The electric vehicle (EV) tax credit, a significant incentive for consumers to purchase electric cars, has been a game-changer in the automotive industry. However, this incentive is not permanent and is subject to expiration. Understanding when the EV tax credit ends is crucial for anyone considering an electric vehicle purchase, as it can impact the overall cost and financial benefits of owning an EV. This paragraph will explore the timeline of the EV tax credit's availability and its potential implications for the future of sustainable transportation.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| End Date | The EV tax credit is set to end on January 1, 2033, according to the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA). |
| Eligibility | Available to individuals and businesses purchasing new electric vehicles (EVs) in the US. |
| Credit Amount | The credit varies based on the vehicle's battery capacity and manufacturer's domestic investment. |
| Battery Capacity | Vehicles with a battery capacity of at least 40 kWh are eligible for the full credit. |
| Manufacturer's Investment | The credit is also tied to the manufacturer's investment in domestic production and research. |
| Phase-Out | The credit starts to phase out for vehicles with a list price over $80,000 for individuals and $100,000 for businesses. |
| Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) | The IRA provides the tax credit and includes provisions to boost domestic EV production and reduce emissions. |
| Extension Possibility | There have been discussions and proposals to extend the credit, but no official decision has been made. |
What You'll Learn
- Legislative Changes: Tax credit expiration dates may be altered by new laws
- Market Impact: Sales volume and industry trends influence credit availability
- Geographical Variations: Tax credit eligibility varies by region and country
- Vehicle Types: Certain EV models may be excluded from the credit
- Income Limits: Household income caps can affect tax credit eligibility

Legislative Changes: Tax credit expiration dates may be altered by new laws
The future of electric vehicle (EV) tax credits is subject to change, and staying informed about potential legislative updates is crucial for those considering purchasing an EV. The tax credit for electric vehicles, which has been a significant incentive for consumers, is not permanent and is subject to expiration. This has already occurred in some countries, and it is essential to understand the potential implications of these changes.
Legislative bodies often review and modify tax policies, and the expiration date of the EV tax credit is no exception. New laws can be introduced to extend the credit period, modify the eligibility criteria, or even phase out the credit over time. For instance, a government might decide to gradually reduce the tax credit amount each year until it eventually sunsets. This approach ensures a smooth transition and provides a clear timeline for consumers and manufacturers alike.
In some cases, the expiration of the tax credit might be extended due to popular demand and the growing importance of environmental initiatives. As more countries recognize the benefits of reducing carbon emissions, there is a higher likelihood of governments reevaluating and extending these incentives. This could result in a longer-term commitment to supporting the EV market, encouraging more consumers to make the switch.
It is worth noting that the timing of these legislative changes can significantly impact the EV market. If the expiration date is extended, it may stimulate further investment and sales, potentially leading to a surge in EV production and infrastructure development. Conversely, a sudden end to the tax credit could create a temporary dip in the market, affecting both consumers and manufacturers.
Staying updated with the latest news and proposals from legislative bodies is essential for anyone interested in the EV industry. Following relevant news sources and industry publications can provide valuable insights into potential changes. Additionally, keeping an eye on government websites and official communications can offer a comprehensive understanding of the current and future state of EV tax credits. Being proactive in this regard will ensure that individuals and businesses can make informed decisions regarding their EV-related plans.
Boosting Electric Vehicle Adoption: Incentives and Strategies
You may want to see also

Market Impact: Sales volume and industry trends influence credit availability
The electric vehicle (EV) tax credit, a significant incentive for consumers to adopt electric cars, has been a driving force behind the rapid growth of the EV market. However, the availability and duration of this credit are crucial factors that can impact sales volumes and industry trends. As the market matures, understanding the relationship between sales volume and credit availability becomes essential for both consumers and industry stakeholders.
Sales volume plays a pivotal role in the EV industry's dynamics. When sales of electric vehicles surge, it often indicates a growing consumer interest and demand. This increased demand can lead to a positive feedback loop, where higher sales volumes further stimulate the market. As a result, more consumers are likely to consider purchasing EVs, knowing that the tax credit is available to offset the initial cost. This, in turn, can accelerate the industry's growth and encourage manufacturers to invest in EV production and research.
Industry trends, such as technological advancements and market competition, also influence the credit's availability. As EV technology improves and becomes more affordable, the tax credit's impact may diminish over time. For instance, if battery technology advances significantly, reducing the cost of EVs, the tax credit might become less necessary for consumers. This shift in industry trends could lead to a reevaluation of the credit's duration and terms by government bodies.
Moreover, the relationship between sales volume and credit availability is a delicate balance. If the tax credit is perceived as a long-term incentive, it can encourage consumers to make a one-time purchase, potentially leading to a short-term sales spike. However, if the credit is expected to end soon, it might prompt consumers to delay purchases, affecting sales volume in the short term. This dynamic can create a complex market response, requiring careful monitoring by industry analysts and policymakers.
