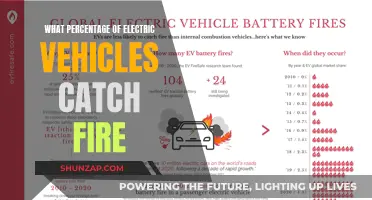
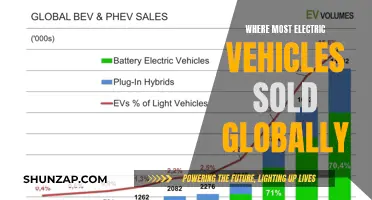
Electric vehicles (EVs) are a key component in the fight against climate change, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional internal combustion engine cars. By eliminating the need for gasoline or diesel, EVs significantly reduce carbon emissions, a major contributor to global warming. The environmental benefits of EVs are twofold: firstly, they produce zero tailpipe emissions, meaning no harmful pollutants or greenhouse gases are released during driving. Secondly, the electricity used to power EVs can often come from renewable sources, further decreasing the carbon footprint of the transportation sector. This shift towards electric mobility is crucial in achieving global sustainability goals and reducing our reliance on fossil fuels.
What You'll Learn
- Energy Efficiency: Electric vehicles convert most of the energy from batteries to power the car, reducing waste
- Zero Emissions: EVs produce no tailpipe emissions, unlike gasoline or diesel cars, which release CO2
- Renewable Energy: Charging EVs with renewable energy sources like solar or wind further lowers carbon footprints
- Battery Technology: Advances in battery tech improve energy storage, enhancing vehicle efficiency and reducing emissions
- Infrastructure: Charging stations and smart grids support EV adoption, contributing to a greener transportation network

Energy Efficiency: Electric vehicles convert most of the energy from batteries to power the car, reducing waste
Electric vehicles (EVs) are revolutionizing the automotive industry and offering a more sustainable alternative to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars. One of the key advantages of EVs is their remarkable energy efficiency, which significantly contributes to reducing carbon emissions.
The energy efficiency of electric cars is primarily attributed to their ability to convert a large portion of the energy stored in their batteries into actual power for the vehicle. Unlike ICE cars, which waste a considerable amount of energy as heat during the combustion process, EVs utilize advanced electric motors and power electronics to minimize energy loss. When an EV accelerates, decelerates, or even idles, it employs regenerative braking, a technology that captures and stores kinetic energy, further enhancing energy efficiency. This regenerative system converts the vehicle's kinetic energy back into electrical energy, which is then stored in the battery, reducing the overall energy consumption.
The efficiency of electric vehicles is evident in their ability to travel longer distances on a single charge compared to their ICE counterparts. Modern EVs can achieve impressive mileage, often exceeding 200 miles on a full charge, thanks to the direct conversion of electrical energy into mechanical power. This efficiency is a result of the simplified power train in EVs, which eliminates the need for complex gearboxes and reduces energy losses associated with traditional transmissions.
Moreover, the energy efficiency of electric cars extends beyond the vehicle itself. The charging infrastructure for EVs is designed to be more efficient, allowing for faster charging times and reduced energy wastage. Smart charging systems can optimize the charging process, ensuring that the vehicle is charged during periods of low energy demand, further minimizing environmental impact.
In summary, electric vehicles' energy efficiency is a critical factor in their ability to reduce carbon emissions. By converting a substantial amount of battery energy into power for the vehicle and employing regenerative braking, EVs minimize waste and maximize energy utilization. This efficiency, combined with the potential for renewable energy sources to power charging stations, makes electric vehicles a key player in the transition towards a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation system.
Vehicle Chassis: Conducting the Electrical Circuit Path
You may want to see also

