The electric vehicle (EV) tax credit is a financial incentive designed to encourage the adoption of electric cars and reduce the environmental impact of transportation. This credit is available to individuals and businesses who purchase or lease eligible electric vehicles. To qualify, the vehicle must meet specific criteria, including being new, purchased or leased after December 31, 2020, and meeting certain performance standards. Additionally, the vehicle must be used primarily for personal transportation, and the buyer or lessee must have a valid tax return filed for the year of purchase or lease. Understanding these qualifications is essential for anyone considering an EV purchase to ensure they can take full advantage of this valuable tax benefit.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
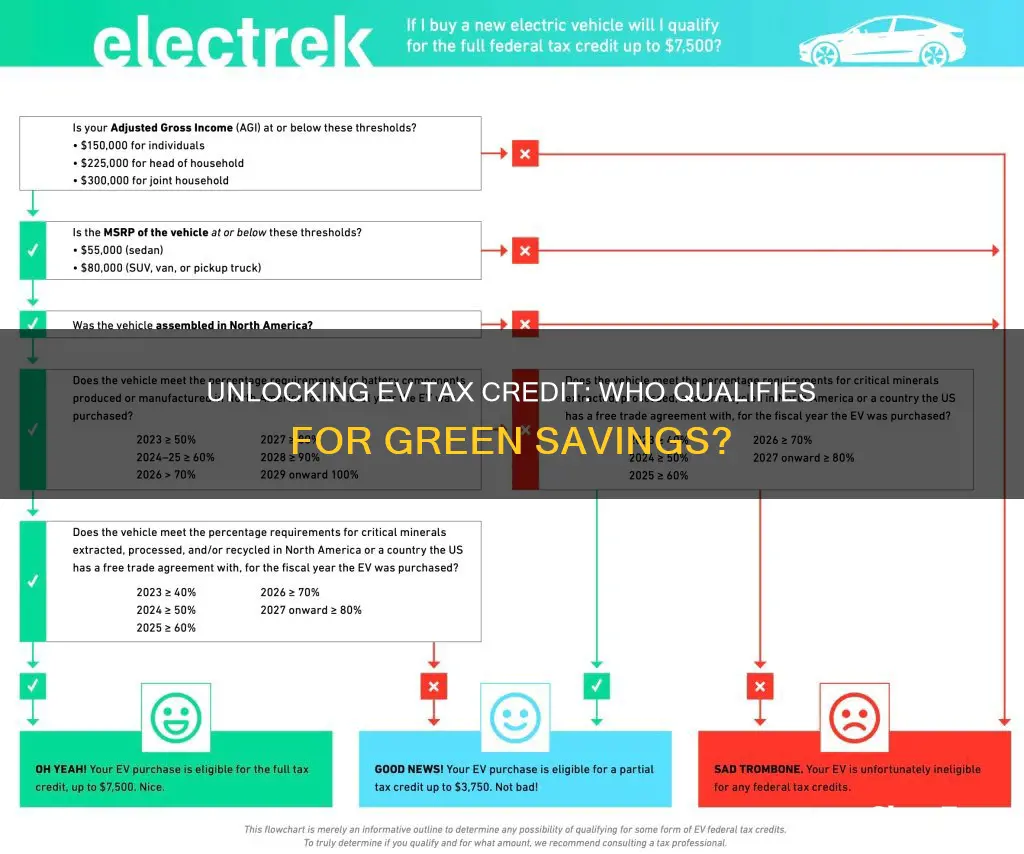
| Income Limit | The income limit for the tax credit is based on the vehicle's price. For vehicles priced up to $80,000, the income limit is $200,000 for individuals and $400,000 for joint filers. For vehicles priced between $80,001 and $150,000, the limit is $300,000 for individuals and $600,000 for joint filers. |
| Manufacturers and Dealers | The tax credit applies to vehicles purchased from participating dealers and manufacturers. This includes Tesla, Ford, Chevrolet, and many other brands. |
| Vehicle Type | The credit is available for new and used electric vehicles, including plug-in hybrids and fuel cell vehicles. |
| Battery Capacity | There is no specific battery capacity requirement, but the vehicle must have a battery that can be charged from an external source. |
| Assembly Location | The vehicle must be assembled in the United States or in a country that has a free trade agreement with the US. |
| Import Duties | The tax credit does not apply to imported vehicles, but it may apply to vehicles assembled in a country with a free trade agreement. |
| Resale and Trade-In | The tax credit can be claimed even if the vehicle is resold or traded in after a certain period. |
| Tax Credit Amount | The credit is typically a percentage of the vehicle's price, up to a certain limit. For example, the credit can be up to 30% of the vehicle's price for vehicles priced below $80,000. |
| Eligibility Period | The tax credit is available for vehicles purchased after December 31, 2020, and before January 1, 2026, or until the credit is fully utilized. |
| Phase-Out | The credit may phase out for individuals with adjusted gross income above certain thresholds. |
What You'll Learn
- Income Limits: Tax credits available for those with income below a certain threshold
- Vehicle Type: Only specific EV models and brands qualify
- Purchase Date: The timing of the purchase affects eligibility
- Residency: Tax credit eligibility may vary by state or country
- Income Verification: Documentation is required to prove income for tax credit claims

Income Limits: Tax credits available for those with income below a certain threshold
The electric vehicle (EV) tax credit is a financial incentive designed to encourage the adoption of electric cars and reduce the environmental impact of the transportation sector. This credit is a significant benefit for individuals and businesses looking to make a positive environmental change while also saving money. However, it's important to understand that this credit is not universally available to everyone; it is means-tested and has specific income thresholds that applicants must meet.
