The question of whether electric vehicles (EVs) are subject to road tax is an important consideration for EV owners and potential buyers. While traditional internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicles often incur road tax, the tax implications for EVs can vary depending on the jurisdiction and specific vehicle characteristics. This paragraph aims to explore the current state of road tax policies for electric vehicles, examining the factors that determine tax liability and providing insights into the financial considerations for EV owners.
| Characteristics | Values |
|---|---|
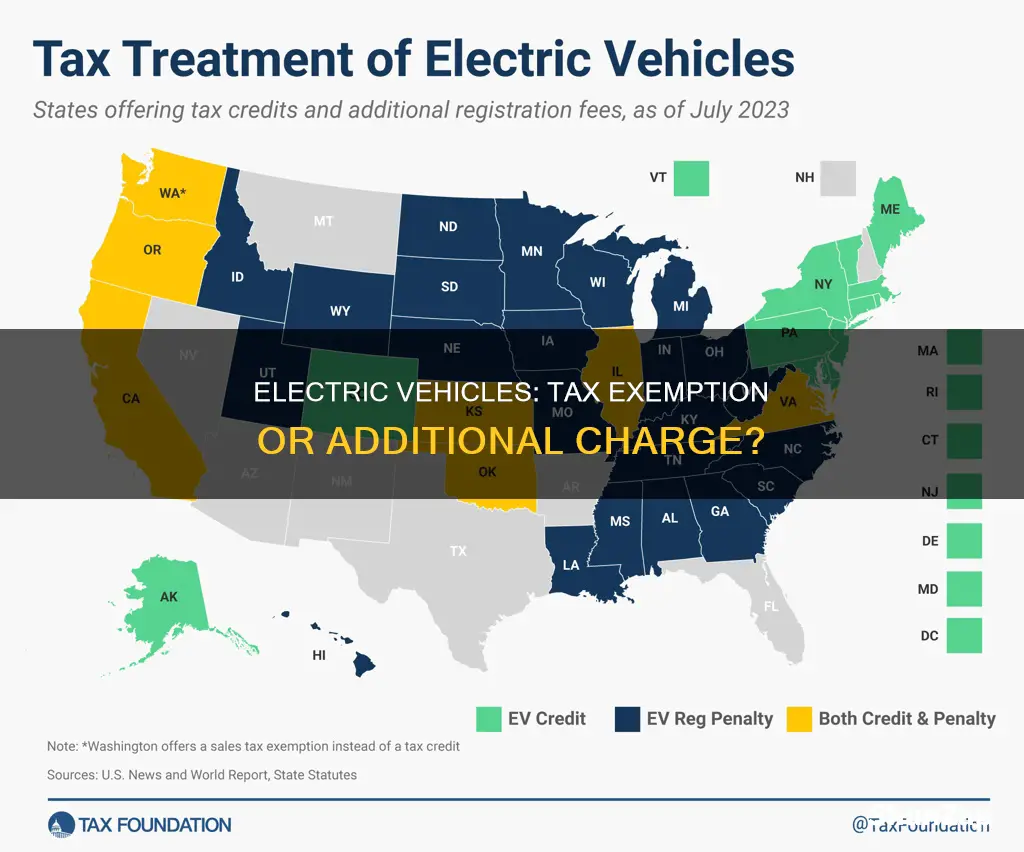
| Road Tax Exemption for Electric Vehicles | In many countries, electric vehicles (EVs) are exempt from road tax or benefit from reduced rates. This is a financial incentive to promote the adoption of cleaner and more sustainable transportation. |
| Environmental Benefits | EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, which helps reduce air pollution and carbon footprints. |
| Government Incentives | Governments often provide additional incentives like tax credits, grants, or subsidies to encourage the purchase of EVs. |
| Vehicle Type | The exemption typically applies to battery-electric vehicles (BEVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). |
| Registration and Licensing | EVs may still be subject to regular vehicle registration and licensing processes, but the tax aspect is often favorable. |
| Timeframe | The road tax exemption can vary in duration, sometimes permanent, and sometimes for a limited period after the vehicle's purchase. |
| Regional Variations | Policies differ by region, with some countries offering full exemptions, while others provide partial relief or specific benefits for certain EV models. |
| Market Growth | The rise in EV sales has led to increased discussions and implementations of road tax policies to support the growing market. |
| Future Trends | As the automotive industry shifts towards electrification, road tax policies are expected to evolve, potentially becoming more favorable for EVs. |
What You'll Learn
- Tax Rates: Different regions have varying tax rates for electric vehicles, often lower than traditional cars
- Exemptions: Many countries offer tax exemptions or reduced rates for electric vehicles to encourage adoption
- Registration Fees: These fees may be lower or waived for electric vehicles, often tied to environmental benefits
- Time-Based Taxation: Some regions impose tax based on the age or mileage of the vehicle, not its type
- Government Incentives: Governments often provide incentives like tax credits or rebates to promote electric vehicle ownership

Tax Rates: Different regions have varying tax rates for electric vehicles, often lower than traditional cars
The concept of road tax for electric vehicles (EVs) is an important consideration for EV owners and potential buyers, especially as governments worldwide are increasingly promoting the adoption of electric mobility to reduce environmental impact. The tax structure for EVs can vary significantly depending on the region, and understanding these variations is crucial for anyone looking to purchase or own an electric car.