Zero Emissions: EVs produce no tailpipe emissions, unlike gasoline or diesel cars, which release CO2
Electric vehicles (EVs) are a game-changer in the fight against climate change, offering a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to traditional gasoline and diesel cars. One of the most significant advantages of EVs is their ability to eliminate tailpipe emissions, which is a major source of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other harmful pollutants.
When it comes to zero emissions, EVs are the clear winner. Unlike conventional vehicles, which release CO2 and other greenhouse gases during combustion, electric cars produce no direct exhaust emissions. This is because EVs are powered by electric motors that run on electricity stored in batteries, eliminating the need for internal combustion engines. As a result, the process of driving an EV does not involve the burning of fossil fuels, which is a major contributor to global warming and air pollution.
The environmental benefits of this emission-free operation are substantial. By removing the tailpipe, EVs significantly reduce the release of CO2, a potent greenhouse gas, into the atmosphere. This is especially crucial in urban areas where traffic congestion and pollution levels are high. Studies have shown that widespread adoption of electric vehicles can lead to substantial decreases in CO2 emissions, helping to improve air quality and mitigate the impacts of climate change.
Furthermore, the environmental impact of EVs extends beyond their operation. The entire lifecycle of an EV, from production to disposal, is more sustainable compared to traditional vehicles. Manufacturing EVs typically requires less energy and generates fewer emissions, and the use of renewable energy sources for charging further reduces their carbon footprint. As the world moves towards a more sustainable energy model, the production and use of electric vehicles become even more environmentally friendly.
In summary, electric vehicles are a powerful tool in the battle against carbon emissions. Their zero-emission nature, coupled with a more sustainable production and energy usage process, makes them a key component in reducing our carbon footprint and creating a greener future. As technology advances and more people embrace EVs, we can expect to see a significant positive impact on the environment and a reduction in the harmful effects of transportation on our planet.
India's Electric Revolution: Are We Ready for the Change?
You may want to see also

Renewable Energy: Charging EVs with renewable energy sources like solar or wind further lowers carbon footprints
The integration of renewable energy sources into the charging infrastructure for electric vehicles (EVs) is a pivotal strategy in the quest to reduce carbon emissions and foster a more sustainable transportation ecosystem. When EVs are charged using electricity generated from renewable sources such as solar or wind power, the environmental benefits are substantial. This approach significantly lowers the carbon footprint associated with vehicle operation, offering a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to traditional internal combustion engines.
Renewable energy sources provide a consistent and environmentally friendly power supply for EV charging stations. Solar panels, for instance, harness the abundant energy from the sun, while wind turbines capture the kinetic energy of wind, both offering clean and virtually limitless power. By utilizing these sources, the electricity used to charge EVs is produced with minimal greenhouse gas emissions, unlike conventional power plants that rely on fossil fuels, which are major contributors to carbon emissions.
The environmental advantages of charging EVs with renewable energy are twofold. Firstly, it directly reduces the carbon emissions associated with vehicle use. Electric vehicles themselves produce zero tailpipe emissions, but the electricity they consume can vary in its environmental impact depending on the source. When renewable energy is used, the carbon footprint of the entire process, from charging to driving, is significantly reduced. Secondly, the widespread adoption of renewable energy for EV charging encourages the development of a more sustainable and resilient energy infrastructure. This shift can lead to a more decentralized and environmentally conscious power generation system.
Implementing renewable energy for EV charging also has the potential to create a more efficient and interconnected energy network. Smart charging systems can be employed to manage the flow of electricity, ensuring that charging occurs during periods of high renewable energy production, thus maximizing the use of clean energy. This technology can also help balance the grid by adjusting charging rates based on real-time energy availability and demand, further optimizing the use of renewable resources.
In summary, the utilization of renewable energy sources for charging electric vehicles is a powerful tool in the fight against climate change. It not only reduces the carbon emissions associated with vehicle operation but also promotes the development of a more sustainable and environmentally conscious energy infrastructure. As the world transitions towards cleaner transportation methods, the synergy between renewable energy and electric vehicles will play a crucial role in achieving global sustainability goals.
Electric Vehicles: Cost-Effective Driving? Uncover the Savings
You may want to see also

Battery Technology: Advances in battery tech improve energy storage, enhancing vehicle efficiency and reducing emissions
The development of advanced battery technology is a pivotal factor in the reduction of carbon emissions from electric vehicles (EVs). Over the years, significant strides have been made in battery chemistry and design, leading to improved energy storage capabilities and overall vehicle efficiency. These advancements are crucial in the transition towards a more sustainable transportation system.
One of the key improvements in battery technology is the development of lithium-ion batteries, which have become the standard for electric vehicles. These batteries offer higher energy density compared to their predecessors, allowing for more efficient storage of electrical energy. This increased energy density means that EVs can travel longer distances on a single charge, reducing the frequency of charging and the overall energy consumption. As a result, the carbon footprint associated with EV usage is significantly lower compared to conventional internal combustion engine vehicles.
Furthermore, advancements in battery management systems have played a crucial role in enhancing vehicle efficiency. These systems optimize the charging and discharging processes, ensuring that the battery operates at its most efficient level. By monitoring and controlling various parameters such as temperature, voltage, and current, the battery management system can prevent overcharging and over-discharging, which can lead to reduced battery life and increased energy waste. This optimization not only extends the lifespan of the battery but also contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly EV operation.
The improved energy storage capacity of modern batteries is another critical aspect. Higher storage capacity allows EVs to carry more energy, enabling them to accommodate larger batteries or reduce the need for frequent charging. This is particularly important for long-distance travel, where range anxiety has been a significant barrier to EV adoption. With extended range, electric vehicles become more practical for everyday use, encouraging a shift away from fossil fuel-based transportation.
Additionally, ongoing research and development in battery technology are focusing on creating more sustainable and environmentally friendly materials. Scientists are exploring alternatives to lithium, such as sodium and solid-state batteries, which offer potential advantages in terms of cost, safety, and sustainability. These innovations aim to reduce the environmental impact of battery production and disposal, further contributing to the overall reduction of carbon emissions in the transportation sector.
In summary, advances in battery technology have been instrumental in improving the efficiency and sustainability of electric vehicles. Through increased energy density, optimized battery management, and the exploration of new materials, EVs are becoming more practical and environmentally friendly. These developments are essential steps towards a greener future, where transportation plays a significant role in reducing carbon emissions and combating climate change.
Powering Up: A Guide to Electric Vehicle Conversion
You may want to see also

