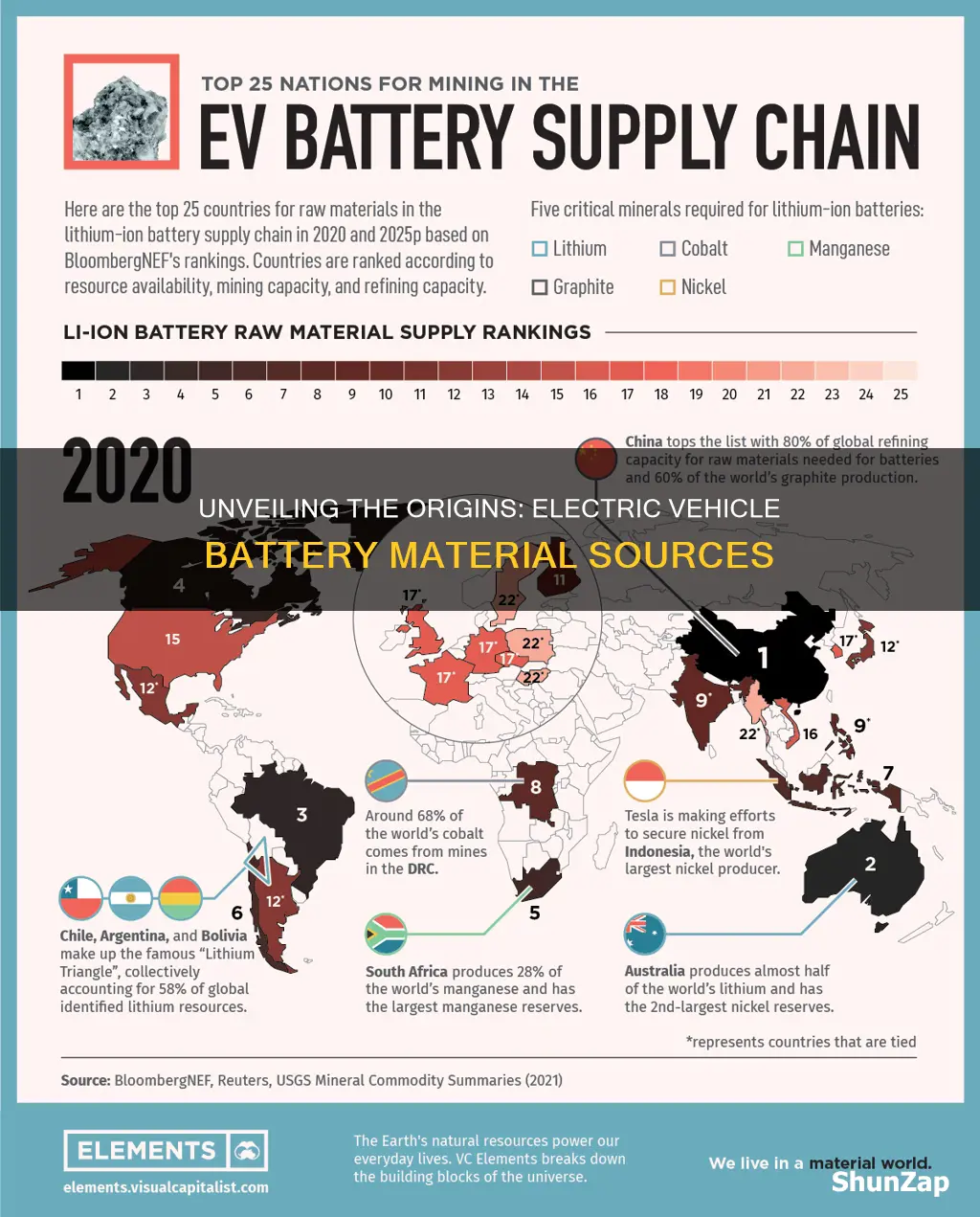
The sourcing of materials for electric vehicle (EV) batteries is a critical aspect of the EV industry, as it directly impacts the sustainability and supply chain resilience of these vehicles. The production of electric vehicles relies heavily on the availability and extraction of specific minerals and metals, which are essential for the manufacturing of lithium-ion batteries. These materials, including lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese, are sourced from various regions around the world, with different countries and mining sites contributing to the global supply. Understanding the geographical distribution and extraction processes of these materials is crucial to ensuring a stable and ethical supply chain for the growing EV market.
