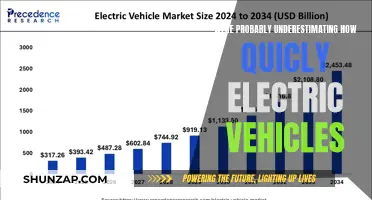
Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained significant popularity as a potential solution to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change. However, despite their environmental benefits, EVs are not a panacea for all our transportation needs. This paragraph will explore the reasons why EVs may not be the ultimate answer to our environmental and societal challenges. It will discuss the limitations of EVs, such as their reliance on finite resources like lithium and cobalt for batteries, the high cost of production and maintenance, and the need for extensive charging infrastructure. Additionally, it will address the environmental impact of EV manufacturing and the potential for increased energy consumption during the charging process. By examining these factors, we can gain a more comprehensive understanding of the complexities surrounding the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
What You'll Learn
- Environmental Impact: EVs may not be as green as thought due to battery production and disposal
- Resource Depletion: Rare earth minerals for batteries are finite and their extraction is harmful
- Energy Source: If powered by fossil fuels, EVs still contribute to emissions and pollution
- Infrastructure: Widespread EV adoption requires significant charging station infrastructure, which is costly and complex
- Cost and Reliability: High initial cost, battery degradation, and limited range are concerns for consumers

Environmental Impact: EVs may not be as green as thought due to battery production and disposal
The environmental benefits of electric vehicles (EVs) have been a topic of much debate, and it's important to consider the full lifecycle of these vehicles to understand their true impact. While EVs are often promoted as a cleaner alternative to traditional internal combustion engines, a closer look reveals that their environmental credentials may not be as straightforward. One of the primary concerns is the production and disposal of their batteries, which can have significant ecological consequences.
Battery manufacturing is an energy-intensive process, requiring substantial amounts of raw materials and energy. The extraction and processing of these materials, such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel, often involve environmentally damaging practices. For instance, lithium mining can lead to habitat destruction and water pollution, while cobalt mining has been associated with human rights abuses and environmental degradation in certain regions. The energy-intensive nature of battery production also contributes to a significant carbon footprint, especially when the electricity used is generated from non-renewable sources.
The environmental impact of EVs extends beyond their production phase. Battery disposal and recycling present unique challenges. As batteries age or become obsolete, they need to be managed carefully to prevent hazardous waste. Improper disposal can lead to soil and water contamination, as batteries contain toxic chemicals and heavy metals. Recycling processes for lithium-ion batteries are still evolving, and not all batteries can be effectively recycled, leading to potential environmental risks.
Furthermore, the large-scale adoption of EVs could put additional strain on the electricity grid, especially if the power is sourced from fossil fuel-based plants. This could result in a net increase in greenhouse gas emissions, particularly if the electricity generation infrastructure is not rapidly decarbonized. Therefore, the environmental benefits of EVs are highly dependent on the energy mix used to power them, and a comprehensive approach to renewable energy sources is necessary to ensure a truly sustainable impact.
In summary, while electric vehicles offer a promising path towards reducing tailpipe emissions, the environmental impact of their battery production and disposal cannot be overlooked. It is crucial to address the challenges associated with raw material extraction, energy consumption, and waste management to ensure that the widespread adoption of EVs contributes positively to the fight against climate change. As the market for EVs grows, so must the focus on sustainable practices throughout their lifecycle.
The Future of EV Tax Credits: What You Need to Know
You may want to see also

Resource Depletion: Rare earth minerals for batteries are finite and their extraction is harmful
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) as a solution to reduce carbon emissions and combat climate change relies on a critical yet often overlooked resource: rare earth minerals. These minerals, including neodymium, praseodymium, and lanthanum, are essential components of the powerful magnets and batteries that power EVs. However, the finite nature of these resources and the environmentally detrimental processes involved in their extraction present significant challenges that cannot be ignored.
The primary concern is the depletion of these rare earth minerals. Despite their name, these elements are not particularly rare in the Earth's crust, but their concentration in economically viable deposits is low. As a result, extracting them requires extensive mining operations, often in regions with limited regulatory oversight. The process of mining and refining these minerals is energy-intensive and can lead to significant environmental degradation, including soil erosion, water pollution, and habitat destruction. For instance, the extraction of neodymium, a key component in the powerful neodymium-iron-boron (NdFeB) magnets used in EVs, is associated with the release of toxic chemicals and heavy metals, posing risks to both human health and local ecosystems.
Furthermore, the global supply chain for rare earth minerals is highly concentrated in a few countries, primarily China, which has dominated the market for decades. This concentration makes the supply vulnerable to geopolitical tensions and economic disruptions. The reliance on a single country for such critical resources could hinder the widespread adoption of EVs, as any disruption in the supply chain could lead to significant delays and increased costs, ultimately affecting the overall viability of the technology.
The environmental impact of extracting these minerals is another critical issue. The process often involves the use of toxic chemicals, such as sulfuric acid and hydrochloric acid, which can contaminate local water sources and soil. The waste generated during the refining process, containing heavy metals and radioactive materials, requires careful management to prevent further environmental damage. Additionally, the energy-intensive nature of the extraction and refining processes contributes to a significant carbon footprint, undermining the very purpose of promoting EVs as a green alternative.
In conclusion, while electric vehicles offer a promising path towards reducing greenhouse gas emissions, the finite nature of rare earth minerals and the harmful extraction processes associated with them present significant challenges. Addressing these issues requires a comprehensive approach, including the development of more sustainable extraction methods, the diversification of supply chains, and the implementation of strict environmental regulations to minimize the ecological footprint of the EV industry. By doing so, we can ensure that the transition to electric mobility is not only environmentally beneficial but also sustainable in the long term.
The Green Revolution: Why Electric Vehicles Rule Over Fossil Fuels
You may want to see also

