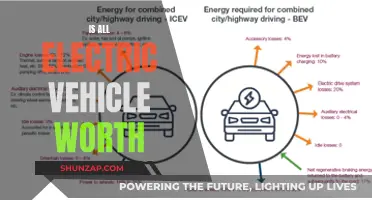
The DCV, or Direct Current Voltage, of an electric vehicle is a crucial aspect of its electrical system. It refers to the maximum voltage output of the vehicle's battery pack, which is essential for determining the vehicle's performance and efficiency. Understanding the DCV is key to optimizing the vehicle's charging, power distribution, and overall performance, making it a fundamental concept for anyone interested in electric vehicles.
What You'll Learn
- Battery Capacity: Measures the energy stored in the EV's battery, typically in kWh
- Power Output: Represents the maximum power the EV can deliver, often in kW
- Efficiency: The ratio of energy output to input, crucial for range and performance
- Charging Speed: Time taken to fully charge the battery, influenced by charger type
- Range: Distance an EV can travel on a single charge, a key consumer metric

Battery Capacity: Measures the energy stored in the EV's battery, typically in kWh
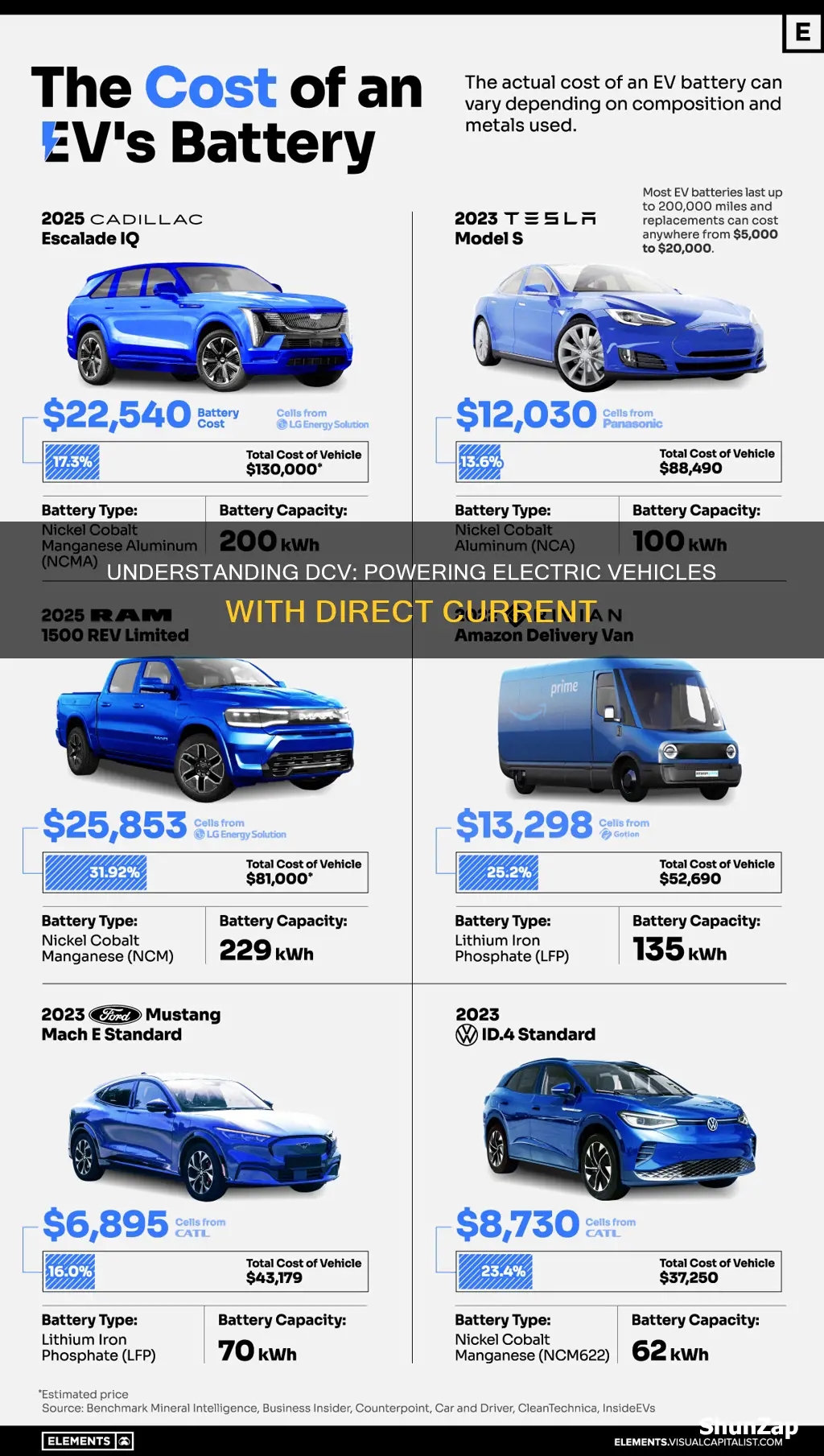
Battery capacity is a crucial aspect of electric vehicles (EVs) and is often one of the primary factors considered by potential buyers. It refers to the amount of energy that can be stored in the EV's battery pack and is typically measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). This measurement is essential because it directly influences the vehicle's range, which is a significant concern for many EV owners.
The battery capacity of an EV determines how far the vehicle can travel on a single charge. Higher kWh batteries generally provide longer ranges, allowing drivers to cover more distance without the need for frequent recharging. For example, a 100 kWh battery can store more energy than a 50 kWh battery, enabling the former to offer a more extended range. This is a critical consideration for those who frequently travel long distances or live in areas with limited charging infrastructure.
Understanding battery capacity is also vital for managing the EV's performance and efficiency. A higher kWh battery can provide more power to the electric motor, resulting in quicker acceleration and potentially a more responsive driving experience. However, it's important to note that larger batteries also tend to be heavier, which can impact the overall efficiency of the vehicle, especially during high-speed driving or when carrying heavy loads.
