Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained significant popularity as a sustainable transportation alternative, but they are not without their challenges. One of the primary concerns is the limited driving range, which can cause anxiety among drivers, especially those who frequently travel long distances. The availability of charging stations is another critical issue, as the infrastructure for EV charging is still developing, and finding a charging station during long trips can be a significant hurdle. Additionally, the high initial cost of EVs, compared to traditional gasoline vehicles, remains a barrier for many potential buyers. Despite these problems, advancements in technology and increasing consumer demand are driving efforts to address these issues and make electric vehicles more accessible and practical for the general public.
What You'll Learn
- Range Anxiety: Limited driving range due to battery capacity, requiring frequent charging
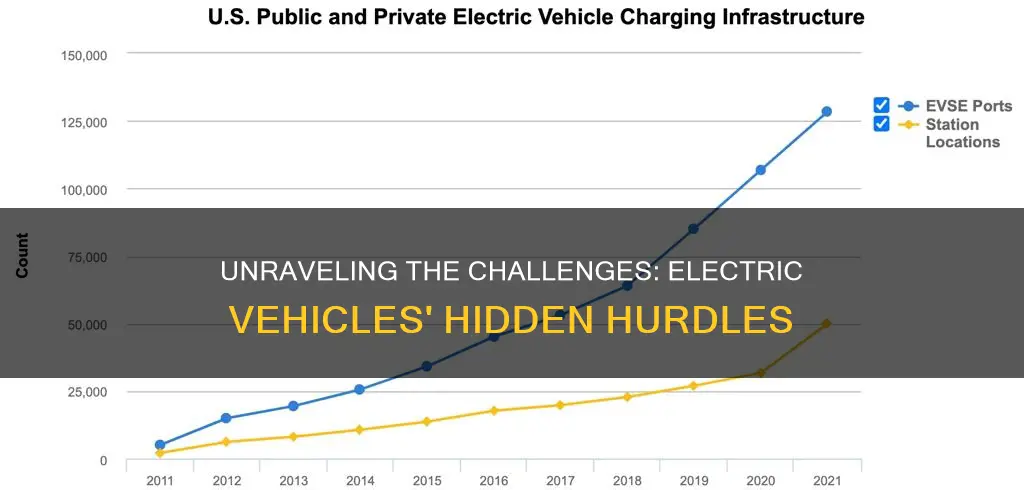
- Charging Infrastructure: Inadequate charging stations can hinder convenience and accessibility
- Battery Degradation: Over time, batteries lose efficiency, impacting long-term performance and value
- High Upfront Cost: Initial purchase price remains a significant barrier for many consumers
- Environmental Impact: Manufacturing and disposal of batteries can have ecological consequences

Range Anxiety: Limited driving range due to battery capacity, requiring frequent charging
The issue of range anxiety is a significant concern for many potential electric vehicle (EV) buyers. This anxiety stems from the fear of running out of power while driving, especially on long journeys or in areas with limited charging infrastructure. The primary cause of this problem is the limited driving range that electric cars can currently offer compared to their gasoline counterparts. While modern EVs have made great strides in improving their range, they still fall short of the distances that conventional cars can travel on a single tank of fuel.
Battery capacity is the main factor contributing to this range limitation. The energy density of lithium-ion batteries, which are commonly used in EVs, is not as high as that of gasoline, allowing for a more compact and lightweight fuel tank. As a result, EVs often require larger and heavier batteries to achieve competitive range, which can impact the overall efficiency and performance of the vehicle. This trade-off between range and other vehicle attributes, such as weight, cost, and charging speed, is a complex challenge that EV manufacturers are continually working to address.
To combat range anxiety, several strategies are being employed. One approach is to develop advanced battery technologies that offer higher energy density, allowing for longer ranges. Researchers are exploring solid-state batteries, which promise higher energy density and faster charging, as a potential solution. Additionally, improving the efficiency of the vehicle's electrical systems and adopting lightweight materials can help maximize the range of existing EV designs.
Another strategy is to enhance the charging infrastructure. Governments and private companies are investing in the expansion of charging networks, making it more convenient for EV owners to find charging stations along their routes. Rapid charging technologies are also being developed, significantly reducing the time required to recharge a battery, thus alleviating the anxiety associated with long-distance travel.
For those who frequently experience range anxiety, several solutions are available. One option is to consider hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs), which combine a traditional gasoline engine with an electric motor and battery. HEVs offer the benefit of extended range and the flexibility to switch between electric and gasoline power, reducing the anxiety associated with running out of charge. Alternatively, EV owners can plan their trips carefully, utilizing navigation systems that provide real-time charging station information, ensuring they always have access to a charging point when needed.
