The global shift towards sustainable transportation has accelerated the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), and the question of how many EVs will be on the road by 2030 is a critical one. With governments and industries worldwide setting ambitious targets to reduce carbon emissions, the future of the automotive industry is being redefined. This paragraph will explore the various factors influencing the projected number of electric vehicles on the market by 2030, including technological advancements, policy incentives, and consumer behavior, while also addressing the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead in this rapidly evolving market.
What You'll Learn
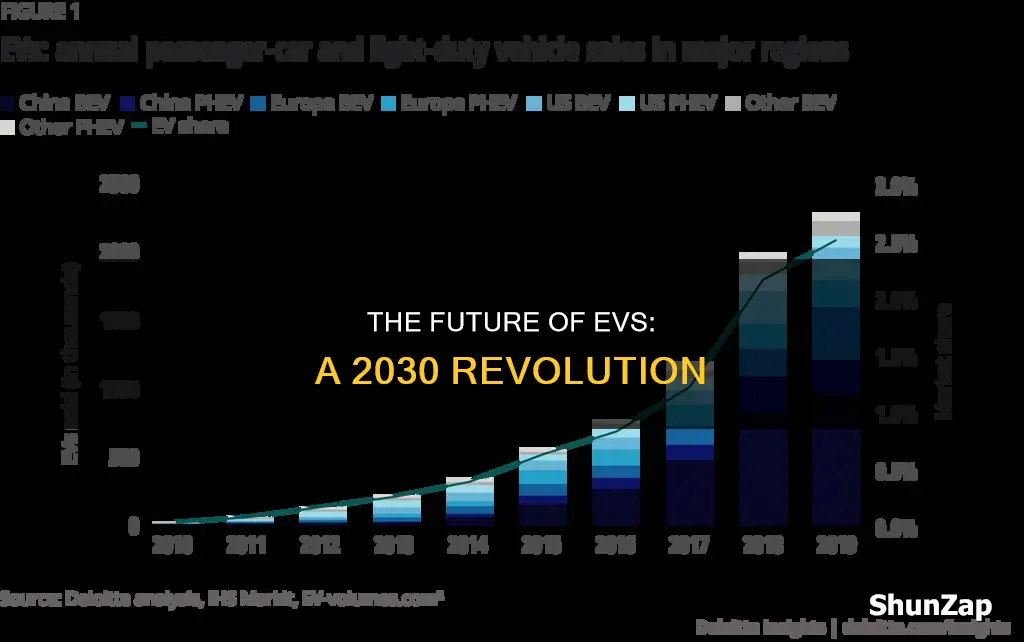
- Market Growth: Global EV sales are projected to reach 35 million by 2030
- Policy Impact: Government incentives and regulations will drive EV adoption
- Infrastructure Development: Expanding charging networks is crucial for widespread EV use
- Technological Advances: Innovations in battery technology will improve EV range and efficiency
- Consumer Behavior: Shifting consumer preferences will accelerate the transition to electric mobility

Market Growth: Global EV sales are projected to reach 35 million by 2030
The global electric vehicle (EV) market is experiencing rapid growth, and projections indicate a significant surge in sales by 2030. According to industry forecasts, the number of electric vehicles sold worldwide is expected to reach an impressive 35 million by the end of the next decade. This remarkable growth is driven by a combination of factors, including increasing environmental concerns, government incentives, and advancements in battery technology.
The rising demand for sustainable transportation options has played a pivotal role in this market expansion. Consumers are increasingly aware of the environmental impact of traditional internal combustion engine vehicles and are seeking greener alternatives. As a result, many car manufacturers are investing heavily in EV production, offering a wide range of models to cater to diverse consumer preferences. This shift in consumer behavior has led to a surge in EV sales, with many countries witnessing a significant increase in the number of electric vehicles on the road.
