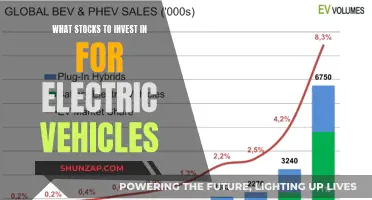
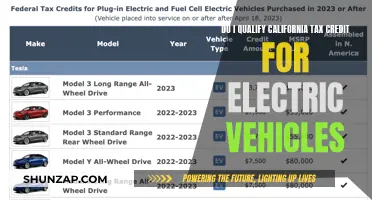
In recent years, the global push towards sustainable transportation has led to the widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). However, not all countries have embraced this shift. One notable exception is Iran, which has imposed a ban on the import and sale of electric vehicles, citing concerns over foreign dependency and the need to prioritize domestic industries. This decision has sparked debates about the balance between environmental goals and economic policies, as well as the potential impact on the automotive industry and consumer choices.
What You'll Learn
- Norway's EV Tax: A controversial tax on electric vehicles was introduced in 2021
- India's EV Ban: The government banned electric vehicles in 2020 due to safety concerns
- China's EV Subsidies: The government provides subsidies to promote electric vehicle adoption
- Germany's EV Incentives: Tax incentives and grants encourage the purchase of electric cars
- France's EV Roadmap: A comprehensive plan to phase out fossil fuel vehicles by 2040

Norway's EV Tax: A controversial tax on electric vehicles was introduced in 2021
The introduction of a controversial tax on electric vehicles (EVs) in Norway in 2021 sparked debate and raised questions about the country's commitment to promoting sustainable transportation. This tax, known as the "EV Tax," has been a subject of discussion among policymakers, environmentalists, and the general public alike. Norway, a pioneer in the adoption of EVs, had previously implemented a range of incentives to encourage the use of electric cars, including tax breaks and subsidies. However, the new tax aimed to address concerns regarding the environmental impact of EVs and the potential strain on public finances.
The EV Tax in Norway was designed to be a temporary measure, with the primary goal of generating revenue to support the country's ambitious climate goals. It imposed a tax of 250,000 Norwegian kroner (approximately $27,000) on the purchase of new EVs, which was significantly higher than the previous tax rate. This substantial tax was intended to discourage the purchase of EVs, especially for those who could afford them, and potentially reduce the number of new electric cars on the road. The revenue generated from this tax was then allocated to various funds, including a climate investment fund and a public transport development fund.
Critics of the EV Tax argue that it contradicts Norway's long-standing commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable mobility. They claim that the tax disproportionately affects lower-income individuals and families who rely on EVs for affordable transportation. The high cost of the tax, they argue, could deter potential EV buyers and hinder the country's progress towards a greener future. Additionally, some environmentalists believe that the tax may discourage the adoption of EVs, which are considered essential for reducing Norway's carbon footprint and improving air quality.
On the other hand, supporters of the tax argue that it is a necessary step to ensure the long-term sustainability of Norway's EV market. They suggest that the tax will help manage the potential surge in EV sales, which could strain the country's infrastructure and public services. By generating revenue, the tax can contribute to the development of necessary infrastructure, such as charging stations and public transport improvements, which are crucial for supporting the widespread adoption of EVs. Furthermore, they emphasize that the tax is temporary and will be re-evaluated to ensure it aligns with Norway's environmental objectives.
The introduction of the EV Tax in Norway highlights the complex balance between environmental goals, economic considerations, and public policy. It demonstrates the challenges of implementing measures that simultaneously promote sustainability and manage potential drawbacks. As the debate continues, Norway's experience serves as a case study for other countries considering similar tax policies, emphasizing the need for careful consideration of the potential impact on various stakeholders and the environment.
Strategies to Lower EV Costs: Tips for Affordable Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

