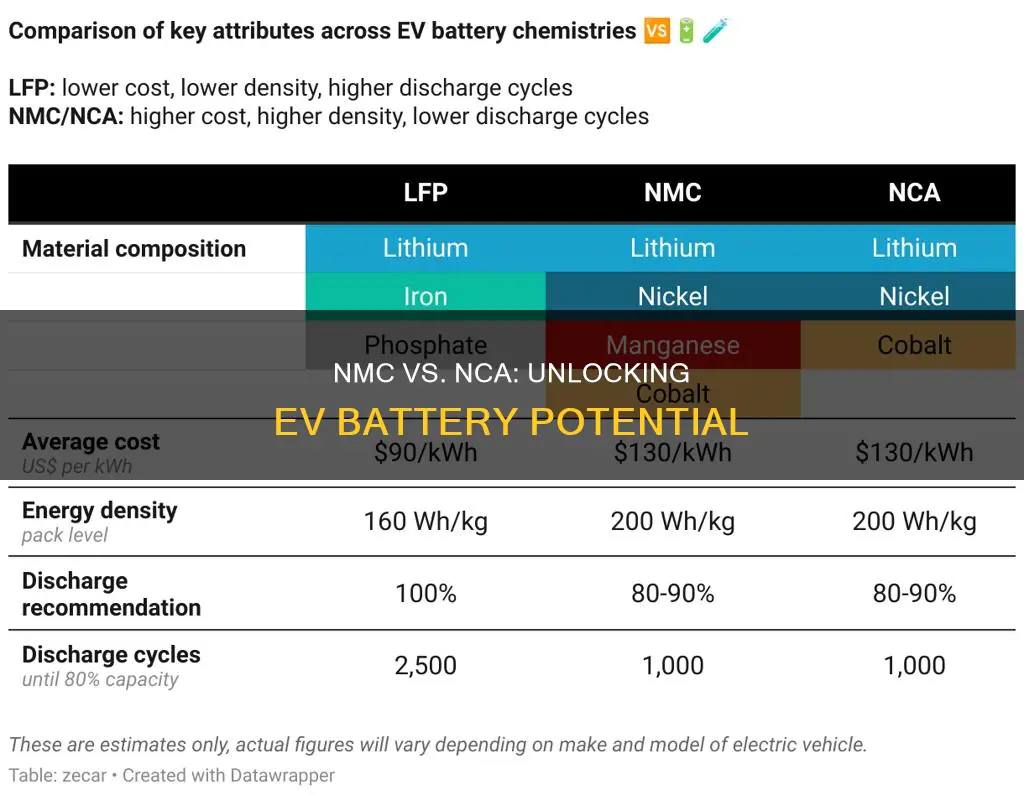
The debate surrounding the choice of battery chemistry for electric vehicles (EVs) is a crucial aspect of the industry's evolution. Among the various options, Nickel-Manganese-Cobalt (NMC) and Nickel-Cobalt-Aluminum (NCA) chemistries have emerged as leading contenders. NMC batteries offer a balance of energy density, cost-effectiveness, and safety, making them a popular choice for many EV manufacturers. On the other hand, NCA batteries provide higher energy density and improved thermal stability, which can be advantageous for high-performance EVs. This introduction sets the stage for a detailed exploration of the advantages and disadvantages of both NMC and NCA chemistries in the context of electric vehicle technology.
What You'll Learn
- Performance: NMC offers higher energy density, faster charging, and longer lifespan for electric vehicles
- Cost: NCA is more cost-effective due to lower material costs and easier manufacturing
- Safety: NMC batteries are generally safer with lower risk of thermal runaway
- Environmental Impact: NCA is more eco-friendly due to fewer resource-intensive materials
- Recycling: NMC batteries are easier to recycle, reducing waste and promoting sustainability

Performance: NMC offers higher energy density, faster charging, and longer lifespan for electric vehicles
NMC (Niobium-Manganese-Cobalt) chemistry has emerged as a leading contender in the quest for improved battery performance in electric vehicles (EVs). One of its most significant advantages is its ability to offer higher energy density, a critical factor in maximizing the range of EVs. Higher energy density means that more energy can be stored in a given volume, allowing for longer driving ranges without increasing the battery size. This is particularly important for EVs, as it addresses a key consumer concern: range anxiety, the fear of running out of battery power during a journey.
The higher energy density of NMC batteries is attributed to the unique combination of its constituent elements. Niobium, a rare earth metal, provides exceptional stability and strength, while Manganese and Cobalt contribute to the battery's high voltage and energy storage capacity. This combination results in a more compact and lightweight battery pack, which is essential for improving the overall efficiency and performance of electric vehicles.
In addition to energy density, NMC batteries also excel in terms of charging speed. The rapid charging capabilities of NMC are a result of its chemical structure, which allows for faster ion movement and reduced internal resistance. This means that EVs equipped with NMC batteries can recharge more quickly, reducing the time spent at charging stations and enhancing the overall convenience of electric vehicle ownership.
The longevity of NMC batteries is another area where it shines. NMC chemistry is known for its stability and resistance to degradation over time. This translates to a longer lifespan for the battery, which is crucial for the long-term reliability and cost-effectiveness of electric vehicles. With fewer performance declines over the years, NMC batteries can provide consistent performance, ensuring that EVs maintain their range and efficiency over an extended period.
Furthermore, the performance benefits of NMC extend to various operating conditions. These batteries demonstrate excellent thermal stability, which is vital for managing the heat generated during high-power driving and rapid charging. This thermal stability contributes to the overall safety and efficiency of the battery system, making NMC an attractive choice for EV manufacturers aiming to optimize their vehicle's performance and safety.
Chevy Spark: Electric Vehicle or Gas-Powered Mystery?
You may want to see also