In many countries, the tax system for EVs is designed to encourage their use by offering financial incentives. These incentives often come in the form of reduced or waived road taxes, which can significantly lower the overall cost of ownership for electric vehicle owners. For instance, in some European countries, electric car buyers are exempt from paying road tax entirely, while in others, the tax is significantly lower compared to conventional gasoline or diesel vehicles. This is a strategic move by governments to promote sustainable transportation and reduce the carbon footprint of their citizens.
The tax rates for EVs are often lower due to the environmental benefits associated with electric mobility. Electric vehicles produce zero tailpipe emissions, which means they contribute to improved air quality and reduced pollution. As a result, governments are more inclined to offer tax benefits to EV owners as a form of encouragement and reward for making eco-friendly choices. This approach not only promotes the use of clean energy vehicles but also helps in building a robust EV market, fostering innovation, and creating a positive feedback loop for further environmental initiatives.
When considering purchasing an EV, it is essential to research the specific tax regulations in your region. Different areas may have unique tax policies, and these can vary based on factors such as vehicle type, power source, and even the purpose of the vehicle (e.g., personal use, commercial). For instance, some regions might offer tax breaks for electric vehicles used for commercial purposes, while others may provide incentives for personal EV purchases. Understanding these nuances can help buyers make informed decisions and potentially save on taxes.
Moreover, the tax benefits for EVs can extend beyond the initial purchase. Many governments also provide tax credits or rebates for EV charging infrastructure, further reducing the overall cost for EV owners. These incentives can make the transition to electric mobility more accessible and attractive to a wider audience. As the global shift towards sustainable transportation continues, staying informed about the tax rates and incentives for electric vehicles in your region is a smart strategy for anyone considering an EV purchase.
Unleashing the Power of EVs: Strategies to Boost Demand and Revolutionize Transportation
You may want to see also

Exemptions: Many countries offer tax exemptions or reduced rates for electric vehicles to encourage adoption
In many countries, governments have implemented various incentives to promote the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) as part of their efforts to reduce environmental impact and encourage the shift towards cleaner transportation. One of the most common incentives is the provision of tax exemptions or reduced rates for electric vehicles. These financial benefits aim to make EVs more affordable and attractive to consumers, ultimately accelerating the transition to sustainable mobility.
For instance, in several European countries, electric car owners are exempt from paying road tax or benefit from significantly reduced rates. This exemption can be a substantial financial advantage, as road tax is typically a recurring annual cost for vehicle owners. By waiving this tax, governments are not only making EVs more accessible but also reducing the long-term ownership costs, which can be a significant barrier for potential EV buyers.
Similarly, in the United States, some states offer tax credits or rebates for the purchase of electric vehicles. These incentives can vary in amount and eligibility criteria, but they generally aim to offset the higher upfront cost of EVs compared to traditional gasoline vehicles. Such financial support can make a substantial difference in the overall affordability of electric cars, making them a more viable option for a wider range of consumers.