For individuals, the income limit is a crucial factor in determining eligibility. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) sets a maximum adjusted gross income (AGI) threshold for EV tax credits. For the 2023 tax year, this threshold is set at $150,000 for single filers and $300,000 for joint filers. This means that individuals with an AGI above these limits are not eligible for the full tax credit. The credit amount is phased out for those with incomes above these thresholds, reducing the benefit proportionally.
For businesses, the rules can be slightly different. Corporate entities may qualify for the tax credit if they meet specific criteria, such as being a manufacturer or importer of electric vehicles. Additionally, businesses with a higher income threshold may be eligible for a different type of EV tax credit, which is designed to support the production and sale of electric vehicles. These credits often have their own set of income-based limitations, ensuring that the support goes to those who need it most.
It's important to note that these income limits are not static and can change over time due to legislative updates and economic considerations. Therefore, it is essential to stay informed about the latest regulations and consult official sources or tax professionals to ensure compliance with the current requirements.
In summary, the electric vehicle tax credit is a valuable incentive, but it is not accessible to everyone. Income limits play a critical role in determining eligibility, with different thresholds for individuals and businesses. Understanding these limits is essential for those looking to take advantage of this credit and make a positive environmental impact while potentially saving on tax liabilities.
Electric Vehicle Prices: A Comprehensive Guide to Average Costs
You may want to see also

Vehicle Type: Only specific EV models and brands qualify
The electric vehicle (EV) tax credit is a significant incentive for consumers to purchase electric cars, but it's important to understand that not all EVs qualify for this benefit. The qualification criteria are primarily based on the vehicle type and its specific attributes. Here's a detailed breakdown of the vehicle type requirements:
When it comes to vehicle type, the EV tax credit is designed to support a wide range of electric cars, but with some specific conditions. Firstly, the vehicle must be a new, qualified electric vehicle, which means it should be purchased new and not a used car. This ensures that the credit is directed towards the promotion of new electric vehicles, encouraging the adoption of cleaner transportation. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) has a list of qualified vehicles that meet the necessary standards, and this list is regularly updated.
The qualification is not limited to a particular brand or manufacturer, but rather, it focuses on the vehicle's specifications. EVs that qualify must have a battery range of at least 100 miles and a battery weight of no more than 100 pounds per kilowatt-hour (kWh). These specifications ensure that the vehicle has sufficient range and battery efficiency to be considered a viable electric car. Additionally, the vehicle should be manufactured in the United States or imported from a country that has a free trade agreement with the U.S., ensuring that the production and supply chain meet certain criteria.
