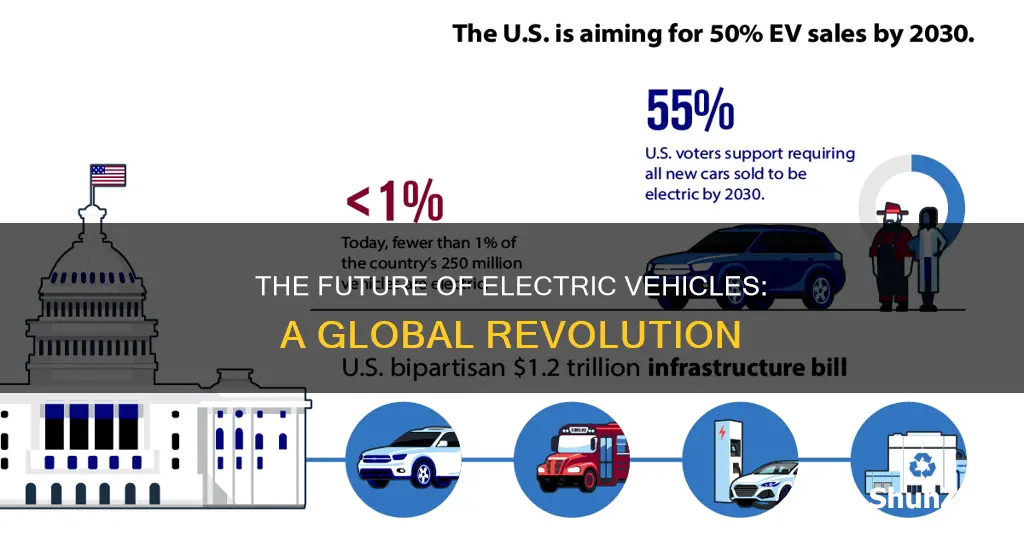
The world is rapidly embracing electric vehicles (EVs) as a sustainable transportation solution, but where are we heading with this technology? The future of EVs is bright, with ongoing innovations in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and vehicle design. As the demand for cleaner and more efficient transportation grows, EVs are becoming increasingly popular, offering a viable alternative to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. This shift towards electrification is not just about reducing emissions but also about transforming the way we think about and interact with our vehicles, paving the way for a more sustainable and connected future.
What You'll Learn
- Environmental Impact: Reduced emissions and resource efficiency compared to traditional vehicles
- Infrastructure Development: Charging stations, battery technology, and grid integration
- Economic Shifts: New markets, jobs, and cost implications for consumers and industries
- Regulatory Changes: Government policies and incentives driving EV adoption
- Technological Advancements: Innovations in battery, charging, and autonomous driving

Environmental Impact: Reduced emissions and resource efficiency compared to traditional vehicles
The environmental benefits of electric vehicles (EVs) are significant and play a crucial role in shaping the future of transportation. One of the most notable advantages is the substantial reduction in emissions compared to conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. Electric cars produce zero tailpipe emissions, meaning they do not release harmful pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), particulate matter (PM), and volatile organic compounds (VOCs) during operation. This is a major step forward in improving air quality, especially in densely populated urban areas where pollution from vehicles is a significant concern. By eliminating these emissions, EVs contribute to a cleaner and healthier environment, reducing the risk of respiratory issues and other health problems associated with air pollution.
The resource efficiency of EVs is another critical aspect of their environmental impact. Traditional vehicles rely on fossil fuels, which are non-renewable resources and contribute to the depletion of Earth's natural reserves. In contrast, electric cars are powered by electricity, which can be generated from a variety of sources, including renewable options like solar, wind, and hydropower. This shift towards renewable energy sources reduces the carbon footprint associated with transportation. EVs also have more efficient energy systems, converting a higher percentage of the electrical energy into actual vehicle movement compared to the energy wasted as heat in ICE vehicles. This increased efficiency means less energy is required to power EVs, further reducing their environmental impact.
The manufacturing process of EVs also contributes to their overall environmental benefit. While the production of electric vehicles does require significant energy and resources, the use of advanced materials and more streamlined manufacturing techniques can lead to a smaller ecological footprint compared to traditional car manufacturing. Additionally, the longevity of EVs is an important factor. With proper care, electric cars can last for many years, and their batteries can be recycled or reused, minimizing waste and the need for new resource extraction.
