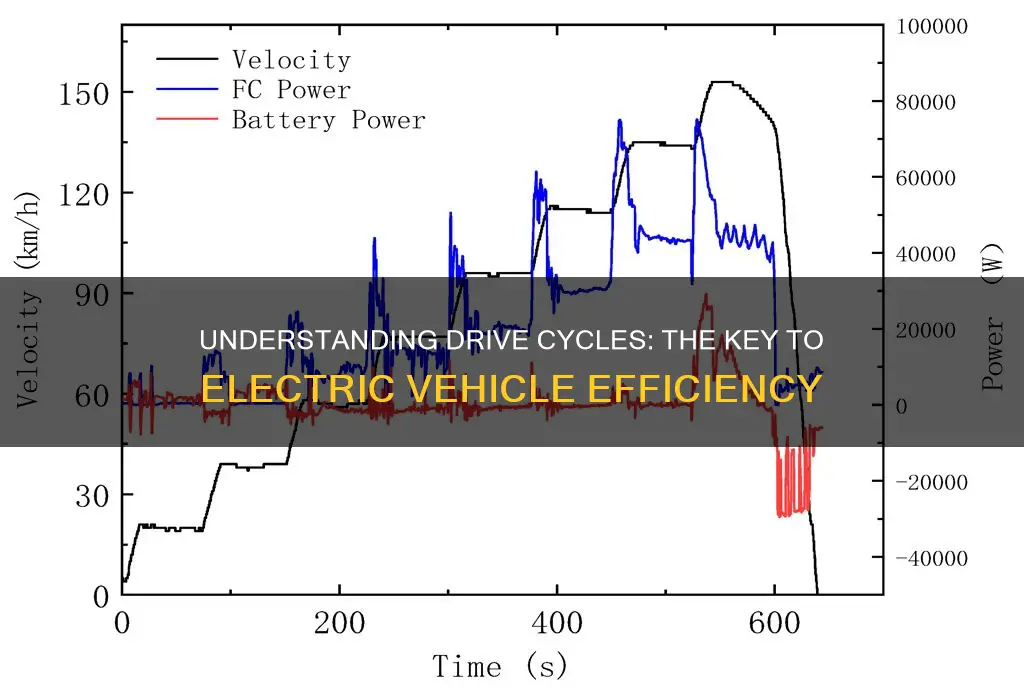
A drive cycle is a specific pattern of driving conditions and behaviors that an electric vehicle (EV) undergoes to test and evaluate its performance, efficiency, and emissions. It is a standardized test procedure designed to mimic real-world driving scenarios, including acceleration, deceleration, idling, and various speed and load conditions. The drive cycle is crucial for manufacturers to ensure that their EVs meet regulatory standards, optimize energy consumption, and provide a reliable and efficient driving experience for customers. This comprehensive evaluation helps in understanding the vehicle's behavior under different driving conditions, allowing for improvements in battery management, motor efficiency, and overall vehicle performance.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Definition | A drive cycle is a standardized test procedure used to evaluate the performance and efficiency of electric vehicles (EVs) under various driving conditions. |
| Purpose | To provide a consistent method for comparing EVs and assessing their real-world driving capabilities, including range, power, and efficiency. |
| Components | Typically, a drive cycle consists of a series of predefined driving patterns, such as city driving, highway driving, and combined cycles, which mimic typical daily driving scenarios. |
| Standards | Various organizations, including the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the International Standard ISO 16840, have established drive cycle standards to ensure consistency and comparability across different EV models. |
| Variables | Factors like speed, acceleration, temperature, and vehicle load are carefully controlled and varied during the test to simulate different driving conditions. |
| Efficiency Measurement | Drive cycles help in measuring the energy efficiency of EVs by tracking energy consumption and output over the defined test procedure. |
| Range Estimation | By analyzing the vehicle's performance during the drive cycle, manufacturers can estimate the EV's range under realistic driving conditions. |
| Real-World Performance | Drive cycles provide a more accurate representation of an EV's performance compared to static tests, as they account for various driving factors. |
| Recent Developments | Modern EVs often utilize advanced battery management systems and regenerative braking, which can influence the results of drive cycles, making them even more relevant for real-world performance evaluation. |
What You'll Learn
- Definition: A drive cycle is a series of driving patterns that simulate real-world driving conditions for EV testing
- Components: It includes acceleration, deceleration, idling, and cruise phases
- Importance: Drive cycles help assess EV performance, efficiency, and battery health
- standardization: Various organizations define standardized drive cycles for consistent testing
- Optimization: Engineers use drive cycles to optimize EV systems for efficiency and range

Definition: A drive cycle is a series of driving patterns that simulate real-world driving conditions for EV testing
A drive cycle is a carefully designed sequence of driving maneuvers and conditions that mimic the diverse and complex nature of everyday driving for electric vehicles (EVs). It serves as a standardized test procedure to evaluate and optimize the performance, efficiency, and reliability of EVs under various operating conditions. This concept is crucial in the automotive industry, especially for EV manufacturers, as it provides a structured approach to assess and improve vehicle capabilities.
