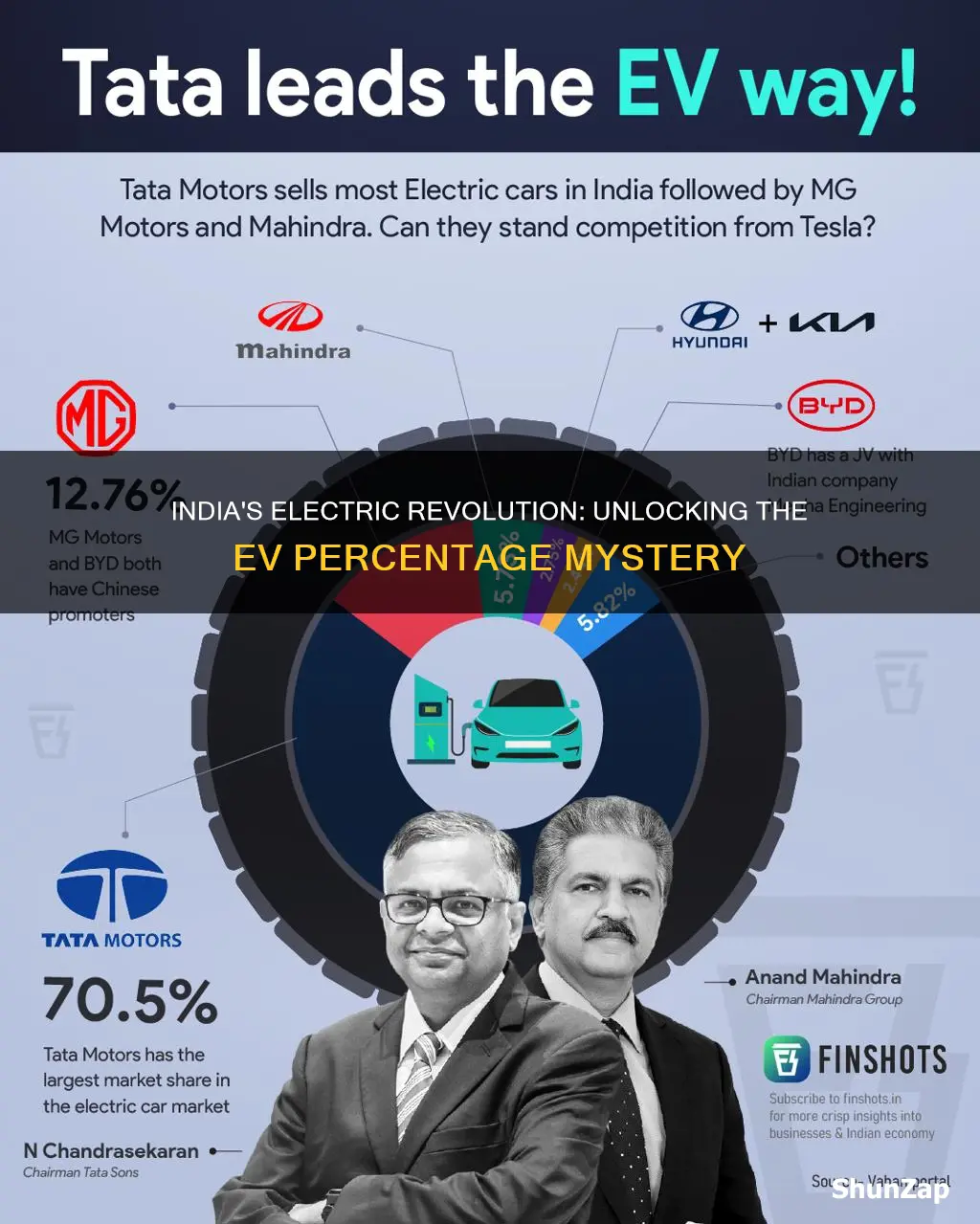
The adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) in India has been steadily rising, but the percentage of EVs on the road remains relatively low compared to other countries. As of 2022, the market share of electric cars in India was approximately 1-2%, with a significant portion of the sales coming from commercial vehicles like buses and taxis. This low penetration rate can be attributed to various factors, including high upfront costs, limited charging infrastructure, and consumer skepticism about the reliability and range of electric vehicles. Despite these challenges, the Indian government has set ambitious targets to promote EV adoption, aiming to increase the number of electric vehicles on the road to 6-7 million by 2025.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Total Electric Vehicles (EVs) in India (as of 2023) | Approximately 1.5 million |
| Percentage of Total Vehicles in India (as of 2023) | Less than 1% |
| Government's Target for 2030 | 10 million EVs on Indian roads |
| EV Sales in 2022 | Over 200,000 units |
| EV Sales in 2023 (projected) | Expected to reach 300,000 units |
| Popular EV Models | Tata Nexon EV, Mahindra eKUV100, MG ZS EV, Tata Tigor EV, etc. |
| Charging Infrastructure | Over 10,000 charging stations across the country |
| Battery Technology | Li-ion batteries dominate the market |
| Range of EVs | Varies from 150 km to 500 km or more, depending on the model |
| Cost of EVs | Starting from ₹5 lakh to over ₹2 crore for luxury models |
| Environmental Impact | Reduced carbon emissions and improved air quality |
| Government Incentives | Tax benefits, subsidies, and other incentives to promote EV adoption |
What You'll Learn
- Market Penetration: India's EV market share and growth rate
- Government Incentives: Tax benefits and subsidies for EV buyers
- Charging Infrastructure: Availability and expansion of charging stations
- Consumer Adoption: Factors influencing EV purchase decisions
- Regional Variations: EV adoption trends across different Indian states

Market Penetration: India's EV market share and growth rate
The Indian electric vehicle (EV) market has been experiencing rapid growth and is poised to become a significant player in the global EV industry. As of 2023, India's EV market share is still relatively small compared to the overall automotive market, but it is growing at an impressive rate. The country's push towards electrification is driven by government initiatives, environmental concerns, and the potential for economic growth.
