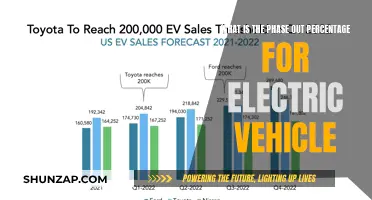
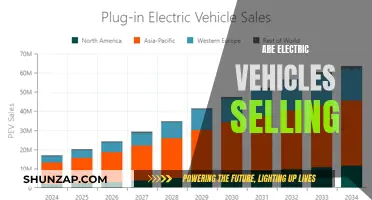
The push towards electric vehicles (EVs) has been a topic of much debate and discussion, with many questioning the role of government intervention. Some argue that governments are forcing the adoption of EVs through subsidies, mandates, and other policies, while others believe that market forces alone are driving the shift towards electric mobility. This paragraph aims to explore the various perspectives on this issue, examining the motivations and methods employed by governments to encourage the use of electric vehicles and the potential implications for the automotive industry and the environment.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Government Incentives | Many governments worldwide offer incentives such as tax credits, rebates, and grants to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs). These programs aim to reduce the upfront cost of EVs and make them more affordable for consumers. |
| Mandates and Regulations | Some countries and regions have implemented mandates and regulations that require a certain percentage of new vehicle sales to be electric. For example, Norway has a zero-emission vehicle (ZEV) mandate, while California's Advanced Clean Cars program sets emissions standards and EV sales targets. |
| Emission Standards | Governments are increasingly setting stricter emission standards to reduce air pollution. These standards often favor electric vehicles over traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles, as EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions. |
| Infrastructure Development | Governments are investing in the development of charging infrastructure to support the growing number of electric vehicles. This includes installing public charging stations, providing incentives for home charging, and integrating smart grid technologies. |
| Research and Development | Governments play a crucial role in funding research and development (R&D) for electric vehicle technology. This includes supporting battery technology, charging systems, and vehicle design to improve performance, range, and sustainability. |
| Public Awareness and Education | Governments and environmental organizations often launch campaigns to raise public awareness about the benefits of electric vehicles, including reduced environmental impact, lower running costs, and improved energy security. |
| Corporate Targets | In some cases, governments set corporate targets or commitments for EV sales, encouraging manufacturers to invest in electric vehicle production and development. |
| International Agreements | Global agreements, such as the Paris Climate Agreement, have prompted governments to take action on climate change, which often includes promoting electric vehicles as part of a broader strategy to reduce greenhouse gas emissions. |
| Market Competition | The government's support for electric vehicles can create a competitive market, driving innovation and potentially lowering prices as more manufacturers enter the EV sector. |
| Long-term Sustainability | The push for electric vehicles is seen as a long-term strategy to ensure a more sustainable transportation system, reduce reliance on fossil fuels, and mitigate the impacts of climate change. |
What You'll Learn
- Government Incentives: Tax credits, subsidies, and grants encourage EV adoption
- Regulations and Mandates: Laws forcing automakers to produce electric vehicles
- Infrastructure Development: Government investment in charging stations and battery recycling
- Public Transportation: Electric buses, trains, and taxis reduce emissions
- Environmental Policies: Stricter emissions standards and carbon taxes drive EV adoption

Government Incentives: Tax credits, subsidies, and grants encourage EV adoption
The idea that governments are actively forcing the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is a misconception. Instead, governments worldwide are implementing various incentives and policies to encourage the shift towards electric mobility, recognizing the environmental benefits and long-term sustainability of EVs. One of the primary methods used by governments to promote EV adoption is through financial incentives. These incentives come in the form of tax credits, subsidies, and grants, which aim to reduce the upfront cost of purchasing EVs and make them more affordable for consumers.