When evaluating EV options, consumers should consider their specific needs and preferences. For daily commuters, a battery capacity that provides a range of 150-250 miles (240-400 km) might be sufficient. On the other hand, long-distance travelers or those in regions with limited charging stations may require a higher kWh battery to ensure they can reach their destinations without range anxiety.
In summary, battery capacity is a key specification for EVs, impacting range, performance, and overall driving experience. It is a critical factor for potential buyers to consider when choosing an electric vehicle, ensuring that the chosen model aligns with their individual requirements and driving habits.
Global Trade of Electric Run Vehicles: A Rising Trend
You may want to see also

Power Output: Represents the maximum power the EV can deliver, often in kW
The power output of an electric vehicle (EV) is a critical specification that indicates its ability to accelerate and perform under various driving conditions. It represents the maximum power that the EV's electric motor can deliver to the wheels, measured in kilowatts (kW). This parameter is essential for understanding the vehicle's performance and capabilities.
When evaluating an EV's power output, it is common to see ratings ranging from 70 kW to over 300 kW for high-performance models. For instance, a typical compact EV might offer around 100-150 kW of power, while luxury or sports-oriented EVs can boast of 200 kW or more. This power is crucial for achieving quick acceleration and maintaining high speeds, especially on highways or when overtaking.
The power output is directly related to the EV's performance characteristics. A higher power output generally translates to faster acceleration and higher top speeds. For example, an EV with a 200 kW motor can accelerate from 0 to 60 mph in as little as 4-5 seconds, providing an exhilarating driving experience. This performance is particularly appealing to enthusiasts who value the thrill of rapid acceleration.
It's important to note that power output is just one aspect of an EV's overall performance. Other factors, such as torque, battery capacity, and efficiency, also play significant roles. Torque, for instance, determines the EV's ability to accelerate from a standstill or climb steep hills. A higher torque output, combined with sufficient power, ensures that the vehicle can handle various driving scenarios effectively.