Cost: NCA is more cost-effective due to lower material costs and easier manufacturing
When considering the cost-effectiveness of battery chemistries for electric vehicles (EVs), Nickel-Cobalt-Aluminum (NCA) emerges as a compelling option. One of the primary reasons for its cost advantage lies in the materials used. NCA batteries utilize a combination of nickel, cobalt, and aluminum, which are relatively abundant and less expensive compared to other alternatives like Nickel-Manganese-Cobalt (NMC). The lower material costs of NCA contribute significantly to its overall affordability.
The manufacturing process of NCA batteries is also streamlined, making it more cost-effective. The production involves fewer steps and simpler processes, reducing the complexity and time required for assembly. This simplicity in manufacturing translates to lower production costs, as it requires less specialized equipment and less energy-intensive processes. As a result, EV manufacturers can produce NCA batteries at a lower price point, making it an attractive choice for cost-conscious consumers.
Furthermore, the cost-effectiveness of NCA extends beyond the initial purchase price. NCA batteries have shown promising longevity and performance, which can lead to reduced maintenance and replacement costs over the lifetime of the EV. This is particularly important for electric vehicles, where battery replacement can be a significant expense for owners. With NCA, the potential for lower maintenance requirements and extended battery life contributes to its overall cost-efficiency.
In summary, NCA's cost-effectiveness is attributed to its use of readily available and less expensive materials, coupled with a simplified manufacturing process. These factors make NCA batteries more affordable for EV manufacturers and consumers alike, addressing the critical aspect of cost in the adoption of electric vehicles. As the demand for sustainable transportation solutions grows, NCA's cost-advantages could play a significant role in making EVs more accessible to a broader market.
Colorado EV Tax Credit: Refundable or Not?
You may want to see also

Safety: NMC batteries are generally safer with lower risk of thermal runaway
NMC (Niobium-Manganese-Cobalt) batteries have gained significant attention in the electric vehicle (EV) market due to their improved safety characteristics compared to their predecessors, such as NCA (Niobium-Cobalt-Aluminum) batteries. One of the key advantages of NMC batteries is their lower risk of thermal runaway, a critical safety concern in EV technology.
Thermal runaway is a self-perpetuating sequence of events where an increase in temperature leads to further exothermic reactions, potentially causing the battery to catch fire or explode. NMC batteries have been engineered to mitigate this risk. The composition of NMC materials, particularly the inclusion of nickel and cobalt, allows for a more stable electrochemical reaction. This stability reduces the likelihood of excessive heat generation during charging or discharging, making NMC batteries safer for EV applications.
The safety of NMC batteries is further enhanced by their design and manufacturing processes. These batteries often feature advanced cooling systems and safety mechanisms to prevent overheating. Additionally, the use of NMC materials in EV batteries can lead to longer cycle life, which indirectly contributes to safety. A battery with a longer lifespan is less likely to degrade rapidly, reducing the chances of thermal issues arising from prolonged use.
In contrast, NCA batteries, while offering high energy density, have been associated with a higher risk of thermal runaway. The higher cobalt content in NCA materials can lead to more exothermic reactions, especially under certain charging conditions. This has prompted researchers and manufacturers to focus on NMC technology to ensure the safety and reliability of EV batteries.
The safety aspect of NMC batteries is a crucial factor in the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. As the demand for sustainable transportation grows, the reliability and safety of EV batteries become even more critical. NMC batteries, with their lower thermal runaway risk, are well-positioned to meet these demands, providing a safer and more stable power source for electric vehicles.
Unleash the Power: 5 Signs to Identify Your Hybrid Electric Vehicle
You may want to see also