India's EV Ban: The government banned electric vehicles in 2020 due to safety concerns
The Indian government's decision to ban electric vehicles in 2020 was a surprising move that sparked debate and concern among environmentalists and the automotive industry. This ban was primarily driven by safety concerns, which the government claimed were critical to public health and road safety. The announcement came as a shock to many, especially considering India's growing interest in promoting sustainable transportation and reducing its carbon footprint.
The safety concerns cited by the government included the potential risks associated with the lithium-ion batteries used in electric vehicles. These batteries, the authorities argued, could pose a fire hazard, especially in densely populated urban areas. The government's statement emphasized the need for stricter regulations and safety standards to protect citizens, especially in the context of rapidly increasing electric vehicle sales and the potential for widespread adoption.
However, critics of the ban argue that the government's decision was more about protecting the traditional automotive industry and its interests rather than genuine safety concerns. They suggest that the ban could hinder India's transition to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation system. The automotive sector in India has been dominated by internal combustion engine vehicles, and the shift to electric vehicles could potentially disrupt this established industry.
Despite the initial backlash, the Indian government has maintained its stance, emphasizing the importance of thorough safety assessments for electric vehicles. The ban has led to a temporary setback for the electric vehicle market in India, but it has also sparked a renewed focus on safety standards and regulations. This incident highlights the challenges and potential obstacles that countries may face when transitioning to new technologies, especially in the context of public health and safety.
As the debate continues, India's electric vehicle ban serves as a reminder that the adoption of new technologies, such as electric mobility, requires careful consideration of potential risks and benefits. It also underscores the need for comprehensive research, robust safety measures, and public awareness to ensure a smooth transition to a more sustainable future.
Electric Vehicles: The Indian Advantage? Exploring the Benefits
You may want to see also

China's EV Subsidies: The government provides subsidies to promote electric vehicle adoption
China has implemented a comprehensive strategy to accelerate the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) through various incentives and subsidies, playing a crucial role in its transition towards a more sustainable transportation system. The Chinese government's approach to promoting EVs is multifaceted, aiming to reduce environmental pollution, improve energy efficiency, and foster technological advancements in the automotive industry.
One of the primary mechanisms is the direct provision of subsidies to consumers. The Chinese government offers financial incentives to individuals and businesses purchasing electric vehicles. These subsidies can vary depending on the type of EV, its battery capacity, and the region of purchase. For instance, the central government provides a subsidy of up to 18,000 yuan (approximately $2,700) for electric passenger vehicles, while local governments may offer additional incentives, making the total subsidy potentially much higher. This financial support significantly reduces the upfront cost of EVs, making them more affordable and attractive to potential buyers.
Furthermore, China has established a robust network of charging infrastructure to support the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. The government has invested heavily in building a comprehensive charging station network across the country. This infrastructure ensures that EV owners have convenient access to charging facilities, addressing a critical concern related to range anxiety and promoting the overall convenience of EV ownership.
In addition to direct subsidies, China also encourages the development of the domestic EV industry through various policies. The government has set mandatory sales targets for EV manufacturers, ensuring a steady demand for electric vehicles. These targets, combined with tax incentives and reduced import tariffs for EV-related components, have spurred significant investment in the country's EV manufacturing sector. As a result, China has become a global leader in EV production, with numerous domestic brands and international companies establishing a strong presence in the market.
The impact of these subsidies and incentives is evident in the rapid growth of the Chinese EV market. Sales of electric vehicles in China have consistently risen, with record-breaking numbers in recent years. This success story has not only reduced the country's reliance on fossil fuels but has also positioned China as a global leader in sustainable transportation and clean energy technologies. The government's proactive approach to promoting EVs has not only benefited the environment but has also driven economic growth and technological innovation within the automotive sector.
Solar-Powered Revolution: Electric Vehicles with Solar Roofs
You may want to see also

Germany's EV Incentives: Tax incentives and grants encourage the purchase of electric cars
Germany has implemented a comprehensive strategy to promote the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) through various incentives and subsidies, aiming to reduce its carbon footprint and transition towards a more sustainable transportation system. The country's approach to EV incentives is multifaceted, combining tax benefits with direct grants to make electric cars more affordable and attractive to consumers.
One of the primary tax incentives is the reduced value-added tax (VAT) on electric vehicles. German residents purchasing new EVs are eligible for a reduced VAT rate of 19%, which is significantly lower than the standard VAT rate of 19%. This tax break not only makes EVs more affordable upfront but also contributes to a lower overall cost of ownership. Additionally, the reduced VAT is applied to the entire value chain, including the purchase, import, and assembly of electric cars, further stimulating the market.
The German government also offers a special tax credit for electric vehicles, which is a percentage of the vehicle's purchase price. This tax credit is designed to provide additional financial relief to EV buyers. The amount of the credit varies depending on the vehicle's CO2 emissions and the manufacturer's market share. Higher CO2 emissions and a smaller market presence often result in a more substantial tax credit, making it easier for consumers to afford electric cars.
In addition to tax incentives, Germany provides direct grants and subsidies to support EV purchases. The government has established the 'Electric Car Grant' program, which offers financial assistance to individuals and businesses buying electric vehicles. This grant can cover a significant portion of the vehicle's cost, making EVs more accessible to a wider range of buyers. The grant amount varies based on factors such as vehicle type, range, and manufacturer, ensuring a diverse range of electric cars are available in the market.
Furthermore, Germany's incentives extend beyond the initial purchase. The government offers reduced registration taxes for electric vehicles, which can further lower the cost of ownership. Additionally, EV owners are exempt from certain road taxes and tolls, providing long-term savings. These incentives collectively contribute to a more favorable environment for EV adoption, making Germany a leading market for electric cars in Europe.
By combining tax incentives and direct grants, Germany has successfully stimulated the EV market, resulting in increased sales and a growing number of electric cars on the road. These incentives not only benefit individual consumers but also support the development of a robust EV infrastructure, including charging stations and battery recycling programs. As a result, Germany's efforts in promoting EVs have positioned the country as a global leader in the transition to sustainable transportation.
California's Electric Revolution: A Green Future or a False Promise?
You may want to see also

