Many governments around the world are encouraging the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) to reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainable transportation. One effective way to incentivize EV purchases is through tax credits and rebates. In the United States, the federal government has implemented several tax credits to support the growth of the EV market. This paragraph will explore the availability and specifics of the federal tax credit for electric vehicles, providing an overview of the benefits and eligibility criteria for consumers looking to make an eco-friendly purchase.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Federal Tax Credit for Electric Vehicles | Yes, there is a federal tax credit available for the purchase of electric vehicles (EVs) in the United States. |
| Eligibility | The credit is typically available to individuals who buy new qualified EVs, including battery electric vehicles (BEVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). |
| Amount of Credit | The credit amount varies based on the vehicle's battery capacity and the manufacturer's production volume. For vehicles with a battery capacity of at least 40 kWh, the credit can be up to $7,500. |
| Income Limit | There is an income limit for claiming the credit. For tax years 2023 and 2024, the credit is phased out for individuals with adjusted gross income (AGI) above $150,000 ($75,000 for single filers). |
| Manufacturers | The credit is available for vehicles from qualified manufacturers, which are determined by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). |
| Effective Dates | The federal tax credit for EVs has been in effect since 2009 and has undergone several changes and extensions over the years. |
| Recent Changes | In 2022, the credit was temporarily increased to $7,500 and made permanent for vehicles with a battery capacity of at least 40 kWh. |
| Additional Information | The credit is part of the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA) of 2022, which aims to boost the production and sale of EVs in the US. |
What You'll Learn

Eligibility: Who qualifies for the federal EV tax credit?
The federal tax credit for electric vehicles (EVs) is a significant incentive for consumers to make the switch to electric mobility. This credit is designed to encourage the adoption of EVs and promote the development of the electric vehicle market in the United States. To qualify for this credit, certain criteria must be met, ensuring that the benefits are directed towards eligible buyers and manufacturers.
Eligibility for the federal EV tax credit is primarily based on the place of purchase and the type of vehicle. The credit is available to individuals who purchase or lease new electric vehicles, including plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs), from dealers or manufacturers who are located in the United States. This means that the vehicle must be primarily manufactured or assembled in the U.S., or in a country with a free trade agreement with the U.S. The vehicle must also meet specific performance and emission standards set by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS).
To be considered a new vehicle, the EV must be purchased or leased directly from the manufacturer or an authorized dealer. This excludes used car purchases, although some states offer their own incentives for used electric vehicles. Additionally, the vehicle must be acquired for personal use, and the purchase or lease must be completed after November 2, 2021, and before January 1, 2026, for the credit to be applicable.
Another important factor is the income level of the purchaser. The credit is generally limited to individuals with adjusted gross income (AGI) below a certain threshold, which is adjusted annually. For tax year 2022, the AGI limit for the full credit is $150,000 for individuals and $300,000 for married couples filing jointly. However, the credit amount is reduced for income above these limits, with a phase-out starting at $150,000 for individuals and $300,000 for joint filers.
Furthermore, the credit is also subject to a cap on the vehicle's price. The credit amount is determined by the vehicle's price, with a maximum credit of $7,500 for vehicles priced below $80,000. For vehicles priced between $80,000 and $100,000, the credit is reduced by $3,750 for every dollar above $80,000. This cap ensures that the credit is targeted towards more affordable EVs, promoting wider adoption.
Powering Up: A Beginner's Guide to Electric Vehicle Ownership
You may want to see also

