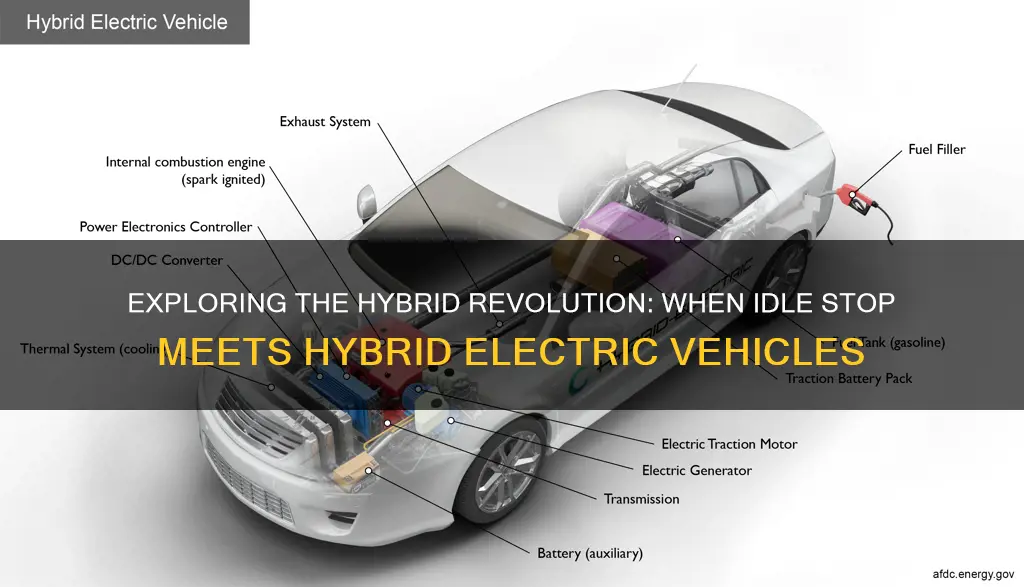
Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) are known for their ability to optimize fuel efficiency and reduce emissions, and one of the key features that contribute to this is the idle stop operation. This technology allows certain HEVs to automatically shut off the engine when the vehicle is stationary and then restart it when needed, such as when the driver applies the accelerator pedal. The type of HEV that incorporates this idle stop function is typically the parallel hybrid design, where the electric motor and internal combustion engine are connected to the wheels, allowing for seamless power distribution and efficient energy management. This design enables the vehicle to switch between electric-only and hybrid modes, providing a smooth driving experience while maximizing fuel economy.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Technology | Hybrid Electric Vehicle (HEV) with Idle Stop |
| Engine Type | Typically a smaller, more efficient gasoline engine |
| Battery Capacity | Varies, but often includes a smaller battery compared to PHEVs |
| Idle Stop Function | Automatically shuts off the engine when stationary to save fuel and reduce emissions |
| Reactivation | Engine restarts automatically when needed (e.g., when driving off or when the air conditioning is active) |
| Performance | Generally offers good fuel efficiency and lower emissions without compromising on driving experience |
| Examples | Toyota Prius, Hyundai Ioniq, Kia Niro |
| Advantages | Improved fuel economy, reduced environmental impact, lower maintenance costs due to fewer moving parts |
| Disadvantages | Limited range compared to plug-in hybrids, slower acceleration due to smaller engine |
What You'll Learn
- Idle Stop Technology: Mechanisms that shut off the engine when stationary to save fuel
- Hybrid System Architecture: Design variations in hybrid vehicles, including parallel and series configurations
- Battery Management: Optimizing battery performance and longevity during idle stop operations
- Engine Restart Control: Systems that smoothly restart the engine after idle stop
- Regenerative Braking: Converting kinetic energy into electrical energy during braking, enhancing efficiency

Idle Stop Technology: Mechanisms that shut off the engine when stationary to save fuel
Idle Stop Technology is a feature found in certain hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) that aims to reduce fuel consumption and emissions by temporarily shutting down the engine when the vehicle is stationary. This technology is particularly useful in urban driving conditions where vehicles often spend a significant amount of time idling at traffic lights or in traffic jams. By implementing this mechanism, HEVs can achieve improved fuel efficiency and contribute to a more environmentally friendly driving experience.