In summary, electric vehicles offer a promising path towards a more sustainable future. Their ability to reduce emissions and improve resource efficiency is a significant step in mitigating the environmental impact of transportation. As technology advances and infrastructure for charging and recycling improves, EVs will become an increasingly viable and environmentally friendly choice for consumers, contributing to a cleaner and greener world. This shift in the automotive industry is essential to addressing the global challenge of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and preserving the planet for future generations.
The Future of Transportation: When Will All Vehicles Go Electric?
You may want to see also

Infrastructure Development: Charging stations, battery technology, and grid integration
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is an undeniable trend, and with it comes the need for a robust and efficient infrastructure network. This network is crucial to support the growing number of EVs on the road, ensuring they can be charged conveniently and sustainably. Three key areas of focus for infrastructure development are charging stations, battery technology, and grid integration.
Charging Stations:
The proliferation of charging stations is essential to address the range anxiety associated with EVs. Public charging stations are becoming increasingly common, offering a convenient way for drivers to recharge their vehicles when needed. These stations can be found in various locations, including shopping malls, parking lots, and along highways. The development of fast-charging technology is a significant advancement, significantly reducing the time required to charge an EV's battery. This technology is particularly important for long-distance travel, allowing drivers to quickly top up their batteries and continue their journey. However, the challenge lies in ensuring equitable distribution of these charging stations across different regions and communities to cater to the diverse needs of EV owners.
Battery Technology:
Battery technology plays a pivotal role in the EV revolution. The development of advanced lithium-ion batteries has been instrumental in improving the range and performance of electric vehicles. Researchers and engineers are constantly working on enhancing battery capacity, energy density, and charging speed. Solid-state batteries, for instance, offer the potential for higher energy density and faster charging times compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. Additionally, the recycling and sustainable disposal of batteries are critical aspects of the EV ecosystem, ensuring that the environmental benefits of EVs are not offset by improper battery management.
Grid Integration:
Integrating EVs with the power grid is a complex but essential task. As more EVs come onto the market, they can act as mobile energy storage devices, drawing power from the grid during periods of low demand and returning it during peak hours. This concept, known as vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology, has the potential to stabilize the grid and provide additional revenue streams for EV owners. However, it also requires significant grid infrastructure upgrades to handle the two-way flow of electricity. Smart grid technologies, such as advanced metering infrastructure and demand response systems, will play a vital role in managing this complex interaction.
In summary, the development of a comprehensive infrastructure network is vital to support the electric vehicle revolution. Charging stations, battery technology, and grid integration are the three critical pillars that will determine the success and widespread adoption of EVs. As the industry continues to evolve, investing in these areas will be essential to create a sustainable and efficient transportation future.
Explore Chrysler's Electric Vehicle Lineup: From SUVs to Sedans
You may want to see also

Economic Shifts: New markets, jobs, and cost implications for consumers and industries
The rise of electric vehicles (EVs) is transforming the automotive industry and driving significant economic shifts. As the world accelerates its transition to sustainable transportation, new markets are emerging, creating opportunities for innovation and growth. One of the most notable economic impacts is the creation of new markets for EV components and services. The demand for electric powertrains, advanced batteries, and charging infrastructure has spurred the development of specialized supply chains and manufacturing hubs. Countries and regions are investing in EV-related industries, fostering the growth of new markets and attracting investments. For example, the European Union's ambitious goal of achieving climate neutrality by 2050 has led to substantial investments in EV manufacturing and battery production, creating jobs and stimulating economic activity.
The shift towards EVs also brings about a change in the job landscape. The traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) automotive sector is undergoing a transformation, with a focus on retraining and upskilling the workforce. As EVs require different manufacturing processes and technologies, workers need to adapt to new skills. This includes expertise in battery assembly, software integration, and electric motor maintenance. Consequently, the automotive industry is witnessing a surge in demand for skilled labor, creating new job opportunities in EV manufacturing, research and development, and service sectors. However, the transition also poses challenges, as some jobs in the ICE sector may become obsolete, requiring careful management and support for affected workers.
