Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained significant popularity as a sustainable transportation alternative, but their environmental impact is a subject of ongoing debate. One crucial aspect of this discussion is whether EVs truly contribute to reducing emissions. While EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, the process of generating electricity to power them can vary in its environmental impact. This paragraph will explore the complex relationship between electric vehicles and emissions, examining the factors that determine their overall contribution to a cleaner environment and the potential challenges they face in achieving a truly sustainable future.
What You'll Learn
- Environmental Impact: EVs reduce carbon emissions, but production and disposal still impact the environment
- Energy Efficiency: Electric cars are more efficient, using less energy per mile than traditional cars
- Renewable Energy: Charging EVs with renewable energy sources can further reduce emissions
- Cost Savings: Lower fuel and maintenance costs can offset higher upfront costs
- Government Incentives: Tax credits and subsidies can make EVs more affordable and environmentally beneficial

Environmental Impact: EVs reduce carbon emissions, but production and disposal still impact the environment
The environmental benefits of electric vehicles (EVs) are well-known, primarily due to their zero-tailpipe emissions, which significantly reduce air pollution and carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions compared to conventional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. However, it's important to consider the entire lifecycle of an EV to fully understand its environmental impact. While EVs are a cleaner alternative on the road, their production and disposal processes can still have environmental consequences.
The manufacturing of electric vehicles involves complex processes that require substantial energy and resources. The production of batteries, in particular, is energy-intensive and can result in significant greenhouse gas emissions. Mining and processing the raw materials for batteries, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, can lead to environmental degradation, habitat destruction, and water pollution if not managed sustainably. Additionally, the manufacturing process itself may involve the use of fossil fuels, contributing to emissions during the early stages of an EV's lifecycle.
Another critical aspect is the end-of-life management of EVs. As batteries degrade over time, they may need to be replaced or recycled. Improper disposal of EV batteries can lead to environmental hazards. If not recycled or disposed of correctly, the chemicals and materials in batteries can leach into the soil and water, causing pollution. However, proper recycling and disposal methods are essential to minimizing these impacts. Many countries and manufacturers are investing in developing efficient recycling processes to ensure that EV batteries are safely and sustainably managed at the end of their useful life.
Despite these considerations, the overall environmental impact of EVs is still favorable compared to ICE vehicles. The reduction in carbon emissions from driving an EV far outweighs the emissions from its production and disposal. As technology advances and manufacturing processes become more efficient, the environmental footprint of EVs continues to improve. Furthermore, the shift towards renewable energy sources for electricity generation further enhances the environmental benefits of EVs, making them an increasingly attractive and sustainable transportation option.
In summary, while the production and disposal of EVs do have environmental implications, the overall environmental impact is positive due to the significant reduction in carbon emissions during operation. The focus on sustainable manufacturing, recycling, and the transition to renewable energy sources will further minimize the environmental footprint of EVs, making them a key component in the fight against climate change and the transition to a greener future.
Unveiling Porsche's Electric Revolution: A Sustainable Sports Car Evolution
You may want to see also

Energy Efficiency: Electric cars are more efficient, using less energy per mile than traditional cars
Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained significant attention as a potential solution to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and improve energy efficiency. One of the key advantages of electric cars is their superior energy efficiency compared to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. This efficiency is a result of several factors that contribute to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly mode of transportation.
Firstly, electric motors are inherently more efficient in converting energy into motion. While traditional cars waste a considerable amount of energy as heat, electric motors produce less waste heat and convert a higher percentage of energy into useful work. This is because electric motors operate at higher efficiency levels, especially at lower speeds, which are common during urban driving conditions. As a result, electric cars use less energy per mile, making them more energy-efficient.
The efficiency of electric vehicles is further enhanced by their ability to recover and reuse energy through regenerative braking. When an EV brakes, the electric motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery. This process significantly reduces the energy lost as heat during braking, improving overall efficiency. In contrast, conventional cars rely solely on friction-based braking systems, which dissipate energy as heat, leading to increased fuel consumption and higher emissions.