Understanding the power output of an EV is essential for buyers as it influences the overall driving experience and performance expectations. When choosing an EV, considering the power output alongside other specifications will help buyers select a vehicle that aligns with their desired driving characteristics and performance needs.
Unraveling the Power of Electric Vehicle Technology: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Efficiency: The ratio of energy output to input, crucial for range and performance
Efficiency is a critical aspect of electric vehicles (EVs), as it directly impacts their performance, range, and overall sustainability. The term "efficiency" in the context of EVs refers to the ratio of energy output to input, which is essentially how effectively the vehicle converts the energy it uses into actual movement. This ratio is crucial because it determines how far an EV can travel on a single charge and how efficiently it utilizes its energy resources.
In the case of electric cars, efficiency is often measured by the DCV (Direct Current Voltage) of the vehicle's battery pack. DCV represents the voltage of the direct current supplied by the battery to the electric motor. A higher DCV indicates that the battery is supplying more power to the motor, resulting in improved efficiency. When the DCV is optimized, the vehicle can achieve better acceleration, higher top speeds, and, most importantly, increased range. This is because a higher DCV means that the electric motor can operate at its most efficient point, converting electrical energy into mechanical energy with minimal loss.
The efficiency of an EV is influenced by various factors, including the design of the motor, the type of battery, and the overall vehicle architecture. For instance, a well-designed electric motor with a high power-to-weight ratio can contribute to better efficiency. Additionally, advanced battery technologies, such as lithium-ion batteries with higher energy density, can store more energy in a smaller volume, leading to improved efficiency and range. The vehicle's aerodynamics also play a significant role; a sleek and streamlined design reduces drag, allowing the vehicle to move more efficiently through the air, thereby increasing overall efficiency.
Optimizing efficiency in EVs is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it directly impacts the vehicle's range, which is a significant concern for potential EV buyers. A more efficient EV can travel longer distances on a single charge, reducing the frequency of charging stops and making long-distance travel more feasible. Secondly, improved efficiency leads to better performance, as the vehicle can accelerate and decelerate more quickly and smoothly. This is particularly important in urban areas where frequent stops and starts are common. Lastly, higher efficiency contributes to reduced energy consumption, which is environmentally friendly and can lead to lower operating costs for EV owners.
In summary, efficiency is a key performance metric for electric vehicles, and it is closely tied to the DCV of the battery pack. By optimizing the DCV and considering various factors that influence efficiency, EV manufacturers can create vehicles that offer an exceptional driving experience, excellent range, and reduced environmental impact. Understanding and improving efficiency is, therefore, a vital aspect of the ongoing development and success of the electric vehicle market.
Unleash the Power: Electric Vehicle Tracking Systems Explained
You may want to see also

Charging Speed: Time taken to fully charge the battery, influenced by charger type
The charging speed of an electric vehicle (EV) is a critical factor in determining its efficiency and convenience. It refers to the time required to fully replenish the battery pack, and several factors influence this process. One of the primary determinants is the type of charger used. There are three main categories of chargers: AC (Alternating Current) chargers, DC (Direct Current) chargers, and fast chargers. AC chargers are the most common and are typically found at home or in public stations. They convert the AC power from the grid to DC power, which is then used to charge the EV battery. The charging speed with an AC charger depends on the EV's onboard charger capacity and the power output of the charger. For instance, a Level 2 AC charger, which provides 240 volts and 30 amps, can fully charge a typical EV battery in 4-8 hours.
DC chargers, on the other hand, deliver direct current to the battery, bypassing the onboard charger. This results in faster charging times compared to AC chargers. DC chargers are often used in public charging stations and can provide a significant boost to the battery in a short period. The charging speed with a DC charger is directly proportional to the power output; higher-powered DC chargers can charge batteries much faster. For example, a 50 kW DC fast charger can replenish a 100 kWh battery in under an hour, making it ideal for long-distance travel.
