Electric vehicles (EVs) are increasingly popular, and as their adoption grows, so does the focus on efficient cooling systems to maintain optimal performance and extend the lifespan of these vehicles. The most popular cooling technology in EVs is a combination of liquid cooling and air cooling. Liquid cooling, which uses a coolant to absorb and transfer heat away from the battery and motor, is highly effective in managing the high temperatures that can occur in these systems. This technology is often paired with air cooling, which uses fans and vents to dissipate heat to the surrounding air. This dual approach ensures that EVs can operate efficiently and safely, even in demanding conditions, making it a key consideration in the design and engineering of these vehicles.
What You'll Learn

Performance: Efficiency and power of cooling systems in EVs
The cooling systems in electric vehicles (EVs) are crucial for maintaining optimal performance and longevity, especially as these vehicles often operate under different thermal conditions compared to traditional internal combustion engines. The efficiency and power of these cooling systems directly impact the overall efficiency and driving range of EVs. Here's an overview of the performance aspects of cooling technologies in electric vehicles:
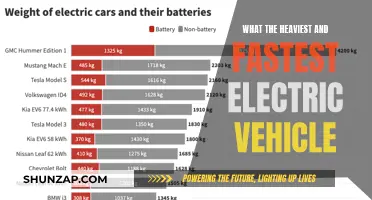
Efficiency in Cooling Systems: One of the primary goals in EV cooling system design is to achieve high efficiency while minimizing energy consumption. Traditional liquid cooling systems, which use a radiator and a coolant to dissipate heat, are widely used in EVs. These systems have been refined to be more efficient, with improved heat exchangers and coolant circulation mechanisms. The use of advanced materials, such as aluminum alloys and composite materials, helps reduce the weight and improve the thermal conductivity of the cooling components, thereby enhancing overall efficiency. For instance, some EV manufacturers employ liquid cooling systems with closed-loop designs, which recirculate the coolant, reducing heat loss and improving thermal management.
Power Dissipation and Performance: The power of a cooling system is its ability to dissipate heat effectively, ensuring that the EV's battery, electric motor, and other components operate within safe temperature limits. High-performance EVs, such as those used in racing or for rapid acceleration, require robust cooling systems to handle the intense heat generated during operation. These vehicles often utilize advanced cooling technologies like liquid-cooled battery packs, which directly cool the battery cells, maintaining optimal performance and extending their lifespan. Additionally, some EVs employ air-to-liquid or liquid-to-air intercoolers to cool the air or liquid before it enters the engine, improving power output and efficiency.
Heat Management and Range: Efficient cooling is critical for maintaining the driving range of EVs, especially in extreme weather conditions. In cold climates, the battery's performance can be significantly impacted by low temperatures, leading to reduced range. Advanced cooling systems, such as those with phase-change materials or thermoelectric cooling, can help maintain battery temperature and overall system efficiency. On the other hand, in hot climates, efficient cooling prevents overheating, ensuring the EV's performance remains consistent. This is particularly important for high-performance EVs, where maintaining optimal temperatures is essential for peak power delivery.
Innovations in Cooling Technology: The market for EV cooling systems is constantly evolving, with manufacturers exploring new technologies to improve performance and efficiency. For instance, some companies are developing cooling systems that use thermally conductive fluids or phase-change materials to enhance heat transfer. Additionally, the integration of cooling systems with thermal management software allows for dynamic control, optimizing cooling based on real-time data. This technology can adjust cooling output based on driving conditions, ensuring efficient and effective thermal management.
In summary, the performance and efficiency of cooling systems in electric vehicles are vital for overall vehicle performance, range, and longevity. As EV technology advances, so do the cooling technologies, ensuring that these vehicles can operate optimally in various environmental conditions. The continuous development of efficient and powerful cooling systems will play a significant role in the widespread adoption and success of electric vehicles.
Debunking Myths: Are Electric Vehicles' Range Claims Reliable?
You may want to see also

Materials: Advanced materials used in EV cooling systems
The development of efficient cooling systems is crucial for electric vehicles (EVs) to maintain optimal performance and extend the lifespan of their battery packs. As the demand for more powerful and compact EVs increases, so does the need for innovative cooling technologies. Advanced materials play a pivotal role in enhancing the performance and reliability of these cooling systems.
One of the key materials making a significant impact in EV cooling is aluminum. Its lightweight nature and excellent thermal conductivity make it an ideal choice for heat sinks and radiators. Aluminum's ability to efficiently transfer heat away from the battery pack helps in maintaining lower operating temperatures, thus improving overall efficiency and reducing the risk of thermal degradation. Modern EVs often utilize advanced aluminum alloys, such as 6061 or 7075, which offer enhanced strength and corrosion resistance, ensuring the cooling system's durability in various environmental conditions.
Another material that has found its way into EV cooling systems is copper. Copper's superior thermal conductivity allows for more efficient heat dissipation. It is commonly used in the form of heat exchangers and cooling fins. These components are designed to maximize the surface area in contact with the cooling medium (often air or liquid), facilitating rapid heat transfer. The use of copper in EV cooling systems not only improves performance but also contributes to a more compact and lightweight design, which is essential for space-constrained electric powertrains.
Advanced ceramics are also emerging as a promising material for EV cooling. Ceramic composites, such as aluminum nitride (AlN) or silicon carbide (SiC), offer exceptional thermal conductivity and high-temperature stability. These materials can be utilized in the construction of heat spreaders and thermal interfaces, effectively drawing heat away from critical components. The lightweight and high-performance nature of ceramics makes them an attractive option for designers, especially in high-performance EVs where weight reduction is a critical factor.
Furthermore, the development of advanced cooling fluids and lubricants is another aspect where materials innovation is evident. These specialized fluids are designed to operate efficiently within the unique temperature ranges of EV cooling systems. They often contain additives that improve thermal stability, corrosion resistance, and lubricity, ensuring the longevity of the cooling system and the overall health of the EV's components.
In summary, the use of advanced materials in EV cooling systems is a critical aspect of improving performance, efficiency, and longevity. From lightweight aluminum alloys to high-performance ceramics and specialized cooling fluids, these materials contribute to more efficient heat management, compact designs, and reliable operation, ultimately driving the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
Unleash Savings: Federal Rebates for Your Electric Vehicle
You may want to see also

