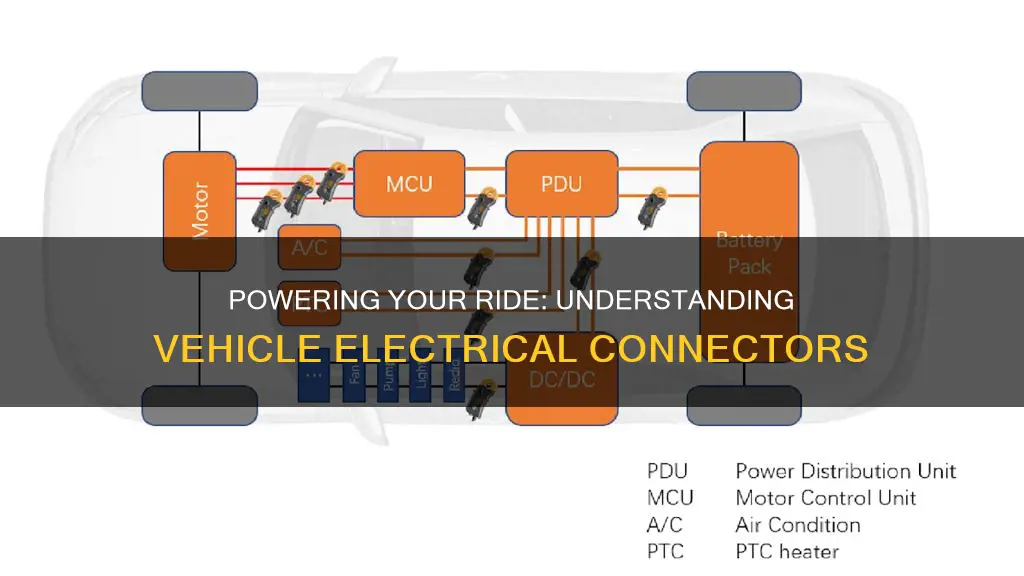
An vehicle electrical connector is a crucial component in modern automobiles, serving as a vital link between various electrical systems and components. These connectors facilitate the transmission of power and data, enabling the seamless operation of engines, lighting systems, sensors, and entertainment devices. They play a critical role in ensuring the reliability and performance of a vehicle's electrical network, allowing for efficient communication and control throughout the vehicle's systems. Understanding the function and importance of these connectors is essential for maintaining and troubleshooting vehicle electrical issues.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Purpose | Connects electrical components in a vehicle, allowing the transfer of power and signals between different parts. |
| Types | Various types exist, such as fuses, relays, and terminals, each serving specific functions. |
| Applications | Used in engines, lighting systems, sensors, entertainment systems, and various other vehicle components. |
| Materials | Typically made of metal (e.g., copper, brass) or plastic, chosen for durability and corrosion resistance. |
| Design | Can be in the form of plugs, sockets, or pins, with different configurations for various connections. |
| Standards | Adhere to industry standards to ensure compatibility and safety, such as ISO or SAE standards. |
| Protection | Often include safety features like fuses or circuit breakers to prevent electrical overloads. |
| Environmental Considerations | Designed to withstand harsh vehicle environments, including vibrations, temperature changes, and moisture. |
| Ease of Use | Facilitate easy installation and removal, allowing for quick repairs or upgrades. |
| Reliability | High reliability is crucial to ensure consistent performance and prevent vehicle malfunctions. |
What You'll Learn
- Power Transfer: Connects battery power to vehicle's electrical system
- Signal Transmission: Facilitates data exchange between sensors and controls
- Grounding: Ensures safe electrical discharge and system stability
- Fuse Protection: Contains fuses to prevent overcurrent damage
- Terminal Design: Specific designs for various connector types and applications

Power Transfer: Connects battery power to vehicle's electrical system
The vehicle electrical connector is a critical component in the power transfer process, facilitating the efficient and safe distribution of electrical energy from the battery to the various systems and components within a vehicle. This connector plays a vital role in ensuring that the electrical system operates optimally, providing power to essential functions such as the engine, lights, sensors, and accessories.
