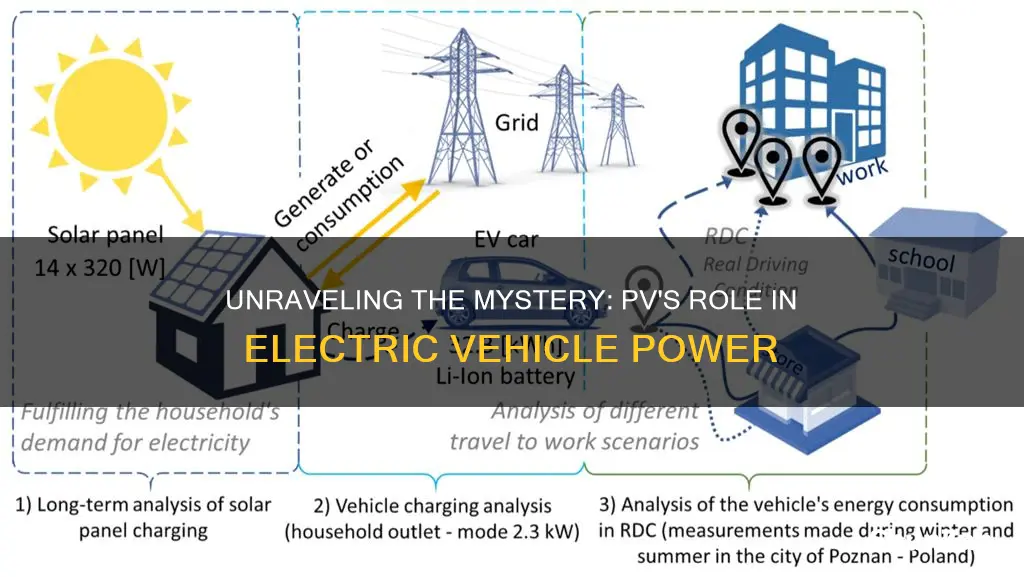
PV, or Power-to-Vehicle, is a crucial concept in the world of electric vehicles (EVs). It refers to the process of converting electrical energy from the grid or renewable sources into the power that drives an EV's motor. This technology is essential for charging electric cars and plays a significant role in the widespread adoption of sustainable transportation. Understanding PV systems is key to optimizing the performance and efficiency of electric vehicles, as it directly impacts their range, charging speed, and overall environmental impact.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| PV (Power Electronics) | Refers to the electronic components and systems used in electric vehicles to convert and control electrical energy. |
| Power Electronics in EVs | Manage the flow of electricity, including charging, discharging, and power distribution. |
| Key Components | Inverters, converters, DC-DC converters, and switches. |
| Inverters | Convert direct current (DC) to alternating current (AC) for use in the vehicle's electrical system. |
| Converters | Convert AC to DC or vice versa, often used in charging systems. |
| DC-DC Converters | Step down high-voltage DC to lower voltages for various vehicle systems. |
| Switches | Electronic switches control the flow of power, enabling efficient energy management. |
| Efficiency | Modern PV systems aim for high efficiency to reduce energy losses during power conversion. |
| Weight and Size | Compact and lightweight designs are crucial for vehicle performance and range. |
| Temperature Management | PV systems must handle high temperatures, often requiring cooling systems. |
| Safety | Protection against electrical faults and overcurrent is essential. |
| Regulation | Compliance with automotive standards and regulations for electromagnetic compatibility. |
| Cost | Ongoing research aims to reduce the cost of PV components to make EVs more affordable. |
| Future Trends | Development of more efficient and powerful converters, improved thermal management, and integration with battery systems. |
What You'll Learn
- Power Output: PV in EVs refers to the power generated by the vehicle's electric motor
- Performance: It indicates the vehicle's acceleration and overall performance capabilities
- Efficiency: PV efficiency measures the energy conversion rate from battery to wheel
- Range: The term can also denote the distance an EV can travel on a full charge
- Charging: PV charging systems allow EVs to recharge using solar or wind power

