The topic of Is the Plug-in Electric Vehicle Credit Refundable? delves into the financial incentives and policies surrounding the adoption of electric vehicles. This discussion is particularly relevant for consumers and policymakers alike, as it explores the potential for financial benefits through tax credits and the possibility of reclaiming these credits, which can significantly impact the overall cost of purchasing an electric vehicle. Understanding the refundability of such credits is crucial for making informed decisions in the rapidly evolving automotive market, where environmental concerns and technological advancements are driving the shift towards sustainable transportation.
What You'll Learn
- Eligibility: Who qualifies for the credit and what vehicles are eligible
- Refund Process: How and when can the credit be refunded
- Tax Implications: Does the credit affect state and federal taxes
- Resale Value: How does the credit impact the resale value of EVs
- Environmental Impact: Does the credit encourage environmental sustainability

Eligibility: Who qualifies for the credit and what vehicles are eligible?
The Plug-in Electric Vehicle (PEV) Credit is a financial incentive designed to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles in the United States. This credit is a valuable tool for both consumers and the environment, as it provides a financial benefit to those purchasing eligible electric vehicles. However, understanding who qualifies for this credit and which vehicles are eligible is crucial to ensure you receive the full benefit.
Eligibility for the PEV Credit is primarily based on the type of vehicle purchased and the individual's status as a vehicle purchaser or lessee. Here's a breakdown:
- Purchasers: Individuals who buy a new plug-in electric vehicle directly from a dealership or manufacturer are eligible for the credit. This includes personal vehicle purchases, where the individual takes ownership of the vehicle.
- Leasees: In some cases, individuals who lease a plug-in electric vehicle may also qualify. However, the rules for leasing are more complex and may vary depending on the state and the specific lease agreement. It is essential to review the guidelines to ensure you meet the criteria.
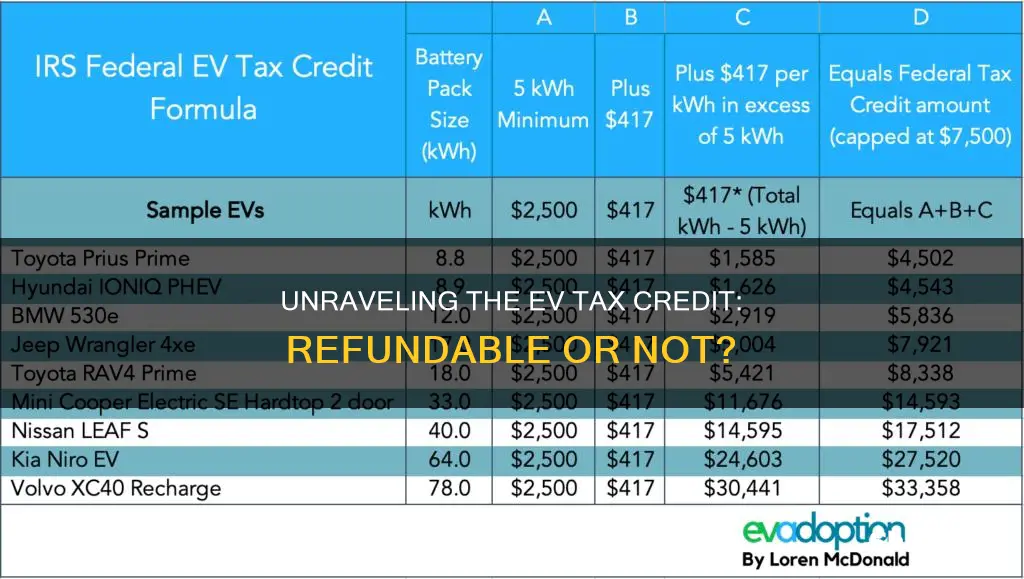
When it comes to eligible vehicles, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) has outlined specific requirements. The vehicle must be a plug-in electric vehicle, which includes:
- All-Electric Vehicles: These vehicles run exclusively on electricity and do not have a gasoline or diesel engine. Examples include fully electric cars and SUVs.
- Plug-in Hybrid Electric Vehicles (PHEVs): PHEVs have both an electric motor and a conventional engine. They can be driven in electric mode for a certain distance before switching to the internal combustion engine.
- Range-Extended Electric Vehicles: These vehicles have an electric motor and a small internal combustion engine that provides additional power when needed.
It's important to note that the vehicle must be new and purchased or leased after the enactment of the credit. Used vehicles or those purchased before the specified date may not qualify. Additionally, the IRS provides a list of eligible vehicle models, and it is the purchaser's responsibility to ensure their vehicle meets these criteria.
Understanding the eligibility criteria is essential to maximize the benefits of the PEV Credit. By qualifying as a purchaser or lessee and owning or leasing an eligible electric vehicle, individuals can take advantage of this financial incentive, contributing to a more sustainable transportation future.
Colorado EV Tax Credit: Unraveling Income Tax Implications
You may want to see also

