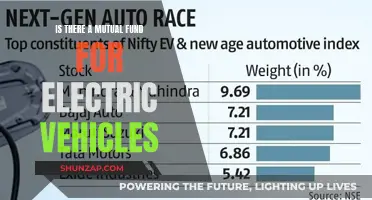
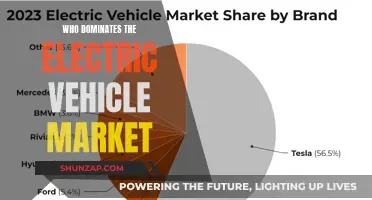
Grid-integrated electric vehicles (EVs) are a cutting-edge technology that revolutionizes the way we interact with transportation and energy systems. These vehicles are designed to seamlessly connect with the electrical grid, allowing for efficient energy management and optimized charging and discharging processes. By integrating with the grid, EVs can not only draw power from the grid during charging but also feed excess energy back into the grid when needed, contributing to a more sustainable and resilient energy infrastructure. This innovative approach enables EVs to become a dynamic part of the energy ecosystem, enhancing grid stability and supporting the transition to a cleaner and more efficient energy future.
What You'll Learn
- Grid-Integrated EVs: Charging and discharging batteries to support the power grid
- Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G): Technology enabling EVs to send power back to the grid
- Smart Grid Interaction: Optimizing EV charging and discharging for grid stability
- Renewable Energy Integration: Using EVs to store and distribute renewable energy
- Grid Services: EVs providing grid support, like load balancing and voltage regulation

Grid-Integrated EVs: Charging and discharging batteries to support the power grid
Grid-Integrated Electric Vehicles (EVs) are a fascinating concept that allows EVs to not only be powered by the grid but also actively participate in supporting the electrical grid. This technology enables EVs to charge and discharge their batteries based on the grid's needs, offering a two-way interaction that benefits both the vehicle owner and the power infrastructure.
The charging and discharging process for these vehicles is a carefully managed system. When the grid experiences a surplus of power, typically during periods of low demand, EVs can be programmed to initiate charging. This is an efficient way to utilize excess energy that might otherwise be wasted. The vehicles can be charged at optimal times, such as overnight or during off-peak hours, ensuring that the charging process does not strain the grid during high-demand periods. By doing so, grid-integrated EVs can help stabilize the power supply and reduce the risk of blackouts or overloading.
During periods of high power demand, the EVs can discharge their stored energy back into the grid. This process, known as vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology, allows the vehicles to act as mobile energy storage devices. For example, if a local area experiences a sudden increase in power usage, the grid can request that specific EVs discharge their batteries to provide additional power. This not only supports the grid's stability but also allows EV owners to potentially earn revenue by selling their stored energy back to the utility company.
The key to making this system work efficiently lies in smart grid management and communication. Advanced algorithms and sensors in the EVs and grid infrastructure must work in harmony to ensure that charging and discharging occur at the right times and in the right amounts. This includes monitoring weather patterns, power generation forecasts, and real-time grid conditions to predict and manage energy supply and demand.
In summary, grid-integrated EVs offer a promising solution to optimize energy usage and support the power grid. By enabling two-way communication and controlled charging and discharging, these vehicles can contribute to a more flexible and resilient energy system, ultimately benefiting both the environment and the economy. This technology is an exciting development in the world of electric transportation and smart grid management.
Revolutionizing the Road: The Karma Electric Vehicle's Impact
You may want to see also

Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G): Technology enabling EVs to send power back to the grid
Vehicle-to-Grid (V2G) technology is an innovative concept that aims to revolutionize the way electric vehicles (EVs) interact with the power grid. It involves a two-way communication and power exchange system, allowing EVs to not only draw electricity from the grid but also send power back when needed. This technology is a significant step towards a more flexible and efficient energy infrastructure, particularly in the context of the growing EV market and the increasing demand for renewable energy sources.
The core idea behind V2G is to utilize the large-scale energy storage and generation capacity of EVs as a distributed resource. Each EV, equipped with V2G-compatible technology, can act as a mobile battery, providing power to the grid during peak demand or when the grid requires additional electricity. This is especially valuable in regions where the grid relies heavily on intermittent renewable sources like solar and wind, which may not always be available. By integrating EVs into the grid, the system can better manage and stabilize the supply and demand dynamics.
The technology enables bidirectional power flow, meaning EVs can receive power from the grid for charging and also discharge electricity back to the grid. This is made possible through advanced battery management systems and smart charging infrastructure. When the grid is in need of additional power, it can send signals to the EVs, instructing them to start charging and, simultaneously, allowing the batteries to discharge and feed power back to the grid. This process ensures that EVs are charged efficiently and that the grid has access to a flexible and rapidly responsive power source.