At its core, the electrical connector serves as a bridge between the battery, which stores electrical energy, and the intricate network of wires and circuits that make up a vehicle's electrical system. It is designed to securely and reliably transmit power, ensuring that the vehicle's electrical components receive the necessary voltage and current. The connector's primary function is to establish a low-resistance path for the flow of electricity, minimizing power loss and ensuring efficient power transfer.
In the context of power transfer, these connectors are typically designed with specific features to accommodate the high-current demands of vehicle electrical systems. They often include heavy-duty terminals and insulated conductors to handle the power requirements of various vehicle functions. For instance, a vehicle's starter motor may require a significant amount of current to turn the engine over, and the electrical connector must be capable of delivering this power safely and efficiently.
The design of these connectors also considers safety and reliability. They are often sealed to protect against moisture and corrosion, ensuring long-term durability. Additionally, they may incorporate mechanisms to prevent incorrect connections, such as color-coded wires or locking systems, which are crucial in maintaining the integrity of the electrical system.
In summary, the vehicle electrical connector is a key enabler of power transfer, connecting the battery's energy to the vehicle's complex electrical network. Its design and functionality are tailored to handle the specific power requirements of a vehicle, ensuring efficient and safe operation while also considering the safety and longevity of the electrical system. Understanding the role of these connectors is essential for maintaining and troubleshooting vehicle electrical issues related to power distribution.
Unraveling the EV Tax Credit: Refundability and Its Impact
You may want to see also

Signal Transmission: Facilitates data exchange between sensors and controls
The role of an electrical connector in a vehicle is to ensure seamless signal transmission, which is the backbone of modern automotive systems. This process involves the intricate dance of data exchange between various sensors and control units, all working in harmony to keep the vehicle running smoothly. At its core, signal transmission is about converting raw sensor data into actionable information that the vehicle's controls can interpret and respond to.
Sensors, such as those monitoring engine performance, speed, temperature, and pressure, generate electrical signals proportional to the physical parameters they measure. These signals are then transmitted through the electrical connector to the vehicle's control units, which include the engine control unit (ECU), transmission control unit (TCU), and other electronic control units (ECUs) dedicated to specific functions. The connector acts as a conduit, ensuring that the data is delivered accurately and promptly to the appropriate control units.
The precision and reliability of signal transmission are critical for the vehicle's performance and safety. For instance, in the case of engine control, the ECU relies on accurate speed and temperature sensor data to adjust fuel injection, timing, and other parameters, ensuring optimal engine performance and fuel efficiency. Similarly, in the transmission system, the TCU uses sensor data to determine when to shift gears, ensuring smooth and efficient power transmission.
Modern vehicles are equipped with sophisticated sensors and controls, and the electrical connector plays a pivotal role in integrating these components. It ensures that the vehicle's electronic systems can communicate effectively, enabling features like anti-lock braking systems (ABS), electronic stability control (ESC), and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS). These systems rely on real-time data exchange to make split-second decisions, enhancing vehicle safety and driver confidence.
In summary, the electrical connector in a vehicle is a vital component that facilitates signal transmission, enabling the seamless exchange of data between sensors and controls. This process is fundamental to the vehicle's ability to monitor and respond to its environment, ensuring optimal performance, safety, and efficiency. Understanding the role of the connector in signal transmission highlights its significance in the intricate network of automotive electronics.
Electric Vehicle Owners: Taxed for a Greener Future?
You may want to see also

Grounding: Ensures safe electrical discharge and system stability
Grounding in vehicle electrical systems is a critical component that ensures the safe operation and stability of the entire electrical network. It serves as a protective measure to prevent electrical hazards and maintain the integrity of the system. The primary purpose of grounding is to provide a low-resistance path for electrical current to flow to the earth, allowing for the safe discharge of any excess charge. This is especially important in vehicles, where electrical systems are complex and involve high-voltage components.