Energy Source: If powered by fossil fuels, EVs still contribute to emissions and pollution
The notion that electric vehicles (EVs) are a panacea for reducing emissions and pollution is a misconception. While EVs themselves produce zero tailpipe emissions, their environmental impact is not solely determined by the vehicle's exhaust. The energy source used to power these vehicles plays a crucial role in their overall environmental footprint. When EVs are charged using electricity generated from fossil fuels, such as coal or natural gas, the process can still result in significant emissions and environmental degradation.
The primary issue lies in the generation of electricity. Many regions still rely heavily on fossil fuel-based power plants to meet their energy demands. When EVs are plugged into these grids, the electricity used to recharge their batteries often originates from these polluting sources. Coal-fired power plants, for instance, release substantial amounts of carbon dioxide (CO2) and other harmful pollutants during the burning of coal. As a result, the environmental benefits of driving an EV are diminished, and in some cases, even negated.
The process of extracting and transporting fossil fuels also contributes to pollution and emissions. The drilling and mining operations required to access these resources can lead to habitat destruction, soil erosion, and the release of toxic chemicals. Additionally, the transportation of fossil fuels via trucks, trains, or ships can result in further air and water pollution, especially if accidents occur. These activities have a direct impact on the environment and can offset the potential gains from reduced tailpipe emissions.
To truly minimize emissions and pollution, a comprehensive approach is necessary. This includes transitioning to renewable and sustainable energy sources for electricity generation. Solar, wind, hydroelectric, and geothermal power are examples of clean energy alternatives that produce little to no greenhouse gas emissions. Encouraging the use of these renewable sources for EV charging would significantly reduce the environmental impact of electric vehicles.
In summary, while EVs themselves are a step towards a cleaner future, their effectiveness in reducing emissions is contingent on the energy source used to power them. Until the majority of electricity generation shifts to renewable sources, EVs may not provide the expected environmental benefits. Addressing this issue requires a broader energy transition strategy, ensuring that the entire lifecycle of EV usage remains environmentally friendly.
The Electric Revolution: Is the EV Market Booming?
You may want to see also

Infrastructure: Widespread EV adoption requires significant charging station infrastructure, which is costly and complex
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) faces a critical challenge: the need for an extensive and sophisticated charging infrastructure. As the number of EVs on the road increases, so does the demand for convenient and efficient charging solutions. However, the development and maintenance of this infrastructure present significant hurdles.
One of the primary concerns is the financial burden associated with building out the necessary charging networks. Installing and maintaining charging stations require substantial investments. These stations are not just simple outlets; they involve specialized equipment, including fast-charging technology, which demands higher costs. The infrastructure needs to be strategically placed to ensure accessibility for EV owners, which often means locating them along highways, in urban areas, and at various public spaces. This strategic placement adds to the overall expense. Moreover, the complexity of the task is not limited to the initial installation. The charging infrastructure must be designed to handle the power demands of a large number of EVs simultaneously, requiring advanced grid management systems to prevent overloading and ensure stability.
The technical complexity of the charging infrastructure is another significant challenge. Designing and implementing a robust network that can support various charging speeds, from slow to rapid, is a complex task. This includes managing the electrical load on the grid, ensuring that the power supply can meet the demands of multiple charging stations without compromising the stability of the power grid. Additionally, the infrastructure must be adaptable to accommodate future technological advancements in EV charging, such as wireless charging and ultra-fast charging, which are still in the development phase.
Furthermore, the widespread adoption of EVs will likely lead to a surge in electricity consumption, putting additional strain on the existing power infrastructure. This could result in regional power shortages or increased reliance on non-renewable energy sources to meet the growing demand. To address this, significant investments in renewable energy sources and smart grid technologies are necessary to ensure a sustainable and reliable power supply for EV charging.
In summary, while electric vehicles offer environmental benefits, the transition to widespread EV adoption requires a comprehensive and costly charging infrastructure. The technical and financial complexities of building and maintaining this infrastructure are significant challenges that need to be addressed to ensure a smooth and sustainable shift towards electric mobility. This includes strategic planning, substantial investments, and the integration of advanced technologies to support the growing demand for EV charging.
Electric Vehicles: The Rapid Overtake in the Automotive Industry
You may want to see also

