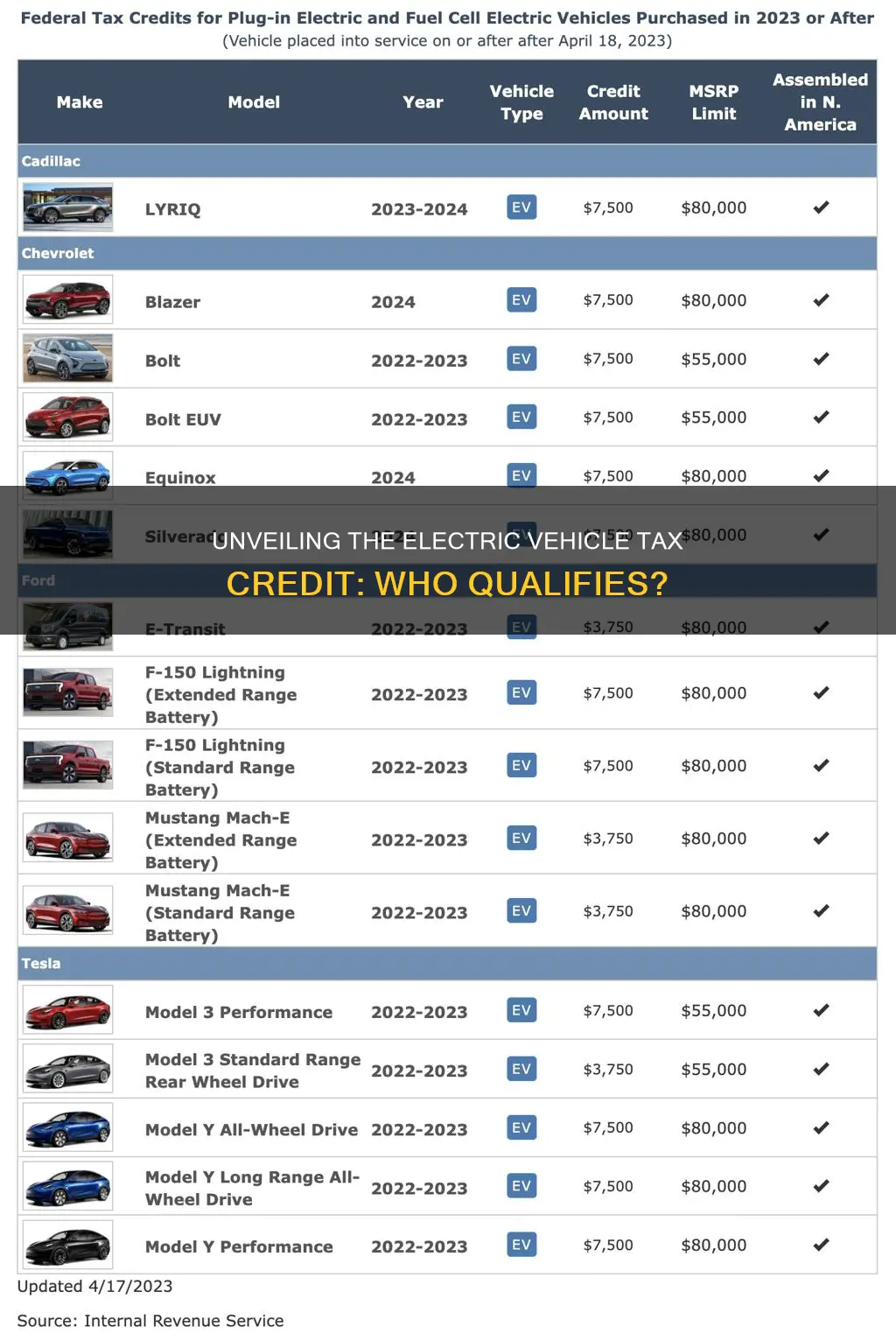
Electric vehicles (EVs) are becoming increasingly popular, and for good reason. Not only are they environmentally friendly, but they also offer a range of benefits, including tax credits. One of the most significant tax credits available for EVs is the $7,500 federal tax credit. This credit can be applied to the purchase of new electric cars, trucks, and motorcycles, making them more affordable for consumers. However, not all EVs qualify for this credit, and understanding the criteria is essential for those looking to take advantage of this financial incentive. This paragraph will explore the factors that determine which electric vehicles are eligible for the $7,500 tax credit, helping consumers make informed decisions about their EV purchases.
What You'll Learn
- Vehicle Type: Battery-electric and fuel-cell electric vehicles
- Price Cap: New vehicles under $80,000, used under $55,000
- Manufacturing Location: Vehicles assembled in North America
- Sales and Production: Vehicles sold and produced after December 31, 2020
- Eligibility Criteria: Vehicles meeting EPA emissions standards and meeting specific requirements