Design: Innovative designs for effective heat management
The quest for efficient heat management in electric vehicles (EVs) is a critical aspect of their development, as it directly impacts performance, range, and overall reliability. One of the most popular cooling technologies in EVs is liquid cooling, which has gained prominence due to its ability to provide precise temperature control and efficient heat dissipation. This method involves a liquid coolant, typically a mixture of water and additives, circulating through a network of tubes and channels to absorb heat from various components and then transfer it to a radiator or cooling fan system. The key advantage of liquid cooling is its ability to maintain optimal temperatures for high-performance EV components, such as batteries, power electronics, and motors, ensuring they operate within safe and efficient ranges.
Innovative designs in liquid cooling systems for EVs often focus on minimizing weight and maximizing heat transfer efficiency. Engineers have developed compact, lightweight radiators with enhanced surface areas to facilitate better heat exchange. These radiators are strategically positioned to optimize airflow and cooling, ensuring that critical components are effectively cooled without adding unnecessary bulk to the vehicle. Additionally, the use of advanced materials, such as high-conductivity copper or aluminum alloys, in the coolant channels and heat exchangers further enhances the system's performance.
Another design approach to effective heat management is the implementation of phase-change materials (PCMs). PCMs are substances that can absorb and release large amounts of heat during phase transitions (e.g., from solid to liquid). In EVs, PCMs can be integrated into the battery pack or other heat-generating components to provide a passive cooling mechanism. When the temperature rises, the PCM absorbs heat, delaying the need for active cooling systems. This not only reduces the energy required for cooling but also contributes to a more sustainable and efficient vehicle design.
For electric motors, innovative cooling designs often involve the use of air-liquid dual cooling systems. This technology combines the benefits of air cooling, which is lightweight and cost-effective, and liquid cooling, which provides precise temperature control. The motor's cooling system may include air ducts and fins to dissipate heat from the motor's surface, while a small liquid cooling loop targets specific hot spots, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. This dual approach allows for efficient heat management while maintaining the simplicity and reliability associated with air cooling.
Furthermore, the integration of smart sensors and control algorithms plays a crucial role in innovative heat management designs. Sensors monitor the temperature of various EV components in real-time, providing data that can be used to adjust cooling systems dynamically. For instance, if the battery temperature rises, the system can activate additional cooling fans or increase the coolant flow rate to maintain safe operating temperatures. This level of control ensures that the EV's cooling system is responsive and efficient, adapting to varying driving conditions and load demands.
Debunking Myths: Do EVs Still Pollute?
You may want to see also

Energy Efficiency: Impact of cooling on EV battery life
The cooling systems in electric vehicles (EVs) play a critical role in maintaining optimal battery performance and longevity. Effective cooling is essential to manage the high temperatures that batteries can reach during operation, especially in high-demand driving conditions. This is a critical aspect of EV design, as battery performance and lifespan are directly influenced by temperature management.
One of the most popular cooling technologies in EVs is liquid cooling, which involves a coolant flowing through the battery pack to absorb and transfer heat. This method is widely adopted due to its ability to efficiently manage heat distribution and maintain a stable temperature across the entire battery module. The coolant, often a specialized liquid, is designed to have a high thermal conductivity, allowing it to quickly transfer heat away from the battery cells. This technology is particularly effective in high-performance EVs, where rapid acceleration and frequent short-distance travel can lead to rapid temperature increases.
The impact of cooling on energy efficiency is significant. When batteries operate within an optimal temperature range, typically between 15°C and 35°C, their performance and efficiency are maximized. Excessive heat can lead to a decrease in voltage and an increase in internal resistance, resulting in reduced energy output and higher energy consumption. Conversely, operating at lower temperatures can also impact efficiency, as it may lead to increased internal resistance and slower reaction times. Therefore, maintaining a consistent and controlled temperature through efficient cooling is crucial for optimizing energy use and extending the overall battery life.
Furthermore, the cooling system's design and placement are critical factors in energy efficiency. Designers often integrate cooling channels and heat sinks directly into the battery pack to enhance heat dissipation. These components facilitate the rapid transfer of heat from the battery cells to the coolant or air, ensuring that temperatures remain within safe limits. Efficient cooling also reduces the risk of thermal runaway, a dangerous condition where batteries overheat and potentially catch fire, which can be devastating for both the vehicle and its occupants.
In summary, the choice and implementation of cooling technology in EVs have a direct and positive impact on energy efficiency and battery life. Liquid cooling, with its ability to manage heat distribution effectively, is a popular choice for maintaining optimal battery performance. By ensuring that batteries operate within the ideal temperature range, EVs can maximize energy efficiency, minimize energy waste, and ultimately provide a more reliable and longer-lasting power source for electric vehicles. This aspect of EV design is a key consideration for manufacturers aiming to optimize the overall driving experience and the longevity of their products.
Choosing the Right Amp Breaker for Your Electric Vehicle
You may want to see also