Infrastructure: Charging stations and smart grids support EV adoption, contributing to a greener transportation network
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is a crucial step towards reducing carbon emissions and combating climate change. While EVs themselves produce zero tailpipe emissions, their environmental impact is further enhanced by the supporting infrastructure, particularly charging stations and smart grids. These elements play a pivotal role in facilitating the transition to electric mobility and ensuring a sustainable future.
Charging stations are the lifeblood of EV ownership, providing the necessary power to recharge batteries. Strategically placed stations along highways, in residential areas, and in commercial hubs ensure that EV drivers can conveniently charge their vehicles. The development of fast-charging stations is particularly important, as it significantly reduces the time required for recharging, making EVs more practical for long-distance travel. These stations utilize advanced technologies to deliver rapid charging, often in under 30 minutes, addressing range anxiety and encouraging more people to make the switch.
Smart grids, an integral part of the energy infrastructure, are designed to efficiently manage and distribute electricity. They enable real-time monitoring and control of energy usage, allowing for dynamic pricing and demand response. When integrated with charging stations, smart grids can optimize the charging process, ensuring that EVs are charged during periods of low energy demand and at the most cost-effective times. This not only reduces the strain on the power grid but also minimizes the environmental impact by avoiding peak-time energy usage, which often relies on more carbon-intensive sources.
The combination of charging stations and smart grids creates a sustainable ecosystem that supports EV adoption. By providing convenient access to charging and optimizing energy usage, this infrastructure enables a greener transportation network. As more EVs hit the roads, the collective reduction in carbon emissions becomes significant. This is especially true when coupled with renewable energy sources, as smart grids can prioritize the use of clean energy for charging, further decreasing the carbon footprint of the transportation sector.
In summary, the infrastructure supporting EV adoption is a critical component in the fight against climate change. Charging stations and smart grids work in tandem to provide a seamless and environmentally friendly experience for EV owners. With continued investment and development, these technologies will play a pivotal role in shaping a sustainable future, where electric vehicles contribute significantly to reduced carbon emissions and a cleaner, greener world.
Electric Vehicles: Malaysia's Green Revolution
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Electric vehicles significantly reduce carbon emissions by eliminating tailpipe emissions, which are a major source of greenhouse gases. EVs are powered by electric motors that run on electricity, typically sourced from renewable energy sources like solar or wind power. This clean energy production process results in zero direct emissions from the vehicle itself, unlike traditional internal combustion engines.
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles can lead to improved air quality, especially in urban areas. By replacing conventional cars with EVs, cities can experience a reduction in harmful pollutants such as nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter, which are associated with respiratory issues and smog. This is particularly beneficial for public health and the environment.
Yes, electric cars have a much lower carbon footprint over their lifetime compared to gasoline or diesel vehicles. While the production of EV batteries does have an environmental impact, the overall emissions savings are substantial. As the electricity grid becomes greener with more renewable energy integration, the carbon benefits of EVs become even more pronounced over time.
Electric vehicles offer a more substantial reduction in emissions compared to hybrid vehicles. Hybrids combine an internal combustion engine with an electric motor, but they still produce tailpipe emissions. EVs, on the other hand, are fully electric and produce no direct emissions during driving, making them a more environmentally friendly choice.
The carbon emissions associated with charging EVs depend on the energy mix used for electricity generation. If the electricity is sourced from renewable and low-carbon sources, the overall emissions are minimal. However, in regions heavily reliant on fossil fuels for electricity generation, charging EVs may have a slightly higher carbon footprint. But even in such cases, EVs still offer significant emissions reductions compared to conventional vehicles.