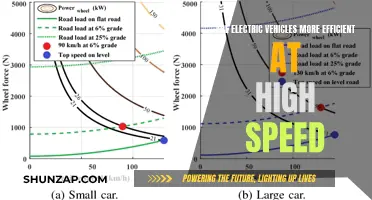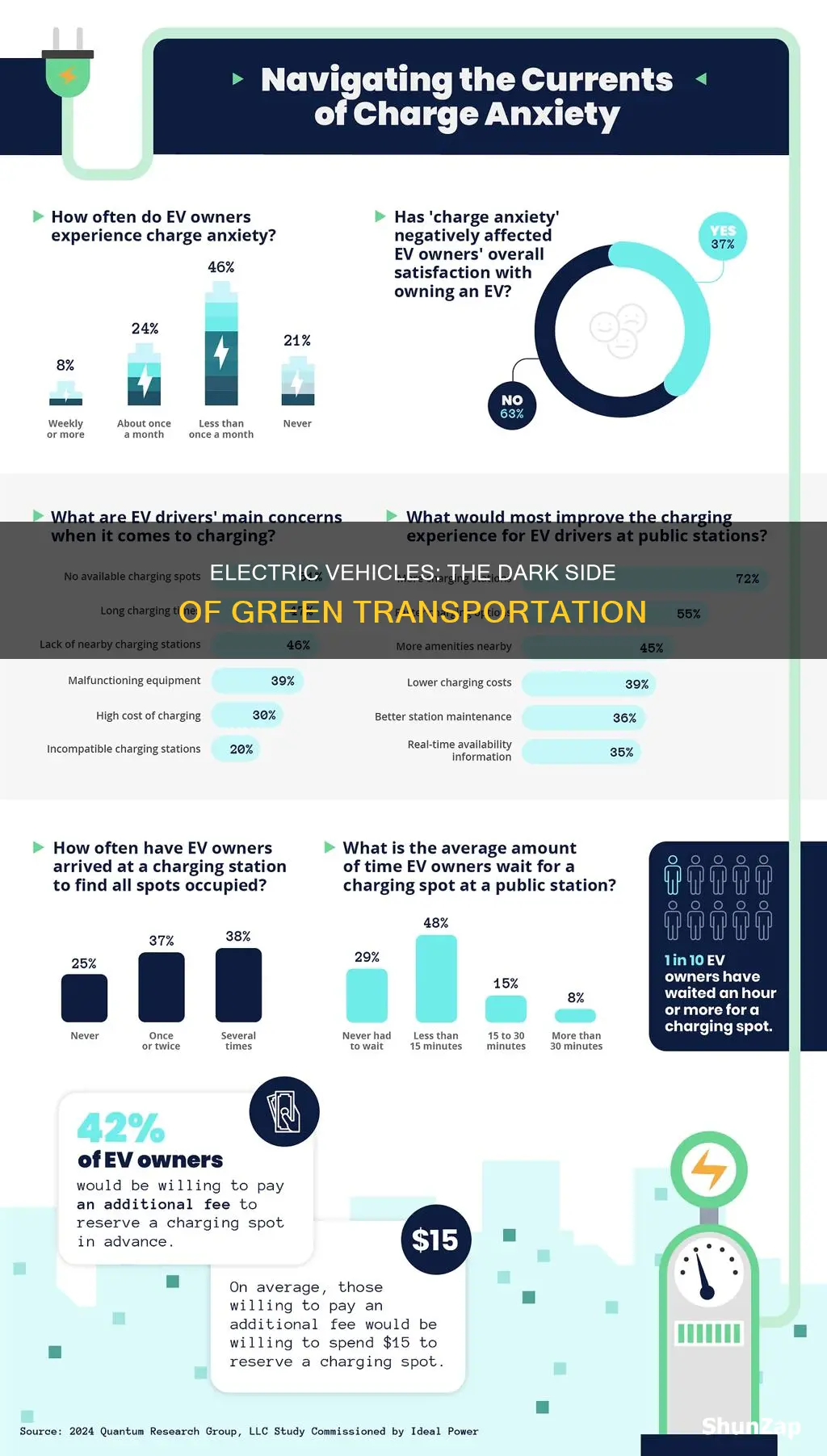
While electric vehicles (EVs) offer numerous benefits, such as reduced environmental impact and lower running costs, they also come with certain drawbacks. One significant concern is the limited driving range, which can be a challenge for long-distance travel. Additionally, the time required to recharge an EV's battery can be substantial, often taking much longer than the time needed to refuel a conventional vehicle. The availability of charging infrastructure is another critical issue, as not all areas have adequate charging stations, potentially causing inconvenience and range anxiety for EV owners. Furthermore, the initial purchase price of EVs can be higher compared to their gasoline counterparts, although this gap is narrowing with technological advancements and government incentives. Lastly, the disposal and recycling of EV batteries raise environmental and ethical questions, as the extraction of raw materials and the proper handling of used batteries require careful consideration.
