California is a leader in the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), with a significant number of EVs on its roads. As of 2022, the state boasts over 1.4 million registered electric vehicles, making it the largest market for EVs in the United States. This rapid growth is driven by a combination of factors, including environmental regulations, incentives for EV buyers, and a robust charging infrastructure. The state's commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and transitioning to a cleaner transportation system has played a pivotal role in this success. With a focus on sustainability and innovation, California continues to be at the forefront of the EV revolution, setting an example for other regions to follow.
What You'll Learn
- Market Penetration: How many EVs are sold in California each year
- Registration Data: How many EVs are registered in California
- Fleet Adoption: How many EVs are in commercial fleets in California
- Public Transportation: How many EVs are used in public transportation in California
- Charging Infrastructure: How many EV charging stations are available in California

Market Penetration: How many EVs are sold in California each year?
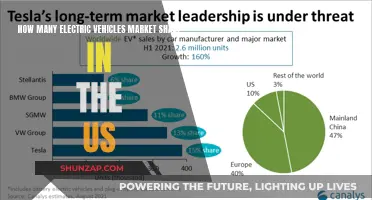
The state of California has been at the forefront of the electric vehicle (EV) revolution, with a significant push towards adopting cleaner transportation methods. As of 2023, California is home to the largest number of electric vehicles in the United States, with an estimated 1.4 million EVs on the road. This number represents a substantial market penetration, especially considering the state's vast population and diverse geography.
The sales of electric vehicles in California have been steadily increasing over the years, driven by various factors. One key factor is the state's aggressive environmental policies and incentives to promote EV adoption. California's Air Resources Board (CARB) has implemented strict emissions standards, pushing automakers to produce more electric cars to meet these regulations. As a result, many car manufacturers have expanded their EV lineups to cater to the California market.
In recent years, the annual sales of EVs in California have shown remarkable growth. According to industry reports, over 300,000 electric vehicles were sold in California in 2022, a significant increase from the previous year. This surge in sales can be attributed to several factors, including the growing consumer interest in sustainable transportation, the expanding charging infrastructure, and the availability of various EV models at different price points.
The market penetration of EVs in California is further supported by the state's robust charging network. With an extensive network of public and private charging stations, EV owners in California have convenient access to charging facilities, addressing range anxiety and encouraging more people to make the switch to electric vehicles.
Moreover, the California government has implemented several incentives to accelerate EV adoption. These include rebates, tax credits, and access to carpool lanes, making electric vehicles more affordable and attractive to consumers. As a result, the state has witnessed a rapid shift towards electric mobility, with EVs becoming a common sight on California's roads.
EVs: Why Your Green Car Costs More to Insure
You may want to see also

Registration Data: How many EVs are registered in California?
California is a leader in the adoption and promotion of electric vehicles (EVs), and its registration data provides valuable insights into the state's progress in this area. As of the latest available statistics, California has seen a significant increase in the number of EVs on its roads. The California Air Resources Board (CARB) reports that as of 2022, there were approximately 1.4 million electric vehicles registered in the state. This number represents a substantial growth from previous years, indicating a strong shift towards electrification. The state's commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality has been a driving force behind this trend.
The registration data offers a comprehensive view of EV ownership across California's diverse regions. It includes a breakdown by county, allowing for an analysis of EV adoption rates in different areas. For instance, the San Francisco Bay Area, known for its environmentally conscious population, has a higher concentration of EVs compared to other regions. This data is crucial for policymakers and researchers to understand the impact of incentives, infrastructure development, and public awareness campaigns.
One interesting aspect of the registration data is the analysis of EV ownership patterns. It reveals that a significant portion of California's EV owners are residents of urban areas, particularly those with higher incomes. This trend suggests that economic factors and the availability of charging infrastructure play a role in EV adoption. Additionally, the data can highlight the popularity of specific EV models, providing insights into consumer preferences and market trends.
The registration statistics also contribute to the state's efforts in meeting its ambitious climate goals. California has set a target to achieve carbon neutrality by 2045, and a substantial portion of EVs on the road is a crucial step towards this objective. By tracking registration data, the state can monitor the progress made and make informed decisions to further accelerate EV adoption. This includes evaluating the effectiveness of existing incentives, such as the California Clean Vehicle Rebate Project, and planning for future infrastructure development.
In summary, the registration data on electric vehicles in California provides a comprehensive and detailed picture of the state's EV market. It offers valuable insights into regional variations, ownership patterns, and the overall growth of EV adoption. With this information, California can continue to lead the way in electrification, ensuring a cleaner and more sustainable future for its residents.
GM's Dominance: Electric Vehicles and Driver Assist Tech
You may want to see also

