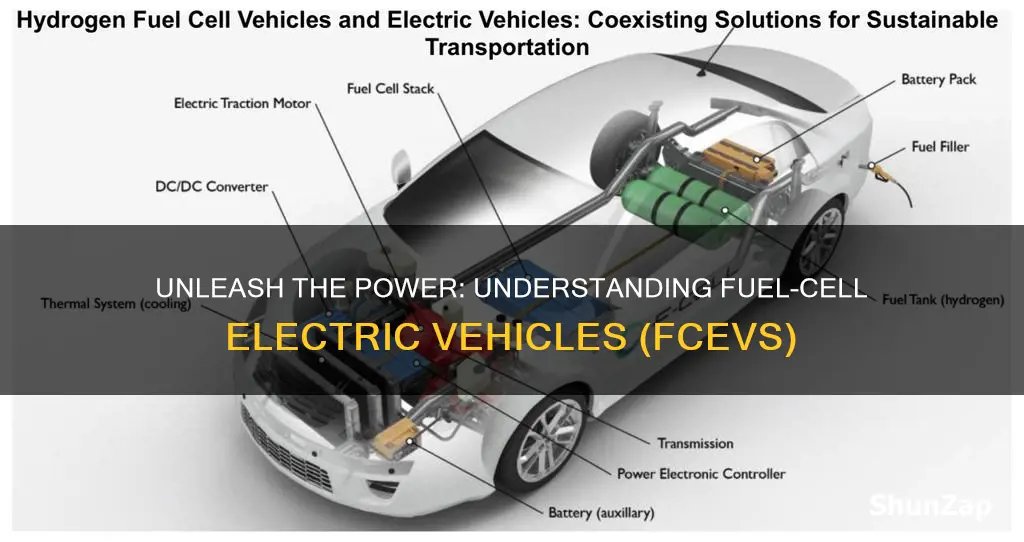
Fuel-cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) are an innovative and sustainable transportation solution that combines the benefits of electric vehicles (EVs) with the efficiency of hydrogen fuel cells. These vehicles produce electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen, emitting only water vapor and warm air as byproducts, making them environmentally friendly. FCEVs offer a longer driving range compared to traditional EVs, with the ability to refuel quickly, similar to conventional gasoline or diesel vehicles. This technology has the potential to revolutionize the automotive industry, providing a cleaner and more efficient alternative to conventional internal combustion engines.
What You'll Learn
- Technology: Fuel cells power EVs, converting hydrogen and oxygen into electricity
- Performance: FCEVs offer high efficiency, rapid refueling, and zero emissions
- Environmental Impact: Zero tailpipe emissions, reducing air pollution and greenhouse gases
- Infrastructure: Hydrogen refueling stations are essential for widespread FCEV adoption
- Challenges: Cost, hydrogen availability, and public perception are barriers to market growth

Technology: Fuel cells power EVs, converting hydrogen and oxygen into electricity
Fuel-cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) are an innovative technology that utilizes fuel cells to power electric vehicles, offering a cleaner and more efficient alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. At the heart of this technology is the fuel cell, a device that generates electricity through a chemical reaction between hydrogen and oxygen. This process is both powerful and environmentally friendly, making FCEVs a promising solution for the future of sustainable transportation.
The fuel cell's operation begins with the storage of hydrogen gas, which is typically compressed and stored in a tank on the vehicle. When the vehicle is in use, the hydrogen is supplied to the fuel cell, where it undergoes a reaction with oxygen from the air. This reaction is facilitated by a catalyst, usually made of a precious metal like platinum, which accelerates the process without being consumed. The key to this technology's efficiency is the direct conversion of chemical energy into electrical energy, bypassing the need for an internal combustion engine.
In the fuel cell, the hydrogen molecules are split into protons and electrons. The electrons are then directed through an external circuit, providing the electrical power needed to run the vehicle's electric motor. Simultaneously, the protons move through a special membrane, creating a flow of ions. This movement of ions and electrons is the essence of the electrochemical reaction, producing electricity. The only byproduct of this process is water, which is released as steam through the vehicle's exhaust, making FCEVs a zero-emission technology.
The technology's efficiency is further enhanced by the fact that the fuel cell can operate at high efficiency, especially when compared to traditional combustion engines. This is because the fuel cell's power generation is a direct process, with minimal energy loss. The electricity generated can be used to power the vehicle's electric motor, and any excess can be stored in batteries or used to power auxiliary systems, ensuring optimal energy utilization.
The development of FCEVs has been a significant focus in the automotive industry due to their potential to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve energy efficiency. While the technology is still evolving and faces challenges such as hydrogen infrastructure and cost, it represents a significant step towards a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation system. As research and development continue, FCEVs are expected to play a crucial role in the transition to a cleaner and more efficient energy future.
Global Electric Vehicle Ban: Which Country Led the Way?
You may want to see also