Market Penetration: India's EV market share has been steadily increasing over the past few years. According to recent data, electric cars and two-wheelers accounted for approximately 2-3% of the total vehicle sales in India in 2022. This percentage might seem small, but it represents a significant rise from the previous years, indicating a growing consumer interest in electric mobility. The Indian government's ambitious target of achieving 6-7 million sales of electric vehicles by 2030 suggests that the market is expected to expand exponentially.
The growth rate of the EV market in India is impressive, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of over 20% predicted for the next five years. This growth is attributed to several factors. Firstly, the government's support is a major driving force. Initiatives such as the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme and the National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP) have provided incentives, subsidies, and infrastructure development, making EVs more affordable and accessible to Indian consumers. Secondly, the environmental benefits of electric vehicles are gaining traction, as Indians become more conscious of their carbon footprint.
Additionally, the Indian automotive industry is embracing electrification, with many traditional automakers investing in EV technology and launching new electric models. This has led to a wider range of EV options available in the market, catering to various consumer preferences and budgets. As a result, the market is witnessing a rapid expansion, with more players entering the space, further driving the growth rate.
However, despite the positive trajectory, there are challenges to be addressed. These include the lack of a comprehensive charging infrastructure, high upfront costs, and consumer skepticism. Overcoming these barriers will be crucial for the EV market to reach its full potential and accelerate its penetration in India.
Electric Vehicle Market: Surplus or Shortage?
You may want to see also

Government Incentives: Tax benefits and subsidies for EV buyers
The Indian government has implemented various incentives to promote the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and accelerate the transition to a more sustainable transportation system. These incentives aim to reduce the upfront cost of EVs, making them more affordable and accessible to a wider population. One of the primary methods to achieve this is through tax benefits and subsidies, which directly impact the financial burden on EV buyers.
Tax benefits play a crucial role in making EVs more attractive to potential buyers. The government offers a reduced Goods and Services Tax (GST) rate for electric vehicles, which is currently set at 12%, compared to the standard GST rate of 18% for conventional vehicles. This tax concession significantly lowers the overall cost of purchasing an EV, making it a more appealing choice for consumers. Additionally, some states in India have introduced their own tax benefits, such as exempting EV buyers from road tax or providing reduced registration fees, further enhancing the financial advantages of owning an electric vehicle.
Subsidies are another powerful tool in the government's strategy to promote EV adoption. The Ministry of Power and the Ministry of Heavy Industries have launched several subsidy programs to support EV buyers. One notable initiative is the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme, which provides financial assistance to individuals and organizations for purchasing electric two- and three-wheelers. The scheme offers a subsidy of up to 50% of the cost, effectively reducing the price of these vehicles and making them more affordable for the general public. Moreover, the government has also introduced the National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP), which aims to achieve 6-7 million sales of hybrid and electric vehicles by 2020, with a focus on providing subsidies and incentives to make EVs more competitive in the market.
These tax benefits and subsidies have had a positive impact on the EV market in India. The reduced costs have encouraged more people to consider purchasing electric vehicles, leading to a gradual increase in the number of EVs on the road. As a result, the percentage of electric vehicles in India has been steadily rising, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation ecosystem.