Tax credits are a powerful tool in this regard. Many countries offer tax credits to individuals and businesses who purchase electric vehicles. For example, in the United States, the federal government provides a tax credit of up to $7,500 for the purchase of new electric cars, which can significantly offset the high initial cost of EVs. This incentive not only makes EVs more accessible but also encourages consumers to make the switch from traditional gasoline vehicles. Similarly, in the UK, the government offers a Plug-in Car Grant, providing up to £3,000 towards the cost of an electric car, further reducing the financial barrier to entry.
Subsidies and grants are additional financial incentives that can be provided by local, state, or national governments. These funds are often directed towards specific projects or initiatives aimed at promoting EV infrastructure and adoption. For instance, governments may offer grants to support the installation of charging stations in public areas, residential complexes, and workplaces, ensuring that EV owners have convenient access to charging facilities. Such infrastructure development is crucial for the widespread acceptance and use of electric vehicles.
The impact of these government incentives is significant. By providing financial relief, governments are directly addressing the primary concern of high upfront costs associated with EVs. This, in turn, increases the affordability and attractiveness of electric vehicles, especially for price-sensitive consumers. As a result, more people are likely to consider and eventually purchase EVs, leading to a gradual but steady increase in their market share.
In summary, government incentives in the form of tax credits, subsidies, and grants play a pivotal role in encouraging the adoption of electric vehicles. These financial incentives not only make EVs more affordable but also contribute to the development of necessary infrastructure. While it is not accurate to say that governments are forcing the adoption of electric vehicles, their proactive measures are undoubtedly driving the transition towards a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation system.
Mastering Battery Module Design: A Guide to Electric Vehicle Power
You may want to see also

Regulations and Mandates: Laws forcing automakers to produce electric vehicles
The concept of government intervention in the automotive industry, specifically mandating the production of electric vehicles (EVs), is a topic of growing interest and debate. Many countries and regions are implementing policies to accelerate the transition to cleaner transportation, and these regulations are indeed forcing automakers to adapt and produce electric vehicles.
One of the primary methods governments use to encourage EV production is through legislation and standards. For instance, the European Union's (EU) landmark legislation, the 'European Green Deal', aims to make Europe climate-neutral by 2050. As part of this deal, the EU has set a target of 100% zero-emission car sales by 2035, which means all new cars sold in the region must be fully electric or have zero tailpipe emissions. This regulation directly impacts automakers, forcing them to invest in EV technology and infrastructure to meet these new standards. Similarly, California, a leader in environmental regulations, has set its own zero-emission vehicle (ZEV) program, requiring automakers to produce a certain percentage of EVs to be sold in the state. These state-level mandates are powerful tools for driving change, as they often have a significant market share and can influence national trends.
In addition to setting standards, governments also employ financial incentives and subsidies to encourage EV production. Many countries offer tax credits, rebates, and other financial benefits to both consumers and automakers who invest in electric vehicle technology. For example, the United States' Inflation Reduction Act provides substantial tax credits for EV purchases and production, aiming to boost domestic EV manufacturing and reduce the overall cost of EVs for consumers. These incentives not only make it more attractive for automakers to produce EVs but also help to lower the barrier to entry for consumers, making the transition to electric vehicles more feasible.
The impact of these regulations and incentives is already being felt across the automotive industry. Many traditional automakers are investing heavily in EV technology, with plans to launch numerous electric vehicle models in the coming years. This shift is not limited to the automotive sector; it also extends to the energy industry, as governments mandate the development of charging infrastructure to support the growing number of EVs on the road. As a result, the market is witnessing a rapid evolution, with a focus on sustainability and reduced environmental impact.
In summary, governments are indeed forcing automakers to produce electric vehicles through a combination of regulations and incentives. These policies are driving innovation, investment, and market transformation, with the ultimate goal of reducing greenhouse gas emissions and promoting sustainable transportation. While the approach may be controversial, the evidence suggests that such mandates are effective in accelerating the adoption of electric vehicles and contributing to a greener future.