Cost and Reliability: High initial cost, battery degradation, and limited range are concerns for consumers
The initial cost of electric vehicles (EVs) is a significant barrier to widespread adoption. While the technology has advanced, the high upfront expense remains a major deterrent for many potential buyers. EVs often carry a premium price tag compared to their gasoline counterparts, and this can be a substantial investment for individuals and families. The cost includes not only the vehicle itself but also the installation of home charging stations, which can further increase the financial burden. Despite the long-term savings potential through reduced fuel and maintenance costs, the immediate outlay is a critical factor that keeps many people from making the switch.
Battery degradation is another critical issue that impacts the reliability and long-term viability of EVs. The performance and range of electric cars are directly tied to the health of their batteries. Over time, these batteries degrade, leading to reduced driving range and, in some cases, decreased overall performance. This degradation can be accelerated by various factors, including extreme temperatures, frequent rapid charging, and driving habits. As a result, EV owners may find themselves facing the need for costly battery replacements or facing the limitations of their vehicles' range, especially during long journeys or in regions with less-developed charging infrastructure.
The limited range of EVs is a concern that often arises from the previous point. While battery technology has improved, the range of most electric vehicles is still not comparable to that of conventional cars. This can be a significant issue for those who frequently travel long distances or live in areas with limited charging options. The anxiety of running out of battery power mid-journey, known as 'range anxiety,' is a real challenge for many EV owners. To address this, some manufacturers offer larger battery packs, but these come at a higher cost, further contributing to the initial expense.
Furthermore, the availability and accessibility of charging infrastructure play a crucial role in the reliability of EVs. The widespread adoption of electric vehicles relies on a robust and convenient charging network. However, the current infrastructure is not yet comprehensive, especially in rural areas and certain regions. Long charging times at public stations can be inconvenient, and the lack of readily available charging points may discourage potential buyers. Until the charging network becomes more extensive and efficient, the reliability of EVs as a practical transportation solution remains a concern.
In summary, the high initial cost, battery degradation, and limited range are significant factors that contribute to the perception that electric vehicles are not the answer to the automotive industry's challenges. These concerns impact consumer confidence and the overall practicality of EVs, especially when compared to traditional vehicles. Addressing these issues through technological advancements, infrastructure development, and cost-effective solutions is essential to making electric vehicles a more attractive and reliable choice for the masses.
Green Revolution: Are Electric Vehicles the Eco-Friendly Choice?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
While EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, the environmental benefits are often offset by the significant carbon footprint associated with their production and the generation of electricity for charging. The manufacturing process of EV batteries requires substantial energy and resources, leading to high greenhouse gas emissions. Additionally, the current energy mix in many regions still relies heavily on fossil fuels, which means that the environmental impact of EVs can vary depending on the local energy sources.
Widespread EV adoption faces several challenges. Firstly, the initial cost of EVs is often higher compared to traditional vehicles, which can be a barrier for many consumers. Secondly, the charging infrastructure for EVs is still developing, and the availability of charging stations varies across regions, causing range anxiety for potential buyers. Lastly, the recycling and disposal of EV batteries present complex environmental and logistical issues that need to be addressed.
The integration of EVs into the power grid can have both positive and negative effects. On the positive side, EVs can act as mobile energy storage devices, helping to balance the grid during peak demand. However, a large-scale EV charging demand can strain the grid, especially if it relies on a centralized power system. This may lead to increased electricity prices and potential blackouts if not managed properly.
EVs are a step towards reducing urban pollution, but they are not the sole or ultimate solution. Urban pollution is a complex issue influenced by various factors such as industrial emissions, transportation infrastructure, and energy generation. While EVs contribute to cleaner air in cities, other measures like improving public transportation, promoting cycling and walking, and implementing stricter emission standards for industries are equally important in combating urban pollution.
The transition to a widespread EV market can have significant economic implications. On the one hand, it may stimulate job growth in the automotive and energy sectors, particularly in battery manufacturing and charging infrastructure development. On the other hand, it could lead to a decline in the traditional automotive industry, affecting jobs and related businesses. Additionally, the shift towards EVs may impact the used car market and insurance sectors, requiring adjustments in existing economic models.