What You'll Learn
- High upfront cost: Initial purchase price can be a barrier for many consumers
- Limited range: Range anxiety remains a concern for long-distance travel
- Charging infrastructure: Access to charging stations is not always convenient or available
- Battery degradation: Over time, batteries may lose efficiency and capacity
- Environmental impact: Manufacturing and disposal of batteries can have ecological consequences

High upfront cost: Initial purchase price can be a barrier for many consumers
The high upfront cost of electric vehicles (EVs) is a significant barrier to entry for many consumers. While the long-term benefits of EVs, such as reduced fuel and maintenance costs, are well-known, the initial purchase price can be a substantial financial hurdle. This is especially true for those on a tight budget or those who are not yet ready to commit to a long-term investment.
The cost of EVs can vary widely depending on the make, model, and features. While some luxury EVs can cost upwards of $100,000, even more affordable models can still be priced in the mid-to-high range. For example, the base model of the popular Tesla Model 3 starts at around $40,000, while the fully loaded version can exceed $60,000. This price point is significantly higher than the average price of a gasoline-powered vehicle, which can be found in the $20,000 to $30,000 range.
There are several reasons for this price disparity. Firstly, EVs are relatively new technology, and the cost of research and development, as well as the specialized components required, can be high. Additionally, the limited production volumes of many EVs can drive up prices due to the higher costs associated with smaller-scale manufacturing. Furthermore, the lack of a second-hand market for EVs, as they are still a relatively niche product, can also contribute to their higher upfront cost.
For many consumers, this high upfront cost can be a deal-breaker. It may be challenging for individuals or families on a tight budget to justify the expense, especially when they can purchase a more conventional vehicle for a similar price. This financial barrier can also be a significant issue for those who are not yet ready to make a long-term commitment to EV ownership, as the initial investment may be too high to take the plunge.
However, it's important to note that the high upfront cost of EVs is a temporary issue. As the technology matures and production volumes increase, the prices of EVs are expected to decrease. Many governments and organizations also offer incentives and subsidies to encourage the adoption of EVs, which can help offset the initial cost. Additionally, the long-term savings and environmental benefits of EVs can provide a compelling argument for those who can afford the initial investment.
Unlocking EV Tax Savings: A Guide to Maximizing Your Credit
You may want to see also

Limited range: Range anxiety remains a concern for long-distance travel
The limited range of electric vehicles (EVs) is a significant concern for potential buyers, especially those who frequently embark on long-distance journeys. While the technology has advanced, the range of EVs is still not comparable to that of conventional gasoline or diesel vehicles. This limitation can induce 'range anxiety,' a term used to describe the fear of running out of battery power during a journey.
EVs typically offer a range of around 100-300 miles on a single charge, which may be sufficient for daily commutes or short trips. However, for longer journeys, the limited range can be a challenge. The infrastructure for charging EVs is improving, but it is not yet as extensive as the network of gas stations. This means that travelers may need to plan their routes carefully, ensuring they have access to charging stations along the way. The availability of fast-charging stations can help reduce the time spent waiting for a charge, but it does not eliminate the need for careful planning.
Range anxiety can be particularly stressful for those who are new to EVs or are not familiar with the charging infrastructure. It may also deter potential buyers who are used to the convenience of refueling their vehicles quickly at gas stations. The anxiety can lead to a sense of insecurity, especially when embarking on a trip, as drivers may constantly worry about finding a charging station or having to deal with a depleted battery.
To address this issue, manufacturers are working on improving battery technology to increase range. Some EVs now offer ranges of over 300 miles on a single charge, which is a significant improvement. Additionally, the development of more efficient charging systems and the expansion of the charging infrastructure are helping to alleviate range anxiety. However, until these improvements are widespread, it is essential for EV owners to plan their trips carefully and be aware of the limitations of their vehicles.
