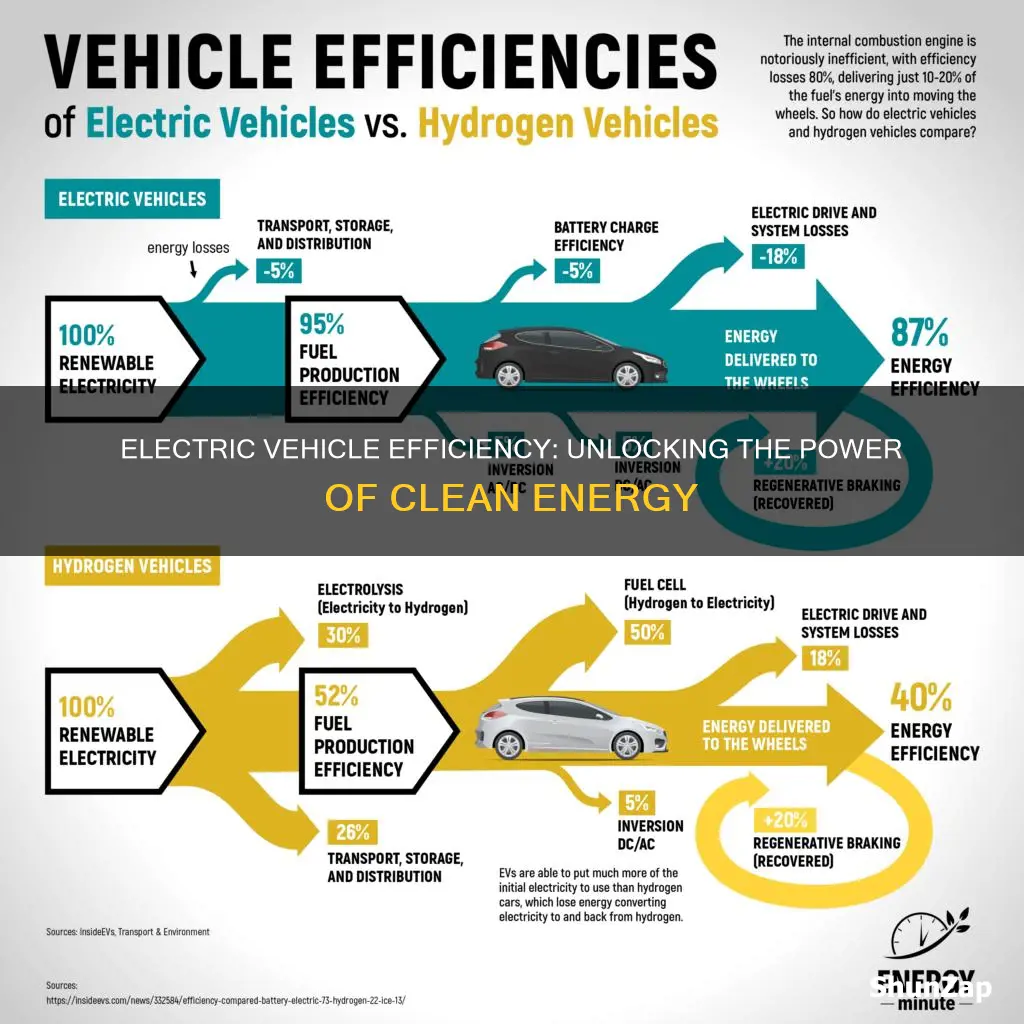
Electric vehicles (EVs) have gained significant popularity as a sustainable transportation alternative, but their efficiency is a key factor in their appeal. The efficiency of an electric vehicle refers to how effectively it converts electrical energy into mechanical energy, resulting in a measure of its overall performance and environmental impact. This efficiency is influenced by various factors, including the vehicle's battery capacity, motor efficiency, and aerodynamic design. Understanding the efficiency of EVs is crucial for consumers and policymakers alike, as it directly impacts the vehicle's range, charging times, and overall cost-effectiveness, making it an essential consideration for those looking to make an environmentally conscious choice in the automotive market.
