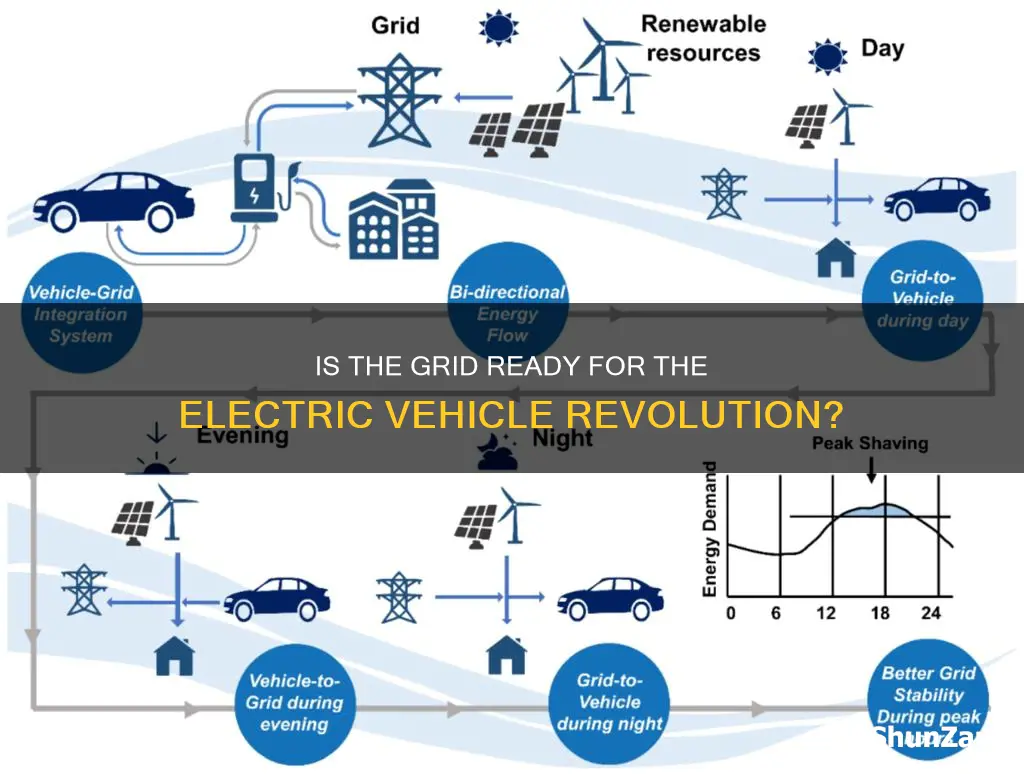
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is rapidly transforming the automotive industry, but the readiness of the power grid to support this shift is a critical question. As more EVs hit the roads, the strain on the existing grid infrastructure becomes a pressing concern. The integration of EVs requires a robust and flexible grid capable of handling the additional load, especially during peak hours. This paragraph will explore the challenges and opportunities associated with the grid's ability to accommodate the growing number of electric vehicles, considering factors such as charging infrastructure, grid stability, and the potential impact on energy consumption and distribution.
What You'll Learn
- Grid Capacity: Can the power grid handle the increased demand from EV charging
- Infrastructure: Are charging stations accessible and reliable across different regions
- Load Balancing: How can the grid manage peak EV charging times without overloading
- Renewable Energy: Can the grid's reliance on renewables support EV charging sustainably
- Smart Grids: Do smart grid technologies enable efficient EV integration and management

Grid Capacity: Can the power grid handle the increased demand from EV charging?
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is an undeniable trend, with environmental concerns and technological advancements driving this shift. However, as the number of EVs on the road increases, so does the demand for charging infrastructure, which raises questions about the capacity of the existing power grid to handle this surge in electricity usage. The integration of EVs into our transportation systems presents a unique challenge for grid management, as the current infrastructure may not be adequately prepared for the potential strain.
The power grid's ability to support EV charging is a critical aspect of the transition to electric mobility. As EVs require substantial electricity to charge, especially during peak hours, the grid's capacity becomes a limiting factor. The traditional grid, designed primarily for centralized power generation and distribution, may struggle to accommodate the decentralized nature of EV charging. With numerous charging stations being installed in various locations, the grid's ability to manage and distribute power efficiently becomes a concern.
