Electric vehicles (EVs) are a rapidly growing segment in the automotive industry, offering an eco-friendly alternative to traditional internal combustion engine cars. The composition of EVs is a fascinating blend of advanced materials and innovative technologies. These vehicles are primarily constructed from lightweight, durable materials such as aluminum, high-strength steel, and advanced composites. The battery pack, a critical component, is often made of lithium-ion cells, which store and release energy efficiently. The electric motor, another key element, is typically crafted from materials like copper and rare earth magnets. The design and manufacturing of EVs involve sophisticated engineering to ensure optimal performance, efficiency, and safety, making them a testament to modern automotive innovation.
What You'll Learn
- Battery Technology: Lithium-ion batteries power EVs, made of cobalt, nickel, and lithium
- Motor Components: Electric motors use copper, aluminum, and rare earth magnets
- Frame Materials: Steel, aluminum, and carbon fiber composites form the vehicle's structure
- Electronics: Microcontrollers, sensors, and wiring harness are essential for vehicle control
- Exterior Materials: Plastic, glass, and lightweight alloys are used for body panels and windows

Battery Technology: Lithium-ion batteries power EVs, made of cobalt, nickel, and lithium
The heart of an electric vehicle (EV) is its battery pack, which is typically a lithium-ion battery. These batteries are the driving force behind the EV's ability to store and deliver the energy required to propel the vehicle. Lithium-ion batteries have become the go-to technology for EVs due to their high energy density, lightweight design, and relatively low cost compared to other battery types.
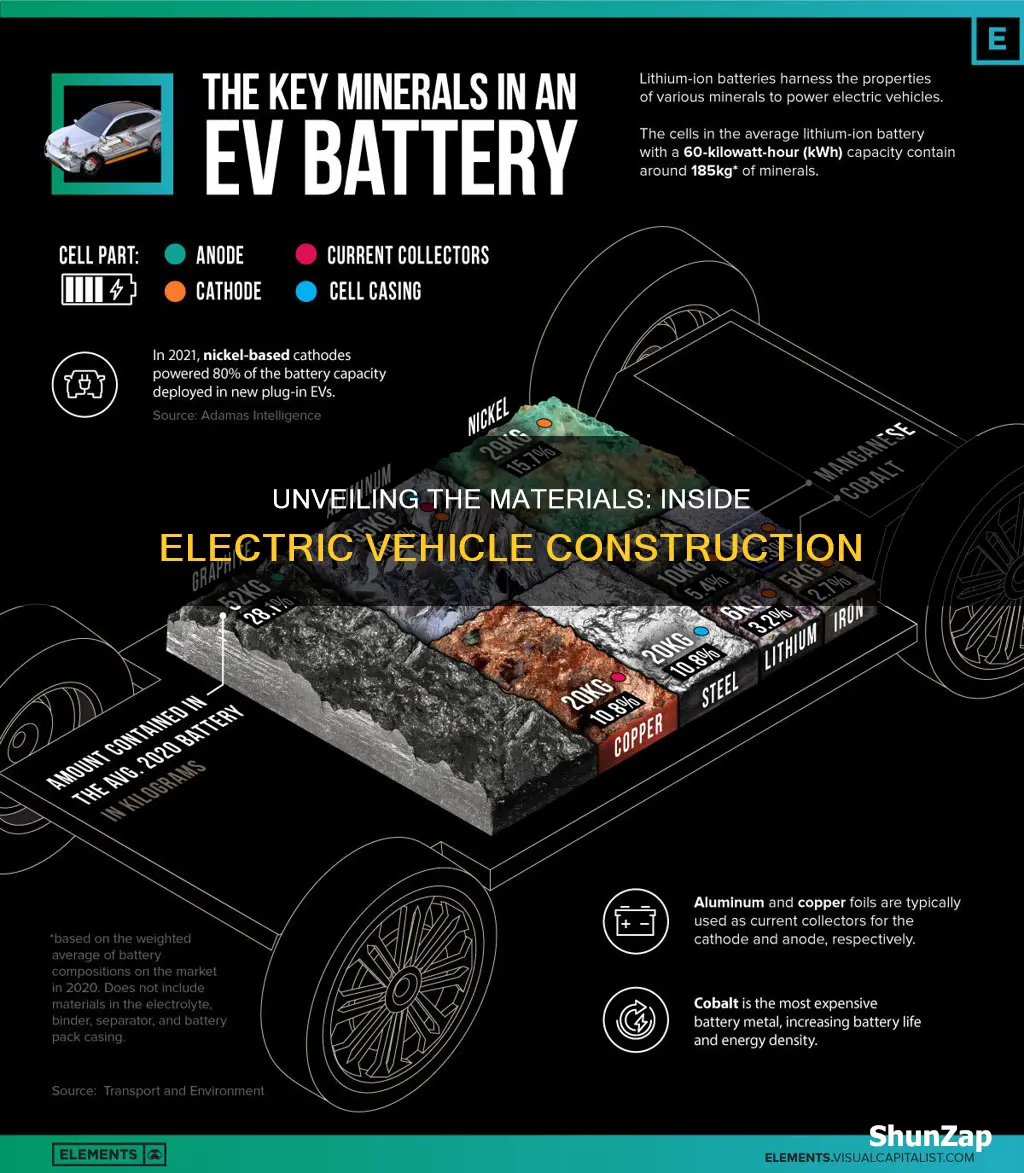
The composition of these batteries is quite intricate. At the core, lithium-ion batteries consist of several key components. One of the primary materials is lithium, which is a lightweight metal that serves as the primary charge carrier within the battery. Lithium's unique properties allow it to move ions between the positive and negative electrodes during charging and discharging, facilitating the flow of electricity.
Cobalt and nickel are also essential in the construction of lithium-ion batteries. These metals are used in the cathode, which is the positive electrode. The cathode material is responsible for storing and releasing lithium ions during the battery's operation. Cobalt and nickel-based cathodes have been widely used due to their high energy storage capacity and stability. These materials contribute to the battery's ability to store a significant amount of energy in a relatively small space, making EVs more efficient and practical for everyday use.