The primary function of Idle Stop Technology is to eliminate unnecessary fuel consumption during prolonged stops. When the driver applies the brakes and comes to a complete stop, the system detects this and automatically switches off the engine. This process is often triggered by sensors that monitor the vehicle's speed, brake pressure, and engine load. Once the engine is shut off, the vehicle relies on its electric motor and battery power to maintain functionality, such as powering the air conditioning, lights, and other electrical systems.
The mechanism behind this technology involves a sophisticated control unit that manages the interaction between the engine, transmission, and other vehicle systems. When the driver releases the brakes and prepares to move off, the control unit sends a signal to restart the engine, ensuring a smooth transition back to normal operation. This process is nearly imperceptible to the driver, providing a seamless driving experience.
One of the key advantages of Idle Stop Technology is its ability to significantly reduce fuel consumption in stop-and-go traffic. Traditional internal combustion engines waste a considerable amount of fuel while idling, especially in urban areas with frequent stops. By implementing this technology, HEVs can save fuel and reduce the overall environmental impact of transportation. Additionally, the technology contributes to a quieter and more comfortable driving environment, as the engine noise is minimized during prolonged stops.
In summary, Idle Stop Technology is a valuable feature in hybrid electric vehicles, offering a practical solution to reduce fuel consumption and emissions. This mechanism's ability to shut off the engine when stationary showcases the potential for improved efficiency and environmental sustainability in the automotive industry. As hybrid technology continues to evolve, such innovations will play a crucial role in shaping the future of eco-friendly transportation.
Unleash the Power: Electric Vehicle Tracking Systems Explained
You may want to see also

Hybrid System Architecture: Design variations in hybrid vehicles, including parallel and series configurations
The architecture of hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) plays a crucial role in determining their efficiency, performance, and overall driving experience. The two primary system configurations are the parallel and series hybrid architectures, each offering distinct advantages and use cases.
Parallel Hybrid System:
In a parallel hybrid configuration, the internal combustion engine (ICE) and the electric motor operate independently, each driving the wheels directly or through a transmission. This setup allows for seamless power distribution between the two sources. When the vehicle is in motion, the ICE and the electric motor can work together, providing a smooth and efficient driving experience. For example, during acceleration, the electric motor delivers an immediate boost of power, while the ICE takes over at higher speeds, optimizing fuel efficiency. One of the key advantages of this design is the ability to use the electric motor for low-speed driving, reducing fuel consumption and emissions. Additionally, the parallel system often includes a generator that recharges the battery pack during deceleration, further enhancing efficiency.
Series Hybrid System:
In contrast, a series hybrid architecture connects the ICE directly to the generator, which produces electricity to power the electric motor and, subsequently, the vehicle's wheels. This configuration is often associated with a larger electric motor, which acts as the primary power source. The ICE's role is to generate electricity and maintain the battery charge, especially during high-speed or high-load conditions. Series hybrids typically offer improved efficiency over long distances, as the electric motor provides the driving force, and the ICE focuses on electricity generation. This design is particularly beneficial for vehicles that require frequent stops and starts, such as city-based cars, as the electric motor can seamlessly handle the stop-and-go traffic without the need for a traditional transmission.
The choice between these two architectures depends on various factors, including the vehicle's intended use, performance requirements, and environmental considerations. Parallel hybrids are often favored for their ability to provide a more conventional driving experience, similar to traditional vehicles, while also offering improved fuel efficiency. Series hybrids, on the other hand, excel in efficiency and performance, especially in urban environments, where frequent stops and starts are common.
