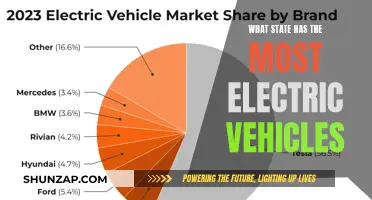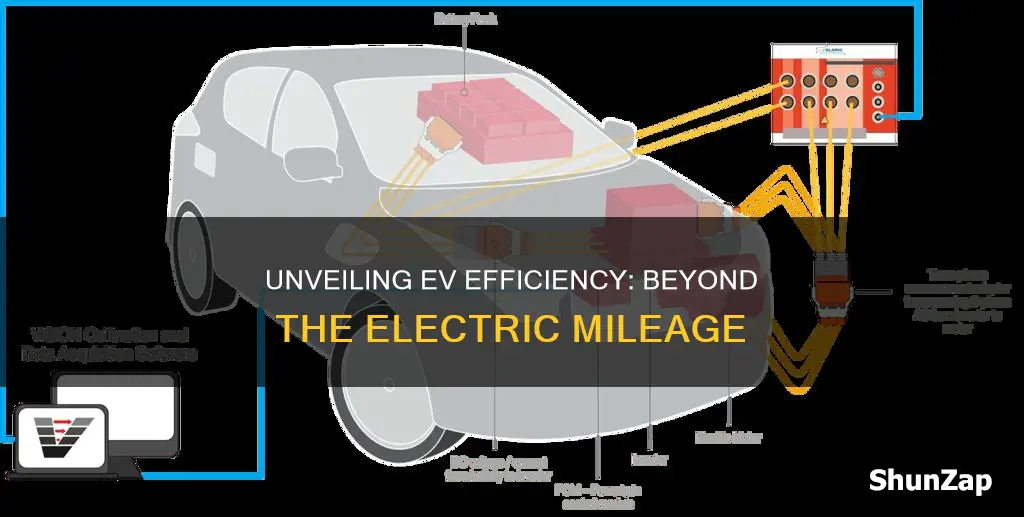
Measuring the efficiency of electric vehicles (EVs) is crucial for assessing their performance and environmental impact. Efficiency in EVs is typically measured by comparing the distance traveled per unit of energy consumed, often expressed in miles per gallon equivalent (MPGe) or kilometers per liter (km/L). This metric helps consumers understand how far an EV can travel on a full charge or a tank of fuel, which is essential for evaluating its practicality and cost-effectiveness. However, efficiency is just one aspect of EV performance; other factors like charging speed, battery capacity, and range also play significant roles in determining the overall efficiency and user experience of electric vehicles.
What You'll Learn
- Energy Consumption: Track and analyze power usage over distance
- Range: Measure the distance an EV can travel on a full charge
- Charging Time: Evaluate the time required to recharge the battery
- Battery Health: Monitor battery degradation and performance over time
- Efficiency Metrics: Use standardized tests to compare EV efficiency

Energy Consumption: Track and analyze power usage over distance
Energy consumption is a critical aspect of evaluating the efficiency of electric vehicles (EVs). Tracking and analyzing power usage over distance is essential to understanding the real-world performance of these vehicles and their potential environmental impact. Here's a detailed look at how this can be achieved:
Data Collection: To measure energy consumption, you need to collect data on power usage during various driving conditions. This can be done through on-board diagnostic tools or specialized devices that can monitor the vehicle's electrical systems. Modern EVs often have built-in data logging capabilities that record energy usage, allowing for post-drive analysis. Additionally, external devices like power meters or energy analyzers can be connected to the vehicle's charging port to measure power input and output during charging sessions.
Distance-Based Analysis: The key to understanding efficiency is to analyze power consumption over a specific distance traveled. By recording the power used during a particular journey, you can calculate the energy efficiency of the EV. This is typically measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh) per 100 kilometers (or miles) traveled. For instance, if an EV consumes 15 kWh of energy to travel 100 miles, its energy efficiency is 15 kWh/100 miles. This metric provides a clear indication of how efficiently the vehicle converts electrical energy into forward motion.