Furthermore, some countries have introduced temporary tax breaks or reduced rates for a specific period to stimulate the market and encourage the rapid adoption of electric vehicles. This strategy can create a sense of urgency among consumers, leading to increased sales and a faster transition to a more sustainable transportation ecosystem.
These tax exemptions and reduced rates are powerful tools in the global effort to combat climate change and promote sustainable practices. By making electric vehicles more affordable and attractive, governments are not only supporting the automotive industry but also contributing to a greener and more environmentally conscious society. As the world continues to prioritize sustainability, such incentives are likely to become even more prevalent and effective in driving the widespread adoption of electric vehicles.
Ford's Future: Electric Vehicles in Transition
You may want to see also

Registration Fees: These fees may be lower or waived for electric vehicles, often tied to environmental benefits
The concept of road tax for electric vehicles is an evolving topic, and many regions are adapting their policies to encourage the adoption of eco-friendly transportation. One aspect that often comes into play is the registration process, which can significantly impact vehicle owners. In many countries, registration fees are a mandatory cost associated with owning a vehicle, and these fees can vary depending on the type of vehicle and its environmental impact.
For electric vehicles (EVs), governments worldwide are recognizing the potential environmental benefits and are implementing strategies to promote their use. As a result, many jurisdictions are offering incentives to make electric vehicle ownership more accessible. One such incentive is the reduction or waiver of registration fees for EVs. This approach is a direct way to encourage citizens to choose environmentally friendly transportation options. By providing financial relief, governments aim to lower the overall cost of owning an electric vehicle, making it more attractive to potential buyers.
The environmental benefits of electric vehicles are well-documented, with reduced carbon emissions and lower air pollution being key advantages. These benefits often lead to a positive impact on public health and the environment. As a result, governments are motivated to support the transition to electric mobility. Lower registration fees for EVs are a strategic move to accelerate this transition, ensuring that the financial barrier to entry is reduced, and more people can contribute to a greener future.
In some regions, the reduction in registration fees is a direct response to the growing popularity of electric vehicles. This strategy not only promotes EV sales but also helps in building a robust charging infrastructure. With more electric vehicles on the road, the demand for charging stations increases, further supporting the EV ecosystem. This approach creates a positive feedback loop, where the reduction in registration fees leads to increased EV adoption, which in turn drives the development of necessary infrastructure.
Additionally, some governments are taking a more comprehensive approach by offering a combination of incentives. These may include reduced registration fees, tax credits, and subsidies for purchasing electric vehicles. Such a multi-faceted strategy ensures that the financial benefits are maximized, making electric vehicles an even more appealing choice for consumers. As the world moves towards a more sustainable future, these incentives play a crucial role in accelerating the transition to cleaner transportation options.
Electric Vehicle Market: Surplus or Shortage?
You may want to see also

Time-Based Taxation: Some regions impose tax based on the age or mileage of the vehicle, not its type
In certain jurisdictions, road tax policies can be quite intricate, with various factors influencing the amount of tax levied on vehicles. One such approach is time-based taxation, which focuses on the age or mileage of the vehicle rather than its type. This method is particularly relevant when considering the implications for electric vehicles (EVs) and their unique characteristics.
Time-based taxation often takes into account the wear and tear that a vehicle undergoes over its lifetime. As vehicles age, they may require more frequent maintenance and repairs, and their performance can deteriorate. This is especially true for mechanical components that are prone to degradation over time. For instance, an internal combustion engine (ICE) vehicle's engine might need more frequent servicing as it ages, leading to higher maintenance costs. In contrast, EVs, with their simpler electric drivetrains, may have lower maintenance requirements, making age-based taxation potentially less applicable.
Mileage-based taxation is another aspect of time-based taxation. This approach considers the distance a vehicle has traveled, which can be a more accurate indicator of its usage and potential wear. For example, a high-mileage EV, despite being electric, may still incur higher tax rates if it has been extensively used, just like a high-mileage ICE vehicle. This method ensures that the tax system reflects the actual usage and potential environmental impact of the vehicle.