Income Limits: Are there income caps for EV tax credits?
The federal tax credit for electric vehicles (EVs) is a significant incentive for consumers to purchase these environmentally friendly vehicles. However, it's important to understand that this credit is not available to everyone equally. One of the key considerations is income limits, which can impact an individual's eligibility for the tax credit.
For the 2023 tax year, the income limits for the EV tax credit are set at $150,000 for single filers and $300,000 for joint filers. This means that individuals or couples with incomes above these thresholds may not qualify for the full tax credit. The credit amount gradually decreases as income increases, and it phases out completely for those exceeding these limits. This phase-out rule ensures that the tax credit is targeted towards lower- to middle-income earners, promoting a more equitable distribution of the incentive.
To calculate the exact credit amount, the IRS provides a formula that takes into account the vehicle's price, battery capacity, and the taxpayer's income. The credit is generally a percentage of the vehicle's cost, and it can be claimed when the vehicle is purchased or leased. It's worth noting that the credit is not a deduction but a direct reduction in the tax liability, which can be especially beneficial for those who owe taxes.
It is essential for potential EV buyers to be aware of these income limits to ensure they understand their eligibility. Tax professionals can provide guidance on how to navigate these rules, especially for those on the cusp of the income thresholds. Additionally, staying informed about any changes in tax laws and regulations is crucial, as these limits may be adjusted in future years.
In summary, the federal tax credit for EVs is a valuable financial incentive, but it is not universally accessible. Income limits play a significant role in determining eligibility, and these limits are set to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles among a broader range of consumers. Understanding these rules is essential for anyone considering purchasing an EV and wanting to take advantage of this tax benefit.
EV Revolution: Will Prices Drop in 5 Years?
You may want to see also

Vehicle Types: Which electric vehicles are eligible?
The federal tax credit for electric vehicles is a significant incentive for consumers to make the switch to electric mobility. This credit is designed to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and promote a more sustainable transportation ecosystem. When it comes to vehicle types, the eligibility criteria are quite comprehensive, covering a wide range of electric-powered automobiles.
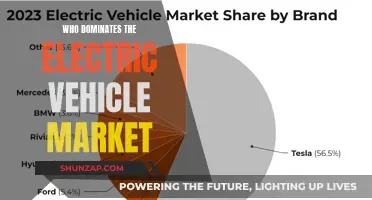
One of the primary categories of eligible vehicles is battery-electric vehicles (BEVs). These are fully electric cars that run exclusively on electricity, storing energy in batteries. BEVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, making them an environmentally friendly choice. Examples of BEVs include popular models like the Tesla Model 3, Chevrolet Bolt, and the recently launched Ford Mustang Mach-E. These vehicles are often at the forefront of the EV market and are highly sought after by environmentally conscious consumers.
In addition to BEVs, plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) are also eligible for the tax credit. PHEVs combine a traditional internal combustion engine with an electric motor and battery. They offer the flexibility of both electric and gasoline power, allowing drivers to choose their preferred mode of operation. The tax credit applies to PHEVs that meet specific criteria, such as having a minimum electric range and meeting certain emissions standards. Vehicles like the Toyota Prius Prime, Hyundai Ioniq Plug-in Hybrid, and the Kia Niro Plug-in Hybrid fall into this category.
Another type of electric vehicle that qualifies for the federal tax credit is fuel cell electric vehicles (FCEVs). These vehicles use hydrogen fuel cells to generate electricity, producing only water vapor as a byproduct. While FCEVs are less common compared to BEVs and PHEVs, they still contribute to the diversity of eligible vehicles. The tax credit supports the development and adoption of hydrogen-powered transportation, which is crucial for the long-term sustainability of the EV market.
It's important to note that the tax credit eligibility is not limited to these vehicle types alone. The criteria also extend to certain low-speed vehicles, such as neighborhood electric vehicles (NEVs) and work vehicles. NEVs are designed for short-distance travel within residential areas, while work vehicles include electric-powered trucks, vans, and buses used for commercial purposes. These categories ensure that the tax credit benefits a wide range of electric vehicle owners, from individual commuters to businesses adopting eco-friendly fleets.
Switzerland's Electric Vehicle Ban: Fact or Fiction?
You may want to see also