The primary purpose of a drive cycle is to replicate the typical driving patterns and scenarios that EV owners encounter in their daily lives. This includes a combination of acceleration, deceleration, cruising, and idling, often with varying speeds, temperatures, and road conditions. By simulating these real-world driving conditions, engineers can thoroughly test and validate the vehicle's performance, ensuring it meets the required standards and customer expectations.
Drive cycles are typically designed with specific parameters and metrics in mind. These may include distance, speed, acceleration, deceleration, and even environmental factors like temperature and humidity. For instance, a drive cycle might start with a cold start, followed by a series of rapid accelerations and decelerations on a city street, then transition to a steady-state cruise on a highway, and finally, end with a prolonged idling period. Each segment of the cycle is carefully crafted to represent a specific aspect of real-world driving.
In the context of EV testing, drive cycles are essential for several reasons. Firstly, they ensure that the vehicle's performance is evaluated consistently and comprehensively. By following a defined sequence, engineers can compare and analyze different aspects of the EV's behavior, such as energy consumption, battery health, and overall efficiency. Secondly, drive cycles help identify potential issues or weaknesses in the vehicle's design, allowing for improvements before the product reaches the market.
Moreover, drive cycles contribute to the development of efficient and effective EV battery management systems. By subjecting the vehicle to various driving conditions, engineers can optimize the battery's charging and discharging patterns, ensuring it operates at its peak performance while also prolonging its lifespan. This is particularly critical for EVs, as battery technology is a significant factor in their overall success and adoption.
Transform Your Ride: A Guide to Electric Brakes Conversion
You may want to see also

Components: It includes acceleration, deceleration, idling, and cruise phases
A drive cycle in an electric vehicle (EV) is a series of predefined driving patterns that simulate real-world driving conditions. These cycles are designed to test and evaluate the performance, efficiency, and behavior of EVs under various operating conditions. The components of a drive cycle include acceleration, deceleration, idling, and cruise phases, each representing specific driving scenarios.
Acceleration Phase: This phase involves the EV rapidly increasing its speed from a standstill or a low speed. It is a crucial part of the drive cycle as it assesses the vehicle's performance, acceleration capabilities, and power delivery. During acceleration, the electric motor delivers maximum torque to the wheels, providing a smooth and responsive driving experience. This phase is often used to test the vehicle's ability to accelerate quickly, especially when overtaking or merging onto highways.
Deceleration or Braking Phase: Here, the EV slows down or comes to a stop. This phase is essential for evaluating the vehicle's braking performance, regenerative braking efficiency, and overall safety. When the driver applies the brakes, the electric motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy, which can be stored in the battery. The deceleration phase tests how effectively the EV can capture and reuse this energy, improving overall efficiency.
Idling Phase: Idling refers to the period when the vehicle is stationary but still consuming power. In an EV, idling typically occurs at traffic lights, in heavy traffic, or when the driver is waiting. During this phase, the vehicle's systems remain active, including the climate control, entertainment systems, and various electronic controls. Idling tests the vehicle's ability to manage power consumption and minimize energy waste, ensuring that the EV can maintain its charge for extended periods when stationary.
Cruise Phase: This phase simulates steady-speed driving on highways or open roads. The EV maintains a constant speed with minimal acceleration or deceleration. The cruise phase is crucial for assessing the vehicle's efficiency, comfort, and stability at consistent speeds. During this phase, the driver can set a desired speed, and the EV's powertrain manages the power distribution to maintain that speed while optimizing energy usage. This phase also tests the vehicle's ability to handle wind resistance and other external factors that affect drag.