Additionally, the design and weight distribution of electric cars contribute to their energy efficiency. EVs typically have a lower center of gravity due to the placement of the battery pack, which improves handling and reduces energy loss. The lightweight construction of many electric vehicles, often utilizing materials like aluminum and carbon fiber, further enhances efficiency by reducing the overall weight, resulting in less energy required to accelerate and maintain speed.
In summary, electric cars offer a more efficient alternative to traditional vehicles, utilizing advanced motor technology and innovative design principles. By using less energy per mile, electric vehicles contribute to reduced emissions and a more sustainable transportation system. As the world seeks to transition towards cleaner energy sources, the energy efficiency of electric cars becomes an increasingly important factor in the debate over the environmental benefits of electric vehicles.
Powering Electric Vehicles: The Role of Inverters in Energy Conversion
You may want to see also

Renewable Energy: Charging EVs with renewable energy sources can further reduce emissions
The integration of electric vehicles (EVs) into our transportation systems offers a promising avenue to combat climate change and reduce emissions. One of the key advantages of EVs is their potential to significantly lower greenhouse gas emissions compared to conventional internal combustion engine vehicles. However, the environmental benefits of EVs extend beyond their tailpipe emissions. When it comes to charging these vehicles, the source of electricity plays a crucial role in determining the overall environmental impact.
Charging EVs with renewable energy sources is a powerful strategy to maximize the emission-reduction potential of electric mobility. Renewable energy, such as solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal power, produces electricity with minimal greenhouse gas emissions. Unlike traditional fossil fuel-based electricity generation, renewable sources offer a cleaner and more sustainable alternative. By utilizing these renewable energy sources to power EV charging stations, we can ensure that the electricity used to recharge these vehicles is generated with a low carbon footprint.
The benefits of renewable energy for EV charging are twofold. Firstly, it directly contributes to reducing the overall emissions associated with vehicle operation. When EVs are charged using renewable energy, the electricity consumption is effectively carbon-neutral, meaning the vehicle's environmental impact is significantly lower compared to using non-renewable energy sources. This is especially important in regions where electricity generation heavily relies on fossil fuels, as the environmental benefits of EVs can be partially offset by the carbon-intensive nature of their charging process.
Secondly, the adoption of renewable energy for EV charging infrastructure promotes the development of a sustainable and resilient energy system. As the demand for EVs continues to grow, the reliance on renewable energy sources for charging can help diversify the energy mix and reduce the strain on traditional power grids. This shift towards renewable energy integration in the transportation sector is essential for long-term environmental sustainability and energy security.
In summary, charging electric vehicles with renewable energy sources is a critical step towards achieving a greener and more sustainable future. By harnessing the power of renewable energy, we can ensure that EVs contribute significantly to reducing emissions and mitigating climate change. This approach not only benefits the environment but also fosters the development of a robust and eco-friendly energy infrastructure for the transportation industry.