France's EV Roadmap: A comprehensive plan to phase out fossil fuel vehicles by 2040
France has embarked on an ambitious journey to become a global leader in the electric vehicle (EV) market and reduce its reliance on fossil fuels. The country's comprehensive EV roadmap, unveiled in 2020, outlines a strategic plan to phase out internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles and accelerate the adoption of electric mobility by 2040. This ambitious goal is part of France's commitment to combat climate change and achieve carbon neutrality.
The roadmap is structured around several key pillars. Firstly, it aims to stimulate the domestic market by offering incentives and subsidies to encourage French citizens to purchase EVs. This includes financial support for consumers, such as reduced registration taxes and subsidies for purchasing electric cars, making them more affordable and attractive to the public. Additionally, the government plans to invest in a robust charging infrastructure network, ensuring convenient and accessible charging stations across the country. This infrastructure development will address range anxiety, a common concern among potential EV buyers, and encourage wider adoption.
Another critical aspect of the plan is the transformation of the automotive industry. France aims to position itself as a global hub for EV manufacturing and technology. This involves supporting the development of domestic EV manufacturers and encouraging the production of electric vehicles within the country. By fostering a competitive EV market, France can create jobs, stimulate economic growth, and reduce its dependence on imported vehicles. The roadmap also emphasizes the importance of research and development, investing in innovative technologies to enhance battery performance, charging speeds, and overall vehicle efficiency.
Furthermore, the French government is committed to phasing out fossil fuel vehicles through a series of regulatory measures. This includes setting strict emission standards, making it increasingly difficult for ICE vehicles to comply with environmental regulations. The plan also involves incentivizing the retirement of older, more polluting vehicles by offering scrappage schemes and providing financial incentives for trade-ins. These measures will contribute to a cleaner environment and reduce the overall carbon footprint of the transportation sector.
In summary, France's EV roadmap is a comprehensive strategy to revolutionize its transportation sector. By combining financial incentives, infrastructure development, industry support, and regulatory measures, the country aims to achieve a significant shift towards electric mobility. This ambitious plan not only addresses environmental concerns but also has the potential to create a thriving EV market, boost economic growth, and establish France as a global leader in sustainable transportation. The success of this roadmap will depend on effective implementation and continued commitment to the transition towards a greener future.
Can Income Limit Your Electric Vehicle Credit?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
As of my cut-off date in January 2023, no major country has completely banned the sale of new electric vehicles (EVs). However, some countries have imposed restrictions or incentives to encourage the adoption of traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles over EVs. For example, India has announced a phase-out of new ICE vehicles by 2030, but this does not equate to a ban on EV sales.
Yes, some countries have implemented policies that indirectly affect EV sales. For instance, the United States has no nationwide ban but has imposed tariffs on imported EVs, which can impact the availability and cost of certain models. Similarly, the European Union has set a target for all new cars to be zero-emission by 2035, but individual member states may have different incentives and regulations that influence the market.
Countries with stringent environmental regulations often have incentives and subsidies to promote EV adoption. For example, Norway, known for its aggressive climate policies, offers substantial tax breaks and exemptions for EV buyers, making it one of the top markets for EVs in Europe. This approach encourages the sale of EVs rather than banning them.
There have been discussions and proposals at various levels, including international agreements and national policies, to accelerate the transition to zero-emission vehicles. However, a global ban on EV sales is not currently a reality. The focus is often on incentivizing the adoption of EVs and phasing out ICE vehicles over time, as seen in the examples of India and the EU's targets.