Implementing V2G technology offers several benefits. Firstly, it provides grid operators with a valuable resource to manage peak demand and reduce the strain on the power infrastructure. This can lead to cost savings and improved grid reliability. Secondly, it empowers EV owners with more control over their energy usage and costs. They can choose when to charge their vehicles and when to release power back to the grid, potentially earning revenue during peak demand periods. Additionally, V2G technology can contribute to the integration of renewable energy sources by providing a means to store excess energy produced by wind or solar farms and discharge it when needed.
The development of V2G technology is an ongoing process, with research and development efforts focused on improving efficiency, safety, and communication protocols. As the EV market expands and more vehicles become integrated with the grid, the potential for a more sustainable and resilient energy system becomes increasingly feasible. This technology has the power to transform the relationship between vehicles and the grid, creating a more dynamic and interactive energy ecosystem.
Subaru's Electric Revolution: Rumors and Speculations
You may want to see also

Smart Grid Interaction: Optimizing EV charging and discharging for grid stability
The concept of grid-integrated electric vehicles (EVs) involves a two-way communication and control system between the electric vehicle and the power grid. This technology enables EVs to not only draw power from the grid but also contribute to the grid's stability by managing their charging and discharging processes efficiently. The interaction between EVs and the smart grid is a crucial aspect of the broader goal of integrating renewable energy sources and ensuring a reliable and sustainable power supply.
When it comes to optimizing EV charging and discharging for grid stability, several key strategies can be employed. Firstly, implementing a demand-response system allows EVs to adjust their charging rates based on grid conditions. During periods of high grid demand, EVs can reduce their charging speed or even discharge power back to the grid, helping to stabilize voltage and frequency. This dynamic approach ensures that the grid remains balanced and prevents potential overloads.
Secondly, vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology plays a significant role in this optimization. V2G systems enable EVs to not only draw power from the grid but also feed electricity back when needed. By participating in V2G programs, EV owners can contribute to grid services, such as peak load reduction and emergency power support. During times of high grid stress, V2G-enabled EVs can discharge stored energy, providing a flexible and localized power source that can help maintain grid stability.
Furthermore, smart charging infrastructure is essential for efficient grid interaction. This includes the use of smart meters and advanced charging stations that can communicate with the grid and adjust charging rates accordingly. These stations can prioritize charging during off-peak hours when electricity prices are lower and the grid has excess capacity. By optimizing charging schedules, the grid can better manage its resources, reducing the likelihood of power shortages or surges.
In addition, predictive analytics and machine learning algorithms can be utilized to forecast grid demands and optimize EV charging patterns. By analyzing historical data and real-time grid information, these algorithms can anticipate periods of high and low demand, allowing EVs to charge or discharge accordingly. This proactive approach ensures that the grid remains stable and that EV owners can manage their vehicle's energy usage effectively.
In summary, grid-integrated electric vehicles offer a promising solution to optimize energy management and enhance grid stability. Through demand-response systems, V2G technology, smart charging infrastructure, and advanced analytics, EVs can actively participate in grid operations, contributing to a more efficient and resilient power network. As the adoption of EVs continues to grow, the integration with smart grids will become increasingly vital for a sustainable and reliable energy future.
Electric Vehicles: Revolutionizing the Automotive Industry
You may want to see also

Renewable Energy Integration: Using EVs to store and distribute renewable energy
The concept of grid-integrated electric vehicles (EVs) is an innovative approach to managing and utilizing renewable energy sources more efficiently. These vehicles are designed to interact with the power grid, allowing them to not only draw electricity from it but also feed power back to the grid when needed. This capability is particularly valuable in the context of renewable energy integration, where EVs can play a dual role in energy storage and distribution.
When EVs are connected to the grid, they can act as mobile energy storage devices. During periods of high renewable energy production, such as sunny days when solar panels are generating more power than required, EVs can charge their batteries. This process is facilitated by smart charging systems that optimize charging times and rates. By storing excess energy, EVs can help balance the grid, especially when the supply of renewable energy fluctuates. For instance, during cloudy days with reduced solar output, EVs can discharge their stored energy back into the grid, ensuring a stable power supply.
The integration of EVs with renewable energy sources also enables a decentralized energy distribution model. Instead of relying solely on centralized power plants, EVs can be utilized to deliver energy to local areas or even individual homes. This is particularly useful in remote or rural locations where extending the power grid might be challenging or costly. For example, a fleet of EVs can be deployed to provide temporary power during natural disasters or in off-grid communities, ensuring access to electricity.