In summary, the Indian government's approach of offering tax benefits and subsidies has been instrumental in making electric vehicles more accessible and affordable. These incentives have played a vital role in driving the adoption of EVs, and with continued support, India is well-positioned to achieve its ambitious targets for electric mobility.
Sparking Safety: A Guide to Electrical Fire Hazards in Cars
You may want to see also

Charging Infrastructure: Availability and expansion of charging stations
The adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) in India is gaining momentum, but the country still has a long way to go in terms of charging infrastructure development. As of 2023, the exact percentage of electric vehicles on Indian roads is difficult to pinpoint, but estimates suggest it is still relatively low compared to the overall vehicle population. This lack of widespread EV ownership is partly due to the limited availability of charging stations, which can be a significant barrier to EV adoption.
India has been working on expanding its charging infrastructure, but the pace of development is crucial to supporting the growing EV market. The government has initiated various schemes and incentives to encourage the production and sale of electric vehicles and has also set targets for the installation of charging stations. For instance, the Ministry of Power has set a goal of installing 10,000 fast-charging stations across the country by 2025. These stations are designed to provide a quick charge to EVs, reducing the time required for a full charge. However, the current number of charging stations is still insufficient to meet the demands of a rapidly growing EV market.
The expansion of charging infrastructure is essential for several reasons. Firstly, it addresses the range anxiety associated with EVs, which is a common concern among potential buyers. With a well-distributed network of charging stations, EV owners can plan their trips more confidently, knowing they can easily find a charging point when needed. Secondly, a robust charging infrastructure encourages the widespread adoption of EVs by providing the necessary convenience and accessibility. This is particularly important in urban areas where parking spaces are often limited, and the availability of charging stations can make a significant difference in the overall EV ownership experience.
The development of charging infrastructure also has environmental benefits. As EVs are powered by electricity, the shift towards electric mobility can help reduce the country's reliance on fossil fuels and lower greenhouse gas emissions. With more charging stations, the integration of EVs into the existing power grid becomes more feasible, allowing for the potential use of renewable energy sources to power these vehicles. This transition to a greener transportation system is a crucial step in India's journey towards sustainable development.
In summary, while the percentage of electric vehicles in India is increasing, the availability of charging stations remains a critical factor in the widespread adoption of EVs. The government's efforts to expand charging infrastructure are essential to support the growing market and encourage a shift towards sustainable transportation. By addressing the charging infrastructure gap, India can accelerate the transition to electric mobility, reduce its carbon footprint, and ensure a more environmentally friendly future.
Troubleshooting: Removing a Stuck Electrical Plug from Your Vehicle
You may want to see also

Consumer Adoption: Factors influencing EV purchase decisions
The Indian market for electric vehicles (EVs) is experiencing a gradual but steady growth, with a focus on sustainable transportation solutions. As of 2023, the percentage of electric vehicles in India is relatively small compared to the overall vehicle population, but it is increasing. The Indian government has set ambitious targets to promote EV adoption, aiming to achieve a significant shift towards electric mobility. This shift is driven by the need to reduce air pollution, improve energy security, and promote sustainable development.
Consumer adoption of electric vehicles in India is influenced by various factors, which can be categorized into economic, environmental, and infrastructure-related considerations. Firstly, the economic factors play a crucial role in purchase decisions. The initial cost of EVs is often a significant barrier for potential buyers, as these vehicles tend to be more expensive than their conventional counterparts. However, the long-term savings on fuel and maintenance costs can be attractive to consumers. Many Indian consumers are also price-sensitive and may opt for more affordable options, which is why the government and manufacturers are working on providing subsidies and incentives to make EVs more accessible and affordable.
Environmental concerns are another driving force behind the adoption of electric vehicles. Indian consumers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of traditional combustion engines and are motivated to contribute to a greener future. The desire to reduce carbon footprints and combat climate change is a powerful motivator for EV purchases. Additionally, the perception of EVs as a status symbol, especially among the urban elite, is growing, further encouraging consumer interest.
Infrastructure development is a critical aspect that influences EV purchase decisions. The availability of charging stations and the convenience of charging at home are essential considerations. India has been working on expanding its charging infrastructure, but the network is still developing, and the lack of convenient charging options can deter potential buyers. Range anxiety, the fear of running out of battery power, is a common concern, especially for those considering long-distance travel. Therefore, investments in a robust and widespread charging infrastructure are vital to encouraging EV ownership.
Furthermore, consumer education and awareness play a significant role in the adoption process. Many potential buyers may have misconceptions or lack knowledge about the technology, performance, and benefits of EVs. Providing accurate information and addressing common myths can help overcome these barriers. Government initiatives, such as awareness campaigns and educational programs, can effectively promote EV ownership and dispel any hesitations.