Boosting EV Speed: Tips for Faster, More Efficient Driving
You may want to see also

Infrastructure Development: Government investment in charging stations and battery recycling
The government's role in promoting electric vehicles (EVs) is multifaceted, and one of the key strategies is investing in the necessary infrastructure to support widespread adoption. This includes the development of charging stations and the establishment of a robust battery recycling system. By doing so, governments can address the concerns of potential EV owners regarding the availability of charging options and the environmental impact of battery disposal.
Charging Station Infrastructure:
The government's investment in charging stations is crucial to ensuring a seamless EV ownership experience. Public charging stations are essential for long-distance travel and provide a convenient solution for EV owners who may not have access to home charging. Governments can incentivize the installation of these stations by offering subsidies or tax benefits to businesses and organizations willing to invest in EV charging infrastructure. This includes the development of fast-charging stations along highways and in urban areas, ensuring that EV owners can quickly recharge their vehicles during their journeys. Additionally, governments can collaborate with private companies to create a network of charging stations, making it more accessible and affordable for the public.
Battery Recycling and Sustainability:
Another critical aspect of government investment is the implementation of a comprehensive battery recycling program. Electric vehicle batteries are large and contain valuable materials, but they also pose environmental challenges if not disposed of properly. Governments can establish partnerships with specialized recycling companies to develop efficient and sustainable battery recycling processes. This involves creating facilities that can safely dismantle and process used batteries, extracting valuable metals like lithium, cobalt, and nickel, which can then be reused in new battery production. By encouraging recycling, governments not only reduce the environmental impact of EVs but also promote a circular economy, ensuring a steady supply of raw materials for the growing EV market.
The benefits of such infrastructure development are twofold. Firstly, it addresses the range anxiety associated with EVs, making them more appealing to a broader audience. Secondly, it contributes to the long-term sustainability of the EV industry, reducing the environmental footprint of the transportation sector. Governments can also play a role in educating the public about the importance of proper battery disposal and the environmental advantages of recycling.
In summary, government investment in charging stations and battery recycling infrastructure is a strategic move to support the electric vehicle market. It addresses immediate concerns and contributes to a greener future, ensuring that the transition to electric mobility is smooth and environmentally conscious. This approach not only encourages the adoption of EVs but also fosters a responsible and sustainable transportation ecosystem.
South Carolina's EV Tax Exemption: A Green Car Owner's Guide
You may want to see also

Public Transportation: Electric buses, trains, and taxis reduce emissions
The push for electric vehicles (EVs) is indeed a significant government initiative, and public transportation plays a crucial role in this transition. Governments worldwide are increasingly recognizing the environmental benefits of electric public transport, which can significantly reduce carbon emissions and improve air quality. This shift is particularly important in densely populated urban areas where traditional public transportation systems often face challenges in terms of efficiency and environmental impact.
Electric buses, trains, and taxis are at the forefront of this green revolution. These vehicles are designed to minimize the environmental footprint of public transportation. For instance, electric buses powered by advanced battery technology can reduce emissions by up to 90% compared to their diesel counterparts. This reduction in emissions is vital for improving air quality, especially in cities where pollution from public transport has been a long-standing concern.
The benefits of electric public transportation extend beyond environmental considerations. These systems are often more energy-efficient, leading to cost savings for both the transport authorities and the passengers. Electric trains and trams, for example, can operate with lower energy consumption, reducing operational costs and providing a more sustainable and affordable public transportation option. Moreover, the adoption of electric vehicles in public transportation can stimulate the development of supporting infrastructure, such as charging stations, which further promotes the growth of the EV market.
Governments are incentivizing the adoption of electric public transportation through various means. Financial incentives, grants, and subsidies are being offered to transport authorities to encourage the purchase of electric buses, trains, and taxis. These incentives not only help in reducing the initial investment burden but also accelerate the transition to cleaner transportation options. Additionally, regulations and policies are being implemented to phase out older, more polluting vehicles and ensure that new public transportation fleets meet stricter environmental standards.
