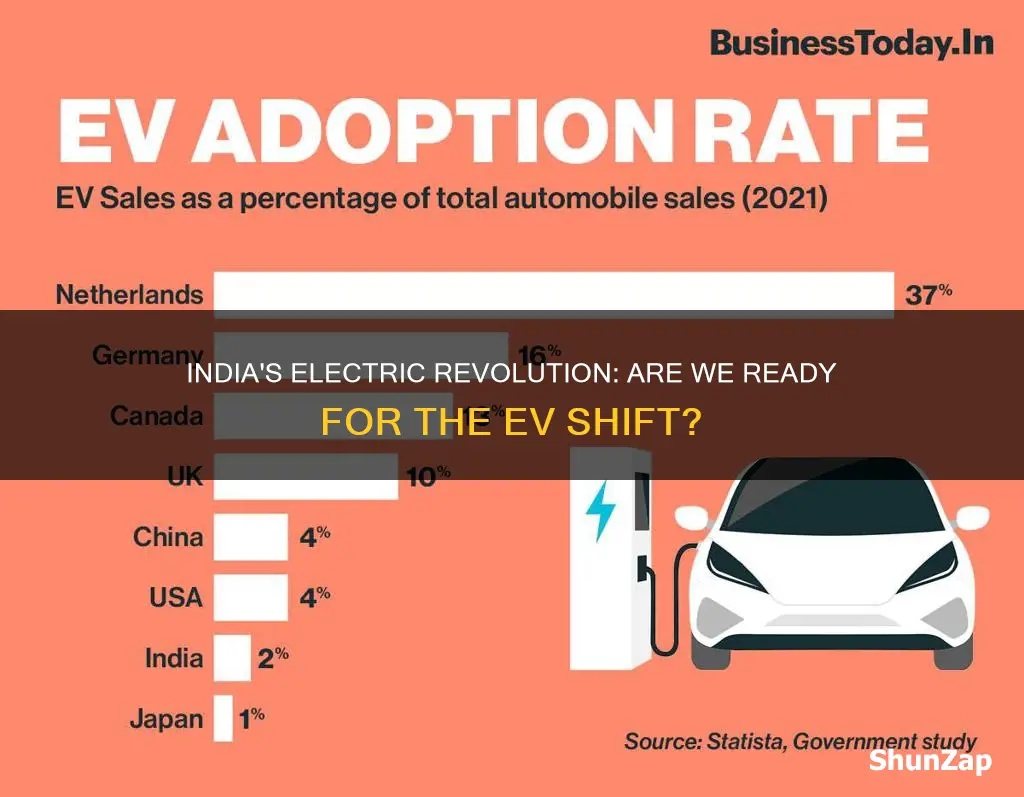
India's transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is a crucial step towards a sustainable future, but is the country prepared for this shift? This group discussion aims to explore the readiness of India's infrastructure, market, and policies to support the widespread adoption of electric cars. Key points will include the current state of EV charging stations, the impact of government incentives, and the challenges faced by the automotive industry in terms of battery technology and supply chain management. Participants will also discuss consumer awareness and the potential economic benefits of a robust EV ecosystem. The discussion will provide valuable insights into the necessary steps to ensure India's readiness for the electric vehicle revolution.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Market Potential | India has a large and growing auto market, with a high potential for electric vehicle (EV) adoption. The country's population, rising disposable income, and increasing urbanization provide a significant consumer base for EVs. |
| Government Support | The Indian government has shown a strong commitment to promoting EVs. It has implemented various policies and incentives, such as tax benefits, subsidies, and infrastructure development, to encourage EV sales and manufacturing. |
| Charging Infrastructure | The country is investing in building a comprehensive charging network. This includes fast-charging stations, home charging solutions, and public charging points, addressing range anxiety and making EVs more convenient for consumers. |
| Battery Technology | India has a growing battery manufacturing ecosystem, with local and international players investing in production facilities. Advances in battery technology, including improved energy density and reduced costs, make EVs more affordable and efficient. |
| Environmental Concerns | India faces severe air pollution and climate change challenges. The shift to EVs is seen as a crucial step towards reducing greenhouse gas emissions and improving air quality, making it an environmentally attractive option. |
| Consumer Awareness | There is a growing awareness among Indian consumers about the benefits of EVs, including lower running costs, reduced environmental impact, and improved performance. This awareness is driving demand and market acceptance. |
| Supply Chain and Manufacturing | The country has a robust automotive supply chain and manufacturing base. Local production of EVs can reduce import dependence, create jobs, and stimulate economic growth. |
| Grid Stability | India's power grid is undergoing modernization to handle the increased demand from EV charging. Smart grid technologies and energy storage solutions are being implemented to ensure stable and efficient power distribution. |
| Brand and Model Availability | Indian consumers have access to a wide range of EV models and brands, catering to various price points and preferences. This diversity is attracting more buyers to the market. |
| After-Sales Services | The development of a robust after-sales service network is crucial for EV adoption. This includes maintenance, repair, and recycling services, ensuring customer satisfaction and long-term sustainability. |
What You'll Learn
- Infrastructure: Charging stations, grid capacity, and renewable energy sources
- Cost and Affordability: Price barriers, subsidies, and economic viability
- Battery Technology: Range, charging speed, and environmental impact
- Consumer Adoption: Public awareness, cultural acceptance, and incentives
- Environmental Impact: Emissions reduction, resource efficiency, and recycling challenges

Infrastructure: Charging stations, grid capacity, and renewable energy sources
India's transition to electric vehicles (EVs) is an exciting prospect, but it requires a robust and sustainable infrastructure to support this shift. The discussion around EV adoption in India should focus on several key aspects of infrastructure development.