In the context of idle stop operation, both configurations can be adapted to include this feature. For parallel hybrids, the electric motor can be utilized to stop the ICE temporarily, reducing fuel consumption during idling. In series hybrids, the electric motor can seamlessly handle the vehicle's power needs during stops, allowing for efficient idle stop functionality. This technology is becoming increasingly important as vehicle manufacturers aim to meet stricter emissions standards and improve overall fuel economy.
Porsche's Electric Future: Rebate Eligibility Explained
You may want to see also

Battery Management: Optimizing battery performance and longevity during idle stop operations
The concept of idle stop technology in hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) is designed to optimize fuel efficiency and reduce emissions by shutting down the engine when the vehicle is stationary. This feature is particularly beneficial for urban driving, where vehicles often spend a significant amount of time idling. However, the frequent activation and deactivation of the engine during idle stop operations can place additional strain on the battery, impacting its performance and longevity. Therefore, effective battery management is crucial to ensure the HEV's overall efficiency and reliability.
During idle stop operations, the battery plays a critical role in supplying power to the vehicle's electrical systems when the engine is off. This includes powering the air conditioning, radio, and other accessories, as well as providing the necessary energy to restart the engine. To optimize battery performance, advanced battery management systems (BMS) are employed. These systems monitor and control various parameters, such as voltage, current, and temperature, to ensure the battery operates within its optimal range. By maintaining the battery at the ideal state of charge, the BMS can enhance efficiency and extend the battery's lifespan.
One key aspect of battery management is temperature control. Extreme temperatures, whether hot or cold, can negatively impact battery performance. During idle stop operations, the battery may experience rapid temperature fluctuations, especially in vehicles with less insulated batteries. To mitigate this, some HEVs employ thermal management systems that regulate the battery temperature. These systems can include heating or cooling elements, or even utilize the vehicle's air conditioning or heating systems to maintain an optimal temperature range. By keeping the battery within the desired temperature window, its performance and longevity can be significantly improved.
Another important strategy for optimizing battery performance during idle stop operations is efficient energy recovery and storage. When the engine is shut off, kinetic energy that would otherwise be lost as heat is captured and stored in the battery. This process, known as regenerative braking, is a hallmark of HEVs and helps recharge the battery. The BMS ensures that this energy is effectively captured and distributed to the battery, maximizing its charge. Additionally, the BMS can prioritize energy usage, ensuring that critical electrical systems remain powered even during extended idle stop periods.
In summary, battery management is a critical component of HEVs with idle stop technology. By implementing advanced BMS, controlling temperature, and efficiently managing energy recovery, these vehicles can optimize battery performance and longevity. This not only enhances the overall efficiency of the HEV but also contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly mode of transportation. As the demand for fuel-efficient vehicles continues to grow, effective battery management will play an increasingly vital role in the widespread adoption of hybrid electric vehicles.
The Evolution of Hybrid and Electric Cars: A Green Revolution
You may want to see also

Engine Restart Control: Systems that smoothly restart the engine after idle stop
The Engine Restart Control system is a crucial component in hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) equipped with idle stop technology. This system ensures a seamless and efficient transition when the vehicle is ready to resume motion after being stationary. The primary goal is to minimize the time and effort required to restart the engine, providing a smooth driving experience while optimizing fuel efficiency.
When the vehicle is stationary and the driver applies pressure to the accelerator pedal, the Engine Restart Control system springs into action. It employs a sophisticated sensor network to detect the driver's intention to restart the engine. These sensors monitor various parameters, including vehicle speed, pedal position, and engine speed, to ensure a precise and timely response. Once the system receives the appropriate signals, it initiates the engine restart process.
The process begins with a controlled electrical pulse to the starter motor, which is designed to minimize the risk of damage to the starter and the battery. This pulse is carefully calibrated to ensure the engine starts smoothly without excessive strain. As the engine turns over, the Engine Restart Control system monitors the engine speed and adjusts the fuel injection and ignition timing accordingly. This fine-tuning process ensures that the engine starts at the optimal point, reducing the risk of stalling and improving overall performance.