The anode, or negative electrode, is typically made from carbon-based materials, such as graphite. During charging, lithium ions move from the cathode to the anode, where they are stored within the graphite structure. This process allows the battery to store energy. When the EV is in use, the stored energy is released as electricity, powering the vehicle's electric motor.
The design and arrangement of these components within the battery pack are crucial for optimizing performance and safety. Battery packs are often composed of multiple individual cells, each containing the anode, cathode, electrolyte, and various protective layers. These cells are carefully arranged to ensure efficient energy storage and delivery while also incorporating safety mechanisms to prevent overheating and other potential hazards.
Understanding Dashes: Decoding Vehicle Electrical Schematics
You may want to see also

Motor Components: Electric motors use copper, aluminum, and rare earth magnets
Electric vehicles (EVs) are a testament to the innovative use of materials in modern transportation. When it comes to the motor components, several key materials play a crucial role in their functionality and performance. One of the most prominent materials is copper, which is widely used in electric motors due to its excellent electrical conductivity. Copper wires are used to create the windings within the motor, allowing for efficient current flow and the generation of magnetic fields. These windings are carefully arranged to produce the desired torque and power output.
Aluminum also finds its place in electric motor construction. It is often utilized in the form of aluminum alloy casings or heat sinks. The lightweight nature of aluminum helps reduce the overall weight of the motor, contributing to improved efficiency and performance. Additionally, aluminum's thermal conductivity is advantageous for managing the heat generated during operation, ensuring the motor operates within safe temperature limits.
Rare earth magnets, a group of powerful permanent magnets, are another essential component of electric motors. These magnets are crafted from rare earth elements, such as neodymium and samarium-cobalt. The unique properties of rare earth magnets enable the creation of compact and lightweight motors with high torque and efficiency. By utilizing these magnets, electric vehicles can achieve superior performance and acceleration compared to traditional internal combustion engine vehicles.
The combination of copper, aluminum, and rare earth magnets in electric motors showcases the intricate engineering required to power these vehicles. Each material contributes to specific aspects of motor performance, from electrical conductivity to weight reduction and magnetic strength. As technology advances, further innovations in motor design and material science will continue to drive the development of more efficient and sustainable electric vehicles.