Consumers are experiencing cost implications as the market for EVs matures. Initially, high production costs and limited supply contributed to higher prices for electric vehicles compared to their ICE counterparts. However, as technology advances and economies of scale take effect, prices are expected to decrease, making EVs more affordable. Governments and businesses are also implementing incentives and subsidies to promote EV adoption, further reducing consumer costs. These economic shifts have the potential to make EVs more accessible to a broader market, fostering a shift in consumer behavior and preferences.
The economic impact of EVs extends beyond the automotive industry, influencing various sectors. The rise of EV-related industries, such as battery recycling and second-life battery applications, creates new business opportunities. Additionally, the integration of EVs with smart grids and energy storage systems opens up possibilities for innovative energy management solutions. Industries like utilities, energy storage manufacturers, and software developers are adapting to the EV market, leading to the creation of new business models and revenue streams.
In summary, the economic shifts associated with electric vehicles are far-reaching. New markets for EV components and services are emerging, driving investments and job creation. The automotive industry is transforming, requiring workforce adaptation and retraining. Consumers are witnessing changing cost dynamics as EVs become more affordable. Furthermore, the influence of EVs extends to various sectors, fostering innovation and the development of new business models. As the world embraces sustainable transportation, these economic shifts will play a crucial role in shaping a greener and more prosperous future.
The Top Electric Vehicles: Unlocking the Longest Range
You may want to see also

Regulatory Changes: Government policies and incentives driving EV adoption
The global shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) is gaining momentum, and governments around the world are playing a pivotal role in accelerating this transition. Regulatory changes and incentives are key drivers in encouraging the widespread adoption of EVs, addressing environmental concerns, and fostering a sustainable future. One of the most common strategies employed by governments is the implementation of subsidies and tax incentives for EV buyers. These financial incentives reduce the upfront cost of purchasing electric cars, making them more affordable and attractive to consumers. For instance, many countries offer tax credits or rebates, which can significantly lower the price of EVs, especially for low- and middle-income families. This approach not only promotes EV sales but also contributes to a more diverse and inclusive market.
In addition to financial incentives, governments are also focusing on infrastructure development to support EV adoption. This includes the establishment of charging stations in public spaces, residential areas, and along major transportation routes. By ensuring convenient and accessible charging options, governments are addressing a critical concern for potential EV owners—range anxiety. Well-planned charging networks encourage people to make the switch, knowing they can easily recharge their vehicles. Moreover, some governments are taking a proactive approach by mandating the inclusion of charging ports in new buildings and residential complexes, further reducing the barriers to EV ownership.
Regulatory changes are another powerful tool in the government's arsenal to promote EV adoption. Stricter emissions standards and regulations are being introduced to phase out the sale of internal combustion engine vehicles. For example, the European Union has set a target to ban the sale of new fossil fuel-powered cars by 2035, pushing manufacturers to invest heavily in EV technology. Such regulations not only drive innovation but also create a market demand for cleaner, more sustainable transportation options. Governments are also implementing policies to phase out the production and sale of coal-fired power plants, further reducing the environmental impact of the EV industry.
The impact of these regulatory changes and incentives is twofold. Firstly, they directly influence consumer behavior, making EVs more desirable and accessible. Secondly, they encourage the development of supporting industries, such as battery manufacturing and recycling, which are essential for the long-term sustainability of the EV market. As a result, governments are not only accelerating the transition to electric mobility but also fostering economic growth and job creation in the green technology sector. This multi-faceted approach to EV adoption is crucial in the fight against climate change and the pursuit of a more sustainable future.
CT's Electric Vehicle Property Tax: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Technological Advancements: Innovations in battery, charging, and autonomous driving
The electric vehicle (EV) market is rapidly evolving, driven by a combination of technological advancements, environmental concerns, and consumer demand. One of the most significant areas of innovation is in battery technology, which has a direct impact on the performance, range, and overall appeal of EVs.