Vehicle Type: Battery-electric and fuel-cell electric vehicles
Battery-electric and fuel-cell electric vehicles are two types of electric vehicles that qualify for the federal tax credit of up to $7,500. This credit is designed to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles and reduce greenhouse gas emissions. Here's a detailed breakdown of these vehicle types and their eligibility:
Battery-electric vehicles (BEVs) are fully electric cars that run exclusively on electricity stored in batteries. They produce zero tailpipe emissions and are a popular choice for environmentally conscious consumers. To qualify for the tax credit, BEVs must meet specific criteria set by the Internal Revenue Service (IRS). These criteria include having a battery capacity of at least 4 kWh and a range of at least 100 miles on a single charge. Additionally, the vehicle must be manufactured in compliance with the IRS's regulations, ensuring it meets certain production and assembly standards.
Fuel-cell electric vehicles (FCEVs) are another type of electric vehicle that uses a fuel cell to generate electricity, typically through the reaction of hydrogen and oxygen. These vehicles produce only water vapor and warm air as byproducts, making them highly environmentally friendly. FCEVs are eligible for the tax credit if they meet specific performance and efficiency standards. The vehicle's fuel cell system must have a power output of at least 40 kW, and it should be capable of achieving a range of a minimum of 100 miles on a single hydrogen fuel tank fill-up. Similar to BEVs, FCEVs must also comply with the IRS's manufacturing and assembly guidelines.
It's important to note that the $7,500 tax credit is a significant incentive for buyers of these vehicles. However, the credit amount can vary depending on the vehicle's battery capacity and the manufacturer's specific contributions to the overall cost. For instance, if a vehicle's battery capacity is below the minimum requirement, the tax credit may be reduced proportionally.
In summary, both battery-electric and fuel-cell electric vehicles are eligible for the federal tax credit, provided they meet the respective performance and manufacturing criteria. This tax credit plays a crucial role in promoting the adoption of zero-emission vehicles and contributing to a more sustainable transportation future.
America's Electric Vehicle Revolution: Top Models and Trends
You may want to see also

Price Cap: New vehicles under $80,000, used under $55,000
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) offers a valuable tax credit of up to $7,500 for the purchase of qualified electric vehicles, which can significantly reduce the cost of going green. This credit is a great incentive for consumers to choose eco-friendly transportation options. When it comes to the price cap for this tax credit, it's important to note that the IRS has set specific limits to ensure the credit is accessible to a wide range of consumers.
For new electric vehicles, the price cap is set at $80,000. This means that any new electric car, truck, or SUV that costs $80,000 or less is eligible for the full $7,500 tax credit. This cap ensures that the credit is available to a diverse market, including those who might not typically consider high-end electric vehicles. It encourages manufacturers to produce a variety of electric models to cater to different budgets.
When it comes to used electric vehicles, the price cap is lower at $55,000. This is a strategic move by the IRS to promote the adoption of used electric cars, which can be more affordable and environmentally friendly options for consumers. By setting a lower price cap, the credit becomes more accessible to a broader audience, potentially increasing the overall demand for electric vehicles.
To qualify for the tax credit, the vehicle must also meet certain performance and emission standards. The IRS provides detailed guidelines on the vehicle's battery capacity, range, and other technical specifications. These standards ensure that the credit is awarded to vehicles that offer a significant environmental benefit and meet a certain level of performance.
It's important to stay updated on the IRS guidelines and any changes to the tax credit program. The rules and eligibility criteria may evolve, so keeping informed ensures that you take full advantage of the incentives available. Additionally, researching specific electric vehicle models and their prices can help determine which ones fall within the price caps, allowing you to make an informed decision when purchasing an electric car.
Unraveling the Mystery: What 'Bev' Means in Electric Vehicles
You may want to see also

Manufacturing Location: Vehicles assembled in North America
The 7500 tax credit is a significant incentive for consumers to purchase electric vehicles (EVs), but it's important to understand which EVs qualify for this benefit. This credit is specifically targeted at EVs that are manufactured in North America, which includes the United States and Canada. The primary goal is to support domestic manufacturing and promote the growth of the EV market within these regions.
Vehicles assembled in North America that qualify for the 7500 tax credit are typically those produced by domestic and international manufacturers who have established production facilities in the United States or Canada. These vehicles must meet certain criteria, including being powered by a battery electric system and meeting specific performance and safety standards. The credit is designed to encourage the production and sale of EVs, reducing the overall cost for consumers and making electric mobility more accessible.
To be eligible, the vehicle must be new and not used, and it should be purchased or leased by an individual or business. The credit amount can vary depending on the vehicle's battery capacity and the manufacturer's location. For instance, vehicles with a battery capacity of at least 7 kWh and assembled in the United States or Canada are eligible for the full $7,500 credit. This incentive is particularly beneficial for consumers in these regions, as it can significantly reduce the upfront cost of purchasing an EV.
It's worth noting that the rules and regulations surrounding this tax credit are subject to change, and it's essential to stay updated with the latest information. The IRS and relevant government agencies provide guidelines and lists of qualifying vehicles, ensuring that consumers can make informed decisions when purchasing an EV. Additionally, some states and local governments may offer additional incentives, further enhancing the benefits for EV buyers.
In summary, the 7500 tax credit is a valuable opportunity for consumers in North America to save on the purchase of electric vehicles. By supporting domestic manufacturing, this credit encourages the adoption of EVs and contributes to a more sustainable future. Prospective buyers should research the specific requirements and eligible models to take full advantage of this incentive.
Battling EV Fires: Rapid Response Strategies for Safety
You may want to see also