Charging Stations: The widespread availability of charging stations is crucial for the successful integration of EVs into the Indian transportation system. The government and private sector should collaborate to establish a comprehensive network of charging stations across urban and rural areas. Fast-charging stations, capable of providing a significant charge in a short time, are essential to reduce the anxiety associated with long charging times. These stations should be strategically placed along highways, in residential areas, and at public facilities like shopping malls and parking lots. Additionally, the development of wireless charging technology can further enhance convenience, allowing for efficient and contactless charging.
Grid Capacity: The electrical grid in India needs to undergo significant upgrades to accommodate the increased demand from EV charging. The current grid infrastructure may struggle to handle the simultaneous charging of millions of electric vehicles, leading to potential overloading and stability issues. Upgrading the grid involves increasing its capacity, improving voltage regulation, and implementing smart grid technologies. Smart meters and advanced monitoring systems can help manage energy distribution efficiently, ensuring that charging stations have the necessary power supply without overburdening the grid. This upgrade process should also focus on making the grid more resilient and adaptable to meet the evolving energy demands of the EV market.
Renewable Energy Sources: Integrating renewable energy sources into the EV infrastructure is vital for India's long-term sustainability goals. The country has vast potential for renewable energy generation through solar, wind, and hydropower. By encouraging the use of renewable energy for EV charging, India can reduce its reliance on fossil fuels and decrease the environmental impact of the transportation sector. Government incentives and subsidies can promote the installation of solar panels on charging stations and residential buildings, allowing for on-site energy generation. Additionally, investing in wind and hydropower projects can provide a stable and clean energy supply for the EV industry, ensuring a more sustainable future for India's transportation needs.
In summary, India's readiness for electric vehicles is closely tied to the development of a robust infrastructure network. The focus on charging stations, grid capacity enhancements, and the integration of renewable energy sources will be pivotal in ensuring a smooth transition to EVs. A comprehensive approach, involving collaboration between government bodies, energy companies, and technology providers, will be essential to address these infrastructure challenges and create a sustainable transportation ecosystem in India.
Ford's Electric Future: A Doubtful Transition?
You may want to see also

Cost and Affordability: Price barriers, subsidies, and economic viability
The adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) in India is a complex issue, and one of the primary concerns is the cost and affordability of these vehicles. India's automotive market is characterized by a wide range of price points, and EVs currently occupy a niche segment. The initial price barrier is a significant challenge, as EVs are generally more expensive than their conventional counterparts. This is primarily due to the higher cost of battery technology, which is a critical component of EVs. The upfront cost of purchasing an EV can be a deterrent for many potential buyers, especially in a country where price sensitivity is high.
To address this issue, governments and automotive manufacturers are exploring various strategies. One approach is to provide subsidies and incentives to make EVs more affordable. These incentives can take the form of tax benefits, grants, or direct subsidies on the purchase of electric vehicles. For instance, the Indian government has introduced the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme, which provides financial assistance to state governments and private entities for promoting EV sales. Such initiatives can significantly reduce the effective price of EVs, making them more accessible to a broader market segment.
Another aspect of cost and affordability is the overall economic viability of EVs in India. The country's energy landscape and infrastructure play a crucial role in determining the feasibility of EV adoption. India has a well-established automotive industry and a robust supply chain, which can support the manufacturing and distribution of EVs. However, the country's electricity sector needs to be more efficient and cost-effective to ensure that the production and operation of EVs are economically viable. The development of a robust charging infrastructure is essential to support the widespread use of EVs, and this requires significant investment.