What You'll Learn
- Mining: Extracting lithium, cobalt, and nickel from the earth
- Recycling: Recovering materials from used batteries to reduce reliance on mining
- Sustainable Sourcing: Prioritizing eco-friendly practices and local suppliers
- International Trade: Global supply chains for battery materials
- Innovation: Developing new methods for material extraction and processing

Mining: Extracting lithium, cobalt, and nickel from the earth
The extraction of raw materials for electric vehicle (EV) batteries is a critical process in the transition to sustainable transportation. Among the key elements are lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which are essential for the production of lithium-ion batteries that power EVs. These materials are primarily sourced through mining, a process that involves extensive exploration, extraction, and processing.
Mining for these battery metals often begins with identifying potential sites through geological surveys and exploration techniques. Lithium, for instance, is commonly found in brine deposits, often in arid regions, while cobalt and nickel are typically extracted from mineral-rich ores. Once a site is identified, the mining process commences, which can vary depending on the mineral type and location. Open-pit mining is a common method for extracting lithium from brine-rich areas, where large volumes of earth are removed to access the lithium-rich brine. This method is efficient but can have significant environmental impacts, including habitat destruction and water pollution.
The extraction of cobalt and nickel often involves underground mining, where specialized equipment is used to access the ore-bearing veins. These minerals are typically found in conjunction with other metals, such as copper and platinum, and their extraction often requires advanced techniques to separate them. The mining process can be challenging and environmentally demanding, requiring careful management of waste and byproducts to minimize ecological damage.
After extraction, the raw materials undergo extensive processing to refine and purify them. This includes crushing, grinding, and chemical treatments to separate the desired metals from impurities. For lithium, this often involves a process called evaporation, where the brine is heated to concentrate the lithium. Cobalt and nickel, on the other hand, are typically processed through a series of chemical reactions to extract the pure metals. These processes are energy-intensive and require significant infrastructure, often near the mining sites to minimize transportation costs and environmental impact.
The sourcing and extraction of these battery materials are crucial aspects of the EV industry's supply chain. As the demand for EVs grows, so does the need for sustainable and responsible mining practices. Efforts are being made to improve mining techniques, reduce environmental impacts, and ensure ethical sourcing, especially for cobalt, which has been associated with human rights issues in some mining regions. The future of EV battery production relies on a continuous supply of these materials, driving innovation in mining and recycling technologies to support the growing demand for sustainable transportation.
Simplifying the Process: A Guide to Registering Your Electric Car
You may want to see also

Recycling: Recovering materials from used batteries to reduce reliance on mining
The sourcing of raw materials for electric vehicle (EV) batteries is a critical aspect of the EV industry, and it has significant environmental implications. While mining is a traditional method of obtaining these materials, the process can be resource-intensive and environmentally damaging. However, a more sustainable approach is emerging through the recycling of used batteries, which offers a way to reduce the industry's reliance on mining and minimize its environmental footprint.
Recycling EV batteries is a complex process that involves several stages. Firstly, used batteries are collected and transported to specialized recycling facilities. These batteries are then carefully disassembled to separate the various components, including the cathode, anode, and electrolyte. Each of these components contains valuable materials that can be recovered and reused. For instance, the cathode often contains lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which are essential for battery performance. Similarly, the anode may comprise graphite, and the electrolyte can be recycled for future use.
The recycling process further involves the treatment and purification of these materials. For example, lithium can be recovered through a process called leaching, where it is dissolved from the cathode material and then precipitated and purified. Cobalt and nickel can also be extracted and refined for reuse in new batteries. This recycling process not only reduces the need for mining but also ensures a consistent supply of these critical materials for the EV industry.
By implementing large-scale battery recycling programs, countries and industries can significantly contribute to a more sustainable future. This approach can help reduce the environmental impact of EV production and encourage a circular economy within the battery supply chain. Additionally, recycling can provide a steady stream of raw materials, ensuring the long-term viability of the EV market and potentially driving down the cost of battery production.
In summary, recycling used EV batteries is a crucial strategy to minimize the environmental impact of the EV industry and reduce its reliance on mining. It offers a sustainable solution by recovering valuable materials, ensuring a consistent supply, and potentially reducing costs. As the demand for EVs continues to grow, implementing effective recycling programs will be essential to support the industry's long-term success while promoting a greener and more responsible approach to battery production and resource management.