Furthermore, the EV tax credit also considers the vehicle's price. The qualified vehicle's manufacturer's suggested retail price (MSRP) must not exceed $80,000 for new cars and $50,000 for used cars (with specific adjustments for certain states). This price cap ensures that the credit is accessible to a broader range of consumers and encourages the purchase of more affordable electric vehicles.
It's worth noting that the EV tax credit is a valuable incentive, but it is not a one-time benefit. The credit is typically available for multiple years, allowing consumers to take advantage of the tax benefit over an extended period. This long-term incentive can significantly impact the decision-making process for EV buyers, making it an essential factor to consider when purchasing an electric vehicle.
In summary, the EV tax credit's vehicle type qualification is a critical aspect of the program, ensuring that the credit supports the right vehicles and encourages the adoption of electric cars with specific attributes. Understanding these requirements is essential for consumers to maximize the benefits of the tax credit and make informed decisions when purchasing an electric vehicle.
Unveiling the Resale Secrets: Electric Vehicles' Value
You may want to see also

Purchase Date: The timing of the purchase affects eligibility
The timing of your electric vehicle (EV) purchase is a crucial factor in determining your eligibility for the federal tax credit. This credit is designed to incentivize the adoption of electric cars and promote a cleaner environment. Here's a breakdown of how the purchase date influences your qualification:
Purchase Date and Eligibility: The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) has specific rules regarding the timing of the purchase. The tax credit is available for vehicles that are purchased and placed in service after December 31, 2021. This means that if you buy an EV before this date, you may not be eligible for the credit. The IRS has been updating its guidelines, and as of my last update, the latest rules state that the vehicle must be acquired and used for business or personal purposes after the specified date. This is a critical point to remember, as it directly impacts your ability to claim the credit.
Recent Purchases: For those who have recently purchased an EV, it's essential to check the exact date of the transaction. The IRS provides guidelines for dealers and manufacturers to ensure accurate reporting of these sales. If your purchase date is after the specified cut-off, you are likely eligible for the tax credit. However, if the purchase was made earlier, you might need to explore other incentives or wait for future updates to the tax credit program.
Planning Ahead: Prospective EV buyers should be aware of these timing constraints. If you're considering an EV purchase, especially if it's for personal use, it's advisable to plan ahead. Keep track of the latest tax credit regulations and ensure that your purchase aligns with the eligibility criteria. This proactive approach can save you from potential disappointment if you miss the deadline.
Stay Informed: Tax regulations can change frequently, so staying informed is crucial. Regularly check the IRS website or consult with a tax professional to ensure you have the most up-to-date information. Being aware of these changes will help you make informed decisions about your EV purchase and tax benefits.
In summary, the purchase date of your electric vehicle is a critical aspect of qualifying for the tax credit. Understanding the eligibility criteria and staying updated on any changes will ensure that you take full advantage of this incentive, making your EV purchase even more rewarding.
Exploring the World of Battery-Powered Cars: An In-Depth Guide
You may want to see also

Residency: Tax credit eligibility may vary by state or country
The availability of tax credits for electric vehicles (EVs) is a significant incentive for many individuals and businesses, but it's important to understand that these benefits are often tied to specific residency requirements. Tax credit eligibility for EVs can vary depending on the state or country you reside in, and these variations can impact who is eligible for the financial incentives.
In the United States, for instance, the federal government has offered a tax credit for EV purchases since 2006. However, the rules surrounding this credit have changed over the years, and certain states have also implemented their own EV incentives. As of my last update in 2023, the federal tax credit for EVs is available to individuals who purchase or lease new electric vehicles, provided they meet specific criteria. These criteria include the vehicle's final assembly in North America, the vehicle's price, and the taxpayer's income level. However, it's crucial to note that not all states offer the same federal tax credit; some states provide additional incentives or have their own residency-based requirements. For example, California has its own EV incentive program, which includes a separate residency-based qualification process.