Furthermore, the cost of battery technology is a critical factor in the economic viability of EVs. India has the potential to develop its battery manufacturing sector, which could reduce the overall cost of EVs. Local production of batteries can lead to economies of scale, making EVs more affordable in the long term. Additionally, the government's focus on promoting renewable energy sources can further enhance the economic viability of EVs by providing a stable and cost-effective power supply.
In conclusion, addressing the cost and affordability of electric vehicles in India requires a multi-faceted approach. Reducing the initial price barrier through subsidies and incentives is essential to stimulate demand. Simultaneously, investments in infrastructure, battery technology, and renewable energy can ensure the long-term economic viability of EVs. By implementing these strategies, India can work towards a more sustainable transportation system and potentially become a global leader in the EV market.
Chevy Spark: Electric Vehicle or Gas-Powered Mystery?
You may want to see also

Battery Technology: Range, charging speed, and environmental impact
Battery technology is a critical component of the electric vehicle (EV) ecosystem, and its advancements are pivotal in addressing the concerns surrounding the adoption of EVs in India. The range of electric vehicles is a significant factor that influences consumer confidence and the overall market acceptance. Modern EV batteries have made remarkable strides, offering improved energy density, allowing for longer driving ranges. This is a crucial aspect for India, where the vast geography and diverse road conditions demand vehicles that can cover substantial distances without frequent charging stops. For instance, the latest models from leading EV manufacturers now boast ranges exceeding 400 kilometers on a single charge, which is a substantial improvement from just a few years ago. This extended range not only makes EVs more practical for long-distance travel but also reduces the anxiety associated with range limitations, a common concern among potential EV buyers.
Charging speed is another essential aspect of battery technology that impacts the user experience. The development of fast-charging batteries has revolutionized the EV charging process. In India, where charging infrastructure is still developing, the ability to quickly recharge batteries is vital. Fast-charging technology can significantly reduce the time required to charge an EV, making it more convenient for daily use. For example, some high-end EVs can now be charged to 80% of their capacity in under an hour, a significant improvement over the traditional charging times of several hours. This rapid charging capability is particularly attractive to urban dwellers who may not have the luxury of time to wait for a full charge.
Environmental impact is a key consideration in the transition to electric mobility. The environmental benefits of EVs are well-documented, with zero tailpipe emissions being a significant advantage. However, the environmental footprint of EV batteries is an area of interest. The production and disposal of batteries can have ecological consequences, but advancements in battery chemistry and recycling technologies are mitigating these issues. For instance, lithium-ion batteries, commonly used in EVs, are now being produced with more sustainable materials, and recycling processes are being refined to recover valuable metals, reducing the environmental impact. Additionally, the use of renewable energy sources for electricity generation further enhances the eco-friendliness of EVs, making them a more sustainable transportation option.
The range of electric vehicles has improved significantly, addressing the initial concern of limited driving distance. Fast-charging technology is also making inroads, ensuring that charging times are manageable. As for environmental impact, the industry is focusing on sustainable practices, from battery production to end-of-life recycling, ensuring that the benefits of EVs outweigh their ecological footprint. These advancements collectively contribute to making electric vehicles a viable and attractive option for India's growing transportation needs.
Unraveling EV Mysteries: A Guide to Diagnostic Techniques
You may want to see also

Consumer Adoption: Public awareness, cultural acceptance, and incentives
India's readiness for electric vehicles (EVs) is a multifaceted discussion, and consumer adoption plays a pivotal role in this transition. Here's an exploration of the key factors influencing public awareness, cultural acceptance, and the role of incentives in promoting EV adoption in India:
Public Awareness:
Creating awareness among the Indian public is crucial for the successful integration of EVs into the mainstream. This involves educating citizens about the environmental benefits of EVs, dispelling misconceptions, and highlighting the long-term cost savings compared to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles. A comprehensive awareness campaign could utilize various media platforms, including television, radio, social media, and community events. Providing accessible information about EV technology, charging infrastructure, and the overall positive impact on the environment can empower potential buyers to make informed choices.
Cultural Acceptance:
India's diverse cultural landscape presents both opportunities and challenges for EV adoption. In some regions, traditional values and a strong attachment to established transportation methods might hinder the acceptance of new technology. Addressing these cultural barriers requires a nuanced approach. Engaging community leaders, influencers, and local organizations can help bridge the gap. Demonstrating the practicality and reliability of EVs through real-life experiences and success stories from early adopters within specific cultural contexts can foster acceptance.
Incentives and Government Support:
Government incentives play a pivotal role in encouraging consumer adoption. Financial incentives such as tax benefits, subsidies, and reduced registration fees can significantly lower the upfront cost of EVs, making them more affordable for a wider range of consumers. Additionally, establishing a robust charging infrastructure network is essential. Government initiatives to provide subsidies or tax benefits for EV charging stations can address range anxiety and make charging more convenient.