Furthermore, the use of EVs for renewable energy storage and distribution can contribute to a more flexible and responsive power grid. As the number of EVs on the road increases, they can collectively provide a significant amount of energy storage capacity. This can be especially beneficial for grid operators who need to manage peak demand and supply. By coordinating the charging and discharging of EVs, grid operators can optimize energy usage, reduce the strain on the grid infrastructure, and potentially lower energy costs for consumers.
In summary, grid-integrated electric vehicles offer a promising solution for renewable energy integration. They can efficiently store and distribute renewable energy, helping to stabilize the grid and provide power in diverse scenarios. As the technology advances and more EVs are adopted, the potential for a more sustainable and resilient energy system becomes increasingly feasible. This approach not only benefits the environment but also contributes to a more reliable and cost-effective energy infrastructure.
Unveiling the Power of Electric Vehicles: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Grid Services: EVs providing grid support, like load balancing and voltage regulation
Grid-integrated electric vehicles (EVs) are a concept that aims to revolutionize the way we interact with and utilize our electrical grid. These vehicles are designed to not only provide transportation but also to actively participate in the management and stability of the power grid. One of the key services these EVs can offer is grid support, which involves various mechanisms to ensure the efficient and reliable operation of the electrical network.
Load balancing is a critical aspect of grid management. The grid's capacity is not always utilized evenly, and during peak hours, the demand can exceed the supply, leading to potential blackouts or instability. Grid-integrated EVs can help address this issue by acting as mobile energy storage devices. When the grid is in need of additional power, these vehicles can discharge their batteries, feeding electricity back into the grid. This process, known as vehicle-to-grid (V2G) technology, allows EVs to become a flexible resource, helping to balance the load and prevent overloading. For example, during periods of high electricity demand, EVs can be programmed to release stored energy, reducing the strain on the central power plant and preventing voltage drops that could lead to blackouts.
Voltage regulation is another essential service that grid-integrated EVs can provide. The electrical grid operates at specific voltage levels, and maintaining these levels is crucial for the safe and efficient distribution of power. When the voltage deviates from the optimal range, it can lead to inefficiencies and even damage to electrical equipment. EVs, equipped with smart charging systems, can monitor the grid's voltage and adjust their charging rates accordingly. During periods of low voltage, they can slow down their charging process, allowing the grid to maintain a stable voltage level. Conversely, when the voltage is too high, EVs can absorb excess energy, acting as a buffer to prevent voltage spikes. This dynamic voltage regulation capability ensures that the grid remains within safe operating limits and enhances the overall stability of the power supply.
The integration of EVs into the grid also enables advanced energy management systems. These systems can optimize charging and discharging cycles, considering factors such as weather forecasts, time-of-use rates, and the grid's current demand. By strategically managing the energy flow, these systems can minimize the environmental impact of EV charging and maximize the benefits to the grid. For instance, during sunny days when solar power generation is high, EVs can be charged using renewable energy, and later, when the sun sets, they can discharge their stored energy to support the grid.
In summary, grid-integrated electric vehicles offer a unique opportunity to enhance grid services and improve overall grid performance. Through load balancing and voltage regulation, these vehicles can contribute to a more stable and efficient power network. As the adoption of EVs continues to grow, the potential for these vehicles to provide valuable grid support becomes increasingly significant, paving the way for a more sustainable and resilient energy infrastructure.
Electric Vehicle Subsidies: Government Support for a Greener Future
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
Grid-integrated electric vehicles, also known as vehicle-to-grid (V2G) vehicles, are electric cars, buses, or other vehicles that can not only draw power from the electrical grid to charge their batteries but also feed electricity back to the grid when needed. These vehicles are equipped with advanced battery management systems and power electronics, allowing them to participate in the two-way energy exchange between the vehicle and the grid.
These vehicles are designed to communicate with the grid infrastructure, often through a smart charging system. When the vehicle is connected to the grid, it can charge its battery during periods of low electricity demand and low cost. The vehicle's battery can then discharge electricity back to the grid during peak demand or when the grid needs additional power. This process is controlled and optimized to ensure efficient energy management and potentially provide financial benefits to both the vehicle owner and the utility company.
The advantages of grid-integrated electric vehicles include improved grid stability, as they can help balance electricity supply and demand. These vehicles can also provide backup power during outages and support grid services like voltage regulation and peak demand reduction. Additionally, vehicle owners may benefit from potential cost savings by charging during off-peak hours and selling excess energy back to the grid. This technology also contributes to a more sustainable transportation system by reducing reliance on fossil fuels and integrating renewable energy sources into the grid.