Understanding these drive cycle components is essential for engineers and manufacturers to design and optimize electric vehicles. By simulating various driving scenarios, they can evaluate the vehicle's performance, efficiency, and overall driving experience, ensuring that EVs meet the demands of real-world transportation.
Porsche's Electric Future: Rebate Eligibility Explained
You may want to see also

Importance: Drive cycles help assess EV performance, efficiency, and battery health
Drive cycles are an essential concept in the world of electric vehicles (EVs) and play a critical role in evaluating and optimizing their performance, efficiency, and overall health. These cycles are carefully designed sequences of driving conditions that mimic real-world driving scenarios, allowing engineers and researchers to thoroughly test and analyze the behavior of EVs under various conditions. By simulating different drive patterns, engineers can gain valuable insights into how EVs perform, how efficiently they consume energy, and how the battery's health is affected over time.
The importance of drive cycles lies in their ability to provide a comprehensive understanding of EV performance. In the real world, driving conditions vary significantly, from stop-and-go city traffic to highway cruising. Drive cycles replicate these diverse scenarios, ensuring that EVs are tested under a wide range of conditions. This comprehensive evaluation helps identify potential issues, such as reduced range in cold weather or increased energy consumption during aggressive driving. By analyzing these cycles, engineers can fine-tune the vehicle's performance, ensuring it meets or exceeds customer expectations.
Efficiency is another critical aspect that drive cycles help assess. Electric vehicles are known for their energy efficiency compared to traditional internal combustion engines. However, efficiency can vary depending on driving habits, terrain, and weather conditions. Drive cycles allow engineers to measure and compare the energy consumption of EVs across different scenarios. For example, a drive cycle might include a mix of city driving, highway travel, and rapid acceleration, providing a realistic assessment of the vehicle's efficiency. This data is invaluable for optimizing the vehicle's power train and energy management systems, ensuring that EVs deliver the best possible fuel economy.
Furthermore, drive cycles are instrumental in monitoring and predicting battery health. The battery is a critical component of any EV, and its longevity and performance are essential for customer satisfaction. Drive cycles help in understanding how different driving patterns impact the battery's health. For instance, rapid acceleration and frequent short trips can put more strain on the battery, potentially leading to faster degradation. By analyzing these cycles, engineers can develop strategies to optimize battery usage, such as implementing regenerative braking systems or smart charging solutions. This ensures that the battery ages gracefully, maintaining its capacity and performance over the vehicle's lifetime.
In summary, drive cycles are a powerful tool for evaluating and improving the performance, efficiency, and battery health of electric vehicles. They provide a realistic and comprehensive assessment of how EVs behave in various driving conditions. By utilizing drive cycles, engineers can make informed decisions to enhance the overall driving experience, increase efficiency, and ensure the long-term reliability of electric vehicles. This is crucial for the widespread adoption of EVs and the transition towards a more sustainable transportation ecosystem.
The Rise of Electric Fleets: A Green Revolution
You may want to see also

standardization: Various organizations define standardized drive cycles for consistent testing
The concept of a drive cycle is crucial in the context of electric vehicles (EVs) as it provides a standardized method to assess and compare their performance, efficiency, and emissions. Various organizations, including government agencies, research institutions, and industry standards bodies, have developed standardized drive cycles to ensure consistent and meaningful testing. These standardized cycles are designed to mimic real-world driving conditions, allowing for accurate evaluation of EVs under different scenarios.
One of the primary reasons for standardization is to ensure that EV testing is conducted in a controlled and reproducible manner. Without standardized drive cycles, different testing protocols could lead to varying results, making it challenging to compare vehicles or assess their performance accurately. Standardization helps in creating a common language and framework for testing, enabling manufacturers, researchers, and regulators to communicate and analyze data effectively.
Several organizations have taken the lead in defining these standardized drive cycles. For instance, the United States Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) has established a standardized test procedure known as the 'EPA Drive Cycle.' This cycle consists of a series of predefined driving maneuvers and speed patterns that simulate various driving conditions. It includes acceleration, deceleration, and steady-state driving segments, ensuring a comprehensive evaluation of the vehicle's performance. Similarly, the European Union's WLTP (Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicle Test Procedure) is another widely recognized standard, which defines a more complex drive cycle to better represent real-world driving patterns.
These standardized drive cycles are meticulously designed to cover a range of driving conditions, including city driving, highway cruising, and even rapid acceleration and deceleration. By incorporating these diverse scenarios, the testing can provide a more accurate representation of an EV's performance and efficiency in everyday use. For example, the EPA drive cycle includes a cold-start phase, which simulates driving in low-temperature conditions, and a high-speed highway segment to assess the vehicle's performance at higher speeds.