Real-World vs. Laboratory Efficiency: It's important to distinguish between laboratory efficiency (often higher due to controlled conditions) and real-world efficiency. Factors like driving style, traffic conditions, temperature, and terrain significantly impact energy consumption. For instance, rapid acceleration or driving in stop-and-go traffic will consume more energy than cruising at a steady speed on a highway. Analyzing power usage over various distances and driving conditions provides a more accurate representation of the vehicle's efficiency in everyday use.
Performance Optimization: Analyzing energy consumption data can also help identify areas for improvement. For example, if an EV consistently shows higher power usage during city driving, it might indicate the need for more efficient braking systems or improved tire-road friction. By understanding these patterns, manufacturers can work on optimizing vehicle design, improving battery management systems, or developing more efficient power electronics to enhance overall efficiency.
Environmental Impact: Tracking energy consumption also has implications for the environmental impact of EVs. Lower energy consumption per mile translates to reduced greenhouse gas emissions and a smaller carbon footprint. This is a crucial aspect of promoting the adoption of electric vehicles as a sustainable transportation alternative. By providing efficient and environmentally friendly transportation options, the analysis of energy usage becomes a powerful tool for encouraging greener practices.
Electric Vehicle Rentals: Exploring Mackinac Island's Green Options
You may want to see also

Range: Measure the distance an EV can travel on a full charge
The range of an electric vehicle (EV) is a critical factor in determining its efficiency and practicality for everyday use. It represents the distance an EV can travel on a single full charge, and it is a key metric for potential buyers to consider when choosing an EV. Measuring and understanding range is essential to evaluating the performance and suitability of EVs for various applications.
To measure the range of an EV, several methods and standards are employed. One common approach is to use standardized test cycles, such as the EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) range test in the United States or the WLTP (Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicle Test Procedure) cycle in Europe. These test cycles simulate real-world driving conditions and provide a consistent way to compare the range of different EVs. During the test, the vehicle is driven on a dynamometer, which simulates various driving conditions, including city, highway, and combined cycles. The energy consumption and distance traveled are recorded, allowing for the calculation of the vehicle's range.
Another method to measure range is through real-world driving experiences and user-reported data. Many EV owners and enthusiasts keep track of their vehicle's range by monitoring the remaining battery charge and the distance traveled. This data can be valuable for understanding the practical range of an EV in different driving conditions and environments. Factors such as temperature, driving style, terrain, and vehicle load can significantly impact range, so real-world measurements provide a more comprehensive understanding of an EV's performance.
It's important to note that range can vary depending on several factors. The efficiency of the EV's battery and motor system plays a crucial role, as more efficient components can store and utilize energy more effectively. Additionally, driving habits and conditions have a significant impact. Aggressive driving, frequent rapid acceleration, and high-speed highway driving will generally consume more energy and reduce range compared to a more moderate and efficient driving style.
In summary, measuring the range of an EV involves standardized test procedures and real-world data collection. Understanding range is essential for consumers to make informed decisions about EV purchases, ensuring that the vehicle's range aligns with their daily driving needs and preferences. As technology advances, the range of EVs continues to improve, making them increasingly viable alternatives to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles.
Powering the Future: Unlocking the Potential of Battery Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Charging Time: Evaluate the time required to recharge the battery
The charging time of electric vehicles (EVs) is a critical factor in assessing their efficiency and practicality for everyday use. It directly impacts the vehicle's range and the convenience of ownership. When evaluating the efficiency of EVs, it's essential to consider the time it takes to replenish the battery, as this can vary significantly depending on several factors.