Power Output: PV in EVs refers to the power generated by the vehicle's electric motor
The term "PV" in the context of electric vehicles (EVs) stands for "Power Output," which is a crucial aspect of understanding the performance and capabilities of these vehicles. When discussing EVs, PV specifically refers to the power generated by the vehicle's electric motor, which is a key differentiator from traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. This power output is a measure of the vehicle's ability to accelerate and perform various tasks, making it a vital specification for potential EV buyers.
In the world of EVs, the electric motor is the primary source of power, and its output is what drives the vehicle forward. This power is measured in kilowatts (kW) or horsepower, and it determines how quickly the EV can accelerate from a standstill and how efficiently it can maintain speed on the highway. For instance, a higher PV rating means the vehicle can deliver more power to the wheels, resulting in faster acceleration and better overall performance. This is particularly important for those who prioritize a dynamic driving experience or need the vehicle for towing or hauling heavy loads.
The power output of an EV is directly related to the efficiency of its electric motor and the overall design of the vehicle. Modern electric motors are designed to provide high torque at low speeds, which is essential for quick acceleration. This is why many EVs offer impressive 0-60 mph times, often rivaling or even surpassing high-performance gasoline or diesel vehicles. The power generated by the electric motor is then distributed to the wheels, providing the necessary traction and control for the driver.
Understanding PV in EVs is essential for consumers as it directly impacts the driving experience and the vehicle's overall utility. A higher PV rating can be an indicator of a more powerful and responsive vehicle, which is especially beneficial for those who frequently drive in challenging conditions or require a vehicle with exceptional performance capabilities. Additionally, the power output of an EV is a critical factor in determining its range, as a more powerful motor may consume more energy, potentially affecting the distance the vehicle can travel on a single charge.
In summary, PV in the context of electric vehicles refers to the power generated by the electric motor, which is a fundamental aspect of EV performance. It determines the vehicle's acceleration capabilities, overall power delivery, and efficiency. As the EV market continues to grow, understanding these technical specifications will empower consumers to make informed decisions when choosing their next electric vehicle.
Electric Vehicles: Unlocking Value Beyond the Price Tag
You may want to see also

Performance: It indicates the vehicle's acceleration and overall performance capabilities
The term "PV" in the context of electric vehicles (EVs) stands for "Power-to-Weight Ratio," which is a crucial metric for understanding a vehicle's performance capabilities. This ratio compares the power output of an EV's electric motor(s) to its weight, providing a clear indication of how efficiently the vehicle can accelerate and perform. A higher power-to-weight ratio means the EV can deliver more power relative to its mass, resulting in quicker acceleration and improved overall performance.
When evaluating an EV's performance, the power-to-weight ratio is a key factor. It directly influences how quickly the vehicle can speed up and how responsive it is during driving. For instance, a sports car with a high power-to-weight ratio will offer rapid acceleration, allowing it to go from 0 to 60 mph in a short time. This is particularly important for electric vehicles, as they often have instant torque, which translates to rapid bursts of speed.
The performance of an electric vehicle is not solely determined by its power-to-weight ratio, but it is a significant contributor. Other factors, such as battery capacity, motor efficiency, and aerodynamic design, also play a role. However, a well-balanced power-to-weight ratio ensures that the EV's performance is not just about raw power but also about how efficiently that power is utilized.
In the world of electric vehicles, manufacturers often provide performance specifications, including the power-to-weight ratio, to give consumers a clear understanding of the car's capabilities. This information is essential for buyers who want to ensure the EV meets their performance expectations, especially for those who enjoy the thrill of acceleration or need a vehicle for racing or track days.
Understanding the power-to-weight ratio and its impact on performance is a valuable aspect of owning or considering an electric vehicle. It empowers buyers to make informed decisions, ensuring they get the performance they desire from their electric car or truck. This metric is a critical piece of the puzzle when it comes to evaluating the overall driving experience and satisfaction of an EV.
Electric Vehicle Decision: Factors to Consider for Your Next Car
You may want to see also

Efficiency: PV efficiency measures the energy conversion rate from battery to wheel
The term "PV" in the context of electric vehicles (EVs) stands for "Power Electronics," which is a crucial component in the vehicle's power train. When discussing efficiency in EVs, one of the key metrics is the Power Electronics (PV) efficiency, which specifically measures the energy conversion rate from the battery to the wheel. This efficiency is vital as it directly impacts the overall performance and range of the vehicle.
In an EV, the battery stores electrical energy, which is then converted by the power electronics system to provide the necessary power to the electric motor. The efficiency of this conversion process is what we refer to as PV efficiency. It is calculated as the ratio of the output power (the power delivered to the wheel) to the input power (the power drawn from the battery). A higher PV efficiency means that more of the energy stored in the battery is effectively utilized to move the vehicle, resulting in improved range and reduced energy wastage.
The design and quality of the power electronics components play a significant role in achieving high PV efficiency. These components include inverters, converters, and switches, which work together to control the flow of electrical energy. Modern EVs often employ sophisticated power electronics designs to minimize energy losses during the conversion process. This includes using advanced switching techniques, optimized component placement, and efficient cooling systems to ensure the power electronics operate at their highest efficiency.
Improving PV efficiency is a critical area of research and development in the EV industry. Engineers and scientists are constantly working on enhancing the performance of power electronics to increase overall vehicle efficiency. This involves reducing the size and weight of the power electronics system while maintaining or improving its efficiency. By doing so, EVs can offer better range, faster charging times, and reduced energy consumption, making them more appealing to consumers.
In summary, PV efficiency is a critical aspect of electric vehicle technology, focusing on the energy conversion process from battery to wheel. It is a measure of how effectively the vehicle's power electronics system can convert and utilize energy, directly influencing the vehicle's performance and range. Ongoing advancements in power electronics design and technology are essential to improving PV efficiency, thereby contributing to the overall sustainability and efficiency of electric vehicles.
Boosting Electric Vehicle Range: Tips for Longer, Stress-Free Drives
You may want to see also

