While electric vehicles (EVs) offer numerous benefits, such as reduced environmental impact and lower running costs, they also present some drawbacks. One significant concern is the limited driving range, which can be a challenge for long-distance travel. Additionally, the time required to charge an EV's battery can be substantial, often taking several hours, compared to the quick refueling of traditional gasoline vehicles. Another issue is the higher upfront cost, which may deter potential buyers, although this is gradually decreasing as technology advances and more models become available. Despite these challenges, many of these problems are being actively addressed by manufacturers, and the widespread adoption of EVs is expected to continue as technology improves and infrastructure expands.
What You'll Learn
- High upfront cost: Initial purchase price can be a barrier for many consumers
- Limited charging infrastructure: Inadequate charging stations can hinder long-distance travel
- Battery degradation: Over time, batteries may lose efficiency, impacting range and performance
- Environmental impact: Manufacturing and disposal of batteries can have ecological consequences
- Dependence on rare earth minerals: Extraction of these minerals raises ethical and sustainability concerns

High upfront cost: Initial purchase price can be a barrier for many consumers
The high upfront cost of electric vehicles (EVs) is a significant deterrent for many potential buyers. While the long-term savings and environmental benefits of EVs are well-documented, the initial purchase price can be a substantial barrier, especially for those on a tight budget. This financial hurdle often prevents individuals from considering EVs as a viable option, despite their growing popularity and the increasing number of models available.
The primary reason for this high cost is the advanced technology and battery systems that power EVs. These vehicles are equipped with sophisticated components, such as powerful electric motors, advanced batteries, and sophisticated electronics, which contribute to a higher manufacturing cost compared to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. Additionally, the limited production volumes of many EVs can drive up prices due to economies of scale not being fully realized.
Another factor is the government incentives and subsidies aimed at promoting EV adoption. While these financial incentives can significantly reduce the overall cost for consumers, they often come with specific eligibility criteria and may not be accessible to all buyers. As a result, even after accounting for these incentives, the initial purchase price of EVs can still be prohibitively expensive for many.
Furthermore, the resale value of EVs is a concern for some buyers. Due to the relatively new technology and the potential for rapid advancements in the EV market, there is a risk that EVs may depreciate more quickly than traditional vehicles. This factor can further discourage potential buyers who are hesitant to invest in a technology that may become obsolete or less desirable over time.
To address this issue, manufacturers and policymakers are exploring various strategies. These include developing more affordable EV models, offering lease or subscription options, and providing incentives for used EV purchases. By making EVs more accessible and affordable, these efforts aim to overcome the high upfront cost barrier and encourage a wider adoption of electric vehicles.
Electric Road Trip: Tips for Planning Your EV Adventure
You may want to see also