Unleash Your Electric Dreams: A Guide to Launching Your EV Empire
You may want to see also

Sustainable Sourcing: Prioritizing eco-friendly practices and local suppliers
The sourcing of materials for electric vehicle (EV) batteries is a critical aspect of the industry's sustainability and environmental impact. As the demand for EVs rises, it is essential to prioritize eco-friendly practices and local suppliers to ensure a more sustainable future. Here's an overview of how this can be achieved:
Eco-Friendly Material Sourcing: The journey of EV battery materials begins with responsible sourcing. Many battery manufacturers are now focusing on obtaining raw materials through sustainable and ethical practices. This includes recycling and reusing materials, ensuring fair trade practices, and minimizing the environmental footprint of extraction. For instance, lithium, a key component in EV batteries, can be sourced through recycling processes, reducing the need for environmentally damaging mining operations. By adopting such methods, the industry can significantly lower its impact on the environment and promote a circular economy.
Local Supplier Networks: Prioritizing local suppliers is another crucial strategy for sustainable sourcing. Building a robust network of local suppliers can reduce the carbon footprint associated with transportation and logistics. Local sourcing also supports the community and local economy, fostering a more resilient and sustainable supply chain. For example, companies can establish partnerships with local mining operations or recycling facilities, ensuring a steady supply of raw materials while also contributing to local development. This approach can lead to the creation of green jobs and a more sustainable local economy.
Sustainable Mining and Extraction: The mining and extraction processes should be designed with sustainability in mind. This involves implementing advanced technologies and techniques to minimize environmental damage. For instance, using water-efficient methods in lithium mining or adopting carbon capture technologies in the extraction of other battery materials can significantly reduce the ecological impact. Additionally, companies can invest in research and development to find more sustainable alternatives to traditional extraction methods, ensuring a greener future for the industry.
Recycling and End-of-Life Management: Effective recycling and end-of-life management of EV batteries are essential to a sustainable supply chain. As batteries age or become obsolete, proper recycling ensures that valuable materials are recovered and reused. This process can be optimized by developing efficient recycling technologies and infrastructure. By encouraging and implementing recycling practices, the industry can reduce its reliance on raw material extraction, minimize waste, and contribute to a more circular and sustainable model.
In summary, sustainable sourcing for EV battery materials involves a comprehensive approach, including eco-friendly extraction, local supplier networks, and efficient recycling systems. By adopting these practices, the electric vehicle industry can significantly reduce its environmental impact, support local communities, and contribute to a greener and more sustainable future. It is a collective effort that requires collaboration between manufacturers, suppliers, and policymakers to drive positive change.
Understanding Electric Auxillary Controls: Powering Vehicle Convenience
You may want to see also

International Trade: Global supply chains for battery materials
The global supply chain for electric vehicle (EV) battery materials is a complex network, with raw materials sourced from various regions around the world. This intricate web of international trade is essential to the production of batteries for EVs, which are a key component in the transition to sustainable transportation. The demand for these materials has grown exponentially as the EV market expands, leading to a strategic focus on securing reliable sources.
One of the primary materials for EV batteries is lithium, a metal that is crucial for the lithium-ion technology used in most electric cars. This element is primarily sourced from South America, with Chile and Argentina being major players. The Andes Mountains region is home to some of the world's largest lithium reserves, and countries like Chile have established themselves as a leading exporter. The extraction and processing of lithium involve advanced techniques, and the industry has attracted significant investment to meet the growing demand.
In addition to lithium, the production of EV batteries requires other critical materials, including cobalt, nickel, and manganese. Cobalt, for instance, is essential for the cathode in lithium-ion batteries, and it is predominantly sourced from the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC). The DRC's rich mineral deposits have made it a central hub for cobalt mining, despite the associated social and environmental challenges. Similarly, nickel, another key component, is largely obtained from Indonesia and the Philippines, which are among the top producers globally.
The global nature of this supply chain also extends to the processing and manufacturing stages. After raw materials are extracted, they often travel across continents to specialized facilities for refining and fabrication. For example, China has become a significant player in the EV battery supply chain, with numerous companies investing in the production of battery cells and modules. This has led to a complex web of international trade, where materials are processed in one country and then exported to another for final assembly.