In conclusion, while electric vehicles offer numerous benefits, the limited range remains a critical consideration for long-distance travel. Range anxiety is a real concern that can impact the overall ownership experience. As the technology advances and the charging infrastructure expands, these issues will likely become less prominent, but for now, potential buyers should be aware of the constraints and plan accordingly.
Transform Your Ride: A Guide to Electric Brakes Conversion
You may want to see also

Charging infrastructure: Access to charging stations is not always convenient or available
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) has brought about numerous benefits, including reduced environmental impact and lower running costs. However, one significant challenge that persists is the issue of charging infrastructure and the lack of convenient access to charging stations. This problem highlights a critical aspect of EV ownership that needs to be addressed for the technology to truly thrive.
In many regions, the availability of charging stations is limited, and this scarcity can lead to range anxiety among EV owners. Range anxiety refers to the fear of running out of battery power before reaching a charging station. This anxiety is a real concern, especially for those who frequently travel long distances or live in areas with inadequate charging infrastructure. The current situation often forces EV owners to plan their trips carefully, ensuring they have access to charging points along the route. This planning can be time-consuming and may restrict spontaneity, which is a common frustration for many potential EV buyers.
The issue of charging infrastructure is further exacerbated in rural areas, where the density of charging stations is often significantly lower compared to urban settings. Rural residents may have to travel long distances to find a charging point, making the transition to EVs less appealing for those living in more remote locations. This disparity in charging accessibility between urban and rural areas is a significant barrier to the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
To address this con, governments and energy companies need to invest in comprehensive charging networks. This includes installing fast-charging stations along major highways and in strategic locations within cities. Additionally, encouraging the development of home charging solutions can empower individuals to charge their vehicles overnight or during periods of low energy demand. By improving the availability and convenience of charging stations, the transition to electric vehicles can become more seamless and appealing to a broader audience.
In conclusion, while electric vehicles offer numerous advantages, the lack of convenient charging infrastructure remains a significant obstacle. It is essential to recognize and address this challenge to ensure the successful integration of EVs into our transportation systems. By doing so, we can work towards a more sustainable future, reducing our reliance on fossil fuels and minimizing the environmental impact of the transportation sector.
Unveiling the Surprising Environmental Impact of Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Battery degradation: Over time, batteries may lose efficiency and capacity
Battery degradation is a significant concern for electric vehicle (EV) owners, as it directly impacts the performance and longevity of their vehicles. Over time, the batteries in EVs can experience a decline in efficiency and capacity, leading to reduced range and overall performance. This degradation is a natural process and is influenced by various factors, including the type of battery, usage patterns, environmental conditions, and maintenance practices.
The degradation of EV batteries is primarily due to the chemical reactions that occur within the battery cells during charging and discharging cycles. Rechargeable lithium-ion batteries, commonly used in EVs, undergo a process called capacity fade. This means that over repeated charge-discharge cycles, the battery's ability to store and deliver energy decreases. The rate of degradation can vary depending on the specific battery chemistry and design. For instance, some lithium-ion batteries may degrade more rapidly due to factors like high charging temperatures or frequent rapid charging.
Several factors contribute to battery degradation. Firstly, the number of charge-discharge cycles plays a crucial role. Each time an EV battery is charged and discharged, the chemical reactions within the cells cause a small amount of capacity to be lost. While modern EVs are designed to manage these cycles efficiently, the cumulative effect over time can lead to reduced performance. Secondly, environmental conditions are significant. Extreme temperatures, both hot and cold, can accelerate battery degradation. High temperatures can cause increased internal resistance and thermal runaway, while cold temperatures can reduce the battery's ability to deliver power effectively.
To mitigate the effects of battery degradation, EV manufacturers employ various strategies. One approach is to use advanced battery management systems (BMS) that monitor and optimize charging and discharging processes. These systems can adjust charging rates, manage temperature, and predict battery health to extend its lifespan. Additionally, some EVs are equipped with regenerative braking systems that recover energy during braking, reducing the strain on the battery and improving overall efficiency.
EV owners can also take certain measures to minimize battery degradation. Regular maintenance, including software updates and battery health checks, can help identify and address potential issues. Proper charging habits, such as avoiding rapid charging at high temperatures and using slow charging when possible, can also contribute to longer battery life. Furthermore, understanding the battery's performance and range limitations can help drivers plan their journeys effectively, ensuring they have sufficient charge for their needs.
India's Electric Revolution: Are We Ready for the Change?