In summary, the market impact of the electric vehicle tax credit is closely tied to sales volume and industry trends. As the EV market evolves, understanding these interconnections is vital for predicting sales patterns and making informed decisions about the credit's future. This knowledge can help stakeholders navigate the market's transition and ensure a sustainable growth trajectory for the electric vehicle industry.
Tesla: The Ultimate Battery Electric Vehicle?
You may want to see also

Geographical Variations: Tax credit eligibility varies by region and country
The availability and duration of tax credits for electric vehicles (EVs) can significantly differ across various geographical regions and countries. These variations are often influenced by government policies, environmental goals, and the overall market demand for EVs. Understanding these geographical differences is crucial for individuals and businesses looking to purchase or invest in electric vehicles.
In the United States, for instance, the federal government has offered a tax credit for EV purchases since 2009. However, the credit amount and eligibility criteria have evolved over time. Initially, the credit was a fixed amount per vehicle, but it has since transitioned to a percentage-based system, currently offering a credit of up to 30% of the vehicle's sale price. Interestingly, this federal tax credit is available nationwide, but certain states have also implemented their own EV incentives, which may provide additional benefits to residents. For example, California's Clean Vehicle Rebate Project offers rebates of up to $7,000 for the purchase or lease of new electric cars, with specific requirements for vehicle models and residency.
In contrast, the European Union has a more unified approach to EV incentives. The EU's Alternative Fuel Infrastructure Regulation (AFIR) provides guidelines for member states to promote the use of alternative fuels, including EVs. Many EU countries have adopted this regulation and introduced their own tax credits or subsidies. For instance, Norway, known for its aggressive EV adoption, offers a tax deduction of up to 50% of the vehicle's price for new electric cars, with a maximum deduction of 200,000 NOK. However, it's important to note that some countries within the EU have different eligibility criteria and application processes for these incentives.
In Asia, the tax credit landscape for EVs is diverse. China, for example, has implemented a series of incentives to boost EV sales, including tax exemptions and subsidies. The country's New Energy Vehicle Tax Policy provides a tax credit of up to 10% of the vehicle's price for electric cars, with certain model and production requirements. On the other hand, Japan's EV tax credit program offers a fixed amount per kilowatt-hour of the vehicle's battery capacity, with a maximum credit of 500,000 yen. These varying approaches reflect the unique economic and environmental priorities of each Asian country.
Furthermore, some countries have specific eligibility criteria based on residency, income, or vehicle specifications. For instance, in the United Kingdom, the Plug-in Car Grant provides a maximum grant of £3,000 for new electric cars, but this is only available to residents in the UK and Northern Ireland. Similarly, in Canada, certain provinces offer tax credits or rebates, but these are often targeted at specific demographics or vehicle types, such as zero-emission vehicles or those with lower emissions.
Understanding these geographical variations is essential for individuals and businesses considering an EV purchase. It ensures that they can take advantage of the most favorable tax incentives available in their region, potentially saving significant amounts of money. Additionally, for businesses, these variations can impact their investment decisions, especially when considering the potential for tax credits in different markets.
Ford's Electric Future: Partnering with Rivian for a Green Revolution
You may want to see also

Vehicle Types: Certain EV models may be excluded from the credit
The federal tax credit for electric vehicles (EVs) is a significant incentive for consumers to go green, but it's important to note that not all EVs qualify for this benefit. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) has specific criteria for what constitutes an eligible vehicle, and understanding these requirements is crucial for potential EV buyers.
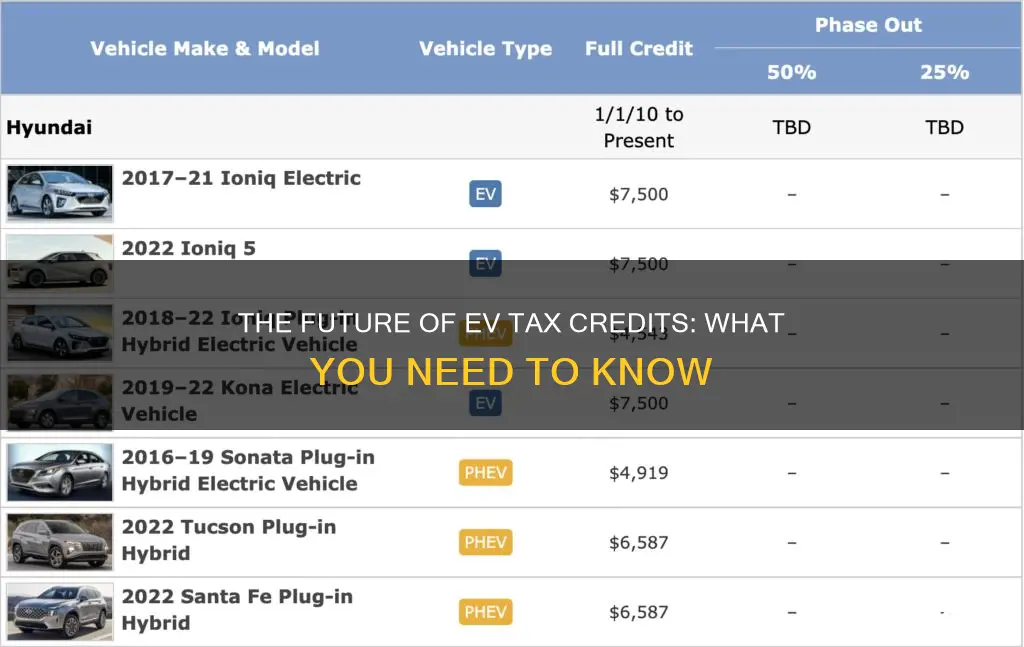
One of the primary factors is the vehicle's battery capacity and range. The tax credit is designed to encourage the purchase of EVs with larger batteries, as these models typically have a higher environmental impact when produced. EVs with a battery capacity of at least 40 kilowatt-hours (kWh) and a range of at least 200 miles are generally eligible for the full tax credit. However, vehicles with lower battery capacities and shorter ranges may still qualify for a partial credit, depending on the specific model and its environmental impact.