In summary, the government's efforts to promote electric vehicles in public transportation are driven by the need to reduce emissions and improve sustainability. Electric buses, trains, and taxis offer a viable solution to the environmental challenges posed by traditional public transport. By embracing these technologies, cities can significantly lower their carbon footprint, enhance air quality, and provide more efficient and cost-effective transportation options for their residents. This transition is a crucial step towards a greener and more sustainable future for public transportation.
Electric Vehicles: The Indian Advantage? Exploring the Benefits
You may want to see also

Environmental Policies: Stricter emissions standards and carbon taxes drive EV adoption
The push towards electric vehicles (EVs) is indeed being driven by environmental policies, with governments implementing stricter emissions standards and carbon taxes to encourage a shift away from traditional internal combustion engines. These policies are a response to the urgent need to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change. By setting more stringent regulations, governments are essentially forcing the market to adapt and prioritize cleaner alternatives.
Stricter emissions standards play a pivotal role in this transition. These standards set limits on the amount of pollutants, such as nitrogen oxides and particulate matter, that vehicles can emit. As these standards become more stringent over time, manufacturers are compelled to invest in and produce cleaner technologies, including electric powertrains. For instance, many countries have phased out the sale of new gasoline and diesel vehicles, setting a clear timeline for the dominance of EVs on the roads. This approach not only reduces air pollution but also accelerates the development and availability of EV technologies.
Carbon taxes are another powerful tool in the government's arsenal to promote EV adoption. By imposing a tax on the carbon content of fossil fuels, governments create a financial incentive for consumers to opt for low- or zero-emission vehicles. The revenue generated from these taxes can then be reinvested in infrastructure development, such as building a robust network of charging stations, which is essential for widespread EV ownership. As a result, the cost of owning and operating an EV becomes more competitive, making it an attractive choice for environmentally conscious consumers.
The combination of stricter emissions standards and carbon taxes has led to a rapid increase in EV sales worldwide. Automakers are responding to these policy changes by expanding their EV lineups, offering a wider range of models to cater to diverse consumer preferences. This shift is evident in the growing number of EV models available in the market, with various price points and features, making it easier for consumers to make the switch. Moreover, governments are also providing incentives such as tax credits and subsidies to further encourage EV purchases, making the transition more accessible and affordable.
In summary, environmental policies, including stricter emissions standards and carbon taxes, are indeed driving the adoption of electric vehicles. These measures create a compelling case for consumers to choose EVs over traditional vehicles, offering both environmental benefits and long-term cost savings. As governments continue to refine and expand these policies, the market will likely see a more significant shift towards sustainable transportation, ultimately contributing to a greener and more environmentally friendly future.
India's Electric Revolution: Strategies for a Sustainable Future
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
While there are no current federal mandates forcing the adoption of electric vehicles, some governments are incentivizing their use through various means. Many countries and regions have implemented incentives such as tax credits, rebates, and subsidies to encourage consumers to purchase EVs. These measures aim to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and promote sustainable transportation.
The approach towards electric vehicles varies across different regions and political ideologies. Some governments have set targets and deadlines for phasing out internal combustion engine vehicles, which could be seen as a form of enforcement. For example, the European Union has proposed a ban on new fossil fuel car sales by 2035. However, it's important to note that these decisions are often made through legislation and incentives rather than direct coercion.
Governments employ various strategies to encourage the shift towards electric mobility. These include building an extensive charging infrastructure, offering purchase grants or tax benefits, providing low-interest loans, and implementing stricter emission standards for traditional vehicles. Additionally, some cities offer incentives like reduced parking fees or access to carpool lanes for EV owners.
Penalties for non-compliance with electric vehicle regulations are not yet widespread. However, as the focus on sustainability increases, there might be future implications for those who resist the transition. For instance, some cities are experimenting with congestion charges or low-emission zones, which could potentially disadvantage those without electric vehicles. Ultimately, the goal is to create a more sustainable transportation system, and governments are providing support and incentives to facilitate this change.