Unraveling the EV Tax Credit: Refundability and Its Impact
You may want to see also

Charging Infrastructure: Inadequate charging stations can hinder convenience and accessibility
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is a crucial step towards a sustainable future, but the current charging infrastructure presents several challenges that need addressing. One of the primary concerns is the lack of adequate charging stations, which significantly impacts the convenience and accessibility of EV ownership.
In many regions, the availability of charging stations is limited, often concentrated in specific areas or along major highways. This distribution can lead to long waiting times for EV owners, especially during peak travel hours or when multiple vehicles require charging simultaneously. For instance, in urban areas, the competition for charging spots in residential neighborhoods or commercial centers can be intense, causing frustration among EV drivers. The situation is further exacerbated in rural regions, where the scarcity of charging stations may force drivers to plan their journeys meticulously, ensuring they have access to charging points.
The inadequate charging infrastructure also contributes to range anxiety, a common issue among potential EV buyers. Range anxiety refers to the fear of running out of battery charge during a journey, which can be mitigated by the availability of convenient charging options. Without a robust network of charging stations, EV owners may feel restricted in their travel plans, limiting their ability to embark on longer trips or explore remote areas. This anxiety can deter potential buyers, especially those who prioritize convenience and the freedom to travel without constant worry about charging availability.
To address this problem, significant investments in charging infrastructure are necessary. Governments and private entities should collaborate to establish a comprehensive network of charging stations, ensuring coverage across various geographical areas. Rapid charging technologies, which can significantly reduce charging times, should be implemented where possible. Additionally, the development of smart charging systems can optimize energy usage, allowing for more efficient management of charging stations and reducing wait times for EV owners.
In conclusion, the inadequate charging infrastructure is a critical issue that hinders the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. By addressing this problem through strategic investments and innovative solutions, we can improve the convenience and accessibility of EVs, making them a more attractive and viable transportation option for the masses.
Exploring the Latest Hybrid and Electric Vehicles: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Battery Degradation: Over time, batteries lose efficiency, impacting long-term performance and value
Battery degradation is a significant concern for electric vehicle (EV) owners, as it directly affects the overall performance and longevity of their vehicles. Over time, the batteries in EVs undergo a natural process of decline, which can lead to reduced efficiency and, consequently, a decrease in the vehicle's range and overall value. This issue is a critical aspect of EV ownership that potential buyers should be aware of.
The degradation of EV batteries is primarily due to the chemical reactions that occur within the battery cells during charging and discharging cycles. Each time an EV is charged, the battery's chemical composition changes, and over numerous charge-discharge cycles, this process can lead to a gradual loss of capacity. This means that the battery may not be able to store as much energy as it initially could, resulting in a reduced driving range. For example, a battery that initially provides a range of 300 miles might, after several years, only offer a range of 250 miles, even with the same charging habits.
Several factors contribute to battery degradation. Firstly, the number of charge-discharge cycles is a major determinant. Each time the battery is fully charged and then fully discharged, it experiences a cycle. Over time, these cycles take a toll on the battery's health. Secondly, the temperature at which the battery operates plays a crucial role. Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can accelerate degradation. For instance, consistently charging and driving in very cold climates can significantly reduce battery life. Additionally, the overall health of the battery, including its age and previous usage, influences its degradation rate.
To mitigate the effects of battery degradation, EV manufacturers employ various strategies. One approach is to design batteries with advanced chemistry that can withstand more cycles and temperature variations. Some companies also offer battery warranties, providing peace of mind for buyers. However, it's important for EV owners to adopt good charging and driving habits. Avoiding rapid charging at very high or very low temperatures and maintaining a moderate charging routine can help preserve battery health.
In summary, battery degradation is a natural process that affects all EV batteries, impacting their long-term performance and value. While manufacturers are working to improve battery technology, understanding and managing this issue is essential for EV owners to ensure they get the most out of their electric vehicles.
Unleash Your Electric Dreams: A Guide to Launching Your EV Empire
You may want to see also

High Upfront Cost: Initial purchase price remains a significant barrier for many consumers
The high upfront cost of electric vehicles (EVs) is a significant challenge that continues to hinder widespread adoption. While the long-term benefits of EVs, such as reduced fuel and maintenance costs, are well-documented, the initial purchase price remains a substantial barrier for many consumers. This financial hurdle is particularly acute for those on a tight budget, as the cost of an EV can often exceed that of a comparable gasoline-powered vehicle.