In other countries, the situation can be even more complex. Many nations have introduced incentives to promote EV adoption, but the residency rules can vary widely. For instance, in the European Union, some member states offer tax credits or rebates for EV purchases, but these benefits are often limited to residents of that particular country or region. Each EU country has its own set of criteria and eligibility rules, which can include factors such as income, vehicle type, and residency duration. Similarly, in Asia, countries like Japan and South Korea provide EV subsidies, but these are typically available only to citizens or permanent residents, with specific residency conditions.
When considering EV tax credits, it is essential to research the residency requirements of the state or country you are in. These requirements can significantly impact your eligibility for the financial incentives. For instance, if you move to a new state or country, you may need to re-evaluate your eligibility for the EV tax credit, as the rules and criteria can change. Additionally, understanding these residency-based eligibility criteria is crucial for businesses looking to invest in EVs, as it can influence their decision-making process and potential savings.
In summary, the residency factor is a critical aspect of qualifying for EV tax credits, as it varies across different regions. Whether you are an individual or a business, being aware of these residency-based requirements is essential to ensure you take advantage of the available incentives and make informed decisions regarding your EV purchases or investments. Always consult official government resources and tax professionals to stay updated on the specific rules and eligibility criteria for your jurisdiction.
The Rise of Electric Vehicles: Are They the Ultimate Winners?
You may want to see also

Income Verification: Documentation is required to prove income for tax credit claims
When it comes to claiming the electric vehicle (EV) tax credit, income verification is a crucial aspect that cannot be overlooked. The tax credit is designed to incentivize the purchase of electric vehicles, but to ensure fair distribution, authorities require proof of income to determine eligibility. This process is an essential step to maintain the integrity of the program and ensure that the benefits reach those who truly need them.
The primary purpose of income verification is to assess an individual's or household's financial situation and determine if they meet the income thresholds set by the tax credit program. These thresholds are often based on federal or state guidelines, and they vary depending on the specific EV tax credit scheme. For instance, some programs may offer tax credits to low-income earners, while others might target middle-income families or individuals. Therefore, providing accurate documentation is vital to demonstrate one's financial status.
The documentation required for income verification can include various sources and types of evidence. Typically, individuals will need to submit pay stubs, tax returns, or income statements from their employers. These documents should reflect the individual's or household's total income over a specific period, usually the previous year. In some cases, self-employed individuals may need to provide business financial records, profit and loss statements, or bank statements to prove their income. It is essential to gather these documents well in advance to ensure a smooth application process.
Additionally, supporting documents such as bank statements, investment portfolios, or any other relevant financial records can be useful to provide a comprehensive view of one's income. These supplementary materials can help illustrate consistent income sources or any other financial activities that might impact eligibility. It is advisable to keep these records organized and easily accessible to streamline the verification process.
In summary, income verification is a critical step in the EV tax credit application process, ensuring that the benefits are granted to eligible individuals. By providing accurate and comprehensive documentation, applicants can demonstrate their financial status and increase their chances of successfully claiming the tax credit. It is always recommended to consult the specific guidelines provided by the tax credit program or relevant authorities to understand the exact documentation requirements.
Unveiling the Perfect Voltage: Optimizing Power for Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The tax credit is available to individuals and businesses who purchase or lease new electric vehicles, including cars, trucks, and motorcycles, that meet specific criteria.
To qualify, the vehicle must be new, have a battery capacity of at least 4 kWh, and be manufactured in compliance with the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) guidelines. It should also be purchased or leased after December 31, 2009.
Yes, the tax credit applies to both purchases and leases. However, the rules for claiming the credit differ between the two methods. For leases, the credit is typically claimed by the lessee, while for purchases, it is claimed by the vehicle owner.
No, there are no specific income limits set by the IRS for this tax credit. It is generally available to all taxpayers who meet the vehicle and purchase/lease requirements.
The tax credit amount varies based on the vehicle's battery capacity and the manufacturer's compliance with IRS guidelines. The credit can be up to a certain percentage of the vehicle's price, and it phases out for vehicles with higher prices and more advanced battery technologies.