Government policies and incentives have also been instrumental in accelerating the adoption of electric vehicles. Many countries have implemented subsidies, tax benefits, and other financial incentives to encourage consumers to make the switch from conventional cars to EVs. These measures have not only made electric vehicles more affordable but have also created a favorable market environment for manufacturers. As a result, the production and sales of electric vehicles have seen a substantial boost, with many automotive companies expanding their EV portfolios.
The technological advancements in battery technology have further fueled the growth of the EV market. Improved battery performance, including higher energy density, faster charging capabilities, and extended driving ranges, have addressed some of the primary concerns associated with early electric vehicles. These advancements have made EVs more practical and appealing to a broader consumer base, including those with long-distance travel needs. As a result, the market is witnessing a rapid evolution of electric vehicle designs, with manufacturers introducing more stylish, efficient, and feature-rich models.
In summary, the global EV market is poised for substantial growth, with sales projected to reach 35 million by 2030. This growth is a testament to the increasing demand for sustainable transportation, the supportive government policies, and the continuous technological advancements in the industry. As the world moves towards a more environmentally conscious future, the electric vehicle market is expected to play a pivotal role in shaping the automotive industry's trajectory.
Ford's Electric Future: A 100% EV Revolution?
You may want to see also

Policy Impact: Government incentives and regulations will drive EV adoption
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) by 2030 is heavily influenced by government policies and incentives, which play a pivotal role in shaping the market and consumer behavior. Governments around the world are implementing various strategies to accelerate the transition to electric mobility, recognizing the environmental benefits and long-term sustainability of EVs. One of the primary tools in this policy toolkit is the provision of incentives to both manufacturers and consumers.
Financial incentives are a powerful motivator for EV manufacturers. Governments can offer subsidies, tax credits, and grants to encourage the production and sale of electric vehicles. These incentives can significantly reduce the cost of EV manufacturing, making it more attractive for companies to invest in the development and assembly of electric cars, buses, and motorcycles. For instance, tax credits for EV purchases can directly lower the upfront cost for consumers, making electric vehicles more affordable and competitive against traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars.
In addition to direct financial support, governments can also implement regulations that mandate a certain percentage of EV sales in the overall market. These regulations, often referred to as 'zero-emission vehicle' (ZEV) standards, ensure a minimum number of electric vehicles are sold each year, pushing manufacturers to invest in and produce EVs. Such standards have already been introduced in several countries, including California, the Netherlands, and Norway, and are expected to be expanded globally. By setting these targets, governments create a stable market for EVs, encouraging manufacturers to adapt their production lines and invest in the necessary infrastructure.
Furthermore, governments can facilitate the growth of the EV market by investing in charging infrastructure. The availability of convenient and efficient charging stations is essential for EV owners, addressing range anxiety and providing a seamless user experience. Governments can provide grants and loans to local authorities and private companies to install charging points in public spaces, residential areas, and along highways. This infrastructure development not only supports the current EV market but also encourages potential buyers to make the switch, knowing they have access to reliable charging solutions.
The impact of these policies is twofold. Firstly, they create a favorable environment for EV manufacturers, stimulating production and innovation. Secondly, they directly influence consumer choices, making electric vehicles more accessible and appealing to a broader audience. As a result, government incentives and regulations are powerful catalysts for the rapid growth of the EV market, contributing significantly to the global target of widespread electric vehicle adoption by 2030.
Unleash the Power: Understanding Fuel-Cell Electric Vehicles (FCEVs)
You may want to see also

Infrastructure Development: Expanding charging networks is crucial for widespread EV use
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is an essential step towards a sustainable future, and a critical aspect of this transition is the development of a robust charging infrastructure. As the number of EVs on the road increases, so does the demand for convenient and accessible charging stations. This is especially true when considering the range anxiety that many potential EV buyers still face, which can be a significant barrier to entry.
To encourage more people to make the switch from traditional internal combustion engine vehicles to EVs, governments and businesses must invest in expanding charging networks. This infrastructure development is key to addressing the concerns of range limitations and ensuring that EV owners have access to reliable charging solutions wherever they go. A comprehensive charging network would include fast-charging stations along major highways, allowing long-distance travelers to quickly recharge their vehicles, as well as slower, more convenient charging points in residential areas, workplaces, and public spaces.