In summary, the factors influencing EV purchase decisions in India include economic considerations, environmental awareness, infrastructure development, and consumer education. Addressing these factors through policy interventions, infrastructure investments, and educational initiatives can accelerate the transition to electric mobility in the country. As the market matures, it is expected that more consumers will embrace electric vehicles, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation ecosystem in India.
Ford's Electric Future: Rumors of Scrapping EV Plans Debunked
You may want to see also

Regional Variations: EV adoption trends across different Indian states
The adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) in India varies significantly across different states, influenced by a multitude of factors including infrastructure, government policies, and local preferences. As of 2023, the country has seen a steady rise in EV sales, but the distribution is not uniform. Here's an analysis of EV adoption trends across various regions:
South India: States like Karnataka, Kerala, and Tamil Nadu have shown a promising trend in EV adoption. Karnataka, for instance, has implemented several incentives to promote EVs, including subsidies and tax benefits. The state's focus on building a robust charging infrastructure has encouraged residents to make the switch. Kerala, known for its scenic beauty, has a growing market for EVs, with many residents opting for electric scooters and cars for their eco-friendly nature. Tamil Nadu has also witnessed a surge in EV sales, with the government's initiatives to reduce pollution playing a crucial role.
North India: The northern states, particularly those with higher pollution levels, have shown a strong inclination towards EVs. Delhi, known for its severe air pollution, has witnessed a rapid increase in EV sales. The government's strict emission norms and the introduction of the 'Electric Vehicle Policy' have been instrumental in this shift. Similarly, states like Punjab and Haryana have also seen a rise in EV adoption, with farmers and urban residents embracing electric vehicles as a cost-effective and environmentally friendly alternative.
Western India: Gujarat and Maharashtra are leading the way in EV adoption in this region. Gujarat has implemented a comprehensive EV policy, offering subsidies and tax benefits, which has resulted in a significant increase in sales. The state's focus on renewable energy sources further strengthens its position as a leader in EV adoption. Maharashtra, with its bustling cities and increasing environmental concerns, has also seen a surge in EV sales. The state's government has been proactive in promoting EVs through various incentives.
Eastern India: West Bengal and Odisha are making notable strides in EV adoption. West Bengal has introduced several schemes to encourage EV ownership, including financial assistance and the development of charging stations. These initiatives have contributed to a growing market for electric vehicles. Odisha, with its rich mineral resources and focus on sustainable development, has also shown a positive trend. The state's government has been actively promoting EVs through awareness campaigns and infrastructure development.
Northeast India: The northeastern states, despite facing unique challenges, are making progress in EV adoption. States like Assam and Meghalaya have taken steps to promote EVs, recognizing the need to reduce their carbon footprint. The region's unique geography and cultural practices have led to the development of innovative EV solutions tailored to local needs.
In conclusion, India's EV market is witnessing a regional shift, with some states leading the way in adoption. The government's policies, combined with local initiatives, are driving this change. As the country continues to invest in EV infrastructure and technology, the regional variations in EV adoption are likely to diminish, contributing to a more sustainable transportation ecosystem.
Electric Vehicle Tax Credit: Unlocking Savings for All Income Levels
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
As of 2023, the electric vehicle market in India is still in its early stages, with a relatively small percentage of the overall automotive market. The exact percentage can vary depending on the source and the specific time frame considered. However, estimates suggest that EVs account for less than 1% of the total vehicle sales in India, with a growing but still minor presence.
The adoption of EVs in India has been increasing steadily over the past few years, driven by government initiatives, environmental concerns, and technological advancements. The Indian government has set ambitious targets to promote EV sales, including subsidies and incentives for manufacturers and buyers. As a result, the market has seen a rise in EV sales, with a focus on two-wheelers and three-wheelers, which have seen significant growth.
Several factors contribute to the percentage of EVs in India:
- Government Policies: The Indian government's push for electrification, including the National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP), has played a crucial role in promoting EV adoption.
- Infrastructure Development: The availability of charging stations and the development of supporting infrastructure are essential for EV ownership.
- Consumer Awareness: Increasing awareness about environmental sustainability and the benefits of EVs is encouraging more people to make the switch.
- Technology and Cost: Advances in battery technology and a gradual decrease in EV prices are making them more affordable and attractive to consumers.
Industry analysts and market research firms predict that the EV market in India will experience significant growth in the coming years. Some estimates suggest that by 2030, the percentage of electric vehicles in India could reach 20-30% of the total vehicle sales, especially if the government's policies and incentives continue to support the industry. This growth is expected to be driven by a combination of factors, including technological improvements, changing consumer preferences, and a more sustainable transportation ecosystem.