Fast charging technology has revolutionized EV charging, offering speeds that can significantly reduce charging times. These chargers use high-voltage direct current to rapidly charge the battery. The charging speed is influenced by the battery's capacity and the charger's power output. Modern fast chargers can provide up to 350 kW of power, allowing for rapid charging times of around 20-30 minutes for a full charge. This technology is particularly useful for EV owners who need to quickly top up their batteries during long journeys.
It's important to note that the charging speed also depends on the EV's battery capacity and the state of charge. A fully depleted battery will take longer to charge than one with a partial charge. Additionally, factors like ambient temperature and battery health can impact charging efficiency. Colder temperatures may slow down charging, while a well-maintained battery can charge faster.
In summary, the time taken to fully charge an EV battery varies based on the charger type, with DC chargers and fast charging technology offering the fastest options. Understanding these charging speeds and their influencing factors is essential for EV owners to plan their charging needs effectively and ensure they have sufficient power for their daily commutes or long-distance travel.
Brazil's Electric Vehicle Revolution: Mandates and Future
You may want to see also

Range: Distance an EV can travel on a single charge, a key consumer metric
The range of an electric vehicle (EV) is a critical factor for potential buyers, as it directly impacts the practicality and usability of the car. It refers to the maximum distance an EV can travel on a single charge, and it is a key metric that consumers should consider when evaluating different models. The range of EVs has improved significantly over the years, with many modern vehicles offering over 200 miles on a single charge, and some even exceeding 300 miles. This is a substantial increase from the early days of EVs, where range was often limited to just 100 miles or less.
Several factors influence the range of an EV. One of the most significant is the battery capacity, measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh). Larger batteries generally provide more range, but they also add weight and cost to the vehicle. Another factor is the efficiency of the electric motor and the overall design of the car. More efficient motors and aerodynamic designs can help maximize the distance traveled per unit of energy. Additionally, the driving conditions and habits of the driver play a role. Aggressive driving, frequent rapid acceleration, and high-speed highway driving will consume more energy and reduce the range.
EV manufacturers often provide estimated range figures based on specific driving conditions and test cycles. These estimates are useful for giving consumers an idea of the vehicle's potential, but it's important to remember that actual range can vary depending on real-world driving habits and environmental factors. For instance, driving in extreme temperatures, whether hot or cold, can impact the range due to the increased energy required for heating or cooling the cabin.
To maximize the range of an EV, drivers can adopt certain practices. Maintaining a steady speed and avoiding rapid acceleration can help conserve energy. Using regenerative braking, which converts kinetic energy back into electrical energy, can also extend the range. Planning routes with charging stations along the way is essential for long-distance travel, ensuring that drivers can recharge their vehicles when needed.
In summary, the range of an electric vehicle is a crucial consideration for buyers, offering a practical insight into the car's capabilities. With advancements in battery technology and design, EVs are becoming more capable, and understanding the factors that influence range can help consumers make informed decisions when choosing their next electric vehicle.
Ford's Electric Future: Shifting Focus or Staying Committed?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
DCV stands for Direct Current Voltage, and it refers to the electrical system's voltage in an electric vehicle. It is the measure of the potential difference between two points in the vehicle's electrical circuit, typically measured in volts (V).
In electric vehicles, the power source is usually a battery that provides direct current (DC). The DCV measures the voltage of this direct current, ensuring the electrical system operates efficiently. On the other hand, Alternating Current (AC) is used in some charging systems, and ACV would refer to the voltage of the AC supply.
Monitoring the DCV is crucial for maintaining the health and performance of an electric vehicle. It helps ensure that the vehicle's electrical components, such as the motor, charger, and battery, are functioning optimally. If the DCV drops significantly, it may indicate a problem with the electrical system, allowing owners to address potential issues before they cause major breakdowns.