Furthermore, implementing policies that offer long-term benefits to EV owners, such as priority lanes for EVs or discounted parking, can further enhance the appeal of electric vehicles. A comprehensive incentive structure, combined with a well-planned charging infrastructure strategy, will be instrumental in accelerating the adoption of EVs in India.
In summary, fostering public awareness, addressing cultural barriers, and providing a strong incentive structure are essential steps in preparing India for the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. A multi-pronged approach involving education, cultural sensitivity, and supportive government policies will contribute to a successful and sustainable EV revolution in the country.
Unveiling the Secrets: A Guide to Spotting Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Environmental Impact: Emissions reduction, resource efficiency, and recycling challenges
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) in India has the potential to significantly reduce the country's carbon footprint and address its environmental challenges. One of the primary environmental impacts of EVs is their role in emissions reduction. Traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles are major contributors to air pollution, emitting harmful gases such as nitrogen oxides (NOx), volatile organic compounds (VOCs), and particulate matter (PM). In contrast, EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, which means they do not release pollutants directly into the atmosphere. This shift from fossil fuel-based transportation to electric-powered vehicles can lead to improved air quality, especially in densely populated urban areas, where the concentration of pollutants is often higher.
Resource efficiency is another critical aspect of the environmental impact of EVs. India, like many other countries, faces the challenge of finite natural resources and the need to move towards a more sustainable economy. EVs are more resource-efficient than their ICE counterparts because they convert a higher percentage of the energy stored in batteries into actual vehicle movement. This efficiency reduces the overall energy consumption and the demand for non-renewable resources, such as oil. Additionally, the use of regenerative braking systems in EVs further enhances resource efficiency by capturing and storing energy that would otherwise be lost during braking.
However, the transition to EVs also presents recycling challenges. As the demand for EVs increases, so does the need for lithium-ion batteries, which are currently the most common type of battery used in electric vehicles. Recycling these batteries is crucial to ensure that the environmental benefits of EVs are not offset by the extraction of raw materials and the generation of waste. The process of recycling lithium-ion batteries involves complex chemical processes and requires specialized facilities. India will need to invest in developing robust recycling infrastructure and technologies to handle the increasing number of batteries that will need to be recycled as the EV market grows.
Furthermore, the recycling of EV batteries also raises concerns about the environmental and health impacts of the recycling process itself. If not managed properly, the recycling of lithium-ion batteries can release toxic substances, such as lead, mercury, and lithium, into the environment. These substances can contaminate soil, water, and air, posing risks to both human health and the ecosystem. Therefore, implementing strict recycling standards and regulations is essential to minimize the environmental impact of EV battery recycling.
In summary, the environmental impact of electric vehicles in India is multifaceted. While EVs offer a promising solution to reduce emissions and improve resource efficiency, the country must also address the challenges associated with battery recycling and the potential environmental and health risks of the recycling process. By focusing on sustainable practices and investing in the necessary infrastructure, India can ensure that the transition to electric vehicles contributes to a greener and more environmentally friendly future.
The Debate: Electric Scooters: A Vehicle or Not?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
India's shift towards electric mobility offers numerous advantages. Firstly, EVs significantly reduce air pollution, which is a critical issue in densely populated urban areas. By adopting electric cars, buses, and two-wheelers, India can improve its air quality, enhance public health, and reduce the carbon footprint associated with transportation. Secondly, EVs provide a more sustainable and cost-effective energy solution. With the country's vast renewable energy resources, especially solar and wind power, India can harness clean energy for its vehicles, reducing reliance on imported fossil fuels and enhancing energy security.
The Indian government has implemented several initiatives to encourage the EV market. These include the Faster Adoption and Manufacturing of Electric Vehicles (FAME) scheme, which provides incentives for EV purchases, and the National Electric Mobility Mission Plan (NEMMP) 2020, aiming to achieve 6-7 million sales of hybrid and electric vehicles by 2020. Additionally, the government has relaxed regulations for EV manufacturing, offering incentives for domestic production and assembly. These measures are expected to boost the EV industry, create jobs, and attract investments, ultimately making India a global hub for electric mobility.
One of the primary challenges is the development of an efficient and widespread charging infrastructure. India needs to invest in a robust network of charging stations to support the growing EV fleet. The government and private sector can collaborate to establish charging stations along highways and in urban areas, ensuring convenience and reducing range anxiety among potential EV buyers. Another challenge is the initial cost of electric vehicles, which can be higher than their conventional counterparts. To address this, the government can offer subsidies, tax benefits, and financing options to make EVs more affordable and accessible to a broader population.