Limited charging infrastructure: Inadequate charging stations can hinder long-distance travel
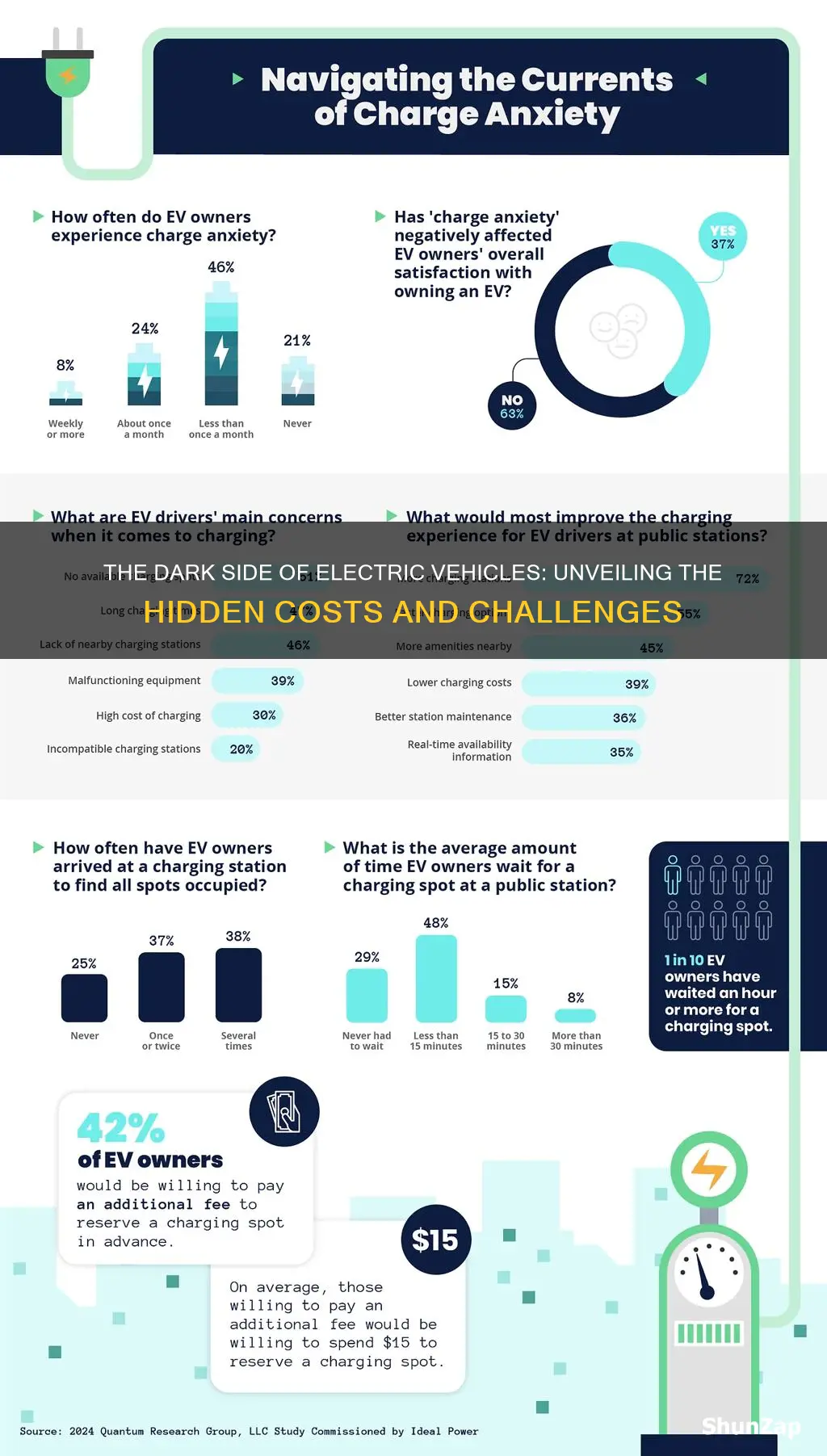
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) has brought about numerous environmental and economic benefits, but it has also exposed certain challenges that need addressing. One significant concern is the limited charging infrastructure, which can significantly impact the practicality of long-distance travel for EV owners.
The current state of charging stations is not yet extensive enough to support the growing number of EVs on the road. This issue is particularly prominent in rural areas and along less-traveled routes, where finding a charging station can be a real struggle. As a result, EV drivers often face the dilemma of range anxiety, worrying about running out of battery power during their journeys. This anxiety can deter potential buyers and hinder the widespread acceptance of electric vehicles.
Long-distance travel in an EV requires careful planning due to the limited range of most models. While modern EVs have improved their range significantly, they still cannot match the distance covered by conventional gasoline vehicles. This means that travelers need to locate charging stations at regular intervals to ensure their journey remains uninterrupted. However, the availability of these stations is not always guaranteed, especially on less-traveled routes.
To address this problem, governments and energy companies are investing in expanding the charging infrastructure. This includes installing more charging stations along highways and in urban areas, making it more convenient for EV owners to plan their trips. Additionally, the development of fast-charging technology is crucial, as it can significantly reduce the time required to recharge a vehicle's battery, making long-distance travel more feasible.
In summary, the limited charging infrastructure is a critical aspect of the EV ownership experience, especially for those planning long journeys. It is essential to continue developing and improving charging networks to ensure that electric vehicles become a more viable and attractive option for all types of travelers, not just those in urban areas with readily available charging stations.
Government Incentives: Are They Enough to Go Electric?
You may want to see also

Battery degradation: Over time, batteries may lose efficiency, impacting range and performance
Battery degradation is a significant concern for electric vehicle (EV) owners, as it directly affects the vehicle's performance and longevity. Over time, the batteries in EVs can experience a decline in efficiency, which has a noticeable impact on the vehicle's range and overall driving experience. This degradation is an inherent issue with lithium-ion batteries, the technology most commonly used in EVs.
The primary cause of battery degradation is the chemical processes that occur during charging and discharging cycles. Each time an EV is charged, the lithium ions move from the negative electrode (anode) to the positive electrode (cathode) and back, creating a cycle of electrochemical reactions. With repeated use, these reactions can lead to the breakdown of the battery's components, including the electrodes and the electrolyte. This degradation is accelerated by factors such as high temperatures, frequent rapid charging, and age.
As the battery ages, its capacity to store energy decreases, resulting in reduced range. This means that an EV may not be able to travel as far on a single charge as it did when new. For example, a car that initially provided a range of 300 miles might, over time, only offer 250 miles or less. This reduction in range can be a significant drawback, especially for long-distance travelers or those who rely on their vehicles for daily commutes.
To mitigate battery degradation, EV manufacturers employ various strategies. One approach is to design batteries with advanced materials and structures that can withstand more cycles of charging and discharging. Additionally, implementing smart charging systems that optimize charging rates and temperatures can help slow down the degradation process. Regular maintenance, such as keeping the battery at an optimal temperature and avoiding frequent rapid charging, can also contribute to preserving battery health.
Understanding the factors that contribute to battery degradation is essential for EV owners to ensure they get the most out of their vehicles. By being mindful of charging habits and environmental conditions, drivers can take proactive steps to minimize the impact of degradation, ensuring their electric vehicles remain efficient and reliable over an extended period.
Unlocking Tax Benefits: Exploring Electric Vehicle Section 179 Eligibility
You may want to see also