One of the primary challenges is the potential for increased power demand during specific times of the day. As EV owners charge their vehicles, especially in residential areas, the collective draw on the grid can be substantial. This could lead to localized power shortages or strain on the grid's infrastructure, causing voltage fluctuations and potential blackouts. Managing this demand requires a sophisticated approach to grid management, including smart grid technologies and dynamic pricing strategies.
To address this issue, several solutions are being explored. Smart grid technologies can play a pivotal role by enabling real-time monitoring and control of power usage. These systems can optimize charging schedules, ensuring that EV charging occurs during periods of lower grid demand. Additionally, implementing demand response programs can encourage EV owners to charge during off-peak hours, reducing the strain on the grid. Another approach is to invest in renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, to provide a more sustainable and decentralized power supply for EV charging stations.
In conclusion, the integration of electric vehicles into our transportation ecosystem requires careful consideration of grid capacity. The power grid's ability to handle increased demand from EV charging is a complex issue that demands innovative solutions. By adopting smart grid technologies, managing charging schedules, and exploring renewable energy sources, we can work towards a more resilient and sustainable power grid that supports the widespread adoption of electric vehicles. This approach ensures that the transition to electric mobility is smooth and environmentally friendly, addressing the challenges posed by the growing demand for EV charging infrastructure.
Rivian's Electric Revolution: Unlocking the Future of Sustainable Driving
You may want to see also

Infrastructure: Are charging stations accessible and reliable across different regions?
The accessibility and reliability of charging stations are critical factors in determining the readiness of the grid to support electric vehicles (EVs). The current state of charging infrastructure varies significantly across different regions, and this disparity presents both challenges and opportunities for the widespread adoption of EVs.
In many urban areas, the availability of charging stations is abundant, with numerous public and private charging points located in convenient spots such as parking lots, shopping centers, and street-side locations. These stations often offer fast-charging capabilities, ensuring that EV owners can quickly replenish their batteries during their daily routines. However, the story is different in rural and suburban regions, where the density of charging stations is notably lower. Long distances between charging points can make long-distance travel more challenging for EV owners in these areas, potentially discouraging the adoption of electric vehicles.
The reliability of charging stations is another crucial aspect. Modern charging infrastructure should be designed to handle the increased demand from a growing number of EVs. This includes ensuring that the power grid can supply sufficient electricity to multiple charging stations simultaneously without experiencing significant drops in voltage or power quality. Upgrading the grid to accommodate the higher power requirements of EV charging is essential to prevent potential blackouts or service interruptions.
To address the regional disparities in charging infrastructure, governments and energy companies should collaborate on comprehensive plans. This may involve expanding the network of charging stations in underserved areas, implementing incentives for businesses to install charging points, and investing in smart grid technologies that can optimize power distribution. Additionally, developing standardized charging protocols and ensuring interoperability between different charging networks can enhance the overall user experience and encourage the adoption of electric vehicles.
In conclusion, the accessibility and reliability of charging stations are vital components of the EV ecosystem. By addressing the current challenges and implementing strategic improvements, the grid can become more accommodating to electric vehicles, fostering a sustainable and efficient transportation future. This includes ensuring a balanced distribution of charging infrastructure across regions and enhancing the overall reliability and efficiency of the charging process.
Electric Vehicles: Unlocking Value Beyond the Price Tag
You may want to see also

Load Balancing: How can the grid manage peak EV charging times without overloading?
The widespread adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) presents a unique challenge for the power grid: managing the surge in electricity demand during peak charging times without overloading the system. This is a critical issue as the integration of EVs into the grid is essential for a sustainable future, but it also requires careful planning and innovative solutions to ensure a stable and reliable power supply.
Load balancing is a key strategy to address this challenge. It involves dynamically adjusting the distribution of electricity to meet the varying demands of EV charging stations while maintaining grid stability. During peak hours, when multiple EVs are charging simultaneously, the grid must ensure that the power supply remains within safe limits to prevent overloading and potential blackouts. One approach to load balancing is the implementation of smart charging systems. These systems use advanced algorithms and communication technologies to optimize charging schedules. By analyzing real-time data on EV battery levels, grid capacity, and weather conditions, smart chargers can adjust the charging rate to match the available power supply. For instance, during periods of high grid demand, the system can reduce the charging speed or schedule charging sessions during off-peak hours, ensuring a balanced load.
Another effective method is the utilization of vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology. V2G allows EVs to not only draw power from the grid but also feed electricity back to it. This two-way communication enables the grid to manage charging sessions more efficiently. During peak times, the grid can request EVs to release stored energy, reducing the need for additional power generation and preventing overloading. V2G technology can also provide valuable grid services, such as frequency regulation and voltage control, further enhancing the grid's ability to handle EV charging demands.
Additionally, the development of flexible and responsive power generation sources is crucial. Renewable energy sources like solar and wind power can be integrated into the grid to provide a more stable and sustainable power supply. These sources can adjust their output based on the grid's needs, ensuring that the power generation matches the demand during peak EV charging times. For example, when the sun is shining brightly, solar panels can generate excess power, which can be stored in EV batteries or used to meet the increased demand from charging stations.
To further optimize load balancing, grid operators can employ demand response programs. These programs incentivize EV owners to charge their vehicles during off-peak hours by offering lower electricity rates or rewards. By encouraging a more flexible charging pattern, the grid can better manage the overall load and reduce the risk of overloading during peak times. In summary, load balancing is a multifaceted approach to ensuring the grid's readiness for electric vehicles. It involves smart charging systems, vehicle-to-grid technology, flexible power generation, and demand response programs. By implementing these strategies, the power grid can effectively manage the surge in electricity demand from EVs, providing a stable and reliable power supply for both current and future generations.
Powering Up: A Beginner's Guide to Electric Vehicle Ownership
You may want to see also

Renewable Energy: Can the grid's reliance on renewables support EV charging sustainably?
The integration of electric vehicles (EVs) into our transportation systems is an ongoing process, and a critical aspect of this transition is ensuring that the power grid can handle the additional demand. The question of whether the grid's reliance on renewable energy sources can support EV charging sustainably is a complex one, and it requires a detailed examination of the current and future energy landscape.
The rise of EVs is undeniable, with their popularity increasing due to environmental concerns and technological advancements. As more vehicles go electric, the strain on the power grid becomes a significant issue. Traditional internal combustion engines do not require the same level of energy infrastructure as EVs, which need frequent and rapid charging. This shift in energy consumption patterns highlights the need for a robust and flexible power grid.
Renewable energy sources, such as solar, wind, and hydropower, have gained prominence as a means to reduce the environmental impact of electricity generation. These sources offer a cleaner and more sustainable alternative to fossil fuels. However, the intermittent nature of renewable energy generation is a challenge. For instance, solar power is dependent on sunlight, and wind power is subject to variable wind conditions. This variability can make it difficult to maintain a consistent power supply, especially during peak EV charging times.
To address this concern, grid operators and policymakers must consider several strategies. Firstly, investing in energy storage solutions is crucial. Advanced battery storage systems can store excess renewable energy during periods of high generation and discharge it when needed, ensuring a more stable power supply. Secondly, smart grid technologies can optimize energy distribution by managing demand and supply in real-time. This includes implementing dynamic pricing and load-balancing mechanisms to encourage off-peak charging, reducing the strain on the grid.
Additionally, the development of fast-charging stations can significantly impact the EV charging experience. These stations can rapidly replenish a vehicle's battery, reducing the time required for charging. By strategically placing these stations along major transportation routes, the grid can support the movement of EVs without overwhelming local power infrastructure. Furthermore, the use of vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology allows EVs to feed power back into the grid, providing additional flexibility and revenue streams.
In conclusion, while the grid's reliance on renewable energy sources presents challenges, it is not an insurmountable obstacle. By implementing innovative solutions such as energy storage, smart grid management, and fast-charging infrastructure, it is possible to support the sustainable growth of EV charging. The transition to a renewable-powered grid that accommodates EVs is a complex process, but with careful planning and technological advancements, it can be achieved, ensuring a greener and more efficient transportation future.
Green Revolution: Strategies to Boost Electric Vehicle Adoption
You may want to see also

Smart Grids: Do smart grid technologies enable efficient EV integration and management?
The concept of smart grids is closely intertwined with the growing adoption of electric vehicles (EVs), and their potential to revolutionize energy management. Smart grid technologies, which involve advanced communication, control, and monitoring systems, are designed to enhance the efficiency and reliability of electricity distribution. As the world shifts towards a more sustainable and environmentally friendly energy landscape, the question of whether smart grids are ready to accommodate the influx of EVs is a critical one.
Smart grids offer a range of capabilities that can significantly facilitate the integration of EVs into the existing power infrastructure. One key aspect is the ability to manage and optimize energy demand. Smart meters and sensors can provide real-time data on electricity usage, allowing for dynamic pricing and demand response programs. This is particularly important for EVs, as it enables the grid to handle the varying and often unpredictable energy demands of these vehicles. By offering incentives for off-peak charging and implementing smart charging algorithms, the grid can ensure that EV charging is synchronized with periods of lower energy demand, reducing strain on the system.
Furthermore, smart grid technologies enable advanced vehicle-to-grid (V2G) interactions. V2G systems allow EVs to not only draw power from the grid but also feed electricity back to it when needed. This two-way communication is made possible through smart meters and bidirectional power flow capabilities. V2G technology can help stabilize the grid by providing additional power during peak demand or absorbing excess power during periods of low demand. For instance, EVs can be programmed to charge during off-peak hours and then discharge electricity back to the grid when prices are higher, creating a flexible and responsive energy market.
The benefits of smart grids in managing EV integration extend beyond energy optimization. These technologies also enhance grid reliability and security. Smart sensors and control systems can detect and isolate faults or faults in the network, minimizing the impact of potential issues. This is crucial for maintaining a stable power supply, especially with the increased complexity of EV charging infrastructure. Additionally, smart grids can facilitate the integration of renewable energy sources, such as solar and wind power, which are essential for reducing the carbon footprint of the transportation sector.
However, the successful implementation of smart grids for efficient EV management also relies on several factors. These include the development of robust communication infrastructure, the standardization of protocols, and the establishment of regulatory frameworks that encourage investment in smart grid technologies. Moreover, public awareness and education about the benefits of smart charging and V2G systems are essential to ensure widespread acceptance and participation.
In conclusion, smart grid technologies have the potential to significantly enhance the efficiency and management of EV integration. They offer a range of tools to optimize energy demand, facilitate V2G interactions, improve grid reliability, and support the integration of renewable energy sources. As the world embraces the transition to electric mobility, investing in and advancing smart grid infrastructure will be crucial to ensuring a smooth and sustainable energy future.
Chrysler's Electric Evolution: A New Era of Sustainable Mobility
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The power grid's ability to support EVs is a complex topic. While the grid can technically handle the additional load, the challenge lies in ensuring a stable and reliable supply during peak hours. Smart grid technologies and demand response programs can help manage this, allowing the grid to adapt and provide the necessary power for EV charging without compromising other essential services.
Upgrading the grid involves several strategies. One approach is to enhance the capacity of power lines and transformers to transmit more electricity. Smart meters and advanced monitoring systems can also optimize energy distribution. Additionally, investing in renewable energy sources and energy storage solutions can reduce the strain on the grid and provide a more sustainable power supply for EVs.
The risk of blackouts is a concern, especially if the grid is not properly managed. However, with the implementation of smart grid technologies, load balancing, and real-time monitoring, power companies can predict and control energy usage. This enables them to prevent overloading and ensure a stable supply. Proper planning and infrastructure development can mitigate the chances of widespread outages.
Yes, some regions have already made significant progress in preparing their grids for EVs. For example, areas with a high penetration of renewable energy sources, like solar or wind power, can provide a more sustainable and environmentally friendly charging infrastructure. Additionally, regions with well-developed high-voltage transmission lines and efficient energy storage systems are better equipped to handle the increased demand.