The primary reason for this disparity is the advanced technology and battery systems that power EVs. These vehicles are equipped with sophisticated components, including powerful electric motors, advanced batteries, and sophisticated electronics, all of which contribute to a higher production cost. Additionally, the limited production volumes of many EVs can drive up prices due to economies of scale not being fully realized.
Furthermore, the lack of a robust used car market for EVs exacerbates the problem. As a relatively new technology, the resale value of EVs is often lower compared to traditional vehicles, which can deter potential buyers from making the investment. This is especially concerning for those who may need to upgrade their vehicles more frequently due to financial constraints.
To address this issue, governments and manufacturers are exploring various strategies. Incentives such as tax credits, rebates, and grants are being offered to reduce the effective purchase price for consumers. Additionally, leasing programs and subscription models are gaining popularity, allowing buyers to access EVs without the substantial upfront cost, making ownership more accessible.
In conclusion, the high upfront cost of electric vehicles is a critical obstacle to their widespread adoption. However, with ongoing efforts to reduce prices, improve resale value, and introduce innovative financing options, the barriers to entry for EVs are gradually being lowered, paving the way for a more sustainable transportation future.
Mastering EV Battery Sizing: A Comprehensive Guide to Powering Your Ride
You may want to see also

Environmental Impact: Manufacturing and disposal of batteries can have ecological consequences
The environmental impact of electric vehicles (EVs) extends beyond their operation, primarily due to the manufacturing and disposal of their batteries. The production of lithium-ion batteries, a common type used in EVs, involves a complex process that can have significant ecological consequences. Mining for the raw materials, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, often occurs in regions with limited environmental regulations, leading to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution. The extraction process can also release toxic chemicals into the environment, posing risks to local ecosystems and human health.
Furthermore, the manufacturing phase requires substantial energy consumption, often derived from non-renewable sources, contributing to greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. The energy-intensive nature of battery production means that the environmental benefits of EVs may be partially offset by the emissions generated during manufacturing. As a result, the lifecycle analysis of EVs should consider not only their operational efficiency but also the environmental impact of their production.
The disposal and recycling of batteries present another set of challenges. When batteries reach the end of their life, they must be handled and recycled properly to minimize environmental harm. Improper disposal can lead to the release of toxic substances into the soil and water, affecting both terrestrial and aquatic ecosystems. Additionally, the recycling process itself can be energy-intensive and may require the use of hazardous chemicals, requiring careful management to ensure minimal ecological impact.
To address these concerns, researchers and manufacturers are exploring more sustainable practices. Developing more efficient recycling methods and encouraging the use of recycled materials in battery production can reduce the environmental footprint of EVs. Moreover, extending the lifespan of batteries through improved design and maintenance can also contribute to minimizing the ecological consequences of manufacturing and disposal.
In summary, while electric vehicles offer a promising path towards reducing greenhouse gas emissions, the manufacturing and disposal of batteries present significant environmental challenges. Addressing these issues through sustainable practices and responsible resource management is crucial to ensuring that the widespread adoption of EVs leads to a net positive environmental impact.
Python's Power: Crafting Electric Vehicle Simulations
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The charging infrastructure for EVs is still developing and can be a significant challenge. The current issue is the availability and accessibility of charging stations, especially in rural areas and during long-distance travel. The lack of standardized charging ports and the varying charging speeds between different EV models can also cause inconvenience. However, efforts are being made to improve charging networks, with many countries investing in the expansion of charging stations to address these concerns.
While EVs are considered more environmentally friendly than traditional gasoline or diesel cars, they still have some environmental implications. The production of EV batteries requires significant energy and resources, leading to potential environmental degradation if not managed sustainably. Additionally, the source of electricity used to charge EVs can vary, and in regions with a high reliance on fossil fuels for power generation, the environmental benefits might be less significant. However, as the energy sector transitions to cleaner sources, the environmental impact of EVs is expected to decrease.
One of the common questions is about the reliability and maintenance of EVs. These vehicles have fewer moving parts compared to traditional cars, which can result in lower maintenance costs and fewer breakdowns. However, the complexity of the battery system and the potential for battery degradation over time are areas of concern. Regular maintenance and monitoring of the battery health are essential to ensure the vehicle's longevity. Manufacturers provide warranties and service packages to address these issues, and advancements in battery technology are continuously being made to improve reliability.
The initial cost of purchasing an EV is often higher than that of conventional vehicles, which can be a significant financial barrier for potential buyers. However, the long-term savings on fuel and maintenance can offset this. Additionally, the availability of government incentives and subsidies for EV owners can make the financial aspect more attractive. The economic challenges also include the potential for higher electricity rates during peak hours, which might impact the overall running costs.