Range: The term can also denote the distance an EV can travel on a full charge
The term "range" is a critical aspect of electric vehicles (EVs) and often a primary consideration for potential buyers. It refers to the distance an EV can travel on a single full charge of its battery. This metric is essential because it directly impacts the practicality and usability of an EV in daily life. A longer range means less frequent charging stops, which is especially beneficial for long-distance travel and reduces the anxiety associated with running out of power.
EVs have come a long way in terms of range, with modern models offering significantly more miles per charge compared to earlier generations. This improvement is largely due to advancements in battery technology, which has led to higher energy density and more efficient power usage. For instance, some high-end EVs can now travel over 300 miles on a single charge, making them viable for most daily commutes and even extended road trips.
Understanding the range of an EV is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it helps buyers choose the right vehicle for their needs. For those with long daily commutes or frequent highway travel, a higher range EV might be necessary. Secondly, it influences the overall cost of ownership. EVs with longer ranges often have more advanced battery systems, which can be more expensive but also provide better performance and reliability.
The range of an EV is not just about the distance it can travel but also about the efficiency of its power usage. Modern EVs are designed to optimize energy consumption, ensuring that every mile is powered by the battery efficiently. This efficiency is further enhanced by features like regenerative braking, which captures and stores energy that would otherwise be lost during braking.
In summary, the range of an electric vehicle is a key performance indicator that determines its suitability for various driving scenarios. With continuous improvements in battery technology, EVs are becoming more practical for a wider range of consumers, offering the convenience of long-distance travel without the environmental impact of traditional gasoline vehicles.
The Future of Transportation: Should You Still Buy Non-Electric Vehicles?
You may want to see also

Charging: PV charging systems allow EVs to recharge using solar or wind power
PV, in the context of electric vehicles (EVs), stands for 'photovoltaic' and refers to a system that harnesses solar energy to power and charge vehicles. This innovative technology is an eco-friendly and sustainable solution for EV owners, offering a way to reduce their carbon footprint and reliance on traditional energy sources.
Charging an EV using PV systems is a straightforward process. It involves installing solar panels on rooftops or in open spaces to capture sunlight and convert it into electricity. This electricity is then fed into a charging station or a dedicated charging port on the EV. The charging process is efficient and clean, as it utilizes renewable energy, which is a significant advantage over conventional charging methods that rely on the grid.
The beauty of PV charging lies in its ability to provide a decentralized and independent power source for EVs. This means that EV owners can generate their own electricity, reducing the strain on the main power grid during peak hours. By utilizing solar or wind power, which are abundant and widely available, PV systems offer a reliable and sustainable charging solution. This is particularly beneficial in remote areas or regions with limited access to the traditional power grid.
Implementing PV charging infrastructure requires careful planning and consideration. It involves assessing the available space for solar panel installation, calculating the energy demands of the EV fleet, and designing an efficient charging network. Governments and businesses can play a crucial role in promoting this technology by providing incentives and subsidies to encourage the adoption of PV charging systems.
In summary, PV charging systems offer a sustainable and efficient way to power electric vehicles. By harnessing solar or wind energy, EVs can be recharged without relying heavily on the traditional power grid. This technology has the potential to revolutionize the EV industry, making it more environmentally friendly and accessible to a wider range of consumers. With further development and integration, PV charging could become a standard feature, contributing to a greener and more sustainable future for transportation.
Unleash the Power: Is an Electric Vehicle Your Next Ride?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
PV, in this context, typically refers to "Power Vehicle" or "Photovoltaic." It is a term often used to describe electric vehicles that can generate electricity through solar panels, allowing for an additional power source or energy storage.
PV technology in electric vehicles involves the use of solar panels to convert sunlight into electricity. This electricity can then be used to charge the vehicle's battery, providing an alternative or supplementary power source. Some vehicles even have integrated solar panels that can directly power certain components, reducing the load on the main battery.
The primary advantage is the potential for increased range and reduced reliance on external charging infrastructure. With PV, the vehicle can generate its own power, especially in sunny conditions, which can extend the driving range. Additionally, it promotes sustainability and reduces the environmental impact of the vehicle.
One challenge is the efficiency of solar panels, as they are not highly efficient at converting sunlight into electricity. This means that the power generated by PV may not significantly contribute to the vehicle's range, especially in regions with less sunlight. Another consideration is the cost and space required for solar panels, which can impact the overall design and manufacturing of the vehicle.