Unlocking EV Affordability: Strategies for Developing Nations
You may want to see also

Frame Materials: Steel, aluminum, and carbon fiber composites form the vehicle's structure
The structural framework of electric vehicles (EVs) is a critical component, providing the necessary strength, rigidity, and safety for the vehicle's overall performance and longevity. The choice of materials for the frame plays a significant role in determining the vehicle's weight, durability, and overall efficiency.
Steel: One of the most traditional and widely used materials in the automotive industry, steel is a cornerstone of EV construction. High-strength steel alloys, such as advanced high-strength steel (AHSS) and dual-phase steel, are now prevalent in EV frames. These alloys offer excellent tensile strength, allowing for thinner gauge materials while maintaining structural integrity. The use of steel in EVs provides a cost-effective solution, ensuring the vehicle's frame can withstand the stresses of everyday driving and potential collisions. Modern steel alloys also contribute to the overall safety of the vehicle, as they can absorb and redistribute crash forces effectively.
Aluminum: Lighter and more corrosion-resistant than steel, aluminum has become a popular choice for EV frames, especially in high-performance electric vehicles. Aluminum alloys, such as 6061 and 7075, offer a good balance of strength and weight reduction. The use of aluminum in the frame reduces the overall vehicle weight, improving energy efficiency and handling. Additionally, aluminum's natural corrosion resistance means that EVs with aluminum frames require less maintenance and are more resistant to the elements, ensuring a longer lifespan.
Carbon Fiber Composites: For high-end and performance-oriented electric vehicles, carbon fiber composites are the material of choice. These composites consist of carbon fibers reinforced with a polymer matrix, offering an exceptional strength-to-weight ratio. Carbon fiber frames provide unparalleled rigidity and strength, contributing to improved handling and overall vehicle performance. While carbon fiber is more expensive than steel or aluminum, its use allows for a more lightweight and robust structure, enhancing the EV's efficiency and driving dynamics. The composite material's ability to absorb and distribute forces evenly also contributes to the vehicle's safety, making it an attractive option for racing and high-performance EVs.
The combination of these frame materials allows EV manufacturers to tailor the vehicle's characteristics to specific needs. Steel provides a cost-effective and safe foundation, aluminum offers lightweight efficiency, and carbon fiber composites deliver exceptional performance and handling. The evolution of frame materials in electric vehicles continues to drive innovation, ensuring that EVs are not only environmentally friendly but also technologically advanced and capable.
Unveiling Tesla's Electric Vehicle: A Patent Mystery
You may want to see also

Electronics: Microcontrollers, sensors, and wiring harness are essential for vehicle control
The heart of any electric vehicle's control system lies in its electronics, which include microcontrollers, sensors, and wiring harnesses. These components work in harmony to ensure the vehicle's smooth operation and efficient performance.
Microcontrollers: These are the brains of the electric vehicle. They are small, integrated circuits that process data and execute instructions. In an electric vehicle, microcontrollers are responsible for controlling various functions, such as motor speed, battery management, and overall vehicle performance. They receive input from sensors, make decisions based on pre-programmed algorithms, and send commands to the vehicle's actuators. Modern microcontrollers are powerful, capable of handling complex tasks and real-time data processing, ensuring the vehicle's responsiveness and safety.
Sensors: Sensors play a critical role in providing the microcontroller with real-time information about the vehicle's status. These include sensors for monitoring temperature, pressure, speed, and various other parameters. For instance, temperature sensors help regulate the vehicle's cooling system, ensuring optimal performance and preventing overheating. Pressure sensors are used in tire monitoring systems to detect under-inflation, improving safety and fuel efficiency. Speed sensors provide feedback to the microcontroller, allowing for precise control of the vehicle's acceleration and deceleration. Each sensor type is designed to measure specific data, contributing to the overall efficiency and safety of the electric vehicle.