Electric Vehicle Efficiency Characteristics
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
| Energy Efficiency (kWh/100 km) | 12-25 kWh/100 km (average) |
| Range (EPA) | 100-400 miles (250-1000 km) |
| Battery Capacity (kWh) | 30-100 kWh (average) |
| Charging Time (0-80%) | 30 minutes to 2 hours (depending on charger type and battery size) |
| Power Consumption (kW) | 50-200 kW (average) |
| Efficiency Improvement Factors | Regenerative braking, lightweight design, aerodynamic design |
| Environmental Impact | Zero tailpipe emissions, lower carbon footprint compared to gasoline vehicles |
| Energy Source | Electricity from renewable or non-renewable sources |
| Efficiency Standards | Varies by region, with some countries setting mandatory efficiency targets |
| Real-World Efficiency | Can vary due to driving conditions, weather, and vehicle age |
What You'll Learn

Energy Consumption: Compare EV efficiency to traditional vehicles
Electric vehicles (EVs) have revolutionized the automotive industry, offering an eco-friendly and efficient alternative to traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) cars. When it comes to energy consumption, EVs showcase remarkable efficiency, leaving their gasoline and diesel counterparts in the dust. One of the most significant advantages of EVs is their ability to convert a higher percentage of energy into actual power compared to traditional vehicles.
The efficiency of EVs is measured in kilowatt-hours per 100 kilometers (kWh/100 km) or miles per gallon equivalent (MPGe). On average, electric cars achieve an efficiency of around 100-150 MPGe, which translates to an impressive energy consumption rate. For instance, a well-known EV, the Tesla Model 3, boasts an EPA-estimated efficiency of 132 MPGe, meaning it consumes less energy to travel a certain distance compared to a conventional car. This efficiency is a result of the direct conversion of electrical energy into motion, eliminating the energy losses associated with the internal combustion process.
In contrast, traditional vehicles, including hybrid cars, have an efficiency of around 40-60 MPGe. This lower efficiency is due to the combined use of an internal combustion engine and an electric motor, which results in more energy being wasted as heat. Hybrid vehicles, while more efficient than their purely gasoline counterparts, still lag behind EVs in terms of energy consumption. The energy-intensive nature of ICEs, which require a significant amount of fuel to generate power, contributes to their lower efficiency.
The superior efficiency of EVs is further emphasized when considering the energy sources. While traditional vehicles burn fossil fuels, EVs primarily draw power from batteries, which can be charged using renewable energy sources. This shift towards cleaner energy sources not only reduces the environmental impact but also contributes to the overall efficiency of the vehicle. As technology advances, EV efficiency continues to improve, with ongoing research focusing on enhancing battery technology and reducing energy losses during charging and discharging.
In summary, electric vehicles demonstrate exceptional energy efficiency, outperforming traditional cars in terms of energy consumption. The direct conversion of electrical energy and the potential for cleaner power sources contribute to their superior performance. As the automotive industry continues to evolve, the efficiency of EVs will play a pivotal role in shaping a more sustainable and environmentally friendly future for transportation.
Peach Pass: Free EV Charging or a Rip-Off?
You may want to see also

Range: How far an EV can travel on a single charge
The range of an electric vehicle (EV) is a critical factor in determining its efficiency and practicality for everyday use. It refers to the distance an EV can travel on a single charge of its battery. This range varies significantly across different EV models, and understanding these variations is essential for potential buyers.
EV range is influenced by several factors, primarily the type and capacity of the battery, the efficiency of the vehicle's electric motor, and the driving conditions. Modern EVs often utilize lithium-ion batteries, which offer a good balance of energy density and cost. The capacity of these batteries is measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), with higher kWh values generally translating to longer ranges. For instance, a 60 kWh battery might provide a range of around 300-350 miles, while a 100 kWh battery could offer over 400 miles on a single charge.
Another crucial aspect is the efficiency of the vehicle's electric motor. More efficient motors can convert a higher percentage of the battery's energy into actual driving power, thus extending the range. This efficiency is often measured in terms of power-to-weight ratio, where a higher ratio indicates a more powerful motor that can also be more efficient. Additionally, the weight of the vehicle itself plays a role, as lighter EVs tend to be more energy-efficient, especially during acceleration and high-speed driving.
Driving conditions also significantly impact EV range. In colder climates, the battery's performance can be reduced due to the increased energy required to heat the cabin and maintain the battery's optimal temperature. Similarly, driving at high speeds or in mountainous terrain requires more energy, which can shorten the range. Therefore, it's essential for EV owners to be mindful of these conditions and plan their trips accordingly.
Modern EVs often come with advanced features to help drivers manage their range effectively. These include real-time range estimates, which provide an accurate prediction of the remaining range based on driving patterns and conditions. Some vehicles also offer regenerative braking systems, which capture and store energy that would otherwise be lost during braking, thus extending the range. Additionally, over-the-air software updates can improve efficiency and range over time as manufacturers refine their EV designs.
