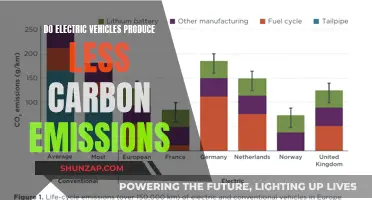
The rise of electric and hybrid vehicles has brought about a revolution in the automotive industry, offering cleaner and more sustainable transportation options. However, beneath the surface, these advancements have sparked a debate about their environmental impact. While they significantly reduce carbon emissions compared to traditional gasoline-powered cars, the production and disposal of their batteries, as well as the sourcing of rare earth minerals, can have detrimental effects on ecosystems and communities. This paragraph delves into the complex relationship between electric and hybrid vehicles and the environment, exploring the challenges and opportunities in creating a truly sustainable transportation future.
What You'll Learn
- Increased Air Pollution: Electric vehicles may emit pollutants during manufacturing and battery disposal
- Resource Depletion: Hybrid and electric cars rely on rare earth metals, causing environmental damage
- Noise Pollution: Electric motors are quieter, but they can still contribute to urban noise issues
- Battery Waste: Improper disposal of lithium-ion batteries poses environmental and health risks
- Grid Impact: High EV charging can strain power grids, potentially leading to increased fossil fuel use

Increased Air Pollution: Electric vehicles may emit pollutants during manufacturing and battery disposal
The environmental impact of electric vehicles (EVs) is a complex issue, and while they are often promoted as a cleaner alternative to traditional gasoline cars, there are several aspects to consider regarding their potential negative effects on air quality. One significant area of concern is the increased air pollution associated with the manufacturing and disposal of electric vehicles, particularly their batteries.
The production of electric vehicles and their components can have a substantial environmental footprint. Manufacturing processes often require substantial energy consumption and can release various pollutants into the atmosphere. For instance, the production of lithium-ion batteries, a common type used in EVs, involves the extraction of raw materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel. These extraction processes can lead to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution if not managed sustainably. Additionally, the manufacturing facilities themselves may emit greenhouse gases and other harmful substances, contributing to air pollution and climate change.
Battery disposal and recycling present another challenge. Lithium-ion batteries contain hazardous materials, and improper disposal can result in significant environmental damage. When these batteries are discarded, they can release toxic chemicals, including lithium, cobalt, and nickel compounds, into the environment. These substances can contaminate soil and water sources, posing risks to ecosystems and human health. Furthermore, the recycling process of batteries is not yet fully optimized, and the energy-intensive nature of recycling can also contribute to air pollution if not carried out efficiently.
The environmental impact of electric vehicles extends beyond their operational phase. The manufacturing and end-of-life management of these vehicles are critical factors in understanding their overall ecological footprint. As the demand for electric transportation grows, it is essential to address these challenges and implement sustainable practices to minimize the adverse effects on air quality and the environment. This includes improving recycling technologies, adopting cleaner production methods, and ensuring responsible disposal of batteries to mitigate the increased air pollution associated with electric vehicle manufacturing and disposal.
Unveiling the Electric Vehicle's MPGe Mystery: A Common Number Revealed
You may want to see also