Purchase Price: How is the price of the EV determined?
The price of an electric vehicle (EV) is determined by various factors, and understanding these elements can help buyers make informed decisions. Firstly, the base price of the EV itself is a significant factor. This is the manufacturer's suggested retail price (MSRP) or the sticker price, which is the initial cost before any discounts or incentives. This price is set by the vehicle's manufacturer and can vary widely depending on the make, model, trim level, and additional features. For instance, a luxury EV with advanced technology and high-end amenities will typically have a higher base price compared to a more basic, entry-level model.
Several factors influence the final purchase price of an EV. One crucial aspect is the availability of incentives and tax credits. Many governments worldwide, including the United States, offer financial incentives to promote the adoption of electric vehicles. These incentives can significantly reduce the overall cost of ownership. For example, in the US, the federal government provides a tax credit for EV purchases, which can be substantial. This credit is based on the vehicle's battery capacity and the manufacturer's production volume, ensuring that a wider range of EVs qualifies for the incentive.
Additionally, the purchase price is influenced by the buyer's location and local regulations. Some regions have their own incentives or subsidies, which can further reduce the cost. Local tax rates and vehicle registration fees also play a role, as these can vary depending on the jurisdiction. It's essential for buyers to research and understand the specific incentives and regulations in their area, as these can impact the overall affordability of the EV.
Another factor affecting the purchase price is the dealership or seller. Negotiation power can vary, and some sellers may offer additional benefits or discounts. These could include accessories, extended warranties, or trade-in allowances. Buyers should be aware of the market value of the specific EV model they desire and use this knowledge to negotiate a better deal.
Lastly, the overall market demand and supply dynamics can influence EV prices. High-demand models with limited availability may have higher prices due to scarcity. Conversely, a surplus of a particular model in the market could lead to more competitive pricing. Staying informed about market trends and new model releases can help buyers make timely purchases and potentially secure better prices.
Unlocking Savings: California's EV Tax Credit Explained
You may want to see also

Timing: When can you claim the credit?
The federal tax credit for electric vehicles is a financial incentive designed to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) and promote a cleaner, more sustainable transportation system. This credit is a significant benefit for EV buyers, as it can directly reduce the cost of purchasing an electric car, truck, or SUV. However, understanding the timing and eligibility criteria for claiming this credit is essential to ensure you receive the full benefit.
The tax credit is available for new and used electric vehicles, but there are specific rules and limitations. For new EVs, the credit is typically available for vehicles that are first sold to the public after December 31, 2009. This means that if you purchase a new electric vehicle after this date, you may be eligible for the tax credit. It's important to note that the credit amount can vary depending on the vehicle's battery capacity and the manufacturer's sales volume.
When it comes to used EVs, the rules are a bit more complex. The credit is generally available for vehicles that were originally sold for use and were not previously claimed for the credit. This means that if you buy a used electric vehicle that was previously owned by someone else, you might still be eligible for the tax credit. However, there are restrictions on the vehicle's age and mileage, ensuring that the credit is primarily targeted at new or recently purchased EVs.
To claim the credit, you must file a federal income tax return, either annually or when you sell the vehicle, whichever comes first. The credit is typically applied as a reduction in your taxable income, and it can be carried forward if the credit exceeds your tax liability. It's recommended to consult with a tax professional or accountant to ensure you understand the specific requirements and deadlines for claiming the credit in your jurisdiction.
Additionally, the Internal Revenue Service (IRS) provides guidelines and updates on the EV tax credit program, so staying informed about any changes in regulations is crucial. The timing of your purchase and the vehicle's eligibility are critical factors in determining your eligibility for the credit. Therefore, it is advisable to plan your EV purchase carefully and seek professional advice to maximize the potential savings.
Unlocking Savings: A Guide to Colorado's EV Tax Credit
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Yes, the federal government offers a tax credit for electric vehicles (EVs) to encourage their adoption and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. The credit is available for new and used EVs, but with certain limitations.
The tax credit amount varies based on the vehicle's price and battery capacity. For model year 2023, the credit ranges from $2,500 to $7,500. Vehicles with a battery capacity of less than 40 kWh qualify for the full $7,500 credit, while those with a higher capacity receive a reduced amount.
Yes, there are income limits to ensure the credit benefits those who need it most. For the full credit, the modified adjusted gross income (MAGI) cannot exceed $150,000 for individuals or $300,000 for joint filers. For a partial credit, the MAGI limit is $200,000 for individuals and $400,000 for joint filers.
The tax credit is available for both buyers and lessees of electric vehicles. However, the rules are slightly different for lessees. Lessees can claim a portion of the credit based on the lease term and the vehicle's value. It's important to consult IRS guidelines or a tax professional to understand the specific rules and eligibility criteria.