Toyota's Electric Future: Rumors of EV Production Halt
You may want to see also

Charging Time: Efficiency vs. charging speed and infrastructure
The efficiency of electric vehicles (EVs) is a multifaceted concept that encompasses various factors, including energy consumption, performance, and environmental impact. When it comes to charging time, the efficiency of EVs is often evaluated in relation to charging speed and the supporting infrastructure.
Charging speed is a critical aspect of EV efficiency. The time it takes to recharge an EV battery can vary significantly depending on several factors. Firstly, the charging power output, measured in kilowatts (kW), plays a crucial role. Higher kW output chargers can replenish the battery faster. For instance, a rapid charger with 50 kW can charge an EV battery much quicker than a slower 3 kW home charger. Secondly, the battery capacity, typically measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), also influences charging time. Larger batteries will take longer to charge, even with high-power chargers. Modern EVs often feature advanced battery management systems that optimize charging rates, ensuring efficient and safe charging processes.
The efficiency of charging infrastructure is another key consideration. The availability and accessibility of fast-charging stations along highways and in urban areas significantly impact the overall efficiency of EV ownership. Well-distributed charging networks allow drivers to plan their journeys more efficiently, reducing the anxiety associated with running out of battery. Additionally, smart charging technologies, which optimize charging times and rates based on grid demand and availability, contribute to overall system efficiency. These technologies can help balance the load on the electricity grid, ensuring that EVs charge efficiently without causing strain during peak hours.
However, the relationship between charging time and efficiency is complex. While faster charging speeds are desirable, they may not always translate to higher overall efficiency. Rapid charging can lead to increased heat generation within the battery, potentially impacting its long-term health and efficiency. Therefore, finding a balance between charging speed and battery longevity is essential for maximizing EV efficiency.
In summary, the efficiency of electric vehicles in relation to charging time involves a trade-off between charging speed and infrastructure. While faster charging speeds are advantageous, they should be complemented by efficient charging infrastructure and smart charging technologies to ensure optimal energy utilization and minimize environmental impact. As the EV market continues to evolve, advancements in charging technology and infrastructure will play a pivotal role in enhancing the overall efficiency and convenience of electric vehicle ownership.
Unleash Your Portfolio's Potential: A Guide to Electric Vehicle Stocks
You may want to see also

Battery Technology: Impact on efficiency and performance
Battery technology plays a pivotal role in determining the efficiency and overall performance of electric vehicles (EVs). The advancements in battery chemistry and design have significantly contributed to the improvement of EV efficiency, making them more viable and competitive in the automotive market. One of the key factors influencing efficiency is the energy density of the battery. Higher energy density allows for more energy storage in a smaller and lighter package, which is crucial for EVs as it directly impacts their range. Modern lithium-ion batteries, the most common type used in EVs, have achieved remarkable energy densities, enabling vehicles to travel longer distances on a single charge. This is particularly important for addressing range anxiety, a common concern among potential EV buyers.
The efficiency of EV batteries is also closely tied to their charging capabilities. Fast-charging technologies have been developed to reduce the time required to recharge batteries, making EVs more convenient for daily use. These rapid-charging systems often employ advanced battery management systems that optimize charging rates while minimizing energy losses. As a result, EVs can now be charged to 80% of their capacity in as little as 30 minutes, significantly improving their usability for long-distance travel.
Another critical aspect of battery technology is its ability to manage temperature. Lithium-ion batteries are sensitive to extreme temperatures, which can impact their performance and longevity. Efficient thermal management systems are now integrated into EVs to maintain optimal battery temperatures. These systems ensure that the batteries operate within the ideal temperature range, maximizing energy output and minimizing energy waste. This is particularly important in regions with extreme climates, where temperature variations can significantly affect EV efficiency.
Furthermore, the development of solid-state batteries is an emerging area of research that promises to revolutionize EV efficiency. Solid-state batteries replace the liquid electrolyte in traditional lithium-ion batteries with a solid conductive material, offering several advantages. These include higher energy density, faster charging times, and improved safety due to the reduced risk of thermal runaway. While solid-state batteries are still in the early stages of development, they have the potential to significantly enhance the performance and efficiency of electric vehicles.
In summary, battery technology is a critical enabler of efficiency and performance in electric vehicles. Continuous advancements in energy density, charging capabilities, thermal management, and emerging technologies like solid-state batteries are collectively driving the improvement of EV efficiency. As battery technology continues to evolve, we can expect further enhancements in the range, charging speed, and overall performance of electric vehicles, making them an increasingly attractive and sustainable transportation option.