Environmental impact: Manufacturing and disposal of batteries can have ecological consequences
The environmental impact of electric vehicles (EVs) extends beyond their operation and includes the manufacturing and disposal of their batteries, which can have significant ecological consequences. The production of lithium-ion batteries, a common type used in EVs, requires substantial energy and resources. Mining for raw materials like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, often involves destructive practices that can lead to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution. For instance, the extraction of lithium from brine pools can result in the drying up of these natural water sources, affecting local ecosystems and communities.
The manufacturing process itself is energy-intensive, often relying on fossil fuels, which contributes to greenhouse gas emissions and air pollution. The chemical processes involved in battery production can also release toxic substances, posing risks to workers and nearby residents. Furthermore, the disposal of these batteries is a complex issue. When batteries reach the end of their life, they must be recycled or disposed of properly to prevent hazardous materials from leaching into the environment. Improper disposal can lead to soil and water contamination, as well as air pollution from the burning of waste.
The environmental impact of battery manufacturing and disposal is a critical aspect of the EV lifecycle that often receives less attention compared to the benefits of reduced emissions during operation. However, it is essential to address these challenges to ensure that the overall environmental impact of EVs is minimized. This includes investing in sustainable mining practices, developing more efficient and environmentally friendly battery production methods, and establishing robust recycling infrastructure. By doing so, we can work towards a more sustainable future where the benefits of electric mobility are maximized while minimizing the ecological footprint associated with battery manufacturing and end-of-life management.
Tax Benefits for Electric Vehicles: A Green Investment
You may want to see also

Dependence on rare earth minerals: Extraction of these minerals raises ethical and sustainability concerns
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) has brought about significant advancements in the automotive industry, offering a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to traditional internal combustion engines. However, the production of these vehicles is not without its challenges and potential drawbacks, particularly regarding the extraction and use of rare earth minerals. These minerals, essential for the manufacturing of EV components, have raised ethical and environmental concerns that warrant attention.
Rare earth minerals, including neodymium, praseodymium, and dysprosium, are crucial for the powerful permanent magnets used in electric motors. These magnets enable the high torque and efficiency required for electric vehicles to perform optimally. The demand for these minerals has surged with the rise of EVs, leading to increased mining activities worldwide. While the extraction of rare earths can provide economic benefits to mining regions, it also poses significant environmental and social challenges.
One of the primary concerns is the environmental impact of mining these minerals. The process often involves destructive techniques, such as open-pit mining, which can lead to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and water pollution. The release of toxic chemicals and heavy metals during the extraction and refining processes can contaminate local water sources and harm ecosystems. Furthermore, the energy-intensive nature of mining and refining rare earth minerals contributes to a significant carbon footprint, undermining the very environmental benefits that EVs aim to provide.
Ethical considerations also come into play due to the complex supply chains of rare earth minerals. Many of these minerals originate from countries with questionable human rights records, where forced labor and child labor have been reported in mining operations. The global demand for rare earths has led to a race to exploit these resources, often at the expense of local communities and their well-being. Ensuring ethical sourcing and fair trade practices throughout the supply chain is essential to address these concerns.
To mitigate these issues, the focus should be on developing more sustainable and ethical alternatives to rare earth minerals. Researchers are exploring ways to reduce or eliminate the use of these minerals in EV technology, such as developing new types of magnets or improving recycling methods. Additionally, promoting responsible mining practices, implementing strict regulations, and supporting local communities affected by mining activities can help address the ethical and sustainability concerns associated with rare earth mineral extraction. By addressing these challenges, the electric vehicle industry can work towards a more environmentally and socially responsible future.
EV Revolution: Will Prices Drop in 5 Years?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
While EVs are known for their reduced carbon footprint compared to traditional gasoline cars, there are still some environmental considerations. The production of EV batteries, particularly lithium-ion batteries, can have significant ecological impacts due to the extraction of raw materials and the energy-intensive manufacturing process. Additionally, the disposal of old batteries is a challenge, as they contain hazardous materials that require proper recycling to minimize environmental harm. However, it's important to note that the environmental benefits of EVs often outweigh these concerns, especially when powered by renewable energy sources.
Like any other vehicle, EVs can experience technical issues, but many of these concerns are often misconceptions or specific to certain models. Range anxiety, the fear of running out of battery charge, is a common worry, but modern EVs offer impressive ranges, and charging infrastructure is rapidly expanding. Some early EV models had issues with battery degradation, but advancements in technology have significantly improved battery longevity. It's also worth mentioning that EVs generally have fewer moving parts, leading to lower maintenance costs and increased reliability over time.
The accessibility of charging stations is a valid concern for potential EV owners. While the number of public charging stations is growing, the infrastructure is still developing, and not all areas have an even distribution of charging points. This can lead to range limitations during long trips. However, many EV owners charge their vehicles at home using personal charging stations, which can be more convenient and cost-effective. The cost of charging varies depending on electricity rates and the efficiency of the charging process. Overall, the charging infrastructure is continuously improving, addressing these concerns and making EV ownership more feasible.