Performance: FCEVs offer high efficiency, rapid refueling, and zero emissions
Fuel-cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) are a groundbreaking innovation in the automotive industry, offering a sustainable and high-performance alternative to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. One of the key performance advantages of FCEVs is their exceptional efficiency. These vehicles utilize hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity, which powers the electric motor. The process is remarkably efficient, converting over 60% of the energy from hydrogen to power, compared to the 20-30% efficiency of conventional gasoline engines. This higher efficiency means FCEVs can travel further on a given amount of energy, making them an attractive option for those seeking an eco-friendly and cost-effective transportation solution.
In terms of refueling, FCEVs provide a unique advantage with their rapid refueling capability. Hydrogen refueling stations are becoming increasingly available, and the process is remarkably quick. While a conventional gasoline vehicle can take several minutes to refuel, an FCEV can be refueled in under 5 minutes, providing a similar convenience to that of a gasoline-powered car. This rapid refueling time is a significant improvement over early fuel-cell vehicles and addresses a critical concern for potential buyers, ensuring that the technology is practical for everyday use.
The environmental benefits of FCEVs are another crucial aspect of their performance. As the name suggests, these vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, meaning they do not release harmful pollutants or greenhouse gases during operation. This is a stark contrast to traditional vehicles, which contribute significantly to air pollution and climate change. By eliminating these emissions, FCEVs contribute to a cleaner and healthier environment, especially in densely populated urban areas where air quality is a growing concern.
Furthermore, the performance of FCEVs extends beyond efficiency and refueling. These vehicles offer a smooth and quiet driving experience due to their electric motor's instant torque delivery. This results in quick acceleration and a responsive driving feel, challenging the notion that electric vehicles are sluggish. The absence of the traditional engine noise also contributes to a more peaceful and enjoyable driving environment.
In summary, FCEVs excel in performance by providing high efficiency, rapid refueling, and zero emissions. These attributes make FCEVs a compelling choice for environmentally conscious consumers who do not want to compromise on performance. As the technology continues to advance and infrastructure improves, FCEVs are poised to play a significant role in the future of sustainable transportation.
Global Shift: All-Electric Vehicles Take Over the World
You may want to see also

Environmental Impact: Zero tailpipe emissions, reducing air pollution and greenhouse gases
Fuel-cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) are a groundbreaking innovation in the automotive industry, offering a sustainable and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. One of the most significant advantages of FCEVs is their ability to produce zero tailpipe emissions, which has a profound impact on reducing air pollution and combating climate change.
At the heart of FCEVs is the fuel cell, a device that converts chemical energy from hydrogen fuel into electricity through a process called electrochemical reaction. This reaction occurs in the fuel cell stack, where hydrogen gas and oxygen from the air are combined to generate electricity, water, and heat. The key environmental benefit here is that the only byproduct of this process is water vapor, which is released into the atmosphere, and warm air, which is expelled from the vehicle. This is in stark contrast to conventional vehicles, which emit a range of pollutants, including nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide, and particulate matter, all of which contribute to air pollution and have detrimental effects on human health and the environment.
By eliminating tailpipe emissions, FCEVs play a crucial role in improving air quality, especially in densely populated urban areas. The reduction of harmful pollutants at the source is essential for public health, as it can help prevent respiratory and cardiovascular diseases associated with poor air quality. Moreover, the absence of tailpipe emissions directly contributes to the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions, a primary driver of global warming and climate change. Greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide and methane, are released during the combustion of fossil fuels in traditional vehicles. FCEVs, however, produce no such emissions, making them a key component in the transition to a low-carbon economy.
The environmental benefits of FCEVs extend beyond the vehicle itself. The hydrogen fuel used in these vehicles can be produced from renewable sources, such as wind or solar power, through a process called electrolysis. This renewable hydrogen production further reduces the carbon footprint of the entire fuel cycle, making FCEVs an even more sustainable option. Additionally, the infrastructure for refueling FCEVs is being developed, ensuring that the necessary support systems are in place to facilitate the widespread adoption of this technology.
In summary, fuel-cell electric vehicles offer a promising solution to the environmental challenges posed by the transportation sector. Their zero-emission nature, coupled with the potential for renewable hydrogen production, provides a pathway to significantly reduce air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. As the world seeks to transition towards a more sustainable future, FCEVs represent a significant step forward in achieving cleaner and greener transportation options.
Cadillac's Electric Revolution: The Future of Luxury EVs
You may want to see also