Wiring Harness: The wiring harness is a network of cables and connectors that interconnect all the vehicle's electronic components. It ensures the seamless flow of data and power between the microcontroller, sensors, and other control units. A well-designed wiring harness is crucial for maintaining signal integrity and minimizing electromagnetic interference. It must be carefully routed to avoid damage from vibrations and extreme temperatures, ensuring the vehicle's reliability and longevity. The harness also includes fuses and relays to protect against electrical faults, further enhancing the vehicle's safety.
In summary, the electronics in electric vehicles are a complex yet vital system. Microcontrollers, sensors, and wiring harnesses work together to enable precise control, efficient performance, and enhanced safety. These components are carefully designed and integrated to meet the unique demands of electric mobility, contributing to the overall success of the electric vehicle market.
Honolulu Zoo: Electric Vehicle Parking Privileges and Fees
You may want to see also

Exterior Materials: Plastic, glass, and lightweight alloys are used for body panels and windows
The exterior of electric vehicles (EVs) is crafted from a variety of materials, each chosen for its specific properties to enhance performance, safety, and aesthetics. Among these materials, plastic, glass, and lightweight alloys play significant roles in shaping the body panels and windows of EVs.
Plastic: Plastic is a versatile and lightweight material that has become a cornerstone in the construction of modern vehicles, including electric ones. It is commonly used for body panels, fenders, bumpers, and interior components. The use of plastic in EVs offers several advantages. Firstly, it contributes to a lower overall vehicle weight, which is crucial for improving energy efficiency and range. Plastic is also known for its excellent impact resistance, making it an ideal choice for areas that require durability without adding excessive weight. Additionally, plastic can be easily molded into various shapes, allowing for innovative and sleek designs that are often seen in the exterior styling of EVs. Modern plastic compounds used in EVs are also designed to be impact-resistant, scratch-resistant, and UV-stable, ensuring that the vehicle maintains its appearance over time.
Glass: Glass is another essential material in the exterior construction of EVs, primarily used for windows. While traditional glass is heavy, modern automotive glass is designed to be lightweight and strong. The windows of electric vehicles are typically made from a specialized type of glass known as safety glass, which is designed to withstand impacts and provide structural integrity. This safety glass is often composed of multiple layers, including a layer of polyvinyl butyral (PVB) sandwiched between two layers of glass. PVB adds strength and helps to prevent the glass from shattering into sharp fragments, making it safer for occupants in the event of a collision. The use of lightweight glass also contributes to the overall weight reduction of the vehicle, further enhancing energy efficiency.
Lightweight Alloys: Lightweight alloys, such as aluminum and magnesium alloys, are increasingly being utilized in the construction of electric vehicle body panels and structural components. These alloys offer a significant weight reduction compared to traditional steel, without compromising on strength and rigidity. Aluminum, in particular, is a popular choice due to its high strength-to-weight ratio, excellent corrosion resistance, and ease of manufacturing. It is often used for the vehicle's chassis, body structure, and even in some cases, for the car's exterior panels. Magnesium alloys, while less common, offer even lower weight and can be used in specific high-stress areas of the vehicle to optimize performance and efficiency. The use of lightweight alloys not only improves the overall weight of the EV but also contributes to better handling, acceleration, and braking performance.
Uncover the Tax Benefits: Electric Vehicles and You
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Electric vehicles (EVs) are typically made from a variety of materials, including advanced composites, high-strength steel, aluminum, and lightweight alloys. These materials are chosen for their strength, durability, and ability to reduce vehicle weight, which is crucial for improving efficiency and range.
Yes, lithium-ion batteries are the most common type used in electric vehicles. These batteries offer a good balance of energy density, weight, and cost. The battery pack is often made up of multiple cells, and its design and materials can vary depending on the manufacturer and the specific EV model.
EVs play a significant role in promoting sustainability. They are made with a focus on reducing environmental impact, often utilizing recycled materials and minimizing the use of hazardous substances. The absence of internal combustion engines in EVs also reduces air pollution and contributes to a greener transportation system.
Body panels in electric vehicles can be made from various materials, including carbon fiber composites, which offer excellent strength-to-weight ratios and contribute to the overall lightweight design. Some manufacturers also use advanced polymers and lightweight alloys to enhance structural integrity while keeping the vehicle's weight optimized.