Environmental Impact: NCA is more eco-friendly due to fewer resource-intensive materials
The environmental impact of lithium-ion battery technology is a critical consideration in the development of electric vehicles (EVs). Among the various cathode materials, Nickel-Cobalt-Aluminum (NCA) has emerged as a promising candidate, offering several advantages over other options like Nickel-Manganese-Cobalt (NMC). One of the key reasons for NCA's environmental superiority is its composition and the associated resource requirements.
NCA cathodes are formulated with a unique blend of nickel, cobalt, and aluminum, which are all relatively abundant elements. This abundance is a significant factor in reducing the environmental footprint of EV battery production. In contrast, NMC cathodes often contain manganese, which, while more abundant than cobalt, still require substantial energy and resources to extract and process. The extraction and processing of manganese can lead to environmental degradation, including habitat destruction and water pollution.
The resource-intensive nature of NMC production is a major concern. The mining and processing of cobalt, for instance, have been associated with severe environmental and social impacts, including habitat destruction, water pollution, and human rights issues. In contrast, the extraction and use of nickel and aluminum in NCA cathodes have a relatively lower environmental impact. Nickel, in particular, is a widely available metal, and its extraction and processing can be more sustainable compared to the mining of cobalt-rich ores.
Furthermore, the energy efficiency of NCA cathodes is another aspect that contributes to their eco-friendliness. The manufacturing process of NCA can be optimized to minimize energy consumption, reducing the overall carbon footprint of EV battery production. This is particularly important in the context of the EV industry's goal to reduce its environmental impact and promote sustainability.
In summary, NCA's environmental superiority over NMC is evident in its use of fewer resource-intensive materials. The abundance of nickel and aluminum, coupled with the reduced need for energy-intensive manganese extraction, makes NCA a more sustainable choice for EV battery cathodes. This aspect is crucial in the ongoing efforts to make electric vehicles more environmentally friendly and to accelerate the transition towards a greener transportation system.
Unlocking EV Affordability: Strategies for Developing Nations
You may want to see also

Recycling: NMC batteries are easier to recycle, reducing waste and promoting sustainability
NMC (Nickel-Manganese-Cobalt) batteries have gained significant attention in the electric vehicle (EV) industry due to their high energy density and improved performance compared to traditional lithium-ion batteries. One of the key advantages of NMC batteries is their recyclability, which plays a crucial role in promoting sustainability and reducing environmental impact.
Recycling NMC batteries is a more straightforward process compared to other lithium-ion battery chemistries. The recycling process typically involves several steps to recover valuable materials and minimize waste. Firstly, the battery is disassembled, separating the cathode and anode materials. The cathode, which is the most valuable component, is then processed to extract nickel, manganese, and cobalt. These metals can be recycled and reused in the manufacturing of new NMC batteries, reducing the need for mining and conserving natural resources. The anode material, often graphite, can also be recycled and repurposed, ensuring a more circular economy for EV battery production.
The ease of recycling NMC batteries is attributed to their chemical composition and the availability of established recycling technologies. The nickel, manganese, and cobalt in NMC cathodes are relatively stable and less prone to degradation during the recycling process. This stability allows for more efficient recovery of these metals, ensuring a higher recycling rate and reducing the environmental impact associated with battery disposal.
Furthermore, the recycling of NMC batteries contributes to waste reduction and sustainability. By implementing efficient recycling practices, the industry can minimize the amount of batteries ending up in landfills, which could otherwise release harmful chemicals and contribute to environmental pollution. Proper recycling also helps in preventing the release of toxic substances into the air and water, ensuring a safer and more environmentally friendly approach to battery disposal.
In summary, NMC batteries' recyclability is a significant advantage in the context of electric vehicles. The ease of recycling these batteries allows for the recovery of valuable materials, reduces waste, and promotes a more sustainable approach to EV battery production and disposal. As the demand for electric vehicles continues to grow, investing in efficient recycling technologies for NMC batteries will be essential to building a greener and more sustainable future.
Mastering Battery Module Design: A Guide to Electric Vehicle Power
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Both NMC and NCA are popular cathode materials used in lithium-ion batteries for electric vehicles. NMC typically refers to lithium-ion batteries with a cathode composition of lithium nickel manganese cobalt oxide (LiNiMnCoO2). It offers a good balance of energy density and safety. NCA, on the other hand, is a lithium-ion battery cathode with a composition of lithium nickel cobalt aluminum oxide (LiNiCoAlO2). NCA provides higher energy density compared to NMC, making it an attractive choice for vehicles that require longer ranges.
NMC batteries are known for their excellent cycle life and thermal stability, which contributes to the overall reliability of electric vehicles. They provide a good balance of power and energy density, ensuring efficient acceleration and decent driving range. NCA batteries, with their higher energy density, can offer even longer ranges, making them ideal for vehicles that require extended travel without frequent charging. However, NCA batteries might have slightly lower cycle life compared to NMC.
NMC batteries are generally considered more mature and widely used in the market, offering a proven track record of performance and safety. They are known for their ability to operate in a wide temperature range, which is beneficial for various climates. NCA batteries, while providing higher energy density, may have a slightly narrower operating temperature range and could be more sensitive to thermal management. However, ongoing research and development aim to improve the performance and address the challenges of both chemistries.