Additionally, the IRS has a list of excluded vehicle types. These include vehicles that are not primarily powered by a battery or electric motor, such as hybrid vehicles that rely heavily on a gasoline engine. Plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) that can be charged from an external power source but also have a significant gasoline engine component may also be excluded. The credit also does not apply to vehicles that are primarily powered by a fuel cell, as these are considered a different technology.
Furthermore, certain EV models produced by specific manufacturers might be excluded. For instance, if a car company has received a significant portion of the available tax credits for that model, the IRS may limit or suspend the credit for new purchases of that particular EV. This is done to ensure a fair distribution of incentives and to encourage a diverse range of EV models in the market.
It is essential for consumers to research and verify the eligibility of the specific EV they are interested in purchasing. The IRS provides detailed guidelines and lists of eligible vehicles on its website, ensuring that buyers can make informed decisions and take advantage of the tax credit accordingly. Understanding these vehicle types and exclusions is key to maximizing the benefits of the federal tax credit for electric vehicles.
Unveiling New York's EV Inspection: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Income Limits: Household income caps can affect tax credit eligibility
The federal tax credit for electric vehicles (EVs) is a significant incentive for consumers to make the switch to cleaner transportation. However, it's important to understand that this credit is not available to everyone, and there are specific criteria that must be met to qualify. One of the primary factors that determine eligibility is household income, which is capped at certain levels.
Household income limits are set by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) and are adjusted annually to account for inflation. For the 2023 tax year, the income caps for EV tax credit eligibility are as follows: For single filers, the cap is $75,000, and for joint returns, it is $150,000. These limits are based on adjusted gross income (AGI) and are designed to ensure that the credit benefits lower- to middle-income families.
If your household income exceeds these caps, you may still be eligible for a reduced tax credit. The credit amount gradually decreases as income increases, following a formula based on the income threshold. For instance, if your income is above the cap but below a certain threshold, you might receive a partial credit. It's crucial to consult the IRS guidelines or a tax professional to understand the exact income ranges and how they apply to your situation.
It's worth noting that some states and local governments also offer EV tax credits or rebates, which may have different income requirements. These additional incentives can further enhance the benefits of purchasing an electric vehicle. When considering an EV purchase, it's essential to research both federal and local programs to maximize your savings.
In summary, household income plays a critical role in determining eligibility for the federal EV tax credit. Understanding the income caps and any state-specific requirements will help you navigate the process effectively. Staying informed about these guidelines ensures that you can take advantage of the financial incentives available to promote the adoption of electric vehicles.
The Electric Revolution: Unlocking the Percentage of New Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The current federal tax credit for electric vehicles was extended and modified by the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) in 2022. The IRA provides a tax credit of up to $7,500 for new electric vehicle purchases, but with some restrictions and a phase-out schedule. The credit is set to decrease by $4,500 for vehicles with a base price over $45,000 and will be completely phased out for vehicles priced above $80,000.
No, the tax credit is not available for all electric vehicles. It is primarily intended for new, fully assembled electric vehicles manufactured in North America. The credit is also subject to a cap on the number of vehicles a manufacturer can claim the credit for, which is designed to encourage a wider range of EV models to be produced and sold.
The Inflation Reduction Act's EV tax credit provisions are expected to be in effect for a significant period. However, the exact duration is uncertain and may be subject to future legislative changes. The current law provides for the credit to be available for vehicles purchased after November 1, 2021, and before January 1, 2033, for vehicles with a base price below $80,000.
There have been discussions and proposals to extend and expand the EV tax credit, but no definitive action has been taken yet. The future of the credit is a topic of political debate, and various stakeholders, including automakers, environmental groups, and policymakers, are advocating for its continuation or enhancement.
If the EV tax credit is not renewed, it could significantly impact the electric vehicle market. Without the credit, the upfront cost of electric cars may become less competitive compared to traditional gasoline vehicles, potentially affecting consumer demand and the overall growth of the EV industry.