Battery Innovations:
- Energy Density: Researchers are pushing the boundaries of energy density, aiming to fit more energy into smaller, lighter batteries. This is crucial for improving the range of EVs, addressing a major consumer concern. For instance, lithium-ion batteries have seen remarkable progress, with some companies developing cells that offer up to 30% higher energy density than traditional ones.
- Fast Charging: Another critical aspect is the development of fast-charging batteries. While current EV charging infrastructure is adequate for overnight charging, the ability to charge a battery in a matter of minutes is a game-changer. This technology is essential for making EVs more practical for long-distance travel and daily use.
- Solid-State Batteries: A promising innovation is the transition from liquid electrolytes to solid-state batteries. These offer higher energy density, faster charging, and improved safety compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. While still in the development phase, solid-state batteries could revolutionize the EV industry, providing a significant leap in performance and longevity.
Charging Infrastructure:
- Ultra-Fast Charging Stations: The development of ultra-fast charging stations is a key focus. These stations can recharge an EV's battery to 80% capacity in as little as 10-15 minutes. Such rapid charging capabilities are essential for supporting the widespread adoption of EVs, especially for long-haul travel and urban mobility.
- Wireless Charging: Another emerging technology is wireless charging, which eliminates the need for physical charging cables. This concept involves inductive charging pads or ground-based charging systems that can power EVs without direct connection. While still in the early stages, wireless charging has the potential to make EV charging more convenient and accessible.
- Smart Grid Integration: Integrating EV charging with smart grid systems allows for more efficient energy management. This technology enables charging during off-peak hours when electricity is cheaper and more abundant, reducing the strain on the grid and lowering energy costs for EV owners.
Autonomous Driving:
- Advanced Driver Assistance Systems (ADAS): The integration of ADAS features is transforming the driving experience. These systems include lane-keeping assist, adaptive cruise control, and automatic emergency braking, which enhance safety and reduce driver fatigue. As ADAS technology advances, it is becoming increasingly capable of handling complex driving scenarios, bringing us closer to fully autonomous vehicles.
- Machine Learning and Sensor Fusion: Autonomous driving relies heavily on machine learning algorithms and sensor fusion. These technologies enable vehicles to perceive their surroundings, make decisions, and navigate through various environments. With continuous improvements in sensor technology and data processing, autonomous EVs are becoming more reliable and efficient.
- Regulation and Safety: As autonomous driving technology advances, regulatory frameworks are being developed to ensure safety and accountability. This includes guidelines for vehicle-to-infrastructure communication, data privacy, and liability in autonomous vehicle accidents. Striking a balance between innovation and safety is crucial for the widespread acceptance of autonomous EVs.
In summary, the future of electric vehicles is shaped by continuous technological advancements in battery technology, charging infrastructure, and autonomous driving systems. These innovations are not only improving the performance and convenience of EVs but also addressing critical challenges such as range anxiety, charging times, and safety. As the industry continues to evolve, we can expect to see even more groundbreaking developments that will further accelerate the transition to a sustainable transportation ecosystem.
Unveiling the Power of Full Hybrid Electric Vehicles: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The main objective is to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. EVs are seen as a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, as they produce zero tailpipe emissions.
Electric cars help decrease air pollution by eliminating the release of harmful pollutants like nitrogen oxides and particulate matter. They also reduce noise pollution, as EVs are generally quieter than conventional vehicles. Additionally, the use of renewable energy sources for charging can further minimize the carbon footprint.
One significant challenge is the development of an extensive and reliable charging infrastructure. The range anxiety associated with EVs, the time required for charging, and the initial higher purchase cost compared to conventional cars are also concerns. However, these issues are being addressed through technological advancements and government incentives.
AA: The rise of EVs has the potential to transform the energy industry. It encourages the integration of smart grids and renewable energy sources. As more people adopt EVs, the demand for electricity will increase, requiring investments in power generation and distribution infrastructure. This shift can also lead to the creation of new business models and opportunities for energy storage and management.
The future of EVs looks promising, with many countries and manufacturers setting ambitious targets for electrification. The technology is expected to become more efficient, affordable, and accessible. As the world moves towards a more sustainable future, electric vehicles are likely to play a pivotal role in reshaping the transportation sector and reducing our reliance on fossil fuels.