Resource Depletion: Hybrid and electric cars rely on rare earth metals, causing environmental damage
The widespread adoption of hybrid and electric vehicles (EVs) has brought about a significant shift towards more environmentally friendly transportation, but it has also inadvertently led to a critical issue: resource depletion. These vehicles, while reducing greenhouse gas emissions, heavily depend on rare earth metals, which are extracted through environmentally damaging processes. This reliance on rare earth metals is a double-edged sword, as it contributes to environmental degradation and poses challenges for long-term sustainability.
Rare earth metals, such as neodymium, praseodymium, and dysprosium, are essential components in the production of powerful permanent magnets used in electric motors. These magnets enable the high-performance, efficient operation of electric and hybrid vehicles. However, the extraction of these metals is an energy-intensive and environmentally costly process. Mining operations often result in habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution, as the extraction process can release toxic chemicals and heavy metals into the surrounding ecosystem.
The demand for rare earth metals has surged with the rise of the EV market. As more hybrid and electric cars are manufactured, the need for these metals intensifies. This increased demand has led to the overexploitation of natural resources, particularly in regions with significant rare earth metal deposits. The environmental impact of mining these metals is severe, as it often involves the destruction of natural habitats and the disruption of local ecosystems. For instance, the extraction of neodymium, a key component in EV motors, has been linked to the degradation of ecosystems in China, where a significant portion of the world's neodymium is sourced.
Furthermore, the process of refining and processing rare earth metals is highly energy-intensive, contributing to carbon emissions and further environmental harm. The energy required for this process often comes from non-renewable sources, exacerbating the carbon footprint of the entire supply chain. As a result, while hybrid and electric cars aim to reduce emissions, the production and supply of the necessary components contribute to environmental degradation and resource depletion.
Addressing this issue requires a multi-faceted approach. Firstly, improving the recycling and recovery of rare earth metals from end-of-life vehicles can significantly reduce the demand for new mining operations. Developing more efficient and sustainable extraction methods can also help minimize environmental damage. Additionally, encouraging the use of alternative materials and technologies that reduce the reliance on rare earth metals could be a long-term solution. By implementing these strategies, the environmental impact of hybrid and electric vehicles can be mitigated, ensuring a more sustainable future for the automotive industry and the planet.
Electric Vehicles: Efficiency at High Speeds Explained
You may want to see also

Noise Pollution: Electric motors are quieter, but they can still contribute to urban noise issues
Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained significant popularity due to their environmental benefits, but it's important to consider the potential drawbacks, including their impact on noise pollution. While electric motors are inherently quieter compared to traditional internal combustion engines, they can still contribute to urban noise issues in certain ways.
One aspect to consider is the overall noise environment in cities. As more EVs hit the roads, the overall noise level in urban areas might not decrease as much as expected. This is because electric motors, despite being quieter individually, produce a different sound profile compared to gasoline or diesel engines. The smooth, continuous hum of an electric motor can blend into the urban soundscape, making it challenging to distinguish from other ambient noises. This can lead to an increase in overall noise levels, especially in densely populated areas with high traffic volumes.
Additionally, the infrastructure supporting EV charging and the vehicles themselves can contribute to noise pollution. The sound of charging stations, which often involves high-voltage power systems, can be audible and potentially disruptive. Furthermore, the design of electric vehicles, particularly those with large batteries and heavy components, can result in unique noise characteristics. These factors, combined with the increasing number of EVs on the road, may lead to a complex urban noise environment.
To address this issue, urban planners and policymakers need to consider comprehensive strategies. This includes implementing noise regulations for EV charging stations, encouraging the development of quieter EV designs, and promoting the use of noise-reducing technologies. For instance, active noise cancellation systems could be integrated into charging stations and vehicles to minimize their acoustic impact.
In conclusion, while electric motors are quieter than their internal combustion counterparts, the widespread adoption of EVs can still impact urban noise levels. A holistic approach, involving technological advancements, infrastructure planning, and regulatory measures, is necessary to mitigate the potential noise pollution associated with electric and hybrid vehicles. By doing so, we can ensure that the environmental benefits of EVs are not overshadowed by unintended consequences.
Electric Vehicles: Sales Rising, But Challenges Remain
You may want to see also

Battery Waste: Improper disposal of lithium-ion batteries poses environmental and health risks
The increasing adoption of electric and hybrid vehicles is undoubtedly beneficial for reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality. However, it is essential to consider the environmental impact of these vehicles throughout their entire lifecycle, including the end-of-life phase, where the improper disposal of lithium-ion batteries can have severe consequences.
Lithium-ion batteries are a critical component of electric vehicles, storing and supplying the energy needed to power the vehicle. While these batteries are designed to be durable and long-lasting, they are not indestructible. Over time, batteries can degrade, and if not managed properly, they may become waste. The improper disposal of these batteries can lead to significant environmental and health hazards.
One of the primary concerns is the release of toxic chemicals. Lithium-ion batteries contain various hazardous materials, including lithium, cobalt, nickel, and manganese. When these batteries are not recycled or disposed of correctly, these substances can leach into the environment. For instance, lithium can contaminate soil and water sources, posing risks to ecosystems and potentially affecting human health. Additionally, the combustion of battery components during improper disposal can release toxic fumes, including heavy metals and volatile organic compounds, which can have detrimental effects on both the environment and human well-being.
The environmental impact of battery waste extends beyond chemical leaks. Improper disposal often involves open-air burning or dumping, which can lead to soil and air pollution. This practice contributes to the release of greenhouse gases and can exacerbate climate change. Furthermore, the extraction of raw materials for battery production has its own environmental footprint, including energy consumption and habitat disruption. By not properly managing the end-of-life stage of batteries, we risk undoing the positive environmental impact of electric vehicles.
To mitigate these risks, it is crucial to establish comprehensive recycling and disposal programs for lithium-ion batteries. Manufacturers and consumers should be encouraged to return used batteries to specialized recycling centers or authorized collection points. These facilities employ advanced technologies to safely recover valuable materials while minimizing environmental harm. Proper disposal ensures that batteries are handled and processed according to strict environmental regulations, reducing the potential for pollution and health hazards.
In summary, while electric and hybrid vehicles offer significant environmental benefits, the improper disposal of lithium-ion batteries can have adverse effects. By raising awareness and implementing effective recycling practices, we can ensure that the environmental advantages of these vehicles are not compromised. It is a collective responsibility to address battery waste and promote sustainable solutions for a greener future.
Electric Vehicles: Cost-Effective in the Foothills? Discover the Benefits
You may want to see also