In the context of electrical connectors, grounding plays a vital role in several ways. Firstly, it helps to prevent electrical shocks. When a vehicle's electrical system is properly grounded, any fault or short circuit that might occur is safely directed to the earth, reducing the risk of electric shock to both the vehicle occupants and anyone in the vicinity. This is particularly crucial in emergency situations or when working on the vehicle's electrical components.
Secondly, grounding ensures system stability. Electrical connectors are often used to join different components of the vehicle's electrical circuit. By grounding these connectors, the system maintains a consistent and stable voltage level. This stability is essential for the proper functioning of various vehicle subsystems, such as the engine control unit, lighting systems, and sensors. Without proper grounding, voltage fluctuations could occur, leading to erratic behavior and potential damage to sensitive electronic components.
Grounding also aids in electromagnetic interference (EMI) suppression. Electrical connectors with grounding pins or rings help to minimize the impact of EMI, which can cause signal degradation and interference in communication systems. This is particularly important in modern vehicles, where electronic control units (ECUs) and advanced driver-assistance systems (ADAS) rely on clean and stable electrical signals for optimal performance.
Furthermore, grounding is essential for the longevity of the vehicle's electrical components. By providing a safe path for electrical discharge, grounding helps prevent the buildup of static electricity, which can damage sensitive electronics. This is especially relevant when working with battery terminals or when connecting and disconnecting components, as static electricity can cause irreversible damage to circuit boards and integrated circuits.
In summary, grounding in vehicle electrical connectors is a fundamental aspect of ensuring safety, stability, and the overall health of the electrical system. It safeguards against electrical hazards, maintains system performance, and protects the vehicle's electronic components from potential damage. Understanding and implementing proper grounding techniques are essential for anyone working with vehicle electrical systems.
Green Revolution: Unlocking Nature's Power with Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Fuse Protection: Contains fuses to prevent overcurrent damage
Fuse protection is a critical component of vehicle electrical connectors, serving as a safeguard against potential electrical hazards. These connectors are designed to manage the flow of electricity within a vehicle's intricate network of wires and circuits. Overcurrent, which occurs when an excessive amount of current flows through a circuit, can lead to severe damage to the vehicle's electrical system. To mitigate this risk, vehicle electrical connectors incorporate fuses, which act as a protective barrier.
Fuses are small, unassuming components that play a vital role in ensuring the safe operation of a vehicle. They are typically made of a thin wire or a piece of metal that is designed to melt or break when exposed to a specific amount of current. This melting or breaking action is a deliberate and controlled response to overcurrent, effectively interrupting the electrical circuit and preventing potential damage. By containing these fuses within the electrical connector, manufacturers create a robust defense mechanism.
The primary function of these fuses is to safeguard the vehicle's sensitive electronic components from the detrimental effects of overcurrent. When an electrical fault occurs, such as a short circuit or a malfunctioning component, the excessive current can quickly overwhelm the circuit. In such scenarios, the fuse acts as a sacrificial element, sacrificing itself to protect the rest of the electrical system. This protective mechanism is especially crucial in high-current applications, where a single component failure could lead to widespread damage.
In the event of an overcurrent situation, the fuse's melting point is exceeded, causing it to heat up and eventually melt or break. This action opens the electrical circuit, effectively isolating the fault and preventing further damage. The melted fuse can then be replaced, restoring the electrical connection once the issue is resolved. This simple yet effective design ensures that the vehicle's electrical system remains resilient and reliable, even in the face of potential electrical malfunctions.
Fuse protection is a fundamental aspect of vehicle electrical connectors, contributing to the overall safety and longevity of the vehicle's electrical system. By incorporating these fuses, manufacturers ensure that their connectors can handle the electrical demands of modern vehicles, providing a robust solution to the challenges posed by overcurrent scenarios. This attention to detail in electrical design is essential for maintaining the integrity and reliability of the vehicle's electrical architecture.