You may want to see also

Environmental impact: Manufacturing and disposal of batteries can have ecological consequences
The environmental impact of electric vehicles (EVs) extends beyond their operation, particularly in the realms of battery manufacturing and disposal. While EVs offer numerous benefits in terms of reduced emissions and energy efficiency, the process of creating and disposing of their batteries presents several ecological challenges.
Battery manufacturing is an energy-intensive process, often requiring significant amounts of raw materials such as lithium, cobalt, and nickel. The extraction and processing of these materials can have detrimental effects on the environment. For instance, lithium mining, a crucial component in lithium-ion batteries, often involves water-intensive processes and can lead to habitat destruction and water pollution if not managed sustainably. Similarly, the extraction of cobalt, another essential material, has been associated with environmental degradation and human rights issues in mining regions. The energy-intensive nature of battery production also contributes to a substantial carbon footprint, further exacerbating the environmental impact.
As the demand for EVs rises, the issue of battery disposal becomes increasingly critical. The batteries used in these vehicles contain hazardous materials, and improper disposal can result in severe environmental consequences. When batteries are discarded in landfills, toxic chemicals can leach into the soil and groundwater, posing risks to ecosystems and human health. Additionally, the recycling and disposal of batteries require specialized infrastructure and processes, which may not be readily available in all regions, leading to potential environmental hazards.
The environmental impact of battery manufacturing and disposal is a complex issue that requires a multifaceted approach. Firstly, improving the sustainability of raw material extraction and processing is essential. This can be achieved through implementing more efficient and environmentally friendly extraction methods, as well as promoting the use of recycled materials in battery production. Secondly, developing robust recycling and disposal systems is crucial. Governments and industries should invest in infrastructure and technologies that enable the safe and efficient recycling of batteries, ensuring that hazardous materials are recovered and reused.
Furthermore, research and development in battery technology can play a significant role in mitigating these environmental concerns. Scientists and engineers are exploring innovative battery designs and materials that offer improved performance and reduced environmental impact. For example, solid-state batteries, which replace the liquid electrolyte with a solid conductive material, have the potential to provide higher energy density while minimizing the risks associated with liquid chemicals.
In summary, while electric vehicles offer a more sustainable transportation option, the manufacturing and disposal of batteries present ecological challenges. Addressing these issues requires a combination of sustainable practices in raw material extraction, efficient recycling systems, and technological advancements in battery design. By tackling these aspects, we can work towards minimizing the environmental footprint of EVs and ensuring a more sustainable future for the automotive industry.
Unleash Savings: Your Guide to Federal EV Credit Claims
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
While EVs offer numerous benefits, there are a few potential drawbacks to consider. Firstly, the initial cost of purchasing an EV can be higher compared to traditional gasoline vehicles, although this is offset by lower running costs over time. Secondly, the range anxiety associated with EVs is a concern, as the fear of running out of battery charge during a journey can be a challenge for those with limited access to charging stations. Lastly, the time required to recharge an EV's battery is significantly longer than refueling a gasoline vehicle, which may be inconvenient for some drivers.
Electric vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, which significantly reduces air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions compared to gasoline-powered cars. However, it's important to note that the environmental benefits depend on the source of electricity used to charge the EV. If the electricity is generated from renewable sources, the overall carbon footprint of EVs is much lower. Nevertheless, the manufacturing and disposal of EV batteries can have environmental implications, and the extraction of raw materials for battery production may raise sustainability concerns.
Some early electric vehicles have faced criticism for their reliability, particularly regarding battery degradation and performance over time. However, modern EVs have made significant advancements in this regard. Most manufacturers now offer warranties on battery performance, ensuring that the range and overall functionality are maintained for an extended period. As technology improves, the reliability of EVs is expected to continue enhancing, addressing many of the initial concerns.
The infrastructure for charging electric vehicles is rapidly expanding, but it still varies across regions. In some areas, the availability of charging stations can be limited, making it challenging for EV owners to find convenient places to recharge. However, many governments and private companies are investing in the development of charging networks, and the number of charging points is increasing steadily. Public charging stations, home charging options, and mobile charging solutions are becoming more accessible, addressing the issue of range anxiety.
Absolutely. Electric vehicles have revolutionized the automotive industry with their instant torque, smooth acceleration, and responsive driving dynamics. EVs offer a unique and engaging driving experience, often providing better handling and cornering capabilities. Additionally, the advanced technology and connectivity features in modern EVs contribute to a more sophisticated and enjoyable driving experience, making them a viable and appealing alternative to conventional cars.