The current state of charging infrastructure varies significantly across regions, and this inconsistency can hinder the growth of the EV market. In some areas, there are already well-established charging networks, but in others, the lack of accessible charging points may discourage potential EV owners from making the purchase. To address this, a strategic approach to infrastructure development is required, focusing on both the quantity and quality of charging stations. This includes ensuring that charging points are conveniently located, easily accessible, and offer a range of charging speeds to cater to different vehicle models and user needs.
The benefits of a well-developed charging network extend beyond just the EV owners. It can stimulate economic growth by creating new job opportunities in the construction and maintenance of charging stations, as well as in the development of associated technologies. Furthermore, a robust charging infrastructure can support the integration of renewable energy sources, as EVs can be used to store excess energy during periods of high generation, helping to balance the grid and reduce the environmental impact of energy production.
In summary, the expansion of charging networks is a vital component in the journey towards widespread EV adoption. It requires collaboration between governments, energy companies, and businesses to ensure that the necessary infrastructure is in place to support the growing number of electric vehicles on our roads by 2030 and beyond. This collaborative effort will not only facilitate the transition to a greener transportation system but also contribute to the overall economic and environmental sustainability of our future.
Chevy Volt: Unveiling Its True Electric Nature
You may want to see also

Technological Advances: Innovations in battery technology will improve EV range and efficiency
The future of electric vehicles (EVs) is closely tied to advancements in battery technology, which will play a pivotal role in addressing the range anxiety associated with EVs and accelerating their widespread adoption. As the demand for EVs continues to surge, the focus on enhancing battery performance becomes increasingly critical.
One of the key innovations in battery technology is the development of solid-state batteries. These batteries replace the liquid or gel electrolytes found in traditional lithium-ion batteries with solid conductors, such as ceramics or polymers. Solid-state batteries offer several advantages, including higher energy density, faster charging capabilities, and improved safety. By utilizing solid electrolytes, these batteries can potentially store more energy in a smaller space, leading to increased vehicle range. For instance, researchers have demonstrated solid-state batteries with energy densities exceeding 1,000 Wh/kg, which is significantly higher than the current industry standard of around 500 Wh/kg for lithium-ion batteries. This breakthrough could enable EVs to travel hundreds of miles on a single charge, making them more practical for long-distance travel and reducing the need for frequent charging stops.
Another area of focus is the development of lithium-ion batteries with enhanced performance. Scientists and engineers are working on improving the energy density, power density, and cycle life of lithium-ion batteries. Energy density, measured in watt-hours per kilogram (Wh/kg), determines how much energy a battery can store. Higher energy density means more energy can be packed into a smaller battery pack, resulting in increased vehicle range. Power density, measured in watts per kilogram (W/kg), is crucial for rapid charging and supporting high-performance driving. Cycle life, or the number of charge-discharge cycles a battery can endure, is essential for the long-term reliability and cost-effectiveness of EVs. By optimizing these parameters, battery manufacturers can significantly improve the overall performance and longevity of EV batteries.
Furthermore, advancements in battery management systems (BMS) are crucial for optimizing battery performance and safety. BMS monitors and controls various aspects of the battery, including temperature, state of charge, and current flow. With improved BMS technology, EVs can better manage the distribution of power to different components, ensuring efficient energy usage and reducing the risk of overheating or overcharging. This can lead to longer battery lifespans and improved overall reliability, making EVs more appealing to consumers.
The integration of artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms into battery management systems is also transforming EV performance. These algorithms can analyze vast amounts of data in real-time, optimizing charging and discharging processes based on driving patterns and environmental conditions. By learning from user behavior and external factors, AI-powered BMS can predict and prevent potential issues, such as battery degradation, and suggest optimal charging strategies. This level of intelligence can significantly enhance the user experience, making EVs more convenient and user-friendly.