Unlocking EV Savings: A Guide to Claiming Your Subsidy
You may want to see also

Terminal Design: Specific designs for various connector types and applications
The design of vehicle electrical connectors is a critical aspect of automotive engineering, ensuring reliable and efficient power transmission and data transfer. Terminal design, in particular, plays a pivotal role in the functionality and performance of these connectors. Different connector types cater to various applications, and understanding the specific terminal designs for each is essential for engineers and manufacturers.
Pin-and-Socket Connectors: These are the most common type of vehicle electrical connectors, featuring a row of pins and corresponding sockets. The terminal design here involves precise engineering to ensure a secure and reliable connection. Each pin is typically designed with a spring-loaded mechanism, allowing for easy insertion and firm retention. The socket, often made of a durable material like brass or copper alloy, provides a stable base for the pin. The key to successful terminal design in this connector type is the alignment and spacing of the pins, ensuring a snug fit without excessive force, which could damage the connector or the mating component.
Blade Connectors: Often used in automotive applications for their simplicity and ease of use, blade connectors feature flat, blade-like terminals. These terminals are designed to be inserted into corresponding slots in the mating connector. The design requires careful consideration of the blade's thickness and width to ensure a secure connection without damaging the connector or the wiring. Blade connectors are commonly used for power distribution and control circuits, where a reliable and cost-effective solution is required.
Fuse Block Connectors: These connectors are designed to accommodate fuses, providing a safe and convenient way to protect electrical circuits. The terminal design here involves creating a secure and insulated space for the fuse element. Each terminal is typically a small, insulated pin or blade, with a precise opening to accommodate the fuse. This design ensures that the fuse can be easily inserted and removed while maintaining electrical isolation. Fuse block connectors are crucial for circuit protection and are often used in high-current applications.
High-Current Connectors: For applications requiring high-current transmission, such as engine control units or power electronics, specialized terminal designs are necessary. These connectors often feature larger terminals with thicker wires to handle increased amperage. The terminal design may include strain relief features to prevent wire damage and ensure a secure connection. Additionally, these connectors might employ crimping or soldering techniques to establish a robust electrical bond.
In summary, terminal design in vehicle electrical connectors is a specialized field, requiring careful consideration of various factors such as connector type, application, and environmental conditions. Each connector type demands a unique approach to terminal design, ensuring reliable connections, efficient power transmission, and data integrity. Understanding these specific designs is vital for engineers to select the appropriate connector for a given application, contributing to the overall performance and safety of modern vehicles.
Ford's Electric Future: Rumors of EV Production Halt
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
An vehicle electrical connector is a crucial component in a vehicle's wiring harness, facilitating the transfer of electrical signals and power between different parts of the car. It acts as a bridge, allowing various systems and components to communicate and function properly.
These connectors are designed with specific features to ensure secure and reliable connections. They often include insulated pins or terminals that make contact with corresponding terminals on the vehicle's circuit board or another connector. This design minimizes the risk of loose connections and short circuits.
There are numerous types of connectors used in vehicles, each serving specific purposes. Some common examples include:
- Blade Connectors: These are flat, rectangular connectors often used for power and signal transmission.
- Fork Connectors: With a unique fork-like shape, they provide a secure connection for various applications.
- Wire Connectors: These connectors join wires together, ensuring a reliable electrical path.
- Automotive-Specific Connectors: Certain connectors are tailored for specific vehicle systems, like engine control units or lighting circuits.
In the event of a malfunction, it is generally recommended to replace the faulty connector rather than attempting to repair it. Over time, connectors can degrade due to factors like corrosion, physical damage, or frequent disconnections. Replacing them ensures the vehicle's electrical system operates safely and efficiently.