Sales and Production: Vehicles sold and produced after December 31, 2020
The Internal Revenue Code Section 30D(e)(2) outlines the requirements for electric vehicles to qualify for the $7,500 tax credit. This credit is available for vehicles sold or produced after December 31, 2020, and is a significant incentive for consumers to purchase electric cars. The credit is designed to encourage the adoption of electric vehicles, reduce greenhouse gas emissions, and promote the development of the domestic electric vehicle market.
To qualify, the vehicle must meet specific criteria, including being powered by a battery that can store at least 4 kilowatt-hours of energy and having a range of at least 62 miles (100 kilometers) as measured by the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). This range requirement is crucial, as it ensures that the vehicle can travel a significant distance on a single charge, making it practical for everyday use. Additionally, the vehicle must be manufactured in the United States and meet certain production requirements.
Manufacturers must ensure that the vehicle's battery and other key components are produced in the U.S. or in a country that has a free trade agreement with the U.S. This includes the battery's cathode, anode, and other essential parts. The production process should also occur in the U.S. or in a country with a free trade agreement. These requirements aim to stimulate domestic manufacturing and create jobs within the electric vehicle industry.
The $7,500 tax credit is a substantial incentive for consumers, as it directly reduces the cost of purchasing an electric vehicle. This credit is in addition to other potential tax benefits, such as state-specific incentives and depreciation allowances. By combining these incentives, consumers can save significantly on the purchase of an electric car, making it an attractive option for those looking to reduce their environmental impact and save money.
It's important to note that the qualifications and requirements for this tax credit are subject to change, and it's advisable to consult the latest IRS guidelines and regulations. Staying informed about these updates will ensure that consumers and manufacturers are aware of the most current criteria for qualifying for the tax credit.
Reimbursing Employees for Electric Vehicles: A Comprehensive Guide
You may want to see also

Eligibility Criteria: Vehicles meeting EPA emissions standards and meeting specific requirements
The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) offers a valuable tax credit of up to $7,500 for the purchase of qualified electric vehicles, but it's important to understand the specific criteria that determine eligibility. One of the key requirements is that the vehicle must meet the Environmental Protection Agency's (EPA) emissions standards. This ensures that the vehicle is environmentally friendly and contributes to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. The EPA has set guidelines for different vehicle types, and electric vehicles (EVs) are categorized based on their battery capacity and range.
To qualify for the tax credit, the electric vehicle must have a battery capacity of at least 40 kilowatt-hours (kWh) and a range of at least 100 miles. These specifications are designed to encourage the adoption of more advanced and efficient electric cars. Vehicles that meet or exceed these standards are considered to have a significant environmental impact and are more likely to contribute to a greener transportation system.
Manufacturers and importers play a crucial role in this process. They are responsible for ensuring that their electric vehicles comply with the EPA's emissions and performance standards. This includes providing accurate information about the vehicle's battery capacity and range, as well as any other relevant specifications that determine its eligibility. It is essential for consumers to verify these details before purchasing an electric vehicle to ensure they qualify for the tax credit.
Additionally, the IRS has specific guidelines for different types of electric vehicles. For example, plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs) have a different set of requirements compared to all-electric vehicles (AEVs). PHEVs must meet certain fuel economy standards, while AEVs focus on battery capacity and range. Understanding these distinctions is vital for consumers to navigate the eligibility criteria effectively.
In summary, the $7,500 tax credit for electric vehicles is a significant incentive for consumers to make eco-friendly choices. However, eligibility is not solely based on the purchase price but also on meeting specific technical requirements. By adhering to the EPA emissions standards and the specified battery capacity and range, electric vehicles can qualify for this valuable tax benefit. It is essential for both manufacturers and consumers to be well-informed about these criteria to ensure a smooth and successful process.
GM's Electric Future: Will Chevy Go All-In?
You may want to see also
Frequently asked questions
The Internal Revenue Code (IRC) Section 30D provides a tax credit of up to $7,500 for the purchase of qualified electric vehicles. This credit is available for new and used electric vehicles, including battery-electric vehicles (BEVs) and plug-in hybrid electric vehicles (PHEVs). However, it's important to note that the credit is generally limited to vehicles with a base price below a certain threshold, which is adjusted annually for inflation.
To qualify, the vehicle must meet specific criteria, such as having a battery capacity of at least 4 kWh and a base price that does not exceed $80,000 for new vehicles and $50,000 for used vehicles (with certain adjustments for inflation). The IRS provides a list of qualified vehicles on its website, and you can also check with the vehicle manufacturer to confirm eligibility.
Yes, there are restrictions. The vehicle must be manufactured or assembled in the United States or a qualifying foreign country. The manufacturer or assembler must also meet certain production volume requirements. Additionally, the vehicle's battery components and critical minerals must originate from the US or a country with which the US has a trade agreement. These rules are designed to encourage domestic production and supply chain resilience.