The key advantage of time-based taxation is its fairness in distributing the tax burden based on the vehicle's actual usage and age. It prevents the situation where newer, more environmentally friendly vehicles, like EVs, might be taxed less than older, less efficient ICE vehicles. This approach encourages the adoption of newer, more sustainable transportation options while ensuring that the tax system remains equitable.
However, implementing time-based taxation requires sophisticated data collection and analysis. Governments need to track vehicle mileage and age accurately, which can be challenging, especially for a rapidly evolving market like EVs. Additionally, the transition to electric mobility may require adjustments to the tax system to ensure it remains relevant and fair.
Rivian's Electric Revolution: Unlocking the Future of Sustainable Driving
You may want to see also

Government Incentives: Governments often provide incentives like tax credits or rebates to promote electric vehicle ownership
Incentivizing the adoption of electric vehicles (EVs) is a common strategy employed by governments worldwide to encourage a shift towards more sustainable transportation. One of the most prevalent incentives is the provision of tax credits or rebates, which directly benefit EV owners and contribute to the overall growth of the electric vehicle market. These financial incentives aim to reduce the upfront cost of purchasing electric cars, making them more affordable and attractive to consumers.
Many countries have implemented tax credit programs for electric vehicle purchases. For instance, in the United States, the federal government offers a tax credit of up to $7,500 for the purchase of new electric vehicles, provided they meet specific criteria, such as being produced in North America and having a battery range of at least 100 miles. This credit significantly lowers the overall cost, making EVs more competitive against traditional gasoline vehicles. Similarly, in the European Union, several member states provide tax benefits or reduced registration fees for electric cars, further enhancing their economic appeal.
Rebates are another form of government incentive that can be particularly effective in stimulating the market. These rebates are often offered as a percentage of the vehicle's purchase price, directly reducing the amount buyers need to pay upfront. For example, some governments provide a rebate of 10-20% on the cost of an electric vehicle, which can be substantial, especially for high-end models. Such incentives not only make EVs more affordable but also encourage manufacturers to invest in and produce a wider range of electric vehicles to cater to diverse consumer preferences.
The impact of these government incentives is twofold. Firstly, they provide financial relief to consumers, making the initial investment in an electric vehicle more manageable. This is crucial in attracting potential buyers who might otherwise be deterred by the higher upfront costs compared to conventional cars. Secondly, these incentives contribute to the development of a robust electric vehicle market, fostering innovation and competition among manufacturers. As a result, consumers benefit from a growing selection of models, improved performance, and potentially lower prices over time.
Furthermore, government incentives for electric vehicles extend beyond the purchase stage. Some jurisdictions offer tax breaks or reduced rates for EV owners when it comes to annual road taxes or vehicle registration fees. This not only provides ongoing savings for EV owners but also ensures that the financial benefits of owning an electric car extend throughout its lifetime. By combining purchase incentives with ongoing cost savings, governments can effectively promote the widespread adoption of electric vehicles and accelerate the transition to a more sustainable transportation ecosystem.
Nissan Kicks: Electric Vehicle or Not? Unveiling the Truth
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Yes, electric vehicles are subject to road tax regulations, but there are some differences. The road tax for EVs is typically calculated based on the vehicle's CO2 emissions, which is a measure of its environmental impact. Since EVs produce zero tailpipe emissions, they often fall into a lower tax bracket or even qualify for exemptions.
The tax amount for EVs is usually based on the vehicle's carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions, which are measured in grams per kilometer (g/km). EVs with lower CO2 emissions may be taxed at a reduced rate or even exempt from road tax, encouraging the adoption of cleaner technologies.
Yes, many countries offer incentives and benefits for EV owners. For instance, some governments provide tax credits or exemptions for the initial registration or annual road tax payment. These incentives aim to promote the use of electric vehicles and reduce the environmental impact of transportation.
In some cases, yes. If you've paid road tax for an EV and later discover that you qualify for an exemption or reduced rate, you may be able to claim a refund. It's important to keep track of your vehicle's tax status and any relevant documentation to ensure compliance with the tax authorities.
Road tax regulations for EVs can vary and may change over time. It's essential to stay informed about any updates or amendments to the tax laws in your region. Governments often review and adjust tax policies to align with environmental goals and technological advancements in the automotive industry.