Unveiling the Power of EVSE: Electric Vehicle Revolution
You may want to see also

Cost Savings: Lower fuel and maintenance costs can offset higher upfront costs
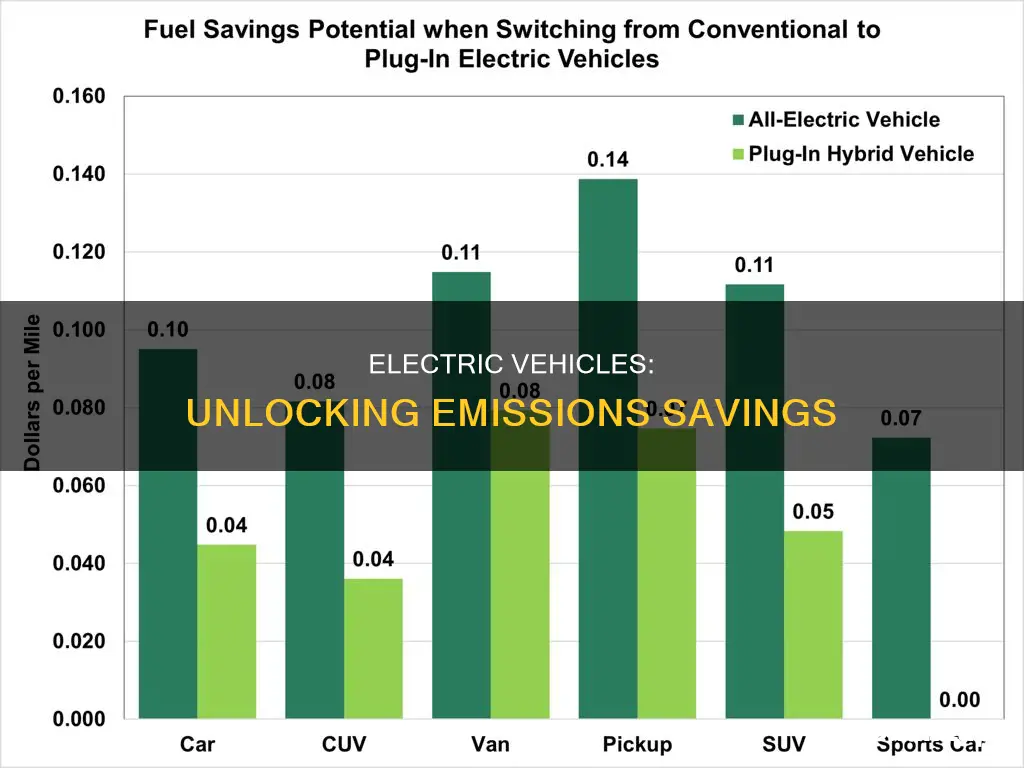
Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained significant popularity in recent years, and one of the key factors driving this trend is the potential for cost savings. While the initial purchase price of an electric car might be higher compared to its gasoline-powered counterparts, the long-term financial benefits can be substantial, especially when considering fuel and maintenance expenses.
One of the most significant advantages of electric vehicles is the substantial reduction in fuel costs. EVs are powered by electricity, which is generally cheaper than gasoline or diesel. The cost of electricity for charging an EV is typically lower per mile compared to the cost of fuel for traditional cars. This is particularly evident when you consider the rising prices of fossil fuels and the increasing demand for energy-efficient solutions. Over time, the savings on fuel can easily offset the higher upfront investment, making electric vehicles an economically viable choice.
In addition to lower fuel expenses, electric cars often require less frequent maintenance, which can lead to significant savings. Traditional internal combustion engines have numerous moving parts that can wear out over time, necessitating regular servicing and replacements. In contrast, electric motors have fewer components, resulting in reduced maintenance needs. This means fewer trips to the mechanic and lower overall maintenance costs for EV owners. With fewer parts to maintain, the risk of unexpected breakdowns is also reduced, providing peace of mind and further contributing to the overall cost-effectiveness of electric vehicles.
The environmental benefits of EVs also play a role in long-term cost savings. As more countries and cities introduce incentives and subsidies for eco-friendly transportation, the financial advantages of going electric become even more appealing. Governments worldwide are promoting the adoption of electric vehicles to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change. These incentives can include tax credits, rebates, or reduced registration fees, directly impacting the owner's wallet. Moreover, the potential for long-term savings through reduced emissions-related costs, such as lower insurance premiums and potential earnings from selling renewable energy credits, further enhances the financial appeal of electric vehicles.
While the initial purchase price of an electric vehicle might be a consideration, the long-term cost savings are undeniable. The reduced fuel and maintenance expenses, coupled with potential government incentives, make EVs an attractive option for those seeking financial efficiency. As technology advances and the infrastructure for charging electric vehicles expands, the accessibility and affordability of electric cars continue to improve, making them an increasingly viable and cost-effective choice for environmentally conscious consumers.
Electric Revolution: A Global Shift Towards Sustainable Driving?