Environmental Impact: Eco-friendly cooling solutions for electric cars
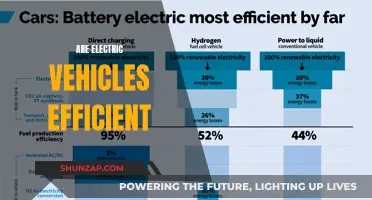
The automotive industry is undergoing a significant transformation with the rise of electric vehicles (EVs), and one of the critical aspects that require careful consideration is cooling technology. As EVs aim to reduce their environmental footprint, traditional cooling systems, such as those using refrigerants, can have a negative impact on the environment. Therefore, exploring eco-friendly cooling solutions is essential for the sustainable development of the EV market.
One of the most promising eco-friendly cooling technologies for electric cars is liquid cooling, which utilizes a closed-loop system to transfer heat away from the battery pack and other critical components. This method is highly efficient as it directly addresses the heat management needs of EVs, ensuring optimal performance and longevity. By using a liquid coolant, typically a mixture of water and additives, the system can absorb and dissipate heat more effectively than air cooling, which is commonly used in conventional vehicles. The closed-loop design also prevents coolant leaks, reducing the risk of environmental contamination.
Another innovative approach is the implementation of phase-change cooling, which utilizes the natural process of phase transitions to regulate temperature. This technology involves a coolant that changes state from liquid to gas, absorbing heat in the process, and then condenses back into a liquid, releasing the heat. Phase-change materials, such as certain organic compounds, can be used to achieve this cooling effect. This method is particularly effective in managing the high temperatures generated by EV batteries and can contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly cooling system.
Furthermore, the use of thermoelectric cooling modules presents an eco-conscious alternative. These modules generate a cooling effect through the direct conversion of electrical energy into a temperature difference. By utilizing thermoelectric materials, the system can provide localized cooling without the need for a large coolant circulation system. This technology is compact, efficient, and can be easily integrated into various parts of the EV, making it an attractive option for manufacturers aiming to reduce the environmental impact of their vehicles.
In addition to these technologies, the development of advanced materials and coatings plays a crucial role in enhancing the eco-friendliness of cooling systems. For instance, researchers are exploring the use of graphene-based materials, which offer excellent thermal conductivity and can be applied as coatings to improve heat dissipation. These materials can be integrated into the cooling system to optimize heat transfer, reducing the overall energy consumption and environmental impact.
In summary, the environmental impact of electric vehicles can be significantly reduced by adopting eco-friendly cooling solutions. Liquid cooling, phase-change cooling, thermoelectric cooling, and advanced material innovations are all contributing to the development of more sustainable cooling technologies. As the EV market continues to grow, these eco-conscious approaches will play a vital role in ensuring that electric cars are not only efficient and high-performing but also environmentally responsible.
Toyota Crown: Electric Future or Traditional Icon?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The most prevalent cooling technology in EVs is liquid cooling, which involves a coolant (often a mixture of water and ethylene glycol) circulating through a network of tubes and heat exchangers. This system efficiently dissipates heat generated by the battery pack, electric motor, and other components, ensuring stable operation even during high-demand driving conditions.
Liquid cooling offers several advantages over air cooling. It provides more effective heat dissipation, allowing for higher power output and faster charging rates. Liquid cooling systems can maintain more stable temperatures, especially in dense battery packs, which is crucial for longevity and performance. Additionally, liquid cooling can be more compact, making it suitable for the limited space available in EV designs.
Yes, while liquid cooling is dominant, some EVs also utilize air cooling, especially for smaller components like inverters and power electronics. Air cooling is simpler and more lightweight, making it a cost-effective solution for certain parts. However, air cooling may not be as efficient as liquid cooling, especially in high-performance EVs, where managing heat becomes more critical.
No, the choice of cooling technology can vary among EV manufacturers based on factors like vehicle type, performance requirements, and design philosophy. Some companies might opt for a combination of liquid and air cooling to balance efficiency and cost. Additionally, advancements in cooling technologies, such as phase-change cooling or advanced materials, might be explored to enhance cooling performance and contribute to the overall efficiency of electric vehicles.