In summary, technological advances in battery technology are set to revolutionize the EV industry. Innovations like solid-state batteries, enhanced lithium-ion chemistry, advanced battery management systems, and AI integration will collectively contribute to increased vehicle range, faster charging, improved safety, and extended battery lifespan. As these advancements continue to unfold, the widespread adoption of EVs becomes more feasible, bringing us closer to a sustainable transportation future.
Electric Vehicle Stocks: Bubble or Sustainable Growth?
You may want to see also

Consumer Behavior: Shifting consumer preferences will accelerate the transition to electric mobility
The global shift towards electric vehicles (EVs) is gaining momentum, and consumer behavior plays a pivotal role in this transition. As environmental concerns and technological advancements take center stage, consumers are increasingly embracing electric mobility, which is expected to significantly impact the automotive industry by 2030. This transformation is driven by a combination of factors, including rising awareness of climate change, government incentives, and the improving performance and accessibility of electric vehicles.
One of the primary catalysts for this change is the growing environmental consciousness among consumers. With a heightened understanding of the environmental impact of traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, many individuals are now prioritizing eco-friendly alternatives. This shift in mindset is evident in the increasing number of consumers who are willing to invest in electric cars, despite the initial higher costs. The desire to reduce carbon footprints and contribute to a sustainable future is a powerful motivator, encouraging people to make choices that align with their values.
Additionally, technological advancements have played a crucial role in making electric vehicles more appealing. Modern EVs offer improved performance, longer ranges, and faster charging times, addressing the initial concerns of potential buyers. The integration of advanced driver-assistance systems and the development of sophisticated infotainment systems have further enhanced the overall driving experience, making electric cars more desirable and competitive against traditional vehicles. As a result, consumers are increasingly open to the idea of electric mobility, especially with the introduction of more affordable and stylish EV models.
Government incentives and policies also significantly influence consumer behavior. Many countries and regions have implemented subsidies, tax benefits, and other financial incentives to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles. These measures have made EVs more affordable and attractive to a broader consumer base. Moreover, the establishment of charging infrastructure networks and the implementation of stricter emission regulations are further driving the shift towards electric mobility. As these supportive policies continue to evolve, they will likely play a pivotal role in accelerating the transition to electric vehicles.
In conclusion, the transition to electric mobility is being propelled by a combination of consumer awareness, technological advancements, and supportive government initiatives. As more people recognize the environmental benefits and improved performance of electric vehicles, their preference for EVs is likely to grow. This shift in consumer behavior will not only benefit the environment but also drive innovation and investment in the EV market, ultimately shaping the future of the automotive industry and contributing to a more sustainable world by 2030.
Firefighting Tips: Battling Electric Vehicle Blazes
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
By 2030, it is estimated that there will be over 30 million electric vehicles on the global market, with this number expected to grow significantly due to increasing environmental awareness and technological advancements.
The adoption of electric vehicles has been steadily rising, with a compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of approximately 25% from 2015 to 2020. This trend is expected to continue, driven by government incentives, stricter emissions regulations, and consumer demand for sustainable transportation options.
Several factors are driving the rapid growth of the EV market. These include technological improvements in battery performance, reducing charging times and increasing range, lower production costs, and a growing consumer preference for eco-friendly vehicles. Additionally, government policies and incentives, such as tax credits and subsidies, play a crucial role in encouraging EV adoption.
The projection of 30 million EVs by 2030 is an ambitious goal, but it aligns with recent reports and industry forecasts. Many automotive manufacturers and energy experts have revised their predictions, anticipating a faster transition to electric mobility. This shift is partly due to the increasing availability of affordable EV models and the declining costs of battery technology.
Despite the positive trajectory, several challenges persist. These include the need for extensive charging infrastructure, ensuring a stable supply chain for critical raw materials, and addressing range anxiety among potential EV buyers. Additionally, the transition to EVs requires a comprehensive strategy to manage the environmental impact of battery production and disposal.







