban areas where traffic congestion and pollution levels are high. By eliminating these emissions, EVs contribute to a significant reduction in the carbon footprint of the transportation sector.
The environmental impact extends beyond the vehicle itself. The production and disposal of traditional vehicles often involve processes that are energy-intensive and environmentally detrimental. In contrast, EV manufacturing can be more energy-efficient, and the recycling and disposal of their batteries can be managed more sustainably. Additionally, the shift towards EVs can lead to a decrease in the demand for fossil fuels, reducing the need for oil drilling and transportation, which are major contributors to environmental degradation.
The widespread adoption of EVs can also have a positive effect on local ecosystems. With reduced emissions, the risk of habitat destruction and pollution-related health issues decreases. This is particularly important in areas where vehicle emissions have historically impacted wildlife and natural resources. Furthermore, the use of renewable energy sources to power EVs can further enhance their environmental benefits, creating a more sustainable energy cycle.
In summary, PEVs and BEVs offer a greener transportation alternative by significantly reducing emissions and pollution. This shift towards electric mobility is a crucial step in mitigating the environmental impact of the transportation sector, leading to improved air and water quality, reduced carbon emissions, and a more sustainable future for our planet.
Firefighting Tips: Battling Electric Vehicle Blazes
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
PEVs (Plug-in Electric Vehicles) and BEVs (Battery Electric Vehicles) are both types of electric vehicles, but they differ in their power sources and driving range. PEVs can be powered by either an internal combustion engine or an electric motor, and they can be plugged into an external power source for charging. BEVs, on the other hand, are fully electric and rely solely on batteries for power, making them zero-emission vehicles.
PEVs offer more flexibility in charging as they can be charged using a conventional gasoline station or a home charging station. This makes them suitable for those who want the convenience of a familiar fueling infrastructure. BEVs, being fully electric, require specialized charging stations or home charging setups, which might be less accessible in certain areas. However, BEVs often have faster charging capabilities when using direct current (DC) fast chargers.
BEVs typically have a more straightforward power train, as they rely solely on electric motors, which can provide instant torque and smooth acceleration. This results in a responsive driving experience. PEVs, with their dual power source, might offer a more balanced performance, especially in colder climates, as the internal combustion engine can provide additional heat for the battery and cabin. However, the overall efficiency and driving range of BEVs are generally higher due to their single-source power system.