Fleet Adoption: How many EVs are in commercial fleets in California?
The adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) in California's commercial fleets is an area of growing interest and importance. As the state continues to lead the nation in EV sales and infrastructure, understanding the extent of EV integration in commercial transportation is crucial for several reasons. Firstly, it highlights the potential for reduced emissions and improved air quality, especially in densely populated urban areas. Secondly, it showcases the economic opportunities and technological advancements that come with embracing sustainable transportation solutions.
California's commercial fleets play a significant role in the state's overall transportation sector. These fleets include a wide range of vehicles, from delivery trucks and vans to buses and taxis, all of which have the potential to be converted to electric power. The state's diverse economy, encompassing various industries such as retail, logistics, and transportation services, presents a vast market for EV adoption.
According to recent studies and reports, the number of electric vehicles in commercial fleets in California is steadily increasing. As of 2022, it is estimated that there are over 100,000 EVs in commercial use across the state. This number includes a mix of fully electric vehicles and plug-in hybrids, with a growing trend towards all-electric powertrains. The transportation sector is a significant contributor to California's greenhouse gas emissions, and the shift towards EVs is a crucial step in achieving the state's ambitious climate goals.
Several factors drive the adoption of EVs in commercial fleets. Firstly, advancements in battery technology have led to improved performance, longer ranges, and reduced charging times, making EVs more practical for long-distance travel and heavy-duty applications. Secondly, the declining costs of EV batteries and the increasing availability of charging infrastructure have made the transition more financially viable for businesses. Additionally, government incentives and subsidies further encourage fleet operators to make the switch, offering tax benefits and grants for the purchase and installation of charging stations.
Fleet operators are increasingly recognizing the benefits of electric vehicles, including reduced operating costs, lower maintenance requirements, and improved fleet efficiency. For example, electric delivery vehicles can offer quieter operation, reduced noise pollution, and lower fuel costs compared to their internal combustion engine counterparts. Moreover, the integration of EVs into commercial fleets aligns with the growing consumer demand for sustainable transportation options, enhancing brand reputation and customer loyalty.
In summary, the number of electric vehicles in commercial fleets in California is substantial and continues to grow. This trend is driven by technological advancements, economic incentives, and the recognition of environmental and operational benefits. As the state's EV market expands, it is essential to monitor and support the continued growth of commercial EV adoption, ensuring a sustainable and resilient transportation system for California's future.
Unlocking California's EV Future: Exploring Tax Credits and Incentives
You may want to see also