Infrastructure: Hydrogen refueling stations are essential for widespread FCEV adoption
The widespread adoption of fuel-cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) relies heavily on the development of a robust and accessible infrastructure, particularly hydrogen refueling stations. These stations are the lifeblood of FCEVs, providing the necessary hydrogen fuel for these vehicles to operate. Without a well-established network of hydrogen refueling stations, the practical use and appeal of FCEVs would be significantly limited.
Hydrogen refueling stations are designed to dispense hydrogen gas to vehicles, typically through high-pressure tanks. The process is similar to refueling conventional gasoline or diesel vehicles but requires specialized equipment and infrastructure. These stations are crucial for several reasons. Firstly, they address the range anxiety associated with electric vehicles, as FCEVs can travel much longer distances on a single refueling compared to battery-electric vehicles. This makes hydrogen refueling stations vital for long-distance travel and commercial applications. Secondly, the availability of refueling stations encourages consumers to make the switch from traditional internal combustion engine vehicles to FCEVs, as the convenience of refueling at dedicated stations mirrors that of conventional vehicles.
The construction and maintenance of hydrogen refueling stations require significant investment and specialized knowledge. The infrastructure includes high-pressure gas storage tanks, compression systems, and dispensing nozzles, all of which must adhere to strict safety regulations. Additionally, the process of refueling hydrogen vehicles involves precise handling and monitoring to ensure safety and efficiency. This technical complexity necessitates a skilled workforce and specialized training to manage the infrastructure effectively.
To facilitate the widespread adoption of FCEVs, governments and energy companies are investing in the development of hydrogen refueling station networks. This includes establishing partnerships and incentives to encourage the construction and operation of these stations. The goal is to create a comprehensive network that is geographically dispersed, ensuring that FCEV owners have convenient access to refueling options wherever they travel. This infrastructure development is a critical step in making FCEVs a viable and attractive alternative to conventional vehicles, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation ecosystem.
In summary, hydrogen refueling stations are indispensable for the successful integration of FCEVs into the transportation landscape. Their establishment and maintenance are essential to address the practical challenges of refueling, range limitations, and consumer convenience. As the technology and infrastructure mature, the widespread adoption of FCEVs can become a reality, paving the way for a cleaner and more sustainable future in the automotive industry.
Government Incentives: Are They Enough to Go Electric?
You may want to see also

Challenges: Cost, hydrogen availability, and public perception are barriers to market growth
The widespread adoption of fuel-cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) faces several significant challenges that hinder their market growth. One of the primary obstacles is the high cost of these vehicles. FCEVs currently carry a premium price tag compared to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, primarily due to the advanced technology and materials required for fuel cell systems. This cost is a substantial barrier for consumers, especially when considering the overall vehicle price, which can be several thousand dollars more than equivalent models with ICEs. The high initial investment often discourages potential buyers, especially those on a budget, from making the switch to FCEVs.
Another critical challenge is the availability of hydrogen, the fuel source for FCEVs. Hydrogen infrastructure is not as developed as gasoline stations, and its distribution and storage present unique logistical challenges. Building a comprehensive hydrogen fueling network requires significant investment and time, and it is not as straightforward as expanding the existing fuel station network. Many regions lack the necessary infrastructure, making it difficult for FCEV owners to find convenient and accessible hydrogen fueling stations. This issue is further exacerbated in rural areas, where the economic viability of hydrogen stations is often questionable.
Public perception also plays a crucial role in the market growth of FCEVs. Despite their environmental benefits, such as zero direct emissions, FCEVs have not yet gained widespread acceptance among the general public. Some consumers are hesitant to embrace new technology, especially when it comes to fuel cells, which are still relatively unknown compared to more established technologies like batteries. Misconceptions about hydrogen safety, range anxiety, and the perceived complexity of FCEVs can influence purchasing decisions. Overcoming these public perception barriers requires extensive education and awareness campaigns to highlight the advantages and reliability of FCEVs.
Additionally, the limited range of FCEVs, primarily due to the energy density of hydrogen, is a concern for potential buyers. While FCEVs offer rapid refueling, their range is generally shorter than that of battery-electric vehicles (BEVs) with advanced battery technology. This range limitation can be a significant deterrent for long-distance travelers and those who require vehicles for extensive daily commutes. To address this, ongoing research and development efforts are focused on improving fuel cell efficiency, exploring alternative fuel storage methods, and enhancing the overall driving range of FCEVs.
In summary, the cost of FCEVs, the availability of hydrogen infrastructure, and public perception are critical challenges that need to be addressed for the market growth of fuel-cell electric vehicles. Overcoming these barriers will require a multi-faceted approach, including technological advancements, infrastructure development, and effective communication strategies to educate the public about the benefits and reliability of FCEVs.
Troubleshooting Short Circuits: A Guide to Vehicle Electrical Issues
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Fuel-Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs) are a type of electric vehicle that uses a fuel cell to generate electricity, which then powers the vehicle's electric motor. These vehicles are considered a zero-emission technology, as they produce no direct exhaust emissions, unlike traditional internal combustion engine vehicles.
FCEVs operate by combining hydrogen gas and oxygen from the air to produce electricity through a chemical reaction in the fuel cell. This process creates water as a byproduct, making FCEVs highly efficient and environmentally friendly. The electricity generated powers the electric motor, which drives the vehicle.
FCEVs offer several advantages. Firstly, they have a longer driving range compared to conventional EVs, especially on a single charge or fill-up. FCEVs can travel over 300 miles on a single hydrogen tank. Secondly, they can refuel much faster than charging an EV battery, typically taking just a few minutes. Additionally, FCEVs produce no harmful emissions, making them a cleaner alternative for the environment.
While FCEVs have great potential, there are some challenges. The primary one is the availability of hydrogen refueling stations, which are currently less widespread than traditional gas stations. Expanding the hydrogen infrastructure is crucial for the widespread adoption of FCEVs. Another challenge is the cost of fuel cells and the overall vehicle, which can be higher compared to conventional EVs. However, as technology advances and production scales, these challenges are expected to diminish over time.