You may want to see also

Government Incentives: Tax credits and subsidies can make EVs more affordable and environmentally beneficial
The financial benefits of electric vehicles (EVs) often extend beyond the initial purchase price, and governments worldwide have recognized this by implementing various incentives to encourage the adoption of EVs. One of the most effective strategies is the use of tax credits and subsidies, which can significantly reduce the overall cost of ownership for EV buyers. These incentives not only make electric vehicles more affordable but also contribute to a greener environment by promoting the reduction of greenhouse gas emissions.
Tax credits are a direct financial benefit to consumers, typically provided as a percentage of the vehicle's purchase price. For instance, many countries offer tax credits that can cover a substantial portion of the EV's cost, making them more accessible to a wider range of buyers. These credits can be especially attractive for high-end electric vehicles, which often carry a premium price tag. By providing tax relief, governments enable individuals and businesses to make the switch to electric mobility without a significant financial burden. This not only stimulates the market but also accelerates the transition to a more sustainable transportation system.
Subsidies, on the other hand, can take various forms, such as direct payments, grants, or reduced registration fees. These incentives are often targeted at specific groups, such as low-income families or businesses looking to promote eco-friendly practices. For example, a government might offer a subsidy to a fleet of taxis, encouraging them to invest in electric vehicles, which can lead to a significant reduction in carbon emissions over time. Subsidies can also be used to support the development of charging infrastructure, ensuring that EV owners have convenient access to charging stations, thus addressing range anxiety and further promoting EV adoption.
The environmental benefits of these government incentives are substantial. By making EVs more affordable, tax credits and subsidies encourage a faster shift towards electric mobility. This rapid transition can lead to a substantial decrease in carbon emissions, as electric vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions. Over time, this can result in improved air quality, reduced pollution, and a significant contribution to global efforts to combat climate change. Moreover, the reduced reliance on fossil fuels can have a positive impact on public health, as air pollution is linked to various respiratory and cardiovascular diseases.
In summary, government incentives in the form of tax credits and subsidies play a crucial role in making electric vehicles more accessible and environmentally friendly. These financial benefits not only lower the upfront cost of EVs but also encourage a faster transition to sustainable transportation. As a result, individuals and businesses are more inclined to choose electric vehicles, leading to a collective effort to reduce emissions and create a cleaner, healthier environment for future generations. This strategy demonstrates a powerful approach to promoting environmental responsibility while also stimulating economic growth in the green technology sector.
Electric Vehicles: Unlocking the True Cost of Green Driving
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
No, electric vehicles do not produce tailpipe emissions. They are powered by electric motors that run on electricity, which can be generated from various sources, including renewable energy like solar and wind power. This makes EVs a cleaner alternative to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, as they help reduce air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions.
EVs significantly reduce emissions by eliminating the need for gasoline or diesel fuel. When charged with electricity, they produce zero direct emissions, unlike ICE vehicles that burn fossil fuels, releasing pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx), carbon monoxide (CO), and particulate matter. This reduction in emissions contributes to improved air quality and a lower carbon footprint.
While the manufacturing and disposal of EVs can have some environmental consequences, their overall environmental impact is generally lower compared to ICE vehicles over their lifecycle. The production of EV batteries and the sourcing of raw materials can result in emissions and environmental degradation, but these effects are typically offset by the reduced emissions during the vehicle's operation.
Yes, widespread adoption of electric vehicles can play a crucial role in achieving global emissions reduction targets. As EVs become more popular, the demand for electricity from renewable sources increases, further reducing the carbon intensity of the transportation sector. This shift can significantly contribute to mitigating climate change and meeting environmental goals.
Many governments and organizations offer incentives and programs to encourage EV ownership and promote emissions reduction. These may include tax credits, rebates, or grants for purchasing EVs, as well as incentives for installing home charging stations. Additionally, some utilities provide special rates for EV charging during off-peak hours, further reducing the environmental impact of EV ownership.