Ensuring a sustainable and ethical supply chain for EV battery materials is a critical challenge. The industry is under scrutiny to address environmental concerns, labor issues, and the potential for human rights violations in certain regions. As a result, there is a growing emphasis on responsible sourcing, with companies implementing due diligence processes to trace the origin of materials and ensure fair and sustainable practices throughout the supply chain. This includes initiatives to promote recycling, reduce environmental impact, and support local communities in the regions where these materials are sourced.
Unraveling the Challenges: Electric Vehicles' Hidden Hurdles
You may want to see also

Innovation: Developing new methods for material extraction and processing
The sourcing of materials for electric vehicle (EV) batteries is a critical aspect of the EV industry, and it has sparked a wave of innovation in developing new methods for extraction and processing. As the demand for EVs rises, so does the need for sustainable and efficient ways to obtain the raw materials required for battery production. This has led to a focus on research and development aimed at improving the extraction processes of key battery components, such as lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese.
One area of innovation is in the development of more environmentally friendly and cost-effective extraction techniques. Traditional mining methods often involve significant environmental impact and can be energy-intensive. To address this, scientists and engineers are exploring alternative approaches. For instance, researchers are investigating the use of renewable energy sources to power extraction processes, reducing the carbon footprint of material sourcing. This includes the implementation of solar-powered or wind-powered facilities for mining and processing, ensuring a more sustainable and green approach.
Another strategy is the optimization of existing extraction processes to increase efficiency and reduce waste. This involves refining techniques like hydrometallurgy, which uses chemical processes to extract metals from ores, and pyrometallurgy, which employs high-temperature processes. By enhancing these methods, researchers aim to improve the overall yield of desired materials while minimizing the loss of valuable resources. This not only reduces the environmental impact but also ensures a more consistent and reliable supply of battery materials.
Furthermore, there is a growing emphasis on recycling and reusing materials to create a closed-loop system for EV battery production. Developing advanced recycling technologies can significantly contribute to the sustainability of the industry. This includes creating efficient processes to recover materials from end-of-life batteries, such as lithium-ion batteries, which are commonly used in EVs. By implementing effective recycling methods, the industry can reduce its reliance on primary material extraction and ensure a more circular economy.
In addition to extraction, processing methods are also being revolutionized. The development of new processing techniques aims to enhance the performance and longevity of EV batteries. For example, researchers are exploring ways to improve the solid-state electrolyte used in solid-state batteries, which could offer higher energy density and safety compared to liquid electrolytes. These advancements in processing will not only improve the overall performance of EVs but also contribute to the development of more sustainable and efficient battery technologies.
Electric Vehicles: Are They Worth the Price Tag?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The materials for electric vehicle (EV) batteries are sourced from various regions around the world, often depending on the specific mineral composition required. For instance, lithium, a key component in lithium-ion batteries, is primarily extracted from brine deposits in countries like Chile, Australia, and Argentina. These countries have significant lithium reserves due to their geological history. Other important minerals include cobalt, nickel, and manganese, which are often obtained from mining operations in Africa, particularly the Democratic Republic of Congo, and also in countries like Indonesia and the Philippines.
Yes, the supply of battery materials is currently dominated by a few key regions. As mentioned, South America, particularly Chile and Argentina, is a major player in lithium production. The Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) is the world's largest producer of cobalt, a critical material for battery performance and longevity. Additionally, Indonesia and the Philippines are significant sources of nickel. However, the concentration of supply in a few regions can lead to geopolitical risks and supply chain vulnerabilities, prompting efforts to diversify and secure sustainable sourcing.
The sourcing of battery materials is subject to various regulations and standards to ensure ethical and sustainable practices. Many countries and international organizations have implemented guidelines and certifications, such as the Responsible Mining Initiative (RMI) and the Conflict-Free Minerals Program, to promote responsible mining and supply chain transparency. Environmental concerns include habitat destruction, water pollution, and the release of toxic substances during mining and processing. Ethical issues often revolve around labor conditions, child labor, and human rights violations in some mining regions.
Absolutely, there is a growing focus on developing more sustainable and environmentally friendly practices in the EV battery material supply chain. Recycling and reusing materials from end-of-life batteries is one approach to reduce the demand for virgin resources. Companies are investing in advanced recycling technologies to extract valuable metals from spent batteries. Additionally, efforts are being made to develop alternative materials and designs that minimize the reliance on critical minerals like cobalt. For instance, solid-state batteries and lithium-sulfur batteries are being researched as potential replacements or complements to traditional lithium-ion technology.