Charging time is influenced by the type of charging station and the EV's battery capacity. There are three main levels of charging: Level 1, Level 2, and DC Fast Charging. Level 1 charging, typically using a standard household outlet, is the slowest and can take several hours to fully charge a battery. This method is generally used for overnight charging at home. Level 2 charging, which requires a dedicated charging station and a 240-volt outlet, is faster and can replenish the battery in a few hours. DC Fast Charging, often found along highways and in public charging stations, can provide an 80% charge in as little as 20-30 minutes, making it ideal for quick top-ups during long-distance travel.
The battery capacity of the EV also plays a significant role in charging time. Larger batteries will take longer to charge, especially when using lower-level charging methods. For instance, a 100 kWh battery will charge much slower than a 50 kWh battery when using the same charging station. Modern EVs often come with advanced battery management systems that optimize charging, ensuring the battery reaches full capacity without overloading it, which can extend the overall lifespan of the battery.
To measure and improve efficiency, EV manufacturers and researchers often conduct charging time tests under controlled conditions. These tests involve monitoring the time taken to charge the battery from empty to full using different charging levels and battery sizes. By analyzing these results, they can provide estimated charging times for real-world scenarios, helping consumers make informed decisions about their EV purchases.
In summary, charging time is a crucial aspect of EV efficiency, and it varies based on charging infrastructure, battery capacity, and charging methods. Understanding these factors allows for better management of EV charging, ensuring that vehicles are ready for daily use and long-distance travel, ultimately contributing to a more sustainable and efficient transportation system.
Electric Vehicles: A Maintenance Advantage or Just a Myth?
You may want to see also

Battery Health: Monitor battery degradation and performance over time
Battery health is a critical aspect of electric vehicle (EV) efficiency, as it directly impacts the vehicle's range, performance, and overall reliability. Monitoring battery degradation and performance is essential to ensure that EVs maintain their efficiency and provide a reliable driving experience. Here's a detailed look at how to measure and monitor battery health:
Battery Degradation Monitoring: Battery degradation is a natural process that occurs over time, and it's a significant factor in EV efficiency. As batteries age, their capacity to store and deliver energy decreases. This degradation can be measured through various methods:
- Capacity Testing: Regular capacity tests can be performed to measure the battery's ability to hold a charge. This is typically done by running a standardized test cycle, such as the ISO 6613-2 or the US06 test, which simulates real-world driving conditions. By comparing the test results with the initial capacity, you can quantify the degradation.
- Voltage and Internal Resistance: Monitoring the battery's voltage and internal resistance can provide insights into its health. Over time, the voltage of individual cells may vary, indicating potential issues. Increased internal resistance can also lead to reduced efficiency and performance.
- Temperature Effects: Temperature plays a crucial role in battery health. Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can accelerate degradation. Monitoring the battery's temperature during operation and storage can help identify potential issues and optimize charging strategies.
Performance Evaluation: Beyond degradation, monitoring the battery's performance is essential to ensure optimal efficiency:
- State of Charge (SoC) Tracking: Accurately tracking the SoC is vital for efficient energy management. Modern EVs use sophisticated sensors and algorithms to monitor SoC, but manual checks can also be performed. Ensuring that the battery is charged to the appropriate levels for different driving conditions is key.
- Power Output and Efficiency: Measuring the battery's power output and efficiency during acceleration and deceleration can provide valuable data. This analysis helps in understanding the battery's response and identifying any performance anomalies.
- Cycling and Load Testing: Subjecting the battery to controlled cycling and load tests can simulate various driving conditions. This method helps in assessing the battery's ability to handle different loads and its overall performance over time.
Long-Term Health Management: To ensure the longevity of EV batteries, a proactive approach to health management is necessary:
- Predictive Analytics: Utilizing machine learning algorithms can enable predictive analytics, forecasting battery health and potential issues before they become critical. This technology can analyze various data points to provide early warnings.
- Charging Strategies: Implementing optimal charging strategies, such as using slow chargers for overnight charging and avoiding rapid charging for long periods, can significantly impact battery health.
- Regular Maintenance: Scheduling regular maintenance checks, including battery inspections and software updates, ensures that any issues are addressed promptly.