Electric Vehicles: Cost-Effective Transportation for Businesses?
You may want to see also

Driving Conditions: Weather, terrain, and efficiency
The efficiency of an electric vehicle (EV) can be significantly influenced by various driving conditions, particularly weather, terrain, and the state of the vehicle itself. These factors play a crucial role in determining the actual range and performance of EVs, which is often a concern for potential buyers.
Weather Conditions:
Weather has a direct impact on the efficiency of electric cars. During colder seasons, heating the cabin and keeping the battery warm can consume a substantial amount of energy, reducing the overall range. This is especially true for older EV models that may not have advanced thermal management systems. In contrast, extreme heat can also affect efficiency as the air conditioning system works harder, drawing more power from the battery. Additionally, heavy rain or snow can impact aerodynamics, requiring more power to maintain speed and potentially reducing efficiency.
Terrain and Driving Style:
The type of terrain and driving habits can greatly influence efficiency. Off-road driving, especially on rough and uneven surfaces, demands more power from the electric motor, leading to increased energy consumption. Similarly, frequent acceleration and deceleration, such as in stop-and-go traffic or when driving in mountainous areas, can drain the battery faster. On the other hand, smooth and steady driving on flat roads can optimize efficiency, allowing the EV to maintain a consistent range.
Impact of Terrain:
Different terrains present unique challenges. Driving uphill requires more power, and the efficiency of the vehicle may decrease as the battery works harder to overcome gravity. Conversely, driving downhill can improve efficiency as the vehicle's kinetic energy is converted back into battery power. The state of the road surface also matters; a well-maintained, smooth road will generally provide better efficiency compared to a bumpy or uneven one.
Vehicle Maintenance and Efficiency:
It's important to note that proper vehicle maintenance can also impact efficiency. Regular servicing, including tire maintenance and keeping the battery healthy, can optimize performance. For instance, underinflated tires create more rolling resistance, reducing efficiency. Additionally, ensuring the EV's cooling system is functioning correctly can prevent overheating, which can negatively affect the battery's performance and overall efficiency.
Understanding these factors is essential for EV owners and prospective buyers to manage expectations and make informed decisions. By considering the driving conditions and adapting their habits, EV drivers can maximize efficiency and ensure a more enjoyable and sustainable driving experience.
Unveiling Arizona's EV Registration Fee: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Electric vehicles are highly efficient, with a much higher energy conversion rate compared to ICE cars. EVs can convert over 77% of the energy stored in their batteries to power the vehicle, whereas ICE cars typically convert only about 20-30% of the energy from fuel to power. This efficiency means that EVs use less energy to travel the same distance, resulting in lower operating costs and reduced environmental impact.
Several factors influence the efficiency of EVs. Firstly, the type and size of the battery play a crucial role, as larger batteries can store more energy, allowing for longer driving ranges. Secondly, the motor efficiency, including the reduction gear and inverter, impacts overall efficiency. Modern electric motors are designed to be highly efficient, converting electrical energy into mechanical power with minimal losses. Additionally, factors like aerodynamics, vehicle weight, and driver behavior (such as acceleration and braking patterns) can also affect efficiency.
Yes, there are several ways to enhance the efficiency of EVs. One approach is to optimize the vehicle's design, including improving aerodynamics to reduce drag, minimizing weight through lightweight materials, and optimizing the placement of components to reduce parasitic losses. Another method is to employ regenerative braking systems, which capture and store energy that would otherwise be lost during braking, thus improving overall efficiency. Additionally, advancements in battery technology, such as using higher-energy-density batteries, can also contribute to increased efficiency.
Efficiency plays a significant role in determining the range of an electric vehicle. A more efficient EV can travel farther on a single charge because it requires less energy to cover the same distance. Factors like driving conditions, temperature, and vehicle maintenance also influence range. For example, driving at higher speeds or in extreme weather conditions may reduce efficiency and range. Therefore, improving efficiency is crucial for extending the driving range of EVs and addressing range anxiety among potential buyers.
Yes, several organizations provide efficiency ratings and standards for EVs. The U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) and the European Union's WLTP (Worldwide Harmonized Light Vehicle Test Procedure) are two common methods to measure and report vehicle efficiency. These standards help consumers compare the efficiency of different EV models. Additionally, some countries have their own efficiency rating systems, ensuring transparency and allowing consumers to make informed choices when purchasing electric vehicles.