One of the key advantages of this system is its ability to prevent engine stalling during restart. By precisely controlling the engine's restart, the system can maintain a steady speed, even under heavy load conditions. This is particularly important in HEVs, where the engine often operates at lower RPMs due to the presence of the electric motor. The Engine Restart Control system's ability to manage this transition ensures that the vehicle can quickly and smoothly resume motion without any abrupt stops or jerks.
Furthermore, the Engine Restart Control system contributes to the overall efficiency of the HEV. By optimizing the engine restart, it reduces the time the engine spends idling, which directly translates to lower fuel consumption and reduced emissions. This feature is especially beneficial in urban driving conditions, where frequent stops and starts are common, and fuel efficiency is a critical factor. The system's ability to smoothly restart the engine after idle stop operations enhances the overall driving experience and aligns with the environmental benefits of hybrid technology.
CT's Electric Vehicle Property Tax: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Regenerative Braking: Converting kinetic energy into electrical energy during braking, enhancing efficiency
Regenerative braking is a key feature of hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) that significantly contributes to their efficiency and performance. This innovative technology harnesses the kinetic energy that would otherwise be lost during braking and converts it into electrical energy, which is then stored in the vehicle's battery. By doing so, regenerative braking not only extends the vehicle's range but also reduces the overall energy consumption, making it an essential component of modern HEVs.
When a driver applies the brakes in a vehicle equipped with regenerative braking, the electric motor switches to generator mode. This means that instead of simply absorbing the kinetic energy and converting it into heat, as in traditional friction brakes, the motor-generator system captures this energy and transforms it back into electrical power. This process is particularly effective during deceleration and when the vehicle is moving at lower speeds, as the kinetic energy is more readily available for conversion.
The efficiency of regenerative braking is a result of its ability to recover energy that would otherwise be wasted. In conventional vehicles, braking systems dissipate kinetic energy as heat, leading to a loss of performance and fuel efficiency. In contrast, HEVs with regenerative braking systems can convert a substantial portion of this energy back into usable power, improving overall efficiency by up to 15%. This technology is especially beneficial in city driving, where frequent stops and starts are common, as it helps to maintain the vehicle's battery charge and reduce fuel consumption.
The process of regenerative braking is seamless and often goes unnoticed by the driver. When the brakes are applied, the electric motor's rotation is reversed, and the kinetic energy is directed back into the battery. This action recharges the battery, providing additional power for the electric motor and, consequently, improving the vehicle's overall performance. The system is designed to work in conjunction with the traditional braking system, ensuring that the vehicle can still stop effectively even when the electric motor is not engaged.
In summary, regenerative braking is a critical technology in HEVs, offering a practical solution to enhance efficiency and performance. By converting kinetic energy into electrical power, it reduces energy waste, extends vehicle range, and contributes to a more sustainable driving experience. This feature is a key differentiator for HEVs, providing drivers with a more environmentally friendly and cost-effective alternative to conventional vehicles.
Understanding kWh: Powering Your Electric Vehicle's Range
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Idle stop is a feature in hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) that automatically shuts off the engine when the vehicle is stationary and the brakes are applied, and restarts it when the driver releases the brake pedal or needs to accelerate. This technology helps to reduce fuel consumption and emissions by preventing the engine from idling unnecessarily.
The majority of Hybrid Electric Vehicles, especially those designed for efficiency and eco-friendliness, incorporate idle stop technology. This includes full-hybrid systems like the Toyota Prius, which can run solely on electric power at low speeds and during stop-and-go traffic, and also offer idle stop capabilities.
While idle stop technology is generally beneficial for fuel economy and environmental impact, it may not be suitable for all driving conditions. In colder climates, frequent restarting of the engine can be challenging, and some drivers might find the process of restarting the engine slightly slower than a conventional vehicle. However, modern HEVs often include advanced systems to manage this, ensuring a smooth and efficient driving experience.