By closely monitoring battery degradation and performance, EV manufacturers and owners can take proactive measures to optimize efficiency, extend battery life, and ensure a consistent driving experience. This approach is crucial for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles and the development of sustainable transportation solutions.
Exploring China's Electric Vehicle Revolution: Top Brands and Models
You may want to see also

Efficiency Metrics: Use standardized tests to compare EV efficiency
The efficiency of electric vehicles (EVs) is a critical aspect of their performance and environmental impact, and standardized tests play a pivotal role in measuring and comparing these efficiencies. These tests provide a consistent and reliable method to assess how effectively EVs convert electrical energy into useful work, offering valuable insights to consumers, manufacturers, and policymakers.
One of the primary metrics used in these standardized tests is the miles per gallon equivalent (MPGe). This unit is specifically designed to measure the efficiency of EVs in terms of energy consumption, similar to how traditional gasoline vehicles are measured in miles per gallon (mpg). MPGe allows for a direct comparison between different EVs, making it easier for consumers to choose the most efficient models. For instance, a higher MPGe rating indicates a more efficient vehicle, meaning it can travel more miles on a single charge or gallon of fuel, respectively.
Standardized tests often involve a combination of real-world and laboratory simulations to ensure a comprehensive evaluation. Real-world MPGe is determined by driving the vehicle on various routes, including city, highway, and combined cycles, to mimic typical driving conditions. This approach provides a more accurate representation of a vehicle's efficiency in everyday use. In contrast, laboratory testing involves measuring efficiency under controlled conditions, such as on a dynamometer, which simulates different driving scenarios to determine the vehicle's performance across various speeds and loads.
To ensure fairness and accuracy, these tests are conducted using specific protocols and procedures. For instance, the US Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) provides guidelines for EV efficiency testing, including the use of standardized driving cycles and test procedures. These standards ensure that all EVs are tested under the same conditions, allowing for direct comparisons. By adhering to these standardized tests, manufacturers can accurately communicate their vehicles' efficiency, and consumers can make informed decisions based on consistent and reliable data.
In addition to MPGe, other metrics such as kilowatt-hours per 100 miles (kWh/100 mi) and grams of CO2 per mile can also be used to assess EV efficiency. These metrics provide a more detailed understanding of a vehicle's environmental impact and energy consumption. Standardized tests that incorporate these various efficiency metrics offer a comprehensive view of EV performance, helping to drive innovation and improve the overall efficiency of the electric vehicle market.
Why Plug-In Hybrids Are the Future of Driving
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The efficiency of EVs is commonly measured using a metric called 'miles per gallon equivalent' (MPGe). This is a standardized unit that represents the energy efficiency of the vehicle in a way similar to how gasoline-powered cars are measured in miles per gallon (mpg). MPGe takes into account the energy content of electricity and provides an estimate of how far an EV can travel on a full battery charge.
Several factors can impact the efficiency of electric vehicles. These include the design and weight of the vehicle, aerodynamics, tire pressure, driving habits, weather conditions, and the efficiency of the battery and electric motor. Maintaining optimal tire pressure, minimizing unnecessary weight, driving smoothly, and using regenerative braking can all contribute to improving the overall efficiency of an EV.
The range of an EV, which is the distance it can travel on a single charge, is directly related to its efficiency. A longer-range EV often indicates better efficiency, as it can cover more miles on a full battery. However, it's important to note that range can vary depending on driving conditions, climate, and the specific model, so efficiency measurements provide a standardized way to compare different EVs.
Yes, there are standardized tests and methods to measure the efficiency of electric vehicles. One common test is the EPA (Environmental Protection Agency) test cycle in the United States, which involves a combination of city and highway driving cycles. This test provides an estimated range and efficiency rating for EVs, giving consumers a clear understanding of the vehicle's performance. Other countries may have similar testing procedures, ensuring consistent and comparable efficiency data for consumers.