Refund Process: How and when can the credit be refunded?
The process of obtaining a refund for the Plug-in Electric Vehicle (PEV) credit involves several steps and considerations. Here's an overview of how and when the credit can be refunded:
Eligibility and Timing: To be eligible for a refund, the vehicle must meet specific criteria, including being purchased or leased after a certain date, which varies depending on the year. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) sets these deadlines annually. It's crucial to check the IRS guidelines for the most up-to-date information regarding eligibility. Refunds are typically processed for vehicles that have not been used for business purposes and are not subject to any other tax credits or deductions.
Documentation: When applying for a refund, you will need to provide detailed documentation. This includes the original purchase or lease agreement, vehicle specifications, and proof of ownership. Ensure that all the required forms are accurately filled out, as any discrepancies may lead to delays or rejection of the refund claim.
Refund Process: The refund is generally issued as a credit to the original purchaser or lessee. This credit can be used to offset any federal income tax liability or applied to future tax payments. If the vehicle is sold or transferred, the credit may be transferable, allowing the new owner to claim the refund. The IRS provides a specific form, such as Form 5472, to facilitate this process, ensuring a smooth transition of the credit.
Timeline: The timeline for receiving a refund can vary. After submitting the necessary documentation, it may take several weeks for the IRS to process the claim. The refund is then issued, and the credit is typically available within a few months. It is advisable to monitor the status of your refund claim and contact the IRS if there are any delays or issues.
Understanding the refund process is essential for PEV credit recipients to ensure they receive the full benefit of the credit and can plan their tax strategy accordingly. The IRS provides comprehensive guidelines and resources to assist taxpayers in navigating the refund process efficiently.
Power Up Your EV: A Guide to Recharging Your Electric Vehicle
You may want to see also

Tax Implications: Does the credit affect state and federal taxes?
The Plug-in Electric Vehicle (PEV) Credit, also known as the Electric Vehicle Tax Credit, is a financial incentive offered by the federal government to promote the adoption of electric vehicles. This credit can significantly reduce the upfront cost of purchasing an electric car, making it more affordable for consumers. However, understanding the tax implications of this credit is essential for taxpayers to ensure they are taking full advantage of the benefits without any unintended consequences.
When it comes to federal taxes, the PEV Credit is generally non-refundable. This means that if the credit exceeds the taxpayer's federal tax liability, the excess amount cannot be refunded as cash. Instead, it can be carried forward to offset future tax liabilities. This aspect of the credit is important to consider, especially for those who may not owe significant federal taxes in the year they purchase an electric vehicle. In such cases, the credit can be carried forward, allowing the taxpayer to benefit from it in subsequent years when their tax liability is higher.
On the state tax front, the impact of the PEV Credit varies widely depending on the jurisdiction. Some states have their own tax incentives or rebates for electric vehicle purchases, which can either complement or replace the federal credit. For instance, a state with a high-income tax rate might offer a more substantial state-level credit to attract electric vehicle buyers. Taxpayers should research their state's specific regulations to understand how the federal credit interacts with state taxes. In some cases, state credits might be non-refundable as well, while in others, they may be fully or partially refundable, providing an immediate tax benefit.
It is crucial for individuals to consult with tax professionals or financial advisors to navigate the complexities of these tax implications. They can provide personalized advice based on an individual's financial situation, state of residence, and specific circumstances related to their electric vehicle purchase. Understanding these tax considerations can help taxpayers make informed decisions and ensure they are maximizing the benefits of the PEV Credit without facing unexpected tax obligations.
In summary, while the PEV Credit is a valuable incentive for electric vehicle buyers, its tax implications vary between federal and state levels. Taxpayers should be aware of these differences to ensure they are taking full advantage of the credit and managing their tax obligations effectively. Proper planning and professional guidance can help individuals make the most of this credit while minimizing any potential tax-related risks.
Ford's Electric Future: Rumors of Scrapping EV Plans Debunked
You may want to see also

Resale Value: How does the credit impact the resale value of EVs?
The impact of the plug-in electric vehicle (EV) credit on resale value is an important consideration for EV owners and potential buyers alike. The credit, which is designed to incentivize the adoption of electric vehicles, can have both positive and negative effects on the resale market.
On the positive side, the credit can make EVs more affordable upfront, which can attract a wider range of buyers. This increased demand can potentially drive up the resale value of EVs, as more people are willing to purchase and own these vehicles. Additionally, the credit can encourage manufacturers to invest in EV technology and infrastructure, leading to improved vehicle quality and performance, which can also enhance resale value.
However, there are potential drawbacks to consider. One concern is that the credit might create a perception of lower value among some consumers. If buyers perceive that the credit is a subsidy or a temporary measure, they may assume that the resale value of EVs will be lower compared to traditional vehicles. This could potentially lead to a decrease in the perceived value of EVs, especially if the credit is not widely known or understood.
Another factor to consider is the potential for resale value depreciation. While the credit can make EVs more attractive initially, the long-term impact on resale value is still uncertain. Some EV owners might be hesitant to sell their vehicles if they believe the credit will be phased out or reduced in the future, leading to potential resale value fluctuations. This uncertainty could create a challenge for those looking to sell their EVs, especially if the market is not yet fully established.
In summary, the plug-in electric vehicle credit can have a significant impact on the resale value of EVs. While it may attract more buyers and potentially increase demand, there are also concerns about consumer perception and long-term resale value stability. Understanding these factors is crucial for EV owners and buyers to make informed decisions and manage expectations regarding the resale value of electric vehicles.
The Green Revolution: Unlocking the True Value of Electric Cars
You may want to see also

Environmental Impact: Does the credit encourage environmental sustainability?
The Plug-in Electric Vehicle (PEV) tax credit is a financial incentive designed to promote the adoption of electric cars, which are generally considered more environmentally friendly than traditional internal combustion engine vehicles. The credit is a significant factor in encouraging consumers to make the switch to electric vehicles, which can have a substantial environmental impact.
One of the primary environmental benefits of PEVs is their reduced carbon footprint. Electric cars produce zero tailpipe emissions, meaning they do not release harmful pollutants like nitrogen oxides (NOx) and particulate matter into the atmosphere. This is a crucial advantage over conventional vehicles, which are a major contributor to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions. By offering a tax credit, governments aim to accelerate the transition to cleaner transportation, thereby improving air quality and public health.
The credit also encourages the development and purchase of advanced battery technologies. As the demand for PEVs increases, manufacturers are investing in research and development to create more efficient and sustainable battery systems. This includes exploring solid-state batteries, which promise higher energy density and faster charging times, and recycling and second-life applications for used batteries, reducing waste and promoting a circular economy.
Furthermore, the PEV credit can indirectly support the growth of renewable energy sources. As more electric vehicles hit the roads, the demand for electricity increases, which can be met by integrating renewable energy sources like solar and wind power into the grid. This shift towards a more sustainable energy mix is essential for reducing the overall environmental impact of the transportation sector.
However, it is worth noting that the environmental benefits of the credit depend on various factors. The source of electricity used to charge PEVs is critical. If the electricity is generated from fossil fuels, the carbon savings may be offset. Therefore, it is essential to ensure that the grid is decarbonized to maximize the environmental advantages of electric vehicles. Additionally, the production and disposal of batteries should be managed sustainably to avoid environmental degradation.
Firefighting Tips: Battling Electric Vehicle Blazes
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The PEV Credit, also known as the Electric Vehicle Tax Credit, is a financial incentive provided by the government to encourage the purchase of plug-in electric vehicles. It offers a tax credit to eligible buyers, reducing their tax liability or increasing their refund.
To qualify, you must purchase or lease a new plug-in electric vehicle, which includes battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). The vehicle must be new, produced for sale, and meet specific environmental and performance standards.
Yes, the PEV Credit is refundable, meaning you can receive the full amount of the credit even if you don't have a tax liability. This is designed to ensure that eligible buyers can access the credit, especially those who may not typically owe federal income taxes, such as individuals with low incomes or those who use tax credits to offset their state income tax liability.
Yes, the PEV Credit can be carried forward for up to 20 years if you don't use it in the current tax year. This allows eligible individuals to utilize the credit in subsequent years, providing a more extended period to benefit from the incentive and potentially saving on future tax liabilities.