Standardization in drive cycle testing is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it ensures fairness and comparability across different EV models and manufacturers. When all vehicles are tested using the same standardized cycle, it becomes easier to identify and analyze performance differences, enabling consumers to make informed choices. Secondly, standardization facilitates regulatory compliance. Many countries and regions have emission standards and regulations for EVs, and standardized drive cycles help in meeting these requirements by providing a consistent and reliable testing method. This consistency also aids in the development of accurate vehicle-to-grid (V2G) models, which simulate the interaction between EVs and the power grid.
Unlocking EV Ownership: The Battery Lease Advantage
You may want to see also

Optimization: Engineers use drive cycles to optimize EV systems for efficiency and range
Drive cycles play a crucial role in the optimization of electric vehicle (EV) systems, particularly in enhancing efficiency and maximizing range. These cycles are carefully designed sequences of driving conditions and patterns that mimic real-world driving scenarios. By simulating various driving conditions, engineers can thoroughly test and fine-tune EV systems, ensuring they perform optimally in diverse environments.
The primary objective of using drive cycles is to optimize the energy consumption of EVs. Electric vehicles rely on precise energy management to achieve efficient performance. Engineers create drive cycles that include a range of speeds, accelerations, and decelerations to mimic typical driving patterns. For instance, a drive cycle might start with a low-speed, gentle acceleration, followed by a steady cruise at highway speeds, and then include rapid accelerations and frequent stops to simulate urban driving conditions. This comprehensive approach allows engineers to evaluate the vehicle's energy usage under different circumstances.
During the optimization process, engineers analyze the vehicle's performance data collected from the drive cycles. This data includes battery usage, motor efficiency, and overall system performance. By studying this information, engineers can identify areas where the EV system can be improved to reduce energy waste. For example, they might discover that the regenerative braking system needs adjustment to optimize energy recovery during deceleration. Or, they could find that the air conditioning system's settings need fine-tuning to balance comfort and energy consumption.
Drive cycles also help engineers optimize the range of EVs, which is a critical factor for potential buyers. By testing the vehicle's performance under various drive cycles, engineers can determine the most efficient routes and driving habits that maximize range. This might involve studying the impact of frequent short-distance trips versus longer, less frequent journeys on the battery life. Through this analysis, engineers can provide valuable insights to consumers, helping them understand how to get the most out of their EV's range.
Furthermore, drive cycles enable engineers to test and improve the overall reliability and longevity of EV systems. By subjecting the vehicle to different driving conditions, they can identify potential issues and weaknesses in the system. This proactive approach ensures that EVs are not only efficient and range-friendly but also durable and safe. In summary, drive cycles are an essential tool in the hands of engineers, allowing them to fine-tune EV systems, improve efficiency, and provide consumers with vehicles that offer an optimal driving experience.
The Green Revolution: Unlocking the True Value of Electric Cars
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
A drive cycle refers to a specific pattern of driving conditions and behaviors that an electric vehicle (EV) might experience during its lifetime. It is a standardized test procedure designed to mimic real-world driving scenarios and assess the vehicle's performance, efficiency, and battery health. The drive cycle typically includes a combination of city driving, highway driving, and various stop-and-go conditions, all of which can significantly impact the EV's range, performance, and overall driving experience.
During a drive cycle test, the EV's performance is evaluated by monitoring various parameters such as speed, acceleration, battery voltage, and power consumption. The test simulates different driving conditions, including rapid acceleration, constant speed cruising, and frequent stops. By analyzing these parameters, engineers can assess the vehicle's responsiveness, efficiency, and ability to handle varying loads. This helps in optimizing the EV's performance, ensuring it meets the required standards, and providing consumers with an accurate representation of its real-world capabilities.
Understanding drive cycles is essential for EV owners as it allows them to optimize their vehicle's performance and efficiency. By knowing the typical drive cycle patterns, owners can adjust their driving habits to maximize range. For example, during stop-and-go traffic, regenerative braking can be utilized to recharge the battery, while highway driving may require more energy-efficient techniques. Additionally, understanding drive cycles can help owners plan their charging needs, ensuring they have sufficient battery capacity for their daily commute and long-distance travel.