Public Transportation: How many EVs are used in public transportation in California?
The adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) in California's public transportation sector is an ongoing process, with a focus on reducing emissions and improving sustainability. As of 2023, the state has made significant strides in integrating EVs into its public transportation infrastructure.
California's public transportation system includes a vast network of buses, trains, and light rail systems, and the transition to EVs is a crucial step towards a greener future. The state's public transportation agencies have been actively acquiring and deploying electric buses, trams, and trains to reduce their carbon footprint. For instance, the San Francisco Municipal Transportation Agency (SFMTA) has been a pioneer in this regard, with a substantial fleet of electric buses in operation. As of 2022, SFMTA's electric bus fleet had grown to over 1,000 buses, making it one of the largest electric bus fleets in the United States. This initiative has significantly contributed to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality in the city.
The California Department of Transportation (Caltrans) has also been involved in the EV revolution. In 2021, Caltrans introduced its first electric-powered train, the Capital Corridor Express, which operates between Sacramento and the San Francisco Bay Area. This move not only showcases the state's commitment to sustainable transportation but also sets a precedent for other public transportation agencies to follow.
In addition to buses and trains, California's public transportation authorities have also embraced electric trams and rail systems. The Los Angeles County Metropolitan Transportation Authority (Metro) has been working on the LA Metro Rail project, which includes the expansion of its light rail system and the introduction of electric trams. As of 2022, Metro had over 50 electric trams in service, with plans to further expand the fleet. These trams are expected to significantly reduce emissions and provide a more sustainable transportation option for residents.
The benefits of EV integration in public transportation are twofold. Firstly, it reduces the reliance on fossil fuels, leading to lower carbon emissions and improved air quality. Secondly, it demonstrates a practical and viable alternative to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles, encouraging further adoption of EVs among the general public.
In summary, California's public transportation system is making substantial progress in adopting electric vehicles, with a focus on buses, trains, trams, and light rail. The state's efforts have resulted in a growing number of EVs on the roads, contributing to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly transportation network. As the technology advances and infrastructure improves, the number of EVs in public transportation is expected to continue rising, further solidifying California's position as a leader in the global transition to electric mobility.
Unraveling the Mystery: The Brain Behind Vehicle Electrical Systems
You may want to see also

Charging Infrastructure: How many EV charging stations are available in California?
California, a leader in the electric vehicle (EV) market, has been actively promoting the adoption of EVs to reduce its carbon footprint. As of 2023, the state has seen a significant rise in the number of electric vehicles on its roads, with an estimated 1.2 million EVs registered, according to the California Air Resources Board (CARB). This number is expected to grow as the state continues to incentivize EV ownership and invest in supporting infrastructure.
The growth of EVs in California has led to a critical need for a robust charging infrastructure network. The availability of charging stations is essential for EV owners to ensure their vehicles are always ready for use, especially for long-distance travel and daily commutes. The state has been working towards expanding this network to accommodate the increasing number of EVs.
As of the latest data, California boasts an extensive network of EV charging stations, with over 30,000 public charging points available across the state. This includes fast-charging stations, which can significantly reduce charging times, and slow-charging stations, which are more common in residential areas and provide a convenient overnight charging solution. The distribution of these charging stations is strategic, aiming to cover urban areas, highways, and popular travel routes to ensure EV owners have access to charging wherever they are.
The California Energy Commission (CEC) has been instrumental in mapping and promoting the development of this charging infrastructure. They have established a comprehensive charging station locator, providing real-time data on the availability of charging stations. This resource is invaluable for EV owners, helping them plan their journeys and locate the nearest charging point when needed. The CEC also offers incentives and grants to encourage the installation of charging stations in both public and private sectors.
Despite the impressive number of charging stations, there are ongoing efforts to further expand and improve the network. The California government, in collaboration with private companies, is working on projects to increase the number of fast-charging stations along major highways, reducing the anxiety associated with long-distance EV travel. Additionally, initiatives to bring charging infrastructure to more rural areas are underway, ensuring that the benefits of EV ownership are accessible to a broader population.
Electric Vehicle Sales Leaders: Who's Dominating the Market?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
As of 2022, California has over 1.4 million electric vehicles registered, making it the state with the highest number of EVs in the United States. This number has been steadily increasing due to the state's incentives and regulations promoting the adoption of electric mobility.
California has implemented several policies and incentives to encourage the use of electric vehicles. These include the California Air Resources Board's (CARB) regulations, which set strict emissions standards, and the Clean Vehicle Rebate Project, offering rebates to residents for purchasing or leasing new electric vehicles. The state's commitment to reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality has been a significant driver for EV adoption.
AA: Yes, California's government has set ambitious goals to further expand the EV market. The state aims to achieve zero-emission vehicle sales by 2035, which will require a significant growth in the number of electric vehicles on the road. The California Air Resources Board has proposed new regulations to accelerate the transition to clean transportation, including incentives for EV charging infrastructure and further reductions in EV costs.