Recharging an electric vehicle (EV) is a crucial aspect of EV ownership, ensuring your car remains ready for the road. The process involves connecting your EV to a power source, typically through a charging station or a home charging setup. There are several methods to recharge, including AC (alternating current) charging, which is common for home use and provides a steady charge, and DC (direct current) fast charging, which is faster and often used in public stations. Understanding the different charging options and their respective times can help EV owners plan their charging needs effectively, ensuring they always have a fully charged vehicle.
What You'll Learn
- Battery Capacity: Understand your EV's battery capacity and range
- Charging Stations: Locate public charging stations and their types
- Home Charging: Install a home charging unit and connect it to your EV
- Charging Rates: Know the charging speeds and power levels
- Maintenance: Regularly maintain your EV to ensure optimal performance

Battery Capacity: Understand your EV's battery capacity and range
Understanding your electric vehicle's (EV) battery capacity is a crucial step towards efficient and effective charging. The battery capacity, often measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), determines how much energy your EV can store and, consequently, how far it can travel on a single charge. This knowledge is essential for planning your daily commutes, long-distance trips, and ensuring you always have enough power to reach your destination.
To find this information, you can typically refer to your EV's owner's manual, which will provide detailed specifications about the battery. Look for terms like 'battery capacity' or 'kWh' to identify the numerical value. For instance, a common range for EV batteries is between 30 kWh and 100 kWh, with some high-end models even reaching 150 kWh or more. The higher the kWh, the more energy your vehicle can store, allowing for longer ranges.
Another way to understand your EV's range is by checking the 'range per charge' metric, which is often displayed on the instrument cluster or through the vehicle's infotainment system. This real-time data provides an estimate of the distance you can travel based on the current battery level. Modern EVs are equipped with advanced technology that continuously monitors and adjusts this range estimate, taking into account various factors like driving conditions, temperature, and even the efficiency of your driving habits.
It's important to note that battery capacity and range can vary depending on several factors. External conditions, such as extreme temperatures, can impact the battery's performance and range. Additionally, driving habits play a significant role; aggressive acceleration and frequent high-speed driving will drain the battery faster, reducing the effective range. Therefore, understanding your specific EV's capabilities and adapting your driving style accordingly is essential for efficient charging and usage.
In summary, knowing your EV's battery capacity and range is fundamental to responsible ownership. It empowers you to make informed decisions about charging, plan your trips effectively, and ensure you never find yourself in a situation where the battery is depleted. With this knowledge, you can fully utilize the benefits of electric mobility and enjoy a seamless driving experience.
Firefighting Strategies: Extinguishing EV Fires: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Charging Stations: Locate public charging stations and their types
Public charging stations are essential infrastructure for electric vehicle (EV) owners, providing a convenient way to recharge their vehicles when home charging is not an option. These stations come in various types, each with its own advantages and use cases. Understanding the different types of charging stations can help EV drivers plan their trips more efficiently and ensure they have access to the right charging solutions.
Fast Charging Stations: These are the powerhouses of the charging world, designed to provide rapid recharging for electric vehicles. Fast chargers typically operate at much higher power levels, often ranging from 50 kW to 350 kW or more. This enables them to replenish a significant portion of an EV's battery in a relatively short time, usually within 30 minutes to an hour. Fast-charging stations are ideal for long-distance travel, allowing drivers to quickly top up their batteries during extended journeys. They are commonly found along highways and major travel routes, ensuring that EV owners can maintain their trips without lengthy stops.
Slow or Level 2 Chargers: In contrast, slow chargers provide a more gradual recharge process, typically delivering power at 240 volts (V) or 208 V, with currents ranging from 16 to 60 amperes (A). These chargers are often found in residential areas, workplaces, and public parking lots. Slow chargers are perfect for overnight charging at home or for extended parking in public spaces. While they charge vehicles more slowly than fast chargers, they are generally more accessible and cost-effective, making them a popular choice for everyday EV charging needs.
Direct Current (DC) Fast Chargers: DC fast chargers are a specialized type of fast-charging station that operates at extremely high power levels, often exceeding 100 kW. These chargers use direct current to rapidly replenish the EV battery, making them highly efficient. DC fast chargers are typically found in locations where high-speed recharging is crucial, such as along major highways and in urban areas with high EV ownership. They are designed to provide a quick boost of energy, allowing drivers to cover long distances with minimal charging stops.
Location and Accessibility: Locating public charging stations is crucial for EV owners to ensure they can find convenient and reliable charging options. Many charging station networks provide real-time data on station availability, power levels, and prices through mobile apps or websites. These platforms allow drivers to plan their routes, identify stations with fast charging capabilities, and even reserve charging spots in advance. Additionally, some charging networks offer membership or subscription plans, providing access to a network of stations across various locations.
In summary, public charging stations play a vital role in the EV ecosystem, offering different charging speeds and convenience levels. Understanding the types of charging stations and their locations empowers EV drivers to make informed decisions, ensuring they can keep their vehicles charged and ready for the road ahead. With the right knowledge and resources, EV owners can confidently navigate the charging infrastructure and enjoy the freedom of electric mobility.
Green Revolution: Strategies to Boost Electric Vehicle Adoption
You may want to see also

Home Charging: Install a home charging unit and connect it to your EV
To ensure a seamless and efficient charging experience for your electric vehicle (EV) at home, consider installing a dedicated home charging unit. This setup offers convenience and often provides faster charging compared to using a standard household outlet. Here's a step-by-step guide to help you through the process:
- Choose the Right Charger: Start by selecting an appropriate home charging unit. The charging speed and power output depend on the type of charger. There are three main types: AC (Alternating Current) chargers, DC (Direct Current) fast chargers, and AC fast chargers. For most home EV owners, an AC Level 2 charger is a popular choice, offering a good balance between charging speed and cost. These chargers typically provide 240 volts and can charge your EV much faster than a standard 120-volt outlet.
- Electrical Assessment: Before installation, it's crucial to assess your home's electrical system. You'll need to ensure that your electrical panel has sufficient capacity to handle the additional load of the charging unit. Consult with a qualified electrician to evaluate your electrical setup and determine if any upgrades are necessary. They can also help you identify the best location for the charger, considering factors like proximity to the vehicle parking area and electrical wiring.
- Installation Process: Once you've chosen the charger and assessed your electrical needs, it's time to install the unit. This typically involves mounting the charger on a wall or a dedicated charging station. The installation process may vary depending on the model, but it generally includes connecting the charger to your home's electrical supply and securing it in place. Ensure that the installation complies with local building codes and safety standards.
- Connecting Your EV: After the charger is installed, it's time to connect your EV. Most home charging units come with a cable that plugs into the vehicle's charging port. Simply connect the cable to your car and ensure a secure connection. Some chargers may also offer wireless charging options, where you park your EV over a charging pad, eliminating the need for a physical cable.
- Setting Up and Monitoring: Once connected, you can set up your home charging unit. This includes programming the charger to your specific EV model and preferences. Many chargers come with user-friendly interfaces, allowing you to monitor charging sessions, set schedules, and manage energy usage. Regularly checking the charger's performance and keeping it well-maintained will ensure a long-lasting and efficient charging experience.
By following these steps, you can create a convenient and efficient home charging solution for your electric vehicle, making the transition to EV ownership even more accessible and enjoyable. Remember, proper installation and regular maintenance are key to maximizing the benefits of home charging.
Electric Convenience: Your Guide to Flying with Style
You may want to see also

Charging Rates: Know the charging speeds and power levels
Understanding the charging rates and speeds of electric vehicles (EVs) is crucial for efficient and effective recharging. The charging speed and power level can vary significantly depending on several factors, including the type of charger, the EV model, and the battery capacity. Here's a detailed breakdown of what you need to know:
Charging Speeds:
- Slow Charging: Typically, this is the slowest charging method and is usually used for overnight charging at home. Slow chargers provide a power output of around 3-7 kW, allowing the battery to recharge at a rate of about 10-25 miles per hour. This method is ideal for maintaining a full charge overnight without causing significant wear and tear on the battery.
- Fast Charging: Fast chargers are more common and can be found in public charging stations. These chargers operate at power levels ranging from 7 kW to 22 kW, enabling the battery to recharge much faster. For example, a 12 kW charger can fully charge an EV in approximately 4-6 hours, depending on the battery size.
- Rapid Charging (DC Fast Charging): This is the fastest charging method and is designed for quick top-ups during long-distance travel. Rapid chargers use direct current (DC) and can provide power levels of 50 kW or higher. A 50 kW charger can add up to 100 miles of range in just 20 minutes, making it a convenient option for EV owners on the go.
Power Levels and EV Models:
Different electric vehicles have varying battery capacities and charging port types, which influence the maximum power level they can accept. For instance, some EVs are equipped with charging ports that support up to 100 kW or more, allowing for ultra-fast charging. It's essential to check your EV's specifications to understand its charging capabilities and ensure you use the appropriate charger.
Charging Efficiency:
The efficiency of charging also plays a role in the overall charging speed. Modern EVs often have advanced battery management systems that optimize charging, ensuring the battery reaches a full charge without overheating or experiencing excessive stress. These systems may adjust the charging rate based on factors like ambient temperature and battery temperature to maintain optimal performance.
In summary, when recharging an electric vehicle, it's essential to consider the charging speeds and power levels to ensure a safe and efficient process. Understanding the different charging methods and their respective rates will help EV owners make informed decisions, whether they are charging at home, using public stations, or planning long-distance trips.
Emergency Disconnect: Guide to Safely Powering Down Electric and Hybrid Vehicles
You may want to see also

Maintenance: Regularly maintain your EV to ensure optimal performance
Maintaining your electric vehicle (EV) is crucial to ensure its longevity, performance, and efficiency. Regular maintenance routines can help prevent unexpected breakdowns, optimize energy consumption, and keep your EV running smoothly. Here are some essential maintenance practices to follow:
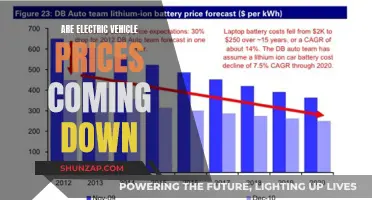
Battery Care: The battery is the heart of your EV, and proper care is essential. Firstly, keep an eye on the battery's charge levels and ensure it is never left critically low for extended periods. Regularly check the battery's health and performance using the vehicle's onboard diagnostics or by consulting the manufacturer's guidelines. Keep the battery terminals clean and free from corrosion to ensure efficient power transfer. It's also a good practice to avoid frequent rapid charging, as this can put additional strain on the battery. Instead, opt for slower charging methods when possible to prolong the battery's lifespan.
Routine Inspections: Schedule regular inspections with a qualified mechanic or EV specialist. These inspections should include a thorough examination of the vehicle's electrical systems, wiring, and connections. Look out for any signs of damage, wear, or loose connections that could lead to performance issues. Check the tires for proper inflation and wear, as underinflated or worn tires can affect handling and energy efficiency. Keep an eye on the brakes and ensure they are functioning optimally, as brake maintenance is critical for safety.
Software Updates: Stay up-to-date with the latest software updates provided by the manufacturer. These updates often include performance enhancements, bug fixes, and new features that can improve your EV's overall functionality. Regular software updates can also optimize charging efficiency, battery management, and driving range. Enable automatic software updates if available, ensuring your EV always has the most recent software version.
Charging Infrastructure: Maintain your home or workplace charging equipment regularly. Inspect the charging cable for any signs of damage or wear, and replace it if necessary. Keep the charging port clean and free from debris to ensure a proper connection during charging. If you have access to a charging station, ensure it is well-maintained and regularly checked for any issues that might affect charging speed or safety.
By following these maintenance practices, you can ensure that your electric vehicle operates at its best, providing efficient performance and a reliable driving experience. Regular care and attention to these aspects will contribute to the overall longevity of your EV.
Mastering EV Repairs: Tips for Troubleshooting and Fixing Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
You can locate charging stations through various means. Many electric vehicle (EV) manufacturers provide their customers with a mobile app that offers real-time data on charging station locations. Additionally, there are numerous third-party apps and websites available, such as PlugShare and ChargeHub, which aggregate data on public charging stations. These platforms often provide details like the type of connector, charging speed, and availability.
There are several types of charging connectors commonly used for electric vehicles, each with its own specifications. The most widely recognized connector is the Combined Charging System (CCS), which is used for fast charging and is compatible with most electric vehicles sold in North America and Europe. Other connectors include the CHAdeMO, which is popular in Japan, and the Tesla Connector, used exclusively for Tesla vehicles. It's essential to check your vehicle's charging port and the connector types supported by the charging station to ensure compatibility.
The charging time for an electric vehicle depends on various factors, including the vehicle's battery capacity, the type of charger, and the charging speed. Typically, a slow charger (Level 1) can fully charge a vehicle overnight, taking around 8-10 hours. Fast chargers (Level 2) can significantly reduce charging time, often taking 3-4 hours for a full charge. Rapid or DC fast chargers can provide an 80% charge in as little as 20-30 minutes, but these are usually found at specific locations and may require a membership or subscription.
Yes, you can charge your electric vehicle at home, and it's a convenient option for many EV owners. To do so, you'll need a home charging station, which can be either a slow charger (Level 1) or a faster Level 2 charger. For a Level 2 charger, you'll require a dedicated circuit and a 240-volt outlet, typically installed by a professional electrician. It's important to check your local regulations and ensure your home's electrical system can handle the load. Additionally, you might be eligible for incentives or tax credits to offset the installation costs.