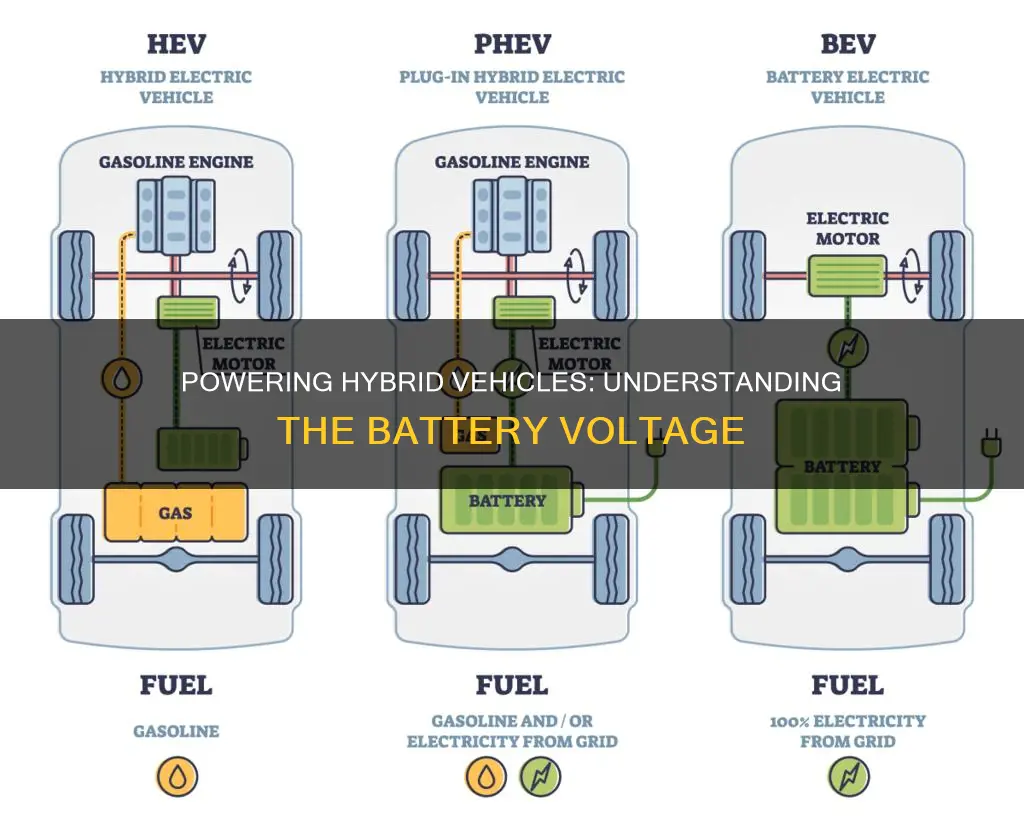
Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) are a popular choice for eco-conscious drivers, combining a traditional internal combustion engine with an electric motor and a high-voltage battery pack. The battery voltage in these vehicles is a critical component, typically ranging from 200 to 300 volts, which powers the electric motor and various auxiliary systems. This high-voltage battery system is designed to provide efficient energy storage and delivery, contributing to the vehicle's overall performance and fuel economy. Understanding the specific voltage of the battery is essential for maintenance, charging, and ensuring the proper functioning of the hybrid system.
What You'll Learn
- Battery Voltage Range: Hybrid EVs typically use 100-150 volts
- Power Electronics: Converters regulate voltage for efficient energy transfer
- Energy Storage: High-capacity batteries store energy for electric propulsion
- Charging Systems: On-board chargers replenish battery power from the grid
- Voltage Regulation: Advanced systems maintain optimal voltage for vehicle performance

Battery Voltage Range: Hybrid EVs typically use 100-150 volts
Hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) have revolutionized the automotive industry by combining traditional internal combustion engines with electric motors, offering improved fuel efficiency and reduced emissions. At the heart of this technology is a sophisticated battery system that powers the electric motor and assists the engine. The voltage of this battery system is a critical aspect of HEV design, and it plays a significant role in determining the vehicle's performance and efficiency.
The battery voltage range in hybrid electric vehicles is typically between 100 and 150 volts. This voltage range is carefully chosen to balance the power requirements of the electric motor and the overall system efficiency. Lower voltages might result in reduced performance, while higher voltages could lead to increased energy consumption and potential safety concerns. The sweet spot of 100-150 volts ensures that the electric motor can provide the necessary torque and power while maintaining a high level of efficiency.
This voltage range is essential for the smooth operation of HEVs. It allows for efficient energy recovery during braking, where the electric motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy back into electrical energy to recharge the battery. Additionally, this voltage enables the electric motor to provide additional power to the internal combustion engine during acceleration, improving overall performance and responsiveness.
The choice of voltage also impacts the vehicle's range and fuel efficiency. With a higher voltage, the electric motor can deliver more power, potentially increasing the vehicle's all-electric range. However, it's a delicate balance, as higher voltages might also lead to increased energy losses. The 100-150-volt range is optimized to provide a good compromise, ensuring that hybrid vehicles can offer both electric-only driving and improved fuel efficiency without compromising on performance.
In summary, the battery voltage in hybrid electric vehicles is a critical design parameter, typically ranging from 100 to 150 volts. This voltage range enables efficient energy management, smooth operation, and improved performance in these vehicles. It showcases the ingenuity of hybrid technology, where careful voltage selection contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly driving experience.
Buick's Electric Future: All-New All-Electric Models on the Horizon
You may want to see also

Power Electronics: Converters regulate voltage for efficient energy transfer
Power electronics play a crucial role in the efficient operation of hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs). These vehicles utilize advanced power electronics converters to manage the complex interplay between the battery, electric motor, and other components. The primary function of these converters is to regulate voltage levels, ensuring optimal energy transfer and system performance.
In HEVs, the battery voltage is typically higher than the voltage required by the electric motor and other accessories. This is where power electronics converters come into play. They act as intermediaries, converting the high-voltage battery output to the appropriate voltage needed for the motor and other vehicle systems. This process is essential for efficient energy utilization and to prevent damage to the components.
The converters employ various topologies, such as DC-DC converters and AC-AC converters, to achieve voltage regulation. DC-DC converters are commonly used to step down the battery voltage to the desired level for the motor. These converters can operate in different modes, including buck, boost, and buck-boost, allowing for efficient voltage conversion. The choice of converter topology depends on the specific requirements of the HEV's power system.
For instance, in a typical HEV, the battery voltage might be around 200-400 volts, while the motor requires a lower voltage of around 100-200 volts. The power electronics converter steps down the voltage, ensuring the motor operates within its optimal range. This efficient voltage regulation contributes to improved energy efficiency, reduced power losses, and enhanced overall performance of the hybrid vehicle.
Additionally, power electronics converters enable the integration of various vehicle systems, such as regenerative braking and voltage stabilization. During regenerative braking, the converters help capture and store energy by adjusting the voltage levels accordingly. This stored energy can then be utilized during acceleration or when additional power is required. The converters also play a vital role in maintaining stable voltage levels across the vehicle's electrical system, ensuring reliable operation.
Mastering the Art of Towing: Electric Connections and Vehicle Preparation
You may want to see also

Energy Storage: High-capacity batteries store energy for electric propulsion
The energy storage system in hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) is a critical component that enables efficient power generation and management. At the heart of this system are high-capacity batteries, which play a pivotal role in storing and releasing energy for electric propulsion. These batteries are designed to provide the necessary voltage and current to power the vehicle's electric motor, ensuring smooth and efficient operation.
High-capacity batteries in HEVs are typically lithium-ion batteries, a popular choice due to their high energy density, long cycle life, and ability to handle rapid charge and discharge cycles. These batteries are engineered to store a significant amount of energy, often in the range of 100 to 200 ampere-hours (Ah), depending on the vehicle's specific requirements. The voltage of these batteries is a crucial factor, as it determines the power output and overall performance.
The voltage of the battery pack in an HEV can vary, but it often falls within the range of 200 to 400 volts. This voltage range is carefully selected to match the power demands of the vehicle's electric motor and other electrical systems. For instance, a higher voltage might be used in performance-oriented HEVs to provide quick acceleration, while a lower voltage could be employed in more fuel-efficient models to optimize energy efficiency.
One of the key advantages of high-capacity batteries in HEVs is their ability to store energy during regenerative braking. When the vehicle decelerates, the electric motor acts as a generator, converting kinetic energy into electrical energy and storing it in the battery. This process, known as regenerative braking, not only helps to recharge the battery but also improves overall energy efficiency by reducing the reliance on the internal combustion engine.
Furthermore, these batteries are designed to provide a stable voltage output, ensuring consistent power delivery to the electric motor. This stability is crucial for maintaining the vehicle's performance and efficiency, especially during rapid acceleration or when the battery is being charged and discharged simultaneously. The advanced battery management systems in HEVs monitor and optimize the battery's performance, ensuring that it operates within safe and efficient parameters.
Toyota's PHEV: Is the Prius Plug-in Electric Drive?
You may want to see also

Charging Systems: On-board chargers replenish battery power from the grid
The charging systems in hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) are designed to efficiently replenish the battery power from the grid, ensuring that the vehicle's electric motor and other components remain powered during operation. On-board chargers play a crucial role in this process, as they are responsible for converting the alternating current (AC) from the grid into direct current (DC) that can be stored in the vehicle's battery pack.
These chargers are typically integrated into the vehicle's electrical system and are designed to handle the specific voltage and current requirements of the battery pack. The voltage of the battery pack in HEVs can vary, but it is commonly found to be around 200-400 volts, depending on the make and model of the vehicle. For example, some popular HEVs like the Toyota Prius use a 200-volt nickel-metal hydride (NiMH) battery pack, while others, such as the Chevrolet Volt, employ a 165-volt lithium-ion battery.
On-board chargers are typically rated for a specific power level, measured in watts or kilowatts, which determines the rate at which they can replenish the battery. The charging power can range from a few kilowatts for slower charging to higher power levels, often exceeding 10 kW, for faster charging capabilities. The charger's efficiency is also a critical factor, as it directly impacts the overall charging time and the vehicle's performance.
When the vehicle is connected to a charging station or plugged into a standard power outlet, the on-board charger activates and begins the process of replenishing the battery. The charger regulates the voltage and current to ensure that the battery is charged safely and efficiently. During this process, the vehicle's electrical system may draw power from the grid, and the charger manages the flow of energy to the battery pack.
Modern HEVs often feature intelligent charging systems that can optimize the charging process based on various factors, such as battery temperature, state of charge, and vehicle operation. These systems may include features like pre-conditioning, where the battery is charged to a specific level before the vehicle is used, and smart charging, which adjusts the charging rate based on the grid's electricity supply and demand. This ensures that the vehicle's battery is always ready for use while also promoting energy efficiency and cost-effectiveness.
Electric Road Trip: Tips for Planning Your EV Adventure
You may want to see also

Voltage Regulation: Advanced systems maintain optimal voltage for vehicle performance
The voltage regulation system in hybrid electric vehicles (HEVs) is a critical component that ensures the stability and efficiency of the vehicle's power electronics. This system is designed to maintain a precise and optimal voltage level across the battery pack, which is essential for the overall performance and longevity of the vehicle. The primary goal of voltage regulation is to provide a consistent and reliable power supply to the electric motor, inverter, and other electrical components, allowing for smooth operation and efficient energy management.
Advanced voltage regulation systems in HEVs are sophisticated and often incorporate multiple sensors and control algorithms. These systems continuously monitor the battery voltage and make real-time adjustments to ensure it remains within an optimal range. The optimal voltage range can vary depending on the specific vehicle and its operating conditions, but generally, it falls between 200 volts and 350 volts. This range is crucial as it allows for efficient power transfer and maximizes the vehicle's energy efficiency. For instance, during acceleration, the system might increase the voltage to provide more power to the motor, while during deceleration, it can reduce the voltage to regenerate energy and maintain a stable voltage level.
One of the key advantages of advanced voltage regulation is its ability to adapt to varying load conditions. When the vehicle's electrical load increases, such as during air conditioning use or operating multiple accessories, the system can automatically adjust the voltage to meet the demand without compromising performance. Conversely, during periods of low load, the system can reduce the voltage to conserve energy and extend the battery life. This dynamic voltage control is particularly important in HEVs, where the battery pack's state of charge needs to be carefully managed to ensure optimal performance and range.
The voltage regulation system also plays a vital role in protecting the battery pack. By maintaining a stable voltage, it prevents overcharging and over-discharging, which can significantly reduce the battery's lifespan. Additionally, the system can detect and mitigate voltage spikes or drops, ensuring the battery operates within safe limits. This is especially critical in HEVs, where the battery pack is often subjected to rapid charge and discharge cycles during driving.
In summary, voltage regulation in hybrid electric vehicles is a sophisticated process that ensures the battery pack operates at its peak efficiency. By maintaining optimal voltage levels, these systems enable smooth vehicle operation, efficient energy management, and extended battery life. The continuous monitoring and adjustment of voltage by advanced control systems contribute to the overall reliability and performance of HEVs, making them a viable and sustainable transportation option.
Revive Your Ride: A Guide to Putting Dead EVs in Neutral
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Hybrid electric vehicles use a combination of an internal combustion engine and an electric motor, and the battery voltage can vary depending on the specific make and model. However, a common voltage range for HEV batteries is between 200V to 400V. For instance, the Toyota Prius uses a 120V battery, while the Ford Fusion Hybrid has a higher voltage of 300V.
The battery voltage plays a crucial role in the overall efficiency and performance of the hybrid vehicle. Higher voltage batteries can provide more electric-only driving range, which is beneficial for reducing fuel consumption and emissions. Lower voltage batteries might focus more on the regenerative braking system, where the electric motor acts as a generator to recharge the battery during braking.
Yes, you can monitor the battery voltage in your hybrid vehicle. Some modern HEVs provide a voltage reading on the dashboard or through the onboard computer. This information is usually accessible when the vehicle is stationary and can give you an idea of the battery's state of charge. However, for precise voltage measurements, it is recommended to use specialized diagnostic tools.
A A: No, battery voltage in hybrid vehicles varies. Different manufacturers and models have their own unique voltage requirements. For example, the Honda Insight Hybrid has a 120V battery, while the Hyundai Sonata Hybrid uses a higher voltage of 300V. The voltage selection is often based on the vehicle's design, intended use, and the specific hybrid system employed.