Grid Impact: High EV charging can strain power grids, potentially leading to increased fossil fuel use
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is undoubtedly an environmental step forward, but it also presents unique challenges to our power grids. As more and more EVs hit the roads, the demand for electricity soars, particularly during peak charging times. This surge in electricity usage can have a significant impact on the stability and efficiency of our power grids.
Power grids are designed to meet the electricity demands of various sectors, including residential, commercial, and industrial. With the rise of EVs, the residential sector's electricity consumption increases significantly. Many EV owners charge their vehicles overnight, taking advantage of lower electricity rates. While this behavior is generally beneficial for cost savings, it can lead to a concentrated influx of power demand during specific hours, causing strain on the grid.
The strain on the power grid becomes more pronounced when multiple EVs are charged simultaneously, especially in densely populated areas. This can result in voltage fluctuations and even power outages if the grid infrastructure is not adequately prepared. To manage this, utility companies often implement time-of-use (TOU) rates, encouraging EV owners to charge during off-peak hours when electricity demand is lower. However, this strategy requires a well-maintained and flexible grid infrastructure, which not all regions currently possess.
The potential strain on power grids due to high EV charging has a direct correlation with the increased use of fossil fuels. When the grid is under stress, power plants may need to operate at higher capacities or even switch to backup fossil fuel sources to meet the rising electricity demand. This can lead to a temporary increase in greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution, especially if the power plants are not equipped with advanced emission control technologies. As a result, the environmental benefits of EVs may be partially offset by the additional fossil fuel consumption during grid strain.
To address this challenge, several solutions are being explored. Smart grid technologies can help manage electricity demand more efficiently by communicating with EVs to charge during optimal times. Additionally, investing in renewable energy sources and improving grid infrastructure can reduce the reliance on fossil fuels and ensure a more stable power supply for EV charging. With careful planning and the implementation of these strategies, we can maximize the environmental benefits of electric vehicles while minimizing their impact on our power grids.
Unleash the Power: 5 Signs to Identify Your Hybrid Electric Vehicle
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
While electric and hybrid vehicles are often promoted as eco-friendly alternatives, they still have some environmental drawbacks. Firstly, the production and disposal of their batteries can lead to significant ecological damage due to the extraction of rare earth minerals and the release of toxic chemicals. Secondly, the electricity used to power electric vehicles often comes from fossil fuel-based power plants, which can result in increased greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution, especially if the grid is not powered by renewable sources.
Hybrid vehicles, which combine an internal combustion engine with an electric motor, can have a positive impact on reducing direct tailpipe emissions compared to conventional cars. However, they still contribute to air pollution, particularly in urban areas with heavy traffic. The emissions from the combustion engine during the 'hybrid' mode, where both motors are active, can release pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter, affecting air quality and public health.
Electric vehicles (EVs) have the potential to significantly reduce carbon emissions, especially when charged with electricity from renewable sources. However, the overall environmental benefit depends on various factors. If the electricity generation process is heavily reliant on coal or other fossil fuels, the carbon footprint of EVs may not be as low as expected. Additionally, the manufacturing and transportation of EVs can have environmental consequences, and the end-of-life disposal